Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / MLA Website Citation

How to Cite a Website in MLA
If you are a student faced with creating an MLA website citation for the first time, you may be confused about where to begin. This guide is here to answer all of your questions and take the guesswork out of creating an MLA citation for websites.
All academic fields require students and researchers to document their sources. Those studying the humanities, including fields in language literature, will typically follow MLA format when structuring their papers as well as when documenting sources.
Citing your sources is a necessary part of any research paper or project. This element serves both to give credit to the researchers and authors whose work informed yours, as well as to preserve academic integrity. Any source that provided you with ideas or information that you have included in your work and which are not considered common knowledge must be included, including websites.
The Modern Language Association is not associated with this guide. All of the information, however, is based on the MLA Handbook, Ninth Edition as well as the MLA website, and is presented as guidance for students writing in this style.
If you are looking for help with APA format , our reference library can provide you with guidance for this and more styles .
What You Need
To cite a website, you should have the following information:
- Title of source.
- Title of the container ,
- Other contributors (names and roles),
- Publication date,
- Location of the source (such as DOI, URL, or page range).
The Modern Language Association refers to these guidelines as “core elements” on page 105 of the Handbook. If your teacher has asked you to cite your sources in this format, these elements will form the foundation for each MLA website citation included in your MLA Works Cited list, as well as the entries for sources in any other format.
If one of the elements does not apply, students may omit it. Supplemental items may also be included when necessary. In addition to the supplemental details discussed below, a list of additional supplemental components can be found on the MLA website.
If it’s an APA citation website page or an APA reference page you need help with, we have many other resources available for you!
Table of Contents
This guide includes the following sections:
- MLA9 Changes
- Citing websites with an author
- Citing websites with no author
- Citing websites with no formal title
- Citing social media websites
- In-text citations
Changes to MLA Citation for Websites in Ninth Edition
In previous editions, students and researchers creating an MLA website citation were not required to include the URL. However, beginning with MLA 8, it is recommended that you include the URL when creating a citation for a website unless your teacher instructs you otherwise. Even though web pages and URLs can be taken down or changed, it is still possible to learn about the source from the information seen in the URL.
When including URLs in a citation, http:// and https:// should be omitted from the website’s address ( Handbook 195). Additionally, If you are creating a citation that will be read on a digital device, it is helpful to make the URL clickable so that readers can directly access the source themselves.
If the website’s publisher includes a permalink or DOI (Digital Object Identifier), these are preferable as they are not changeable in the same manner as URLs. Whether you include a URL, permalink, or DOI, this information should be included in the location portion of your citation.
Another change that occurred with the eighth edition that impacts how to cite a website in MLA is the removal of the date the website was accessed. While you may still find it useful to include this information or your teacher may request it, it is no longer a mandatory piece of your citation. Should you choose to add this optional information, you may list it after the URL in the following manner:
- Accessed Day Month Year.
- Accessed 2 May 1998.
- Accessed 31 Apr. 2001.
- Accessed 17 Sept. 2010.
For an overview of additional formatting changes in the ninth edition, including resources to help with writing an annotated bibliography , check out the rest of EasyBib.com’s writing and citation guides, and try out our plagiarism checker for help with grammar and to avoid unintentional plagiarism.
MLA 9: Citing Websites With an Author
To make an MLA 9 citation for a website, you will need the following pieces of information:
- author’s name
- title of the article or page
- title of the website
- name of the publisher (Note: Only include the name of the publisher when it differs from the name of the website.)
