
- Chapter Seven: Presenting Your Results
This chapter serves as the culmination of the previous chapters, in that it focuses on how to present the results of one's study, regardless of the choice made among the three methods. Writing in academics has a form and style that you will want to apply not only to report your own research, but also to enhance your skills at reading original research published in academic journals. Beyond the basic academic style of report writing, there are specific, often unwritten assumptions about how quantitative, qualitative, and critical/rhetorical studies should be organized and the information they should contain. This chapter discusses how to present your results in writing, how to write accessibly, how to visualize data, and how to present your results in person.
- Chapter One: Introduction
- Chapter Two: Understanding the distinctions among research methods
- Chapter Three: Ethical research, writing, and creative work
- Chapter Four: Quantitative Methods (Part 1)
- Chapter Four: Quantitative Methods (Part 2 - Doing Your Study)
- Chapter Four: Quantitative Methods (Part 3 - Making Sense of Your Study)
- Chapter Five: Qualitative Methods (Part 1)
- Chapter Five: Qualitative Data (Part 2)
- Chapter Six: Critical / Rhetorical Methods (Part 1)
- Chapter Six: Critical / Rhetorical Methods (Part 2)

Written Presentation of Results
Once you've gone through the process of doing communication research – using a quantitative, qualitative, or critical/rhetorical methodological approach – the final step is to communicate it.
The major style manuals (the APA Manual, the MLA Handbook, and Turabian) are very helpful in documenting the structure of writing a study, and are highly recommended for consultation. But, no matter what style manual you may use, there are some common elements to the structure of an academic communication research paper.
Title Page :
This is simple: Your Paper's Title, Your Name, Your Institutional Affiliation (e.g., University), and the Date, each on separate lines, centered on the page. Try to make your title both descriptive (i.e., it gives the reader an idea what the study is about) and interesting (i.e., it is catchy enough to get one's attention).
For example, the title, "The uncritical idealization of a compensated psychopath character in a popular book series," would not be an inaccurate title for a published study, but it is rather vague and exceedingly boring. That study's author fortunately chose the title, "A boyfriend to die for: Edward Cullen as compensated psychopath in Stephanie Meyer's Twilight ," which is more precisely descriptive, and much more interesting (Merskin, 2011). The use of the colon in academic titles can help authors accomplish both objectives: a catchy but relevant phrase, followed by a more clear explanation of the article's topic.
In some instances, you might be asked to write an abstract, which is a summary of your paper that can range in length from 75 to 250 words. If it is a published paper, it is useful to include key search terms in this brief description of the paper (the title may already have a few of these terms as well). Although this may be the last thing your write, make it one of the best things you write, because this may be the first thing your audience reads about the paper (and may be the only thing read if it is written badly). Summarize the problem/research question, your methodological approach, your results and conclusions, and the significance of the paper in the abstract.
Quantitative and qualitative studies will most typically use the rest of the section titles noted below. Critical/rhetorical studies will include many of the same steps, but will often have different headings. For example, a critical/rhetorical paper will have an introduction, definition of terms, and literature review, followed by an analysis (often divided into sections by areas of investigation) and ending with a conclusion/implications section. Because critical/rhetorical research is much more descriptive, the subheadings in such a paper are often times not generic subheads like "literature review," but instead descriptive subheadings that apply to the topic at hand, as seen in the schematic below. Because many journals expect the article to follow typical research paper headings of introduction, literature review, methods, results, and discussion, we discuss these sections briefly next.
Introduction:
As you read social scientific journals (see chapter 1 for examples), you will find that they tend to get into the research question quickly and succinctly. Journal articles from the humanities tradition tend to be more descriptive in the introduction. But, in either case, it is good to begin with some kind of brief anecdote that gets the reader engaged in your work and lets the reader understand why this is an interesting topic. From that point, state your research question, define the problem (see Chapter One) with an overview of what we do and don't know, and finally state what you will do, or what you want to find out. The introduction thus builds the case for your topic, and is the beginning of building your argument, as we noted in chapter 1.
By the end of the Introduction, the reader should know what your topic is, why it is a significant communication topic, and why it is necessary that you investigate it (e.g., it could be there is gap in literature, you will conduct valuable exploratory research, or you will provide a new model for solving some professional or social problem).
Literature Review:
The literature review summarizes and organizes the relevant books, articles, and other research in this area. It sets up both quantitative and qualitative studies, showing the need for the study. For critical/rhetorical research, the literature review often incorporates the description of the historical context and heuristic vocabulary, with key terms defined in this section of the paper. For more detail on writing a literature review, see Appendix 1.
The methods of your paper are the processes that govern your research, where the researcher explains what s/he did to solve the problem. As you have seen throughout this book, in communication studies, there are a number of different types of research methods. For example, in quantitative research, one might conduct surveys, experiments, or content analysis. In qualitative research, one might instead use interviews and observations. Critical/rhetorical studies methods are more about the interpretation of texts or the study of popular culture as communication. In creative communication research, the method may be an interpretive performance studies or filmmaking. Other methods used sometimes alone, or in combination with other methods, include legal research, historical research, and political economy research.
In quantitative and qualitative research papers, the methods will be most likely described according to the APA manual standards. At the very least, the methods will include a description of participants, data collection, and data analysis, with specific details on each of these elements. For example, in an experiment, the researcher will describe the number of participants, the materials used, the design of the experiment, the procedure of the experiment, and what statistics will be used to address the hypotheses/research questions.
Critical/rhetorical researchers rarely have a specific section called "methods," as opposed to quantitative and qualitative researchers, but rather demonstrate the method they use for analysis throughout the writing of their piece.
Helping your reader understand the methods you used for your study is important not only for your own study's credibility, but also for possible replication of your study by other researchers. A good guideline to keep in mind is transparency . You want to be as clear as possible in describing the decisions you made in designing your study, gathering and analyzing your data so that the reader can retrace your steps and understand how you came to the conclusions you formed. A research study can be very good, but if it is not clearly described so that others can see how the results were determined or obtained, then the quality of the study and its potential contributions are lost.
After you completed your study, your findings will be listed in the results section. Particularly in a quantitative study, the results section is for revisiting your hypotheses and reporting whether or not your results supported them, and the statistical significance of the results. Whether your study supported or contradicted your hypotheses, it's always helpful to fully report what your results were. The researcher usually organizes the results of his/her results section by research question or hypothesis, stating the results for each one, using statistics to show how the research question or hypothesis was answered in the study.
The qualitative results section also may be organized by research question, but usually is organized by themes which emerged from the data collected. The researcher provides rich details from her/his observations and interviews, with detailed quotations provided to illustrate the themes identified. Sometimes the results section is combined with the discussion section.
