

Extended Essay: Formal vs. Informal Writing
- Extended Essay- The Basics
- Step 1. Choose a Subject
- Step 2. Educate yourself!
- Using Brainstorming and Mind Maps
- Identify Keywords
- Do Background Reading
- Define Your Topic
- Conduct Research in a Specific Discipline
- Step 5. Draft a Research Question
- Step 6. Create a Timeline
- Find Articles
- Find Primary Sources
- Get Help from Experts
- Search Engines, Repositories, & Directories
- Databases and Websites by Subject Area
- Create an Annotated Bibliography
- Advice (and Warnings) from the IB
- Chicago Citation Syle
- MLA Works Cited & In-Text Citations
- Step 9. Set Deadlines for Yourself
- Step 10. Plan a structure for your essay
- Evaluate & Select: the CRAAP Test
- Conducting Secondary Research
- Conducting Primary Research
- Formal vs. Informal Writing
- Presentation Requirements
- Evaluating Your Work
Differences Between Informal and Formal Essays
When writing your extended essay you should use language that is formal and academic in tone. The chart below gives you some idea of the differences between informal and formal essays. See the box below for examples of the differences in tone in informal and formal essays written on identical topics. A PDF of this chart, and the examples below, is in the box to the right , along with a list of tips for avoiding colloquial writing.
Examples of Informal and Formal Tone in Essay Writing
The following examples highlight the differences between formal and informal tone.
Language B - English
- Formal vs. Informal Writing A chart giving the differences between informal and formal essays in seven areas (author's viewpoint; subject/content (sources of evidence); tone; structure; location of the research question; vocabulary; and purpose. Also included are examples comparing informal and formal writing for essays in English, biology, and psychology.
- How to Avoid Colloquial (Informal) Writing While it may be acceptable in friendly e-mails and chat rooms, excessive colloquialism is a major pitfall that lowers the quality of formal written text. Here are some steps/tips that you can follow to help improve your overall writing.
- << Previous: Plagiarism
- Next: Presentation Requirements >>
- Last Updated: Sep 3, 2024 10:01 AM
- URL: https://libguides.westsoundacademy.org/ee

Home > Blog > Tips for Online Students > Tips for Students > Formal vs. Informal: Best Writing Practices
Tips for Online Students , Tips for Students
Formal vs. Informal: Best Writing Practices
Updated: June 19, 2024
Published: April 5, 2020

In this article
Langston Hughes once said, “The prerequisite for writing is having something to say.” But you are probably aware that there are many different styles of writing — and it pays to know which to use situationally. When it comes to formal vs informal writing styles, there is a time and place for each. By understanding their nuances and respective best practices, you can continue to improve your writing.
We will break all of this down and more, with examples. This can serve as a useful guide on formal vs informal writing for you throughout your educational journey (and beyond).
Defining Formal vs Informal Writing Styles
Formal writing is written for an audience you do not know on a personal level. It is often the main style in academic writing (unless otherwise noted) and is more complex than informal writing. Formal writing is serious.
Informal writing consists of short sentences and is used in more personal settings, such as writing a letter to a friend or writing a diary entry. It is much more relaxed than formal writing.
Photo by Annie Spratt on Unsplash
Which style is appropriate.
Knowing the difference between formal and informal writing is only half the battle. The other important aspect is knowing which to use. Here are some examples of when you would use formal vs informal writing.
Use Formal Writing When:
- Writing professionally (reaching out to a client or prospect)
- Academic writings (essays, research papers, etc.)
- Job applications ( resume writing , CVs, and cover letters)
- Reaching out to someone you do not know