- date the page or site was published (if available)
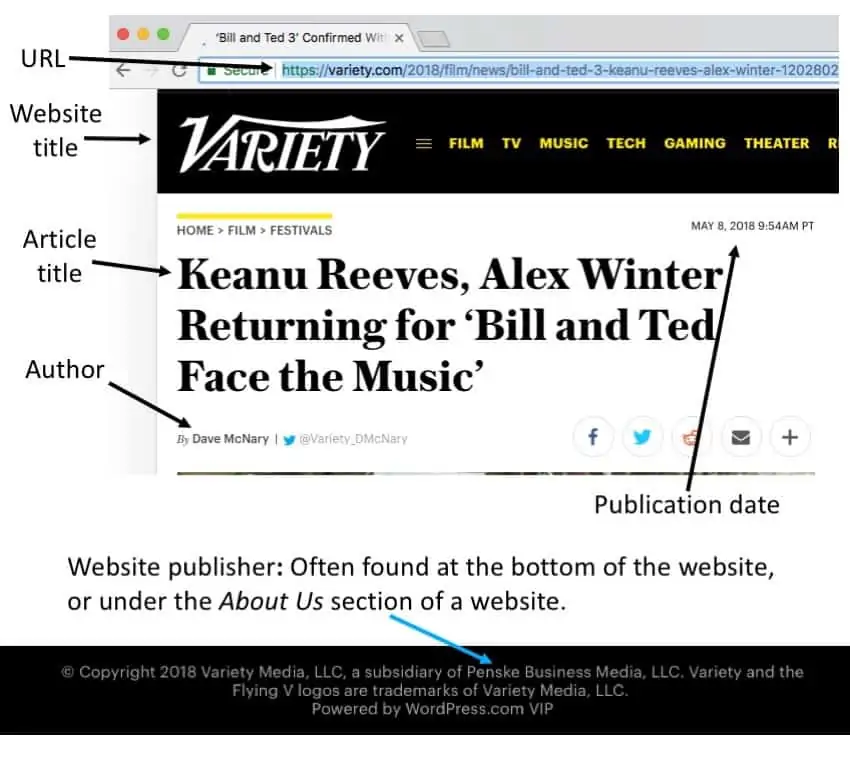
Citing a Website in MLA
Place the author’s name in reverse order, the last name first, followed by a comma, and then the first name followed by a period. The title of the web page or article is placed in quotation marks, with a period before the end quotation. The title of the website is written in italics followed by a comma. If the name of the publisher differs from the name of the website, include it after the title. Immediately following the publisher is the date that the page or article was published or posted. Finally, end with the URL, permalink, or DOI, followed by a period.
View Screenshot | Cite your source
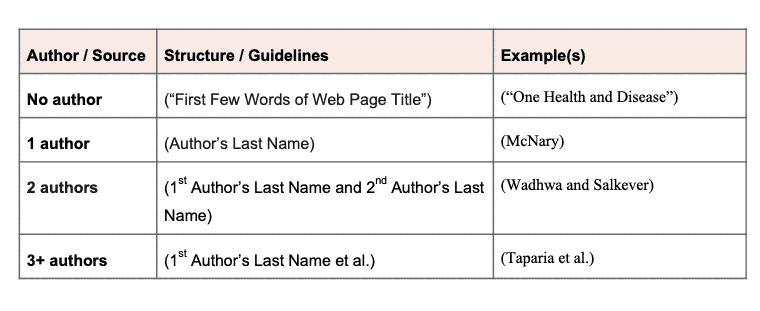
In-text website citation with one author
The in-text citation for a website with an author is reflected as the author’s last name in parentheses, followed by a period. Unless the website includes numbered paragraphs or sections, you should not include any additional information. For the website used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
Cite your source
An APA parenthetical citation is similar, except it also includes the year the source was published.
To learn more about formatting MLA in-text & parenthetical citations , be sure to check out the rest of EasyBib.com’s resources and citation guides.
How to cite a website with two authors in MLA 9
According to Section 5.7 of the Handbook , for a website with two authors, place the authors’ names in the same order as the source (similar to an APA citation ). The first name should be formatted in reverse order as was done for a single author. The second name, however, is written as First Name Last Name and is followed by a period, as demonstrated in the template that follows:
In-text website citation with two authors
The in-text citation for a website with two authors should include both authors’ last names, in the order in which they are listed in the source and your works cited:
How to cite a website with three or more authors in MLA 9
For a source with three or more authors, you should place the authors’ names in the same order as the source. The first name is listed in reverse order and is followed by a comma and et al. Et al is the abbreviation for et alia, a gender-neutral Latin phrase meaning “and others.”
In-text website citation with 3+ authors
The in-text citation for a website with three or more authors should contain only the first author’s last name, followed by et al. ( Handbook 232):
Click on this page if you’re looking for information on how to create an APA in-text citation .