Critical/rhetorical researchers would include their analysis often with different subheadings in what would be considered a "results" section, yet not labeled specifically this way.
Discussion:
In the discussion section, the researcher gives an appraisal of the results. Here is where the researcher considers the results, particularly in light of the literature review, and explains what the findings mean. If the results confirmed or corresponded with the findings of other literature, then that should be stated. If the results didn't support the findings of previous studies, then the researcher should develop an explanation of why the study turned out this way. Sometimes, this section is called a "conclusion" by researchers.
References:
In this section, all of the literature cited in the text should have full references in alphabetical order. Appendices: Appendix material includes items like questionnaires used in the study, photographs, documents, etc. An alphabetical letter is assigned for each piece (e.g. Appendix A, Appendix B), with a second line of title describing what the appendix contains (e.g. Participant Informed Consent, or New York Times Speech Coverage). They should be organized consistently with the order in which they are referenced in the text of the paper. The page numbers for appendices are consecutive with the paper and reference list.
Tables/Figures:
Tables and figures are referenced in the text, but included at the end of the study and numbered consecutively. (Check with your professor; some like to have tables and figures inserted within the paper's main text.) Tables generally are data in a table format, whereas figures are diagrams (such as a pie chart) and drawings (such as a flow chart).
Accessible Writing
As you may have noticed, academic writing does have a language (e.g., words like heuristic vocabulary and hypotheses) and style (e.g., literature reviews) all its own. It is important to engage in that language and style, and understand how to use it to communicate effectively in an academic context . Yet, it is also important to remember that your analyses and findings should also be written to be accessible. Writers should avoid excessive jargon, or—even worse—deploying jargon to mask an incomplete understanding of a topic.
The scourge of excessive jargon in academic writing was the target of a famous hoax in 1996. A New York University physics professor submitted an article, " Transgressing the Boundaries: Toward a Transformative Hermeneutics of Quantum Gravity ," to a special issue of the academic journal Social Text devoted to science and postmodernism. The article was designed to point out how dense academic jargon can sometimes mask sloppy thinking. As the professor, Alan Sokal, had expected, the article was published. One sample sentence from the article reads:
It has thus become increasingly apparent that physical "reality", no less than social "reality", is at bottom a social and linguistic construct; that scientific "knowledge", far from being objective, reflects and encodes the dominant ideologies and power relations of the culture that produced it; that the truth claims of science are inherently theory-laden and self-referential; and consequently, that the discourse of the scientific community, for all its undeniable value, cannot assert a privileged epistemological status with respect to counter-hegemonic narratives emanating from dissident or marginalized communities. (Sokal, 1996. pp. 217-218)
According to the journal's editor, about six reviewers had read the article but didn't suspect that it was phony. A public debate ensued after Sokal revealed his hoax. Sokal said he worried that jargon and intellectual fads cause academics to lose contact with the real world and "undermine the prospect for progressive social critique" ( Scott, 1996 ). The APA Manual recommends to avoid using technical vocabulary where it is not needed or relevant or if the technical language is overused, thus becoming jargon. In short, the APA argues that "scientific jargon...grates on the reader, encumbers the communication of information, and wastes space" (American Psychological Association, 2010, p. 68).
Data Visualization
Images and words have long existed on the printed page of manuscripts, yet, until recently, relatively few researchers possessed the resources to effectively combine images combined with words (Tufte, 1990, 1983). Communication scholars are only now becoming aware of this dimension in research as computer technologies have made it possible for many people to produce and publish multimedia presentations.
Although visuals may seem to be anathema to the primacy of the written word in research, they are a legitimate way, and at times the best way, to present ideas. Visual scholar Lester Faigley et al. (2004) explains how data visualizations have become part of our daily lives:
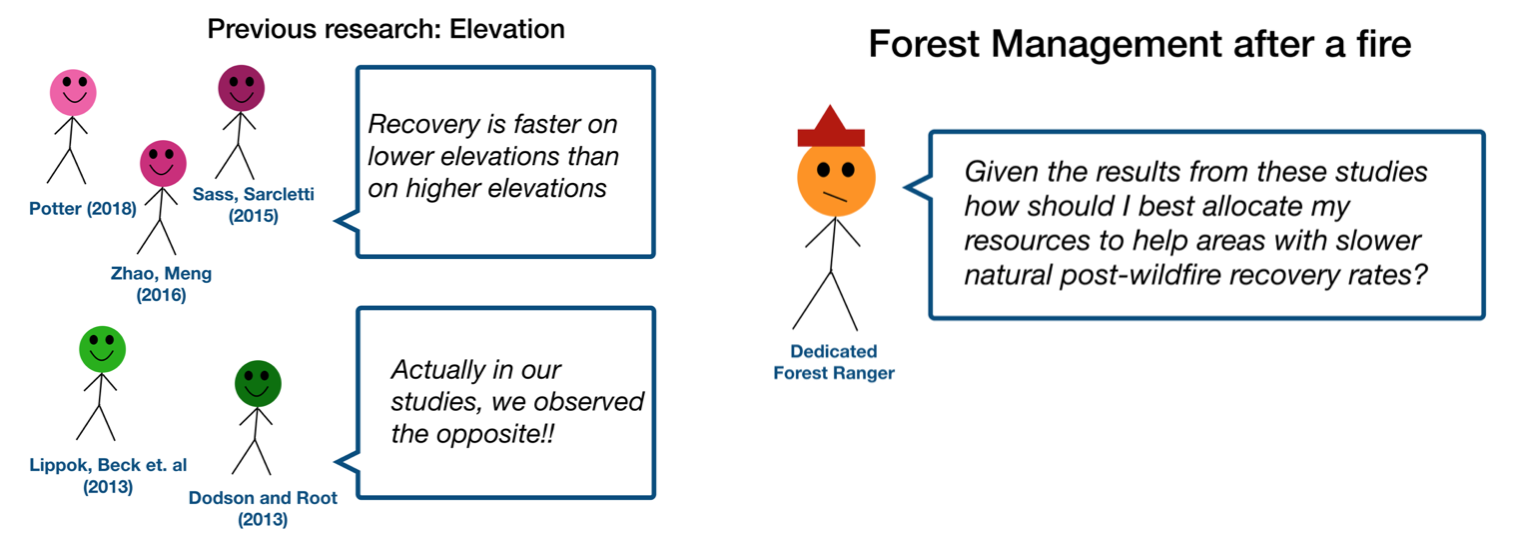
Visualizations can shed light on research as well. London-based David McCandless specializes in visualizing interesting research questions, or in his words "the questions I wanted answering" (2009, p. 7). His images include a graph of the peak times of the year for breakups (based on Facebook status updates), a radiation dosage chart , and some experiments with the Google Ngram Viewer , which charts the appearance of keywords in millions of books over hundreds of years.
