

Position Paper
Ai generator.

1. Sample Position Paper

Size: 382 KB
2. Position Paper Format

Size: 351 KB
3. Student Position Paper Example

Size: 388 KB
4. High School Position Paper Example

5. Position Paper Outline Example

6. Education Position Paper Example

Size: 950 KB
7. Position Paper Introduction Example

Size: 140 KB
8. Position Paper Template

Size: 563 KB
9. Poverty Position Paper Example

Size: 156 KB
10. Position Paper Essay Example
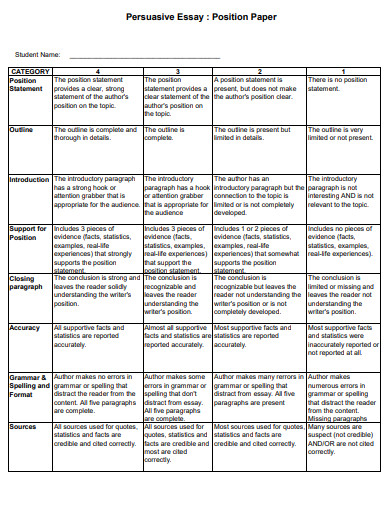
Size: 11 KB
11. Position Paper Bullying Example

Size: 22 KB
12. Position Paper Teenage Pregnancy Example
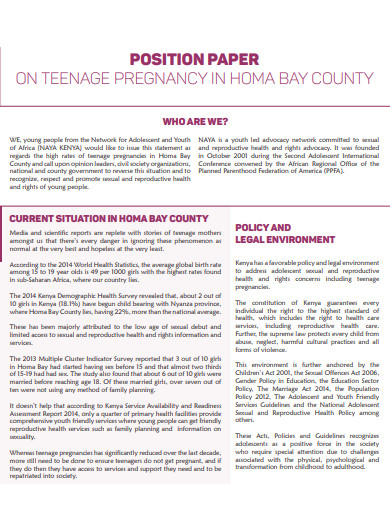
Size: 92 KB
13. Position Paper on Depression Example

Size: 225 KB
14. College Position Paper Example

Size: 311 KB
15. Position Paper on Business Example

Size: 703 KB
16. Research Position Paper Example

17. Mental Health Position Paper Example

Size: 355 KB
18. Position Paper on Social Media Example

Size: 125 KB
19. Law Position Paper Example

Size: 273 KB
20. Early Pregnancy Position Paper Example

Size: 566 KB
21. Position Paper Argument Example

22. Writing a Position Paper Example

Size: 73 KB
23. Position Paper Guide Example

24. Simple Position Paper Example

Size: 767 KB
25. Basic Position Paper Example

Size: 181 KB
26. Standard Position Paper Example

27. Printable Position Paper Example

Size: 877 KB
28. Position Paper Policy Example

Size: 72 KB
29. Position Paper Checklist Example
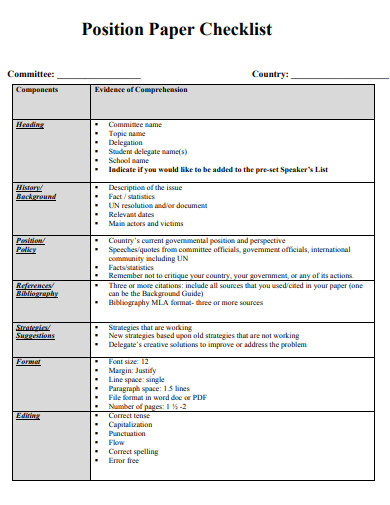
Size: 81 KB
30. Health Position Paper Example

Size: 43 KB
What is a Position Paper?
How to write a position paper.
Are you ready to make your voice heard and influence opinions? Our step-by-step guide will walk you through the process of writing a persuasive position paper. From defining your stance to addressing counterarguments, we’ll provide you with the tools and strategies to create a compelling and impactful document. Let’s get started on your journey to persuasive writing success!
Step 1: Define Your Position:
Begin by clearly defining your stance on the issue at hand. Conduct thorough research to gather relevant information, statistics, and expert opinions that support your position. Consider the context and the target audience to tailor your arguments effectively.
Step 2: Create an Outline:
Developing a well-structured outline is essential for organizing your thoughts and ensuring a logical flow in your position paper. Use different outline formats such as alphanumeric or decimal to categorize your main points, supporting evidence, and counterarguments.
Step 3: Craft a Compelling Introduction:
The introduction sets the tone for your position paper and should grab the reader’s attention. Start with a thought-provoking observation , a simple sentence that highlights the importance of the issue, or provide relevant context to establish the significance of your position. Clearly state your thesis statement, which encapsulates your main argument.
Step 4: Present Your Arguments:
In the body paragraphs, present your arguments in a clear and concise manner. Use a persuasive tone and employ various literary devices , such as metaphors or rhetorical question , to engage the reader. Support your claims with credible evidence, including data, research findings, and expert opinions. Use strong verbs and common nouns to convey your message effectively.