MLA 9 Citation for Websites with No Author
Sometimes, websites do not state who wrote the information on the page. When no author is listed, you may omit the author information from the MLA citation for the website and begin, instead, with the title ( Handbook 108).
Note about web pages by organizations/corporations: Often, web pages are published by organizations or corporations with no author indicated. In these cases, you can assume that the publisher also authored the web page (like the example above). Since the author and publisher are the same in these cases, you can skip showing an author and just indicate the organization /corporation as the publisher ( Handbook 119 ).
In-text website citation with no author
The in-text citation for a website without an author is noted with the first noun phrase or words in the title in quotations and parenthesis, followed by a period. Unless the website includes numbered paragraphs or sections, you should not include any additional information. For the website used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
MLA 9 Citation for Websites Without a Formal Title
When citing a web page that does not include a formal title, it is acceptable to include a description of the page. Do not place the description in italics or quotation marks. Follow the description with the name of the website.
In-text website citation without a title
The in-text citation for a website without a formal title uses a shortened version of the webpage description for the in-text citation. Use the first noun phrase of the description from your Works Cited citation in parenthesis, followed by a period. For the website used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
MLA 9 Citation for Social Media Websites
In an increasingly digital world, social media platforms have become one of the most popular sources students turn to when writing a research paper. From Black history facts , to quotes from notable people, such as Martin Luther King and Winston Churchill , social media has become a mega influence in our world.
When citing social media in your work, follow the same format as an MLA citation for a website. Here are some examples of ways you can cite various social media platforms in your work:
How to cite Twitter in MLA 9
Many notable individuals use Twitter as a platform to share intriguing ideas. It’s a shame Twitter was unavailable to long-gone scientists, authors, and presidents such as Albert Einstein , Mark Twain , and Abraham Lincoln . Luckily, we have the Twitter profiles of today’s great minds at our fingertips!
To cite a tweet, you will begin with the account holder’s name and their Twitter handle in square brackets, followed by a period ( Handbook 118). After this, in quotations, you should enter the full text of the tweet, including any hashtags. The publisher, Twitter, is then listed in italics, followed by the date the tweet was posted in day, month, year format. Finally, include a URL to the tweet followed by a period.
Note: When the account name and username are similar, the username can be excluded from the citation. For example, if the account’s username was @FirstNameLastName or @OrganizationName.
In-text website citation of a Twitter post
The in-text citation for a Twitter post is reflected as the author’s last name in parentheses, followed by a period. For the tweet used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
How to cite Instagram in MLA 9
To cite an Instagram post, begin with the account holder’s name and their username in square brackets. In quotations, list the title of the photo, if it is given. If there is no title, write a brief description of the picture but do not place it in italics or quotation marks. The publisher, Instagram, is then listed in italics. Any other contributors (such as the photographer, if it is not the same as the account holder) are then listed, after which you will add the date the photo was published and the URL.
In-text website citation of an Instagram post
The in-text citation for an Instagram post is reflected as the author’s last name or the name of the account in parentheses, followed by a period. For the Instagram post used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:

How to cite Facebook in MLA 9
To cite a Facebook post, begin with the account holder’s name or username. In quotations, list the title or caption of the post, if it is given. If there is no title or caption, write a brief description of the post, but do not place it in italics or quotation marks. Examples: Image of Malcolm X, or, Muhammed Ali headshot.
The publisher, Facebook, is then listed in italics, after which you will add the date posted and URL.
In-text website citation of a Facebook post
The in-text citation for a Facebook post is reflected as the author’s last name or the name of the account in parentheses, followed by a period. For the Facebook post used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
Social media and website comments
Citing the comments left on social media or a website begins with the commenter’s name or username. To indicate that you are citing a comment, follow the name with a period and then the words Comment on , followed by the title of the source (for example, the name of the article) in quotation marks. This is then followed by the title of the website in italics, and the publisher, if applicable. The date is then listed, followed by the URL, permalink, or DOI.
In-text citation of a social media comment
The in-text citation for a social media comment is reflected as the author’s last name in parentheses, followed by a period. For the post used in the example above, the in-text citation would be written as follows:
In-text Citations for Websites
In-text citations generally consist of parentheses and the last names of the authors or the first few words of the web page title.