The public domain image below creatively maps U.S. Census data of the outflow of people from California to other states between 1995 and 2000.
Visualizing one's research is possible in multiple ways. A simple technology, for example, is to enter data into a spreadsheet such as Excel, and select Charts or SmartArt to generate graphics. A number of free web tools can also transform raw data into useful charts and graphs. Many Eyes , an open source data visualization tool (sponsored by IBM Research), says its goal "is to 'democratize' visualization and to enable a new social kind of data analysis" (IBM, 2011). Another tool, Soundslides , enables users to import images and audio to create a photographic slideshow, while the program handles all of the background code. Other tools, often open source and free, can help visual academic research into interactive maps; interactive, image-based timelines; interactive charts; and simple 2-D and 3-D animations. Adobe Creative Suite (which includes popular software like Photoshop) is available on most computers at universities, but open source alternatives exist as well. Gimp is comparable to Photoshop, and it is free and relatively easy to use.
One online performance studies journal, Liminalities , is an excellent example of how "research" can be more than just printed words. In each issue, traditional academic essays and book reviews are often supported photographs, while other parts of an issue can include video, audio, and multimedia contributions. The journal, founded in 2005, treats performance itself as a methodology, and accepts contribution in html, mp3, Quicktime, and Flash formats.
For communication researchers, there is also a vast array of visual digital archives available online. Many of these archives are located at colleges and universities around the world, where digital librarians are spearheading a massive effort to make information—print, audio, visual, and graphic—available to the public as part of a global information commons. For example, the University of Iowa has a considerable digital archive including historical photos documenting American railroads and a database of images related to geoscience. The University of Northern Iowa has a growing Special Collections Unit that includes digital images of every UNI Yearbook between 1905 and 1923 and audio files of UNI jazz band performances. Researchers at he University of Michigan developed OAIster , a rich database that has joined thousands of digital archives in one searchable interface. Indeed, virtually every academic library is now digitizing all types of media, not just texts, and making them available for public viewing and, when possible, for use in presenting research. In addition to academic collections, the Library of Congress and the National Archives offer an ever-expanding range of downloadable media; commercial, user-generated databases such as Flickr, Buzznet, YouTube and Google Video offer a rich resource of images that are often free of copyright constraints (see Chapter 3 about Creative Commons licenses) and nonprofit endeavors, such as the Internet Archive , contain a formidable collection of moving images, still photographs, audio files (including concert recordings), and open source software.
Presenting your Work in Person
As Communication students, it's expected that you are not only able to communicate your research project in written form but also in person.
Before you do any oral presentation, it's good to have a brief "pitch" ready for anyone who asks you about your research. The pitch is routine in Hollywood: a screenwriter has just a few minutes to present an idea to a producer. Although your pitch will be more sophisticated than, say, " Snakes on a Plane " (which unfortunately was made into a movie), you should in just a few lines be able to explain the gist of your research to anyone who asks. Developing this concise description, you will have some practice in distilling what might be a complicated topic into one others can quickly grasp.
Oral presentation
In most oral presentations of research, whether at the end of a semester, or at a research symposium or conference, you will likely have just 10 to 20 minutes. This is probably not enough time to read the entire paper aloud, which is not what you should do anyway if you want people to really listen (although, unfortunately some make this mistake). Instead, the point of the presentation should be to present your research in an interesting manner so the listeners will want to read the whole thing. In the presentation, spend the least amount of time on the literature review (a very brief summary will suffice) and the most on your own original contribution. In fact, you may tell your audience that you are only presenting on one portion of the paper, and that you would be happy to talk more about your research and findings in the question and answer session that typically follows. Consider your presentation the beginning of a dialogue between you and the audience. Your tone shouldn't be "I have found everything important there is to find, and I will cram as much as I can into this presentation," but instead "I found some things you will find interesting, but I realize there is more to find."
Turabian (2007) has a helpful chapter on presenting research. Most important, she emphasizes, is to remember that your audience members are listeners, not readers. Thus, recall the lessons on speech making in your college oral communication class. Give an introduction, tell them what the problem is, and map out what you will present to them. Organize your findings into a few points, and don't get bogged down in minutiae. (The minutiae are for readers to find if they wish, not for listeners to struggle through.) PowerPoint slides are acceptable, but don't read them. Instead, create an outline of a few main points, and practice your presentation.
Turabian suggests an introduction of not more than three minutes, which should include these elements:
- The research topic you will address (not more than a minute).
- Your research question (30 seconds or less)
- An answer to "so what?" – explaining the relevance of your research (30 seconds)
- Your claim, or argument (30 seconds or less)
- The map of your presentation structure (30 seconds or less)
As Turabian (2007) suggests, "Rehearse your introduction, not only to get it right, but to be able to look your audience in the eye as you give it. You can look down at notes later" (p. 125).
Poster presentation
In some symposiums and conferences, you may be asked to present at a "poster" session. Instead of presenting on a panel of 4-5 people to an audience, a poster presenter is with others in a large hall or room, and talks one-on-one with visitors who look at the visual poster display of the research. As in an oral presentation, a poster highlights just the main point of the paper. Then, if visitors have questions, the author can informally discuss her/his findings.
To attract attention, poster presentations need to be nicely designed, or in the words of an advertising professor who schedules poster sessions at conferences, "be big, bold, and brief" ( Broyles , 2011). Large type (at least 18 pt.), graphics, tables, and photos are recommended.
A poster presentation session at a conference, by David Eppstein (Own work) [CC-BY-SA-3.0 ( www.creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0 )], via Wikimedia Commons]
The Association for Education in Journalism and Mass Communication (AEJMC) has a template for making an effective poster presentation . Many universities, copy shops, and Internet services also have large-scale printers, to print full-color research poster designs that can be rolled up and transported in a tube.
Judging Others' Research
After taking this course, you should have a basic knowledge of research methods. There will still be some things that may mystify you as a reader of other's research. For example, you may not be able to interpret the coefficients for statistical significance, or make sense of a complex structural equation. Some specialized vocabulary may still be difficult.
But, you should understand how to critically review research. For example, imagine you have been asked to do a blind (i.e., the author's identity is concealed) "peer review" of communication research for acceptance to a conference, or publication in an academic journal. For most conferences and journals , submissions are made online, where editors can manage the flow and assign reviews to papers. The evaluations reviewers make are based on the same things that we have covered in this book. For example, the conference for the AEJMC ask reviewers to consider (on a five-point scale, from Excellent to Poor) a number of familiar research dimensions, including the paper's clarity of purpose, literature review, clarity of research method, appropriateness of research method, evidence presented clearly, evidence supportive of conclusions, general writing and organization, and the significance of the contribution to the field.