Use Informal Writing When:
- Writing to a friend
- Sharing a story or writing a personal blog
- Writing creatively
- Instructed to do so (if in school)
- Writing dialogue and conversations
- Writing an outline
If you are unsure of whether to use informal or formal writing, it’s generally the rule of thumb to start out writing formally. Then, when you make the connection and you see how the other side responds, you can ease up on the formality.
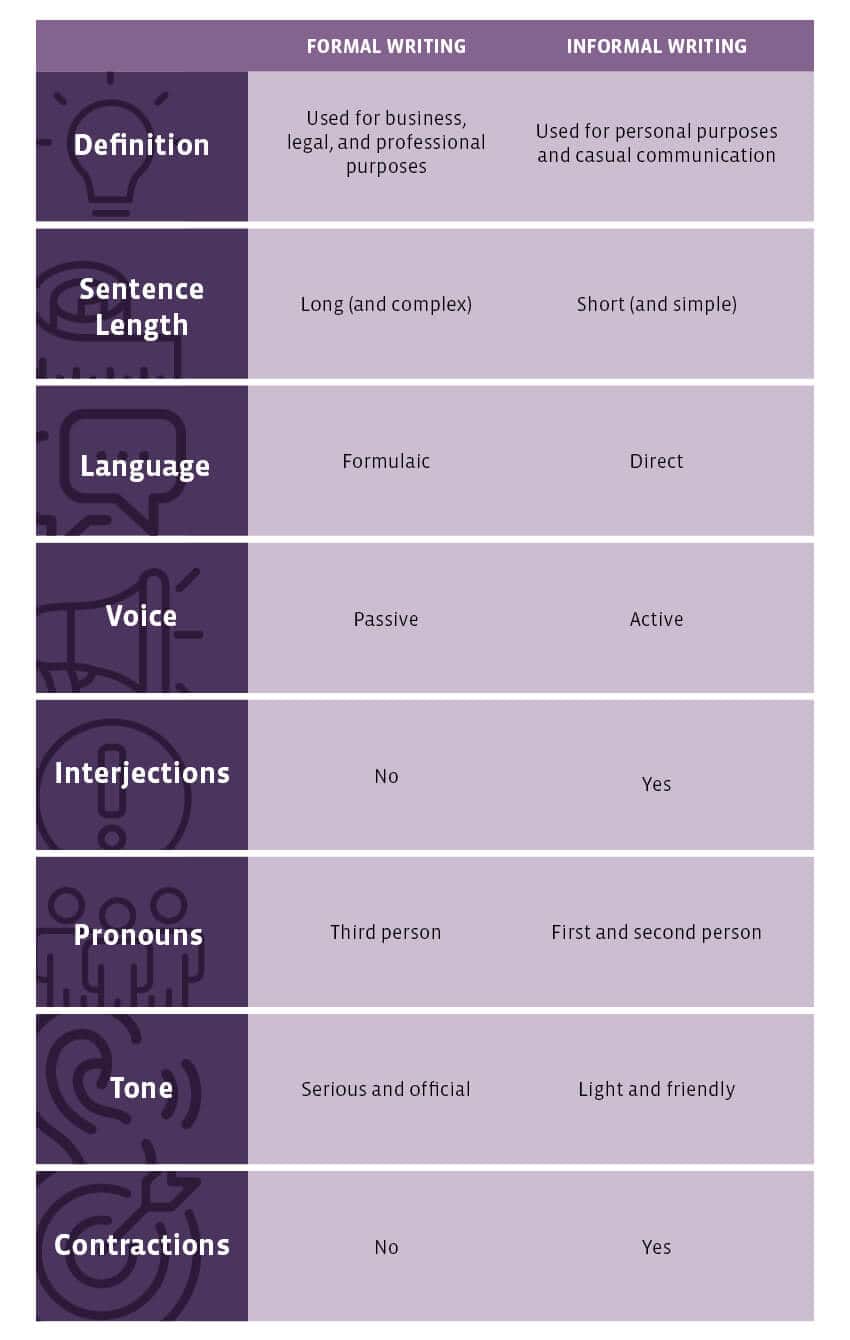
Key Features of Formal vs. Informal Writing
While the above gives a simple overview of the differences and uses of each style, let’s take a deeper look into what each style entails. That way, it should become more obvious how to recognize and structure each.
Formal writing tends to include the following:
- Long and complex sentences: Sentences tend to be compound and contain commas to link two ideas or use transitions like “Furthermore” and “To exemplify,”
- Does not use contractions: Would use “cannot” instead of “can’t”
- Objective: Does not offer personal opinions
- Doesn’t use colloquial language: You won’t see any slang or common everyday vocabulary
- Diverse vocabulary words: Vocabulary is of a higher level
- Use of words that are subject-specific: For example, if you are writing about biology, you’d use words like “epithelial cells” instead of “skin cells”
- Use of third person: Does not use first person pronouns like “I” or “me”
Informal writing includes the following:
- Can use first person, second or third: You can use any type of pronouns, including “I”
- Can use slang: The use of everyday language and slang terms can be used, such as “It was cool that…”
- Active voice: Sentences tend to be written with a subject acting on the verb, such as “We chilled the drinks and went out to the sea” instead of “The drinks were chilled…”
- Personal emotional tone can be detected: Since the writing is personal, it can include feelings and the sharing of emotions
- Contraction and abbreviation: It’s okay to use “can’t” instead of “cannot” or “it’s” instead of “it is”
- Empathy: You can put yourself in the shoes of your audience and address their problems directly. This shows the author as coming from a place of understanding their situation.
Formal vs Informal Writing Comparison Guide
Additional Considerations
There are a few more things to take into account when starting out on any writing endeavor. These include the following 3 questions:
- “Who is my audience?” – This is the first question you should ask when writing anything. You want to write to your audience, so you have to define them.
- “How formal is the project I’m working on?” – This goes hand-in-hand with the audience and the project goals. However, knowing the level of formality will help you write accordingly.
- “What medium should I use?” – For both informal and formal writing, you can produce the piece digitally or by hand. If it is for academic purposes and on the job, you’ll want to type your work. But, if you choose to write a formal letter by hand (such as a thank-you letter after a job interview), then it is advised to write on thicker card stock paper to look more professional. Remember, presentation is everything when it comes to formal work!
Here’s an Example!
Along with this list of references , here is a (meta) example on how this article would be written both formally and informally:
- Formal: When writing academically or professionally, it is important to show respect to your audience by electing to write in a formal style, rather than informally. This means that sentences are longer than usual and tend to feel complex. Writing complex sentences with hyperfluent vocabulary shows your audience that you are well-informed on the subject matter. Furthermore, this writing style depicts unbiased information eluding emotions and first-person pronouns from the content.
- Informal: Formal writing feels harder than informal writing. I think it’s because I can’t use contractions or short sentences. The only reason I’d write informally is if I had to, like if it was professional or academic. But when I write like this about formal writing, it’s easier. My vocabulary doesn’t matter as much. As you can see, I still care about grammar. Writing like this feels like I am talking to a friend.
Photo by Glenn Carstens-Peters on Unsplash
Tying it all together.
There are many differences between formal vs. informal writing. That being said, they both serve their respective purposes. That’s why it’s important to understand both styles, as well as when to use them.
When writing professionally or academically, opt for formal writing. Remember to leave out contractions and remain unbiased.
On the other hand, informal writing comes from within. It’s aimed towards a personal audience, so you can write as if you are speaking to them. That way, you can use contractions, shorter sentences, colloquialism, and the like.
Regardless of why you are writing, always be sure to reread your work to check for typos and mistakes. The most important thing for writing is having something to say, but it’s also making sure that what you say can be understood!
At UoPeople, our blog writers are thinkers, researchers, and experts dedicated to curating articles relevant to our mission: making higher education accessible to everyone. Read More