Since there are no page numbers, unless the web page includes numbered paragraphs or sections, you don’t need to include any additional information.
When you have multiple authors, place them in the same order they are listed in the source.
If what you really need is an APA book citation or a reference for an APA journal , there are more guides on EasyBib.com for you to explore.
Visit our EasyBib Twitter feed to discover more citing tips, fun grammar facts, and the latest product updates.
Troubleshooting
Solution #1: when and how to reference entire websites versus specific pages in mla.
Reference an entire website when your information comes from multiple pages or if you are describing the entirety of the website. If your information is only from one page, only cite the singular page.
Whole website, author known
- Write the author’s name in last name, first name format with a period following.
- Next, write the name of the website in italics.
- Write the contributing organization’s name with a comma following.
- List the date in day, month, year format with a comma following.
- Lastly, write the URL with a period following.
Works cited example:
Night, Samuel. Food Creations , International Hypothetical Chefs’ Club, 21 May 2021, www.foodcreationshypotheticalwebsite.com/best_macaroni_recipe.
In-text example:
Whole website, author unknown
- If there is no specific author, begin the citation by writing the website name in italics.
Food Creations , International Hypothetical Chefs’ Club, 21 May 2021, www.foodcreationshypotheticalwebsite.com/best_macaroni_recipe.
( Food Creations )
Webpage, author known
If information is from only a few pages or the pages cover multiple topics, reference each page
- If an author is named, write the author’s name in last name, first name format.
- If a title is not provided, create your own description of the page.
- List the title of the website in italics with a comma following.
- Write the date that the page was created followed by a comma.
- Lastly, list the URL followed by a period.
Blake, Evan. “Best Southern Macaroni Recipe.” Food Creations , International Hypothetical Chefs’ Club, 21 May 2021, www.foodcreationshypotheticalwebsite.com/best_macaroni_recipe.
Webpage, author unknown
If an author is not named, write the name of the page in quotation marks with a period following.
“Best Southern Macaroni Recipe.” Food Creations , International Hypothetical Chefs’ Club, 21 May 2021, www.foodcreationshypotheticalwebsite.com/best_macaroni_recipe.
(“Best Southern Macaroni Recipe”)
Solution #2: Referencing a conversation on social media in MLA
The in-text citation should identify the author and talk about the format (e.g., video, post, image, etc.) in prose.
Lilly West’s photo of traditional Japanese sweets shows an example of nature influencing Japanese design.
The basic structure of a works-cited reference for social media stays the same no matter the format or the social media service (e.g., Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc.). Here are works- cited-list entry guidelines:
- The name is listed in last name, first name format with a period following. If an organization, just write the organization’s name as it’s usually presented.
- If the username is very different from the author’s real name, include it in brackets after the user’s real name but before the period.
- Write the title, post text, or description of the post in quotation marks. End it with a period.
- Write the website name in italics with a comma afterward.
- List the day, month, and year that the post was created followed by a comma.
- List the URL followed by a period. Leave out “https://” and “http://”.
Facebook example:
West, Lily. “Kyoto Japanese sweets.” Facebook , 30 May 2021, www.facebook.com/hypotheticalexample/thispostisnotreal.
Twitter reference example:
West, Lily [@lilianhypotheticalwestbest]. “Kyoto Japanese sweets.” Twitter, 30 May 2021, www.twitter.com/hypotheticalexample/thispostisnotreal.
Instagram reference example:
West, Lily [@lilianhypotheticalwestbest]. “Kyoto Japanese sweets.” Instagram , 30 May 2021, www.instagram.com/hypotheticalexample/thisphotoisnotreal.
Solution #3: How to cite a social media post without a title or text
If there is no text or title where the title element usually goes, instead describe the post without quotation marks. Example:
West, Lily [@lilianhypotheticalwestbest]. Photo of traditional Japanese sweets on a green plate. Instagram , photographed by Bethany Lynn, 30 May 2021, www.instagram.com/hypotheticalexample/thisphotoisnotreal.