Beyond academia, it is likely you will more frequently apply the lessons of research methods as a critical consumer of news, politics, and everyday life. Just because some expert cites a number or presents a conclusion doesn't mean it's automatically true. John Allen Paulos, in his book A Mathematician reads the newspaper , suggests some basic questions we can ask. "If statistics were presented, how were they obtained? How confident can we be of them? Were they derived from a random sample or from a collection of anecdotes? Does the correlation suggest a causal relationship, or is it merely a coincidence?" (1997, p. 201).
Through the study of research methods, we have begun to build a critical vocabulary and understanding to ask good questions when others present "knowledge." For example, if Candidate X won a straw poll in Iowa, does that mean she'll get her party's nomination? If Candidate Y wins an open primary in New Hampshire, does that mean he'll be the next president? If Candidate Z sheds a tear, does it matter what the context is, or whether that candidate is a man or a woman? What we learn in research methods about validity, reliability, sampling, variables, research participants, epistemology, grounded theory, and rhetoric, we can consider whether the "knowledge" that is presented in the news is a verifiable fact, a sound argument, or just conjecture.
American Psychological Association (2010). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (6th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
Broyles, S. (2011). "About poster sessions." AEJMC. http://www.aejmc.org/home/2013/01/about-poster-sessions/ .
Faigley, L., George, D., Palchik, A., Selfe, C. (2004). Picturing texts . New York: W.W. Norton & Company.
IBM (2011). Overview of Many Eyes. http://www.research.ibm.com/social/projects_manyeyes.shtml .
McCandless, D. (2009). The visual miscellaneum . New York: Collins Design.
Merskin, D. (2011). A boyfriend to die for: Edward Cullen as compensated psychopath in Stephanie Meyer's Twilight. Journal of Communication Inquiry 35: 157-178. doi:10.1177/0196859911402992
Paulos, J. A. (1997). A mathematician reads the newspaper . New York: Anchor.
Scott, J. (1996, May 18). Postmodern gravity deconstructed, slyly. New York Times , http://www.nytimes.com/books/98/11/15/specials/sokal-text.html .
Sokal, A. (1996). Transgressing the boundaries: towards a transformative hermeneutics of quantum gravity. Social Text 46/47, 217-252.
Tufte, E. R. (1990). Envisioning information . Cheshire, CT: Graphics Press.
Tufte, E. R. (1983). The visual display of quantitative information . Cheshire, CT: Graphics Press.
Turabian, Kate L. (2007). A manual for writers of research papers, theses, and dissertations: Chicago style guide for students and researchers (7th ed.). Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
- Carmine Gallo

Five tips to set yourself apart.
Never underestimate the power of great communication. It can help you land the job of your dreams, attract investors to back your idea, or elevate your stature within your organization. But while there are plenty of good speakers in the world, you can set yourself apart out by being the person who can deliver something great over and over. Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired together are more memorable); don’t underestimate the power of your voice (raise and lower it for emphasis); give your audience something extra (unexpected moments will grab their attention); rehearse (the best speakers are the best because they practice — a lot).
I was sitting across the table from a Silicon Valley CEO who had pioneered a technology that touches many of our lives — the flash memory that stores data on smartphones, digital cameras, and computers. He was a frequent guest on CNBC and had been delivering business presentations for at least 20 years before we met. And yet, the CEO wanted to sharpen his public speaking skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center

Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research
How to Make a Successful Research Presentation
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor’s standpoint. I’ve presented my own research before, but helping others present theirs taught me a bit more about the process. Here are some tips I learned that may help you with your next research presentation:
More is more
In general, your presentation will always benefit from more practice, more feedback, and more revision. By practicing in front of friends, you can get comfortable with presenting your work while receiving feedback. It is hard to know how to revise your presentation if you never practice. If you are presenting to a general audience, getting feedback from someone outside of your discipline is crucial. Terms and ideas that seem intuitive to you may be completely foreign to someone else, and your well-crafted presentation could fall flat.
Less is more
Limit the scope of your presentation, the number of slides, and the text on each slide. In my experience, text works well for organizing slides, orienting the audience to key terms, and annotating important figures–not for explaining complex ideas. Having fewer slides is usually better as well. In general, about one slide per minute of presentation is an appropriate budget. Too many slides is usually a sign that your topic is too broad.

Limit the scope of your presentation
Don’t present your paper. Presentations are usually around 10 min long. You will not have time to explain all of the research you did in a semester (or a year!) in such a short span of time. Instead, focus on the highlight(s). Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
You will not have time to explain all of the research you did. Instead, focus on the highlights. Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
Craft a compelling research narrative
After identifying the focused research question, walk your audience through your research as if it were a story. Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling.
- Introduction (exposition — rising action)
Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story. Introduce the key studies (characters) relevant in your story and build tension and conflict with scholarly and data motive. By the end of your introduction, your audience should clearly understand your research question and be dying to know how you resolve the tension built through motive.
- Methods (rising action)
The methods section should transition smoothly and logically from the introduction. Beware of presenting your methods in a boring, arc-killing, ‘this is what I did.’ Focus on the details that set your story apart from the stories other people have already told. Keep the audience interested by clearly motivating your decisions based on your original research question or the tension built in your introduction.
- Results (climax)
Less is usually more here. Only present results which are clearly related to the focused research question you are presenting. Make sure you explain the results clearly so that your audience understands what your research found. This is the peak of tension in your narrative arc, so don’t undercut it by quickly clicking through to your discussion.
- Discussion (falling action)
By now your audience should be dying for a satisfying resolution. Here is where you contextualize your results and begin resolving the tension between past research. Be thorough. If you have too many conflicts left unresolved, or you don’t have enough time to present all of the resolutions, you probably need to further narrow the scope of your presentation.
- Conclusion (denouement)
Return back to your initial research question and motive, resolving any final conflicts and tying up loose ends. Leave the audience with a clear resolution of your focus research question, and use unresolved tension to set up potential sequels (i.e. further research).
Use your medium to enhance the narrative
Visual presentations should be dominated by clear, intentional graphics. Subtle animation in key moments (usually during the results or discussion) can add drama to the narrative arc and make conflict resolutions more satisfying. You are narrating a story written in images, videos, cartoons, and graphs. While your paper is mostly text, with graphics to highlight crucial points, your slides should be the opposite. Adapting to the new medium may require you to create or acquire far more graphics than you included in your paper, but it is necessary to create an engaging presentation.
The most important thing you can do for your presentation is to practice and revise. Bother your friends, your roommates, TAs–anybody who will sit down and listen to your work. Beyond that, think about presentations you have found compelling and try to incorporate some of those elements into your own. Remember you want your work to be comprehensible; you aren’t creating experts in 10 minutes. Above all, try to stay passionate about what you did and why. You put the time in, so show your audience that it’s worth it.