Step 5: Address Counterarguments:
Acknowledge and address potential counterarguments to strengthen your position. Anticipate opposing viewpoints and provide well-reasoned rebuttals. This demonstrates your ability to consider different perspectives and strengthens the overall credibility of your position paper.
Step 6: Craft a Convincing Conclusion:
In the conclusion paragraph, summarize your main arguments and restate your thesis statement. Emphasize the strengths of your position and highlight the weaknesses of opposing viewpoints. End with a compelling call to action or a thought-provoking statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
Are citations necessary in a position paper?
Yes, citations are crucial in a position paper to provide evidence for your claims and give credit to the original sources. Use a recognized citation style, such as APA or MLA, to ensure accuracy and consistency.
What elements should be included in a position paper?
A position paper should include an introduction, body paragraphs with supporting arguments, counterarguments, and a conclusion. Additionally, it should have a clear thesis statement , well-structured paragraphs, and logical transitions between ideas.
Can I use compound sentences in a position paper?
Yes, using compound sentences can enhance the clarity and coherence of your position paper. However, ensure that the sentences are concise and effectively convey your message without becoming overly complex.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- Privacy Policy

Home » Position Paper – Example, Format and Writing Guide
Position Paper – Example, Format and Writing Guide
Table of Contents
A position paper is a critical document that outlines an individual’s or organization’s stance on a particular issue or topic. It provides a well-reasoned argument supported by evidence, aiming to persuade readers to adopt a specific viewpoint. Whether for academic purposes, policy advocacy, or professional discussions, a well-crafted position paper demonstrates analytical thinking and effective communication. This article explores the format, provides an example, and offers a step-by-step guide for writing a compelling position paper.