Solution #4: How to cite a social media post with a long title or text
If the text is very long, you can shorten it by adding ellipsis at the end of the text. Example:
West, Lily [@lilianhypotheticalwestbest]. “Nothing is better in life than feeling like all of the effort you’ve invested has finally. . . .” Twitter, 17 Feb. 2021, www.twitter.com/hypotheticalexample/thispostisnotreal.
- Works Cited
MLA Handbook . 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
Published October 31, 2011. Updated June 5, 2021.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau. Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
It’s 100% free to create MLA citations. The EasyBib Citation Generator also supports 7,000+ other citation styles. These other styles—including APA, Chicago, and Harvard—are accessible for anyone with an EasyBib Plus subscription.
No matter what citation style you’re using (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.), the EasyBib Citation Generator can help you create the right bibliography quickly.
Yes, there’s an option to download source citations as a Word Doc or a Google Doc. You may also copy citations from the EasyBib Citation Generator and paste them into your paper.
Creating an account is not a requirement for generating MLA citations. However, registering for an EasyBib account is free, and an account is how you can save all the citations you create. This can help make it easier to manage your citations and bibliographies.
Yes! Whether you’d like to learn how to construct citations on your own, our Autocite tool isn’t able to gather the metadata you need, or anything in between, manual citations are always an option. Click here for directions on using creating manual citations.
If any important information is missing (e.g., author’s name, title, publishing date, URL, etc.), first see if you can find it in the source yourself. If you cannot, leave the information blank and continue creating your citation.
It supports MLA, APA, Chicago, Harvard, and over 7,000 total citation styles.
If there is no author, the title becomes the website page’s identifier.
In-text example (no author): ( Honey Bee Medley )
Works cited example (no author): Honey Bee Medley . Hivemind Press, 2018, www.hivebees.com/honey-bees.
If there is no publication date, include an accessed date instead.
Works cited example (no author, no date): Honey Bee Medley . Hivemind Press, www.hivebees.com/honey-bees. Accessed 17 Nov. 2020.
If there is no title, briefly describe the source.
Works cited example (no author, no date, no title): Collage of honey bees. Hivemind Press, www.hivebees.com/honey-bees. Accessed 17 Nov. 2020.
To cite a website that has no page number in MLA, it is important that you know the name of the author, title of the webpage, website, and URL. The templates for an in-text citation and works-cited-list entry of a website that has no page number, along with examples, are given below:
In-text citation template and example:
You can use a time stamp if you are referring to an audio or video. Otherwise, use only the author’s surname.
(Author Surname)
Works-cited-list entry template and example:
Author or Organization Name. “Title of the Webpage.” Website Name . Publication Date, URL.
Dutta, Smita S. “What is Extra Sensory Perception?” Medindia . 16 Nov. 2019, www.medindia.net/patients/patientinfo/extra-sensory-perception.htm#3 .
Abbreviate the month in the date field.
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Works Cited Page: Basic Format

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
According to MLA style, you must have a Works Cited page at the end of your research paper. All entries in the Works Cited page must correspond to the works cited in your main text.
Basic rules
- Begin your Works Cited page on a separate page at the end of your research paper. It should have the same one-inch margins and last name, page number header as the rest of your paper.
- Only the title should be centered. The citation entries themselves should be aligned with the left margin.
- Double space all citations, but do not skip spaces between entries.
- Indent the second and subsequent lines of citations by 0.5 inches to create a hanging indent.
- List page numbers of sources efficiently, when needed. If you refer to a journal article that appeared on pages 225 through 250, list the page numbers on your Works Cited page as pp. 225-50 (Note: MLA style dictates that you should omit the first sets of repeated digits. In our example, the digit in the hundreds place is repeated between 2 25 and 2 50, so you omit the 2 from 250 in the citation: pp. 225-50). If the excerpt spans multiple pages, use “pp.” Note that MLA style uses a hyphen in a span of pages.
- If only one page of a print source is used, mark it with the abbreviation “p.” before the page number (e.g., p. 157). If a span of pages is used, mark it with the abbreviation “pp.” before the page number (e.g., pp. 157-68).