For more insight into research presentations, check out these past PCUR posts written by Emma and Ellie .
— Alec Getraer, Natural Sciences Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Uncategorized
The 6-Steps to Persuasively Presenting Your Results

I know, reporting research results is supposed to be cut and dried. No emotion, no opinion, just the facts. That might be true for academia and basic research, but in the world of business it’s all about using the results to help us make “good” decisions. Here is a great way to synthesize and summarize your results in a way that will help your audience easily process what the results mean and then make a sound decision based on those results.
How to Present Your Results and Get Recommendations Implemented
“Our competitors have already launched Wickety Widget to stellar results, but they are missing out on a key customer segment. Can we interest 1000 soccer moms to buy our Wacky Wodget in the next quarter and take that segment for ourselves?”
- Tell a story. It’s not news anymore that we base many decisions more on an emotional basis than on a logical basis. Since your data is the logic – give your audience and emotional hat to hang your data on. Tell them the story behind the objective of your research. How did this burning issue develop? What observations or opportunities did you identify that prompted the research. What benefits did you think were possible…if only…? Telling a good story will lend context to the data and help your audience formulate an opinion and make decisions. Use your data as supporting evidence to the key points of the story. In other words, instead of using your data and charts to drive the story, use the story to drive the data and the charts.
- Give the Answer in the Chart Title. Charts generally confuse people — especially table charts. That’s why it’s brilliant strategy to give your chart title as a conclusion to what the chart means. For example “85% of our target market prefers the purple flying elephant logo.” This way, when they see the chart, they won’t have to do their own analysis, they will simply confirm what you’ve already told them and this is what will stay in their memory.
Don’t just present the data, take this golden opportunity to think of creative solutions, recommendations and implementation strategies. Look for creative ways to create mock-ups and other physical representations of solutions. Actually seeing a solution gets people excited and relieves them of the responsibility to think of something. You look like a hero and your recommendation just took another step toward becoming reality.
- Give them a payoff. Tell your audience why this idea is good for them. How will they benefit from implementing these recommendations.
- Tell them how to take action. Come prepared with an action you want them to take. Do they need to approve a budget? Have the paperwork there and ready for their signature. Do they need to get together for another meeting? Have access to a calendar and schedule that date. You’ll never have the audience this excited again, so take advantage of it.
This outline will take a little longer to prepare than your standard Power Point presentation, but it will only take about ten minutes to deliver and will get your audience saying “YES” to your recommendations.
Try it and let us know how it worked.
About the Author: Ivana Taylor is CEO of Third Force, a strategic firm that helps small businesses get and keep their ideal customer. She’s the co-author of the book “Excel for Marketing Managers” and proprietor of DIYMarketers, a site for in-house marketers. Her blog is Strategy Stew. You can reach her directly at [email protected] .
MORE LIKE THIS

Experimental vs Observational Studies: Differences & Examples
Sep 5, 2024
Interactive Forms: Key Features, Benefits, Uses + Design Tips
Sep 4, 2024

Closed-Loop Management: The Key to Customer Centricity
Sep 3, 2024

Net Trust Score: Tool for Measuring Trust in Organization
Sep 2, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Research Guide
Chapter 7 presenting your findings.
Now that you have worked so hard in your project, how to ensure that you can communicate your findings in an effective and efficient way? In this section, I will introduce a few tips that could help you prepare your slides and preparing for your final presentation.
7.1 Sections of the Presentation
When preparing your slides, you need to ensure that you have a clear roadmap. You have a limited time to explain the context of your study, your results, and the main takeaways. Thus, you need to be organized and efficient when deciding what material will be included in the slides.
You need to ensure that your presentation contains the following sections:
- Motivation : Why did you choose your topic? What is the bigger question?
- Research question : Needs to be clear and concise. Include secondary questions, if available, but be clear about what is your research question.
- Literature Review : How does your paper fit in the overall literature? What are your contributions?
- Context : Give an overview of the issue and the population/countries that you analyzed
- Study Characteristics : This section is key, as it needs to include your model, identification strategy, and introduce your data (sources, summary statistics, etc.).
- Results : In this section, you need to answer your research question(s). Include tables that are readable.
- Additional analysis : Here, include any additional information that your public needs to know. For instance, did you try different specifications? did you find an obstacle (i.e. your data is very noisy, the sample is very small, something else) that may bias your results or create some issues in your analysis? Tell your audience! No research project is perfect, but you need to be clear about the imperfections of your project.
- Conclusion : Be repetitive! What was your research question? How did you answer it? What did you find? What is next in this topic?
7.2 How to prepare your slides
When preparing your slides, remember that humans have a limited capacity to pay attention. If you want to convey your convey your message in an effective way, you need to ensure that the message is simple and that you keep your audience attention. Here are some strategies that you may want to follow:
- Have a clear roadmap at the beginning of the presentation. Tell your audience what to expect.
- Number your slides. This will help you and your audience to know where you are in your analysis.
- Ensure that each slide has a purpose
- Ensure that each slide is connected to your key point.
- Make just one argument per slide
- State the objective of each slide in the headline
- Use bullet points. Do not include more than one sentence per bullet point.
- Choose a simple background.
- If you want to direct your audience attention to a specific point, make it more attractive (using a different font color)
- Each slide needs to have a similar structure (going from the general to the particular detauls).
- Use images/graphs when possible. Ensure that the axes for the graphs are clear.
- Use a large font for your tables. Keep them as simple as possible.
- If you can say it with an image, choose it over a table.
- Have an Appendix with slides that address potential questions.
7.3 How to prepare your presentation
One of the main constraints of having simple presentations is that you cannot rely on them and read them. Instead, you need to have extra notes and memorize them to explain things beyond what is on your slides. The following are some suggestions on how to ensure you communicate effectively during your presentation.
- Practice, practice, practice!
- Keep the right volume (practice will help you with that)
- Be journalistic about your presentation. Indicate what you want to say, then say it.
- Ensure that your audience knows where you are going
- Avoid passive voice.
- Be consistent with the terms you are using. You do not want to confuse your audience, even if using synonyms.
- Face your audience and keep an eye contact.
- Do not try reading your slides
- Ensure that your audience is focused on what you are presenting and there are no other distractions that you can control.
- Do not rush your presentation. Speak calmly and controlled.
- Be comprehensive when answering questions. Avoid yes/no answers. Instead, rephrase question (to ensure you are answering the right question), then give a short answer, then develop.
- If you lose track, do not panick. Go back a little bit or ask your audience for assistance.
- Again, practice is the secret.
You have worked so hard in your final project, and the presentation is your opportunity to share that work with the rest of the world. Use this opportunity to shine and enjoy it.