Position Paper
A position paper is a formal essay that presents a detailed argument on a specific issue, articulating the author’s position and backing it with evidence, research, and logical reasoning. Its primary goal is to clarify the stance and convince the audience of its validity.
For example, a student may write a position paper arguing for the benefits of renewable energy policies, supporting the stance with data on environmental impact, economic advantages, and technological advancements.
Purpose of a Position Paper
- Clarify Position : Helps articulate a clear and concise stance on an issue.
- Persuade Audience : Aims to convince readers by presenting compelling arguments and evidence.
- Promote Dialogue : Encourages constructive discussion and critical thinking about the topic.
- Demonstrate Knowledge : Shows the author’s depth of understanding and ability to analyze complex issues.
Format of a Position Paper
A position paper typically follows a standard format to ensure clarity and logical flow. Below is the general structure:
- A concise and descriptive title that reflects the issue and stance.
- Example : “The Case for Renewable Energy: Addressing Climate Change Through Sustainable Solutions.”
2. Introduction
- Briefly introduce the topic and its relevance.
- Clearly state your position or thesis statement.
- Provide context or background information on the issue.
- Example : “With climate change posing a significant threat to global ecosystems, transitioning to renewable energy is imperative. This paper argues that renewable energy policies are essential for mitigating environmental degradation and fostering sustainable economic growth.”
3. Arguments Supporting Your Position
- Present 2–3 strong arguments that justify your stance.
- Back each argument with credible evidence, such as data, research studies, or expert opinions.
- Use logical reasoning to connect evidence with your claims.
- Evidence : Studies show solar and wind energy can reduce CO2 emissions by up to 80% compared to fossil fuels.
- Evidence : Job creation in renewable energy industries outpaces traditional energy sectors.
4. Counterarguments and Rebuttals
- Address potential opposing viewpoints or criticisms.
- Provide reasoned rebuttals to demonstrate why your position remains valid.
- Example : “Critics argue that renewable energy is costly. However, recent advancements in solar panel technology have significantly reduced costs, making renewables more affordable than fossil fuels in many regions.”
5. Conclusion
- Summarize the key points made in the paper.
- Reinforce the importance of your position and its implications.
- Include a call to action or suggest further research.
- Example : “Embracing renewable energy is not just a necessity but a responsibility. Governments and organizations must prioritize policies that accelerate this transition for a sustainable future.”
6. References
- Provide a list of sources cited in your paper to enhance credibility.
- Follow the required citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
Example of a Position Paper
“Reducing Plastic Waste: A Call for Global Action”
Introduction :
Plastic pollution has reached alarming levels, threatening marine ecosystems and public health. With over 8 million tons of plastic entering the oceans annually, immediate action is necessary to address this crisis. This paper argues that implementing strict regulations on plastic production and promoting biodegradable alternatives are essential for mitigating the impacts of plastic waste.
Arguments Supporting the Position :
- Environmental Impact : Plastic waste harms marine life and ecosystems. Studies indicate that over 1 million marine animals die annually due to plastic ingestion or entanglement. Regulating plastic production can reduce this catastrophic impact.
- Health Concerns : Microplastics have been detected in food, water, and air, posing health risks to humans. Policies reducing plastic use will decrease exposure to these harmful particles.
- Economic Benefits of Alternatives : Promoting biodegradable materials can stimulate new industries and create green jobs. For example, a study by the Environmental Policy Institute highlights that transitioning to biodegradable packaging could generate over 100,000 jobs globally.
Counterarguments and Rebuttals :
- Counterargument : Plastic is cheap and versatile, making it difficult to replace.
- Rebuttal : While plastic is inexpensive, its environmental and health costs far outweigh its short-term economic benefits. Investments in research and subsidies for biodegradable alternatives can address affordability concerns.
Conclusion :
Reducing plastic waste requires a collaborative effort between governments, industries, and individuals. By implementing stricter regulations and fostering innovation, we can protect ecosystems, improve public health, and create sustainable economic opportunities. The time to act is now.
References :
- Jambeck, J. R., et al. (2015). “Plastic Waste Inputs from Land into the Ocean.” Science , 347(6223), 768–771.
- World Economic Forum. (2020). The New Plastics Economy .
- Environmental Policy Institute. (2021). “Economic Opportunities in Biodegradable Packaging.”
Step-by-Step Writing Guide
Step 1: choose a relevant topic.
Select a topic that aligns with your interests and is significant to your audience. Ensure the topic allows for a clear position to be taken.
- Example Topics :
- “Should Social Media Be Regulated to Prevent Misinformation?”
- “The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Education.”
Step 2: Research Thoroughly
Gather credible evidence to support your position. Use academic articles, books, reputable websites, and expert opinions to build a strong foundation.
Step 3: Outline Your Paper
Organize your arguments, counterarguments, and supporting evidence into a logical structure. Use the format provided earlier to create a clear outline.
Step 4: Write the Draft
Start with a compelling introduction that captures the reader’s attention and clearly states your position. Develop each section systematically, ensuring smooth transitions between paragraphs.
Step 5: Revise and Edit
Review your paper for clarity, coherence, and accuracy. Eliminate redundant arguments, strengthen weak points, and proofread for grammar and formatting errors.
Step 6: Cite Your Sources
Provide proper citations for all sources used to enhance credibility and avoid plagiarism.
Tips for Writing an Effective Position Paper
- Be Clear and Concise : Avoid vague statements and focus on presenting a clear position.
- Use Credible Evidence : Support your arguments with reliable and well-documented evidence.
- Address Counterarguments : Acknowledge opposing views to demonstrate thorough understanding.
- Maintain a Formal Tone : Use professional language and avoid overly emotional appeals.
- Stay Focused : Stick to the main topic and avoid deviating into unrelated issues.
A position paper is a powerful tool for presenting well-reasoned arguments and influencing discussions on critical issues. By following the format, leveraging credible evidence, and addressing counterarguments, writers can craft compelling papers that effectively communicate their stance. Whether in academia, policymaking, or professional settings, mastering the art of position paper writing is invaluable for making an impact.
- Corey, S. (2020). Writing Effective Position Papers: A Practical Guide for Researchers and Advocates . Sage Publications.
- Purdue Online Writing Lab. (2023). “Position Paper Resources.”
- Babbie, E. (2021). The Practice of Social Research (15th ed.). Cengage Learning.
- Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . Sage Publications.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Artist – Definition,Types and Work Area

What is Science – Definition, Methods, Types

Physicist – Definition, Types and Work Area

Anthropologist – Definition, Types, Work Area

Chemist – Definition, Types and Work Area

Researcher – How to become a Researcher

IMAGES
VIDEO