- If you're citing an article or a publication that was originally issued in print form but that you retrieved from an online database, you should type the online database name in italics. You do not need to provide subscription information in addition to the database name.
- For online sources, you should include a location to show readers where you found the source. Many scholarly databases use a DOI (digital object identifier). Use a DOI in your citation if you can; otherwise use a URL. Delete “http://” from URLs. The DOI or URL is usually the last element in a citation and should be followed by a period.
- All works cited entries end with a period.
Additional basic rules new to MLA 2021
New to MLA 2021:
- Apps and databases should be cited only when they are containers of the particular works you are citing, such as when they are the platforms of publication of the works in their entirety, and not an intermediary that redirects your access to a source published somewhere else, such as another platform. For example, the Philosophy Books app should be cited as a container when you use one of its many works, since the app contains them in their entirety. However, a PDF article saved to the Dropbox app is published somewhere else, and so the app should not be cited as a container.
- If it is important that your readers know an author’s/person’s pseudonym, stage-name, or various other names, then you should generally cite the better-known form of author’s/person’s name. For example, since the author of Alice's Adventures in Wonderland is better-known by his pseudonym, cite Lewis Carroll opposed to Charles Dodgson (real name).
- For annotated bibliographies , annotations should be appended at the end of a source/entry with one-inch indentations from where the entry begins. Annotations may be written as concise phrases or complete sentences, generally not exceeding one paragraph in length.
Capitalization and punctuation
- Capitalize each word in the titles of articles, books, etc, but do not capitalize articles (the, an), prepositions, or conjunctions unless one is the first word of the title or subtitle: Gone with the Wind, The Art of War, There Is Nothing Left to Lose .
- Use italics (instead of underlining) for titles of larger works (books, magazines) and quotation marks for titles of shorter works (poems, articles)
Listing author names
Entries are listed alphabetically by the author's last name (or, for entire edited collections, editor names). Author names are written with the last name first, then the first name, and then the middle name or middle initial when needed:
Do not list titles (Dr., Sir, Saint, etc.) or degrees (PhD, MA, DDS, etc.) with names. A book listing an author named "John Bigbrain, PhD" appears simply as "Bigbrain, John." Do, however, include suffixes like "Jr." or "II." Putting it all together, a work by Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. would be cited as "King, Martin Luther, Jr." Here the suffix following the first or middle name and a comma.
More than one work by an author
If you have cited more than one work by a particular author, order the entries alphabetically by title, and use three hyphens in place of the author's name for every entry after the first:
Burke, Kenneth. A Grammar of Motives . [...]
---. A Rhetoric of Motives . [...]
When an author or collection editor appears both as the sole author of a text and as the first author of a group, list solo-author entries first:
Heller, Steven, ed. The Education of an E-Designer .
Heller, Steven, and Karen Pomeroy. Design Literacy: Understanding Graphic Design.
Work with no known author
Alphabetize works with no known author by their title; use a shortened version of the title in the parenthetical citations in your paper. In this case, Boring Postcards USA has no known author:
Baudrillard, Jean. Simulacra and Simulations. [...]
Boring Postcards USA [...]
Burke, Kenneth. A Rhetoric of Motives . [...]
Work by an author using a pseudonym or stage-name
New to MLA 9th edition, there are now steps to take for citing works by an author or authors using a pseudonym, stage-name, or different name.
If the person you wish to cite is well-known, cite the better-known form of the name of the author. For example, since Lewis Carroll is not only a pseudonym of Charles Dodgson , but also the better-known form of the author’s name, cite the former name opposed to the latter.
If the real name of the author is less well-known than their pseudonym, cite the author’s pseudonym in square brackets following the citation of their real name: “Christie, Agatha [Mary Westmacott].”
Authors who published various works under many names may be cited under a single form of the author’s name. When the form of the name you wish to cite differs from that which appears on the author’s work, include the latter in square brackets following an italicized published as : “Irving, Washington [ published as Knickerbocker, Diedrich].”.
Another acceptable option, in cases where there are only two forms of the author’s name, is to cite both forms of the author’s names as separate entries along with cross-references in square brackets: “Eliot, George [ see also Evans, Mary Anne].”.

IMAGES
VIDEO