Since this is the first iteration of the Guide, I expect that there are going to be multiple typos and structure issues. Please feel free to let me know, and I will correct accordingly. ↩︎
Note that you would still need to refine some of the good questions even more. ↩︎
How to Present Results in a Research Paper
- First Online: 01 October 2023
Cite this chapter

- Aparna Mukherjee 4 ,
- Gunjan Kumar 4 &
- Rakesh Lodha 5
1218 Accesses
The results section is the core of a research manuscript where the study data and analyses are presented in an organized, uncluttered manner such that the reader can easily understand and interpret the findings. This section is completely factual; there is no place for opinions or explanations from the authors. The results should correspond to the objectives of the study in an orderly manner. Self-explanatory tables and figures add value to this section and make data presentation more convenient and appealing. The results presented in this section should have a link with both the preceding methods section and the following discussion section. A well-written, articulate results section lends clarity and credibility to the research paper and the study as a whole. This chapter provides an overview and important pointers to effective drafting of the results section in a research manuscript and also in theses.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Conclusions

Research Method

Research Questions and Research Design
Kallestinova ED (2011) How to write your first research paper. Yale J Biol Med 84(3):181–190
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
STROBE. STROBE. [cited 2022 Nov 10]. https://www.strobe-statement.org/
Consort—Welcome to the CONSORT Website. http://www.consort-statement.org/ . Accessed 10 Nov 2022
Korevaar DA, Cohen JF, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, Gatsonis CA, Glasziou PP et al (2016) Updating standards for reporting diagnostic accuracy: the development of STARD 2015. Res Integr Peer Rev 1(1):7
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD et al (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n71
Page MJ, Moher D, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD et al (2021) PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n160
Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups | EQUATOR Network. https://www.equator-network.org/reporting-guidelines/coreq/ . Accessed 10 Nov 2022
Aggarwal R, Sahni P (2015) The results section. In: Aggarwal R, Sahni P (eds) Reporting and publishing research in the biomedical sciences, 1st edn. National Medical Journal of India, Delhi, pp 24–44
Google Scholar
Mukherjee A, Lodha R (2016) Writing the results. Indian Pediatr 53(5):409–415
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lodha R, Randev S, Kabra SK (2016) Oral antibiotics for community acquired pneumonia with chest indrawing in children aged below five years: a systematic review. Indian Pediatr 53(6):489–495
Anderson C (2010) Presenting and evaluating qualitative research. Am J Pharm Educ 74(8):141
Roberts C, Kumar K, Finn G (2020) Navigating the qualitative manuscript writing process: some tips for authors and reviewers. BMC Med Educ 20:439
Bigby C (2015) Preparing manuscripts that report qualitative research: avoiding common pitfalls and illegitimate questions. Aust Soc Work 68(3):384–391
Article Google Scholar
Vincent BP, Kumar G, Parameswaran S, Kar SS (2019) Barriers and suggestions towards deceased organ donation in a government tertiary care teaching hospital: qualitative study using socio-ecological model framework. Indian J Transplant 13(3):194
McCormick JB, Hopkins MA (2021) Exploring public concerns for sharing and governance of personal health information: a focus group study. JAMIA Open 4(4):ooab098
Groenland -emeritus professor E. Employing the matrix method as a tool for the analysis of qualitative research data in the business domain. Rochester, NY; 2014. https://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=2495330 . Accessed 10 Nov 2022
Download references
Acknowledgments
The book chapter is derived in part from our article “Mukherjee A, Lodha R. Writing the Results. Indian Pediatr. 2016 May 8;53(5):409-15.” We thank the Editor-in-Chief of the journal “Indian Pediatrics” for the permission for the same.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Clinical Studies, Trials and Projection Unit, Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, India
Aparna Mukherjee & Gunjan Kumar
Department of Pediatrics, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India
Rakesh Lodha
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rakesh Lodha .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Retired Senior Expert Pharmacologist at the Office of Cardiology, Hematology, Endocrinology, and Nephrology, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, US Food and Drug Administration, Silver Spring, MD, USA
Gowraganahalli Jagadeesh
Professor & Director, Research Training and Publications, The Office of Research and Development, Periyar Maniammai Institute of Science & Technology (Deemed to be University), Vallam, Tamil Nadu, India
Pitchai Balakumar
Division Cardiology & Nephrology, Office of Cardiology, Hematology, Endocrinology and Nephrology, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, US Food and Drug Administration, Silver Spring, MD, USA
Fortunato Senatore
Ethics declarations
Rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Mukherjee, A., Kumar, G., Lodha, R. (2023). How to Present Results in a Research Paper. In: Jagadeesh, G., Balakumar, P., Senatore, F. (eds) The Quintessence of Basic and Clinical Research and Scientific Publishing. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1284-1_44
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1284-1_44
Published : 01 October 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-99-1283-4
Online ISBN : 978-981-99-1284-1
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Qualitative Data Analysis
23 Presenting the Results of Qualitative Analysis
Mikaila Mariel Lemonik Arthur
Qualitative research is not finished just because you have determined the main findings or conclusions of your study. Indeed, disseminating the results is an essential part of the research process. By sharing your results with others, whether in written form as scholarly paper or an applied report or in some alternative format like an oral presentation, an infographic, or a video, you ensure that your findings become part of the ongoing conversation of scholarship in your field, forming part of the foundation for future researchers. This chapter provides an introduction to writing about qualitative research findings. It will outline how writing continues to contribute to the analysis process, what concerns researchers should keep in mind as they draft their presentations of findings, and how best to organize qualitative research writing
As you move through the research process, it is essential to keep yourself organized. Organizing your data, memos, and notes aids both the analytical and the writing processes. Whether you use electronic or physical, real-world filing and organizational systems, these systems help make sense of the mountains of data you have and assure you focus your attention on the themes and ideas you have determined are important (Warren and Karner 2015). Be sure that you have kept detailed notes on all of the decisions you have made and procedures you have followed in carrying out research design, data collection, and analysis, as these will guide your ultimate write-up.
First and foremost, researchers should keep in mind that writing is in fact a form of thinking. Writing is an excellent way to discover ideas and arguments and to further develop an analysis. As you write, more ideas will occur to you, things that were previously confusing will start to make sense, and arguments will take a clear shape rather than being amorphous and poorly-organized. However, writing-as-thinking cannot be the final version that you share with others. Good-quality writing does not display the workings of your thought process. It is reorganized and revised (more on that later) to present the data and arguments important in a particular piece. And revision is totally normal! No one expects the first draft of a piece of writing to be ready for prime time. So write rough drafts and memos and notes to yourself and use them to think, and then revise them until the piece is the way you want it to be for sharing.
Bergin (2018) lays out a set of key concerns for appropriate writing about research. First, present your results accurately, without exaggerating or misrepresenting. It is very easy to overstate your findings by accident if you are enthusiastic about what you have found, so it is important to take care and use appropriate cautions about the limitations of the research. You also need to work to ensure that you communicate your findings in a way people can understand, using clear and appropriate language that is adjusted to the level of those you are communicating with. And you must be clear and transparent about the methodological strategies employed in the research. Remember, the goal is, as much as possible, to describe your research in a way that would permit others to replicate the study. There are a variety of other concerns and decision points that qualitative researchers must keep in mind, including the extent to which to include quantification in their presentation of results, ethics, considerations of audience and voice, and how to bring the richness of qualitative data to life.
Quantification, as you have learned, refers to the process of turning data into numbers. It can indeed be very useful to count and tabulate quantitative data drawn from qualitative research. For instance, if you were doing a study of dual-earner households and wanted to know how many had an equal division of household labor and how many did not, you might want to count those numbers up and include them as part of the final write-up. However, researchers need to take care when they are writing about quantified qualitative data. Qualitative data is not as generalizable as quantitative data, so quantification can be very misleading. Thus, qualitative researchers should strive to use raw numbers instead of the percentages that are more appropriate for quantitative research. Writing, for instance, “15 of the 20 people I interviewed prefer pancakes to waffles” is a simple description of the data; writing “75% of people prefer pancakes” suggests a generalizable claim that is not likely supported by the data. Note that mixing numbers with qualitative data is really a type of mixed-methods approach. Mixed-methods approaches are good, but sometimes they seduce researchers into focusing on the persuasive power of numbers and tables rather than capitalizing on the inherent richness of their qualitative data.
A variety of issues of scholarly ethics and research integrity are raised by the writing process. Some of these are unique to qualitative research, while others are more universal concerns for all academic and professional writing. For example, it is essential to avoid plagiarism and misuse of sources. All quotations that appear in a text must be properly cited, whether with in-text and bibliographic citations to the source or with an attribution to the research participant (or the participant’s pseudonym or description in order to protect confidentiality) who said those words. Where writers will paraphrase a text or a participant’s words, they need to make sure that the paraphrase they develop accurately reflects the meaning of the original words. Thus, some scholars suggest that participants should have the opportunity to read (or to have read to them, if they cannot read the text themselves) all sections of the text in which they, their words, or their ideas are presented to ensure accuracy and enable participants to maintain control over their lives.
Audience and Voice
When writing, researchers must consider their audience(s) and the effects they want their writing to have on these audiences. The designated audience will dictate the voice used in the writing, or the individual style and personality of a piece of text. Keep in mind that the potential audience for qualitative research is often much more diverse than that for quantitative research because of the accessibility of the data and the extent to which the writing can be accessible and interesting. Yet individual pieces of writing are typically pitched to a more specific subset of the audience.
Let us consider one potential research study, an ethnography involving participant-observation of the same children both when they are at daycare facility and when they are at home with their families to try to understand how daycare might impact behavior and social development. The findings of this study might be of interest to a wide variety of potential audiences: academic peers, whether at your own academic institution, in your broader discipline, or multidisciplinary; people responsible for creating laws and policies; practitioners who run or teach at day care centers; and the general public, including both people who are interested in child development more generally and those who are themselves parents making decisions about child care for their own children. And the way you write for each of these audiences will be somewhat different. Take a moment and think through what some of these differences might look like.
If you are writing to academic audiences, using specialized academic language and working within the typical constraints of scholarly genres, as will be discussed below, can be an important part of convincing others that your work is legitimate and should be taken seriously. Your writing will be formal. Even if you are writing for students and faculty you already know—your classmates, for instance—you are often asked to imitate the style of academic writing that is used in publications, as this is part of learning to become part of the scholarly conversation. When speaking to academic audiences outside your discipline, you may need to be more careful about jargon and specialized language, as disciplines do not always share the same key terms. For instance, in sociology, scholars use the term diffusion to refer to the way new ideas or practices spread from organization to organization. In the field of international relations, scholars often used the term cascade to refer to the way ideas or practices spread from nation to nation. These terms are describing what is fundamentally the same concept, but they are different terms—and a scholar from one field might have no idea what a scholar from a different field is talking about! Therefore, while the formality and academic structure of the text would stay the same, a writer with a multidisciplinary audience might need to pay more attention to defining their terms in the body of the text.
It is not only other academic scholars who expect to see formal writing. Policymakers tend to expect formality when ideas are presented to them, as well. However, the content and style of the writing will be different. Much less academic jargon should be used, and the most important findings and policy implications should be emphasized right from the start rather than initially focusing on prior literature and theoretical models as you might for an academic audience. Long discussions of research methods should also be minimized. Similarly, when you write for practitioners, the findings and implications for practice should be highlighted. The reading level of the text will vary depending on the typical background of the practitioners to whom you are writing—you can make very different assumptions about the general knowledge and reading abilities of a group of hospital medical directors with MDs than you can about a group of case workers who have a post-high-school certificate. Consider the primary language of your audience as well. The fact that someone can get by in spoken English does not mean they have the vocabulary or English reading skills to digest a complex report. But the fact that someone’s vocabulary is limited says little about their intellectual abilities, so try your best to convey the important complexity of the ideas and findings from your research without dumbing them down—even if you must limit your vocabulary usage.
When writing for the general public, you will want to move even further towards emphasizing key findings and policy implications, but you also want to draw on the most interesting aspects of your data. General readers will read sociological texts that are rich with ethnographic or other kinds of detail—it is almost like reality television on a page! And this is a contrast to busy policymakers and practitioners, who probably want to learn the main findings as quickly as possible so they can go about their busy lives. But also keep in mind that there is a wide variation in reading levels. Journalists at publications pegged to the general public are often advised to write at about a tenth-grade reading level, which would leave most of the specialized terminology we develop in our research fields out of reach. If you want to be accessible to even more people, your vocabulary must be even more limited. The excellent exercise of trying to write using the 1,000 most common English words, available at the Up-Goer Five website ( https://www.splasho.com/upgoer5/ ) does a good job of illustrating this challenge (Sanderson n.d.).
Another element of voice is whether to write in the first person. While many students are instructed to avoid the use of the first person in academic writing, this advice needs to be taken with a grain of salt. There are indeed many contexts in which the first person is best avoided, at least as long as writers can find ways to build strong, comprehensible sentences without its use, including most quantitative research writing. However, if the alternative to using the first person is crafting a sentence like “it is proposed that the researcher will conduct interviews,” it is preferable to write “I propose to conduct interviews.” In qualitative research, in fact, the use of the first person is far more common. This is because the researcher is central to the research project. Qualitative researchers can themselves be understood as research instruments, and thus eliminating the use of the first person in writing is in a sense eliminating information about the conduct of the researchers themselves.
But the question really extends beyond the issue of first-person or third-person. Qualitative researchers have choices about how and whether to foreground themselves in their writing, not just in terms of using the first person, but also in terms of whether to emphasize their own subjectivity and reflexivity, their impressions and ideas, and their role in the setting. In contrast, conventional quantitative research in the positivist tradition really tries to eliminate the author from the study—which indeed is exactly why typical quantitative research avoids the use of the first person. Keep in mind that emphasizing researchers’ roles and reflexivity and using the first person does not mean crafting articles that provide overwhelming detail about the author’s thoughts and practices. Readers do not need to hear, and should not be told, which database you used to search for journal articles, how many hours you spent transcribing, or whether the research process was stressful—save these things for the memos you write to yourself. Rather, readers need to hear how you interacted with research participants, how your standpoint may have shaped the findings, and what analytical procedures you carried out.
Making Data Come Alive
One of the most important parts of writing about qualitative research is presenting the data in a way that makes its richness and value accessible to readers. As the discussion of analysis in the prior chapter suggests, there are a variety of ways to do this. Researchers may select key quotes or images to illustrate points, write up specific case studies that exemplify their argument, or develop vignettes (little stories) that illustrate ideas and themes, all drawing directly on the research data. Researchers can also write more lengthy summaries, narratives, and thick descriptions.
Nearly all qualitative work includes quotes from research participants or documents to some extent, though ethnographic work may focus more on thick description than on relaying participants’ own words. When quotes are presented, they must be explained and interpreted—they cannot stand on their own. This is one of the ways in which qualitative research can be distinguished from journalism. Journalism presents what happened, but social science needs to present the “why,” and the why is best explained by the researcher.
So how do authors go about integrating quotes into their written work? Julie Posselt (2017), a sociologist who studies graduate education, provides a set of instructions. First of all, authors need to remain focused on the core questions of their research, and avoid getting distracted by quotes that are interesting or attention-grabbing but not so relevant to the research question. Selecting the right quotes, those that illustrate the ideas and arguments of the paper, is an important part of the writing process. Second, not all quotes should be the same length (just like not all sentences or paragraphs in a paper should be the same length). Include some quotes that are just phrases, others that are a sentence or so, and others that are longer. We call longer quotes, generally those more than about three lines long, block quotes , and they are typically indented on both sides to set them off from the surrounding text. For all quotes, be sure to summarize what the quote should be telling or showing the reader, connect this quote to other quotes that are similar or different, and provide transitions in the discussion to move from quote to quote and from topic to topic. Especially for longer quotes, it is helpful to do some of this writing before the quote to preview what is coming and other writing after the quote to make clear what readers should have come to understand. Remember, it is always the author’s job to interpret the data. Presenting excerpts of the data, like quotes, in a form the reader can access does not minimize the importance of this job. Be sure that you are explaining the meaning of the data you present.
A few more notes about writing with quotes: avoid patchwriting, whether in your literature review or the section of your paper in which quotes from respondents are presented. Patchwriting is a writing practice wherein the author lightly paraphrases original texts but stays so close to those texts that there is little the author has added. Sometimes, this even takes the form of presenting a series of quotes, properly documented, with nothing much in the way of text generated by the author. A patchwriting approach does not build the scholarly conversation forward, as it does not represent any kind of new contribution on the part of the author. It is of course fine to paraphrase quotes, as long as the meaning is not changed. But if you use direct quotes, do not edit the text of the quotes unless how you edit them does not change the meaning and you have made clear through the use of ellipses (…) and brackets ([])what kinds of edits have been made. For example, consider this exchange from Matthew Desmond’s (2012:1317) research on evictions:
The thing was, I wasn’t never gonna let Crystal come and stay with me from the get go. I just told her that to throw her off. And she wasn’t fittin’ to come stay with me with no money…No. Nope. You might as well stay in that shelter.
A paraphrase of this exchange might read “She said that she was going to let Crystal stay with her if Crystal did not have any money.” Paraphrases like that are fine. What is not fine is rewording the statement but treating it like a quote, for instance writing:
The thing was, I was not going to let Crystal come and stay with me from beginning. I just told her that to throw her off. And it was not proper for her to come stay with me without any money…No. Nope. You might as well stay in that shelter.
But as you can see, the change in language and style removes some of the distinct meaning of the original quote. Instead, writers should leave as much of the original language as possible. If some text in the middle of the quote needs to be removed, as in this example, ellipses are used to show that this has occurred. And if a word needs to be added to clarify, it is placed in square brackets to show that it was not part of the original quote.
Data can also be presented through the use of data displays like tables, charts, graphs, diagrams, and infographics created for publication or presentation, as well as through the use of visual material collected during the research process. Note that if visuals are used, the author must have the legal right to use them. Photographs or diagrams created by the author themselves—or by research participants who have signed consent forms for their work to be used, are fine. But photographs, and sometimes even excerpts from archival documents, may be owned by others from whom researchers must get permission in order to use them.
A large percentage of qualitative research does not include any data displays or visualizations. Therefore, researchers should carefully consider whether the use of data displays will help the reader understand the data. One of the most common types of data displays used by qualitative researchers are simple tables. These might include tables summarizing key data about cases included in the study; tables laying out the characteristics of different taxonomic elements or types developed as part of the analysis; tables counting the incidence of various elements; and 2×2 tables (two columns and two rows) illuminating a theory. Basic network or process diagrams are also commonly included. If data displays are used, it is essential that researchers include context and analysis alongside data displays rather than letting them stand by themselves, and it is preferable to continue to present excerpts and examples from the data rather than just relying on summaries in the tables.
If you will be using graphs, infographics, or other data visualizations, it is important that you attend to making them useful and accurate (Bergin 2018). Think about the viewer or user as your audience and ensure the data visualizations will be comprehensible. You may need to include more detail or labels than you might think. Ensure that data visualizations are laid out and labeled clearly and that you make visual choices that enhance viewers’ ability to understand the points you intend to communicate using the visual in question. Finally, given the ease with which it is possible to design visuals that are deceptive or misleading, it is essential to make ethical and responsible choices in the construction of visualization so that viewers will interpret them in accurate ways.
The Genre of Research Writing
As discussed above, the style and format in which results are presented depends on the audience they are intended for. These differences in styles and format are part of the genre of writing. Genre is a term referring to the rules of a specific form of creative or productive work. Thus, the academic journal article—and student papers based on this form—is one genre. A report or policy paper is another. The discussion below will focus on the academic journal article, but note that reports and policy papers follow somewhat different formats. They might begin with an executive summary of one or a few pages, include minimal background, focus on key findings, and conclude with policy implications, shifting methods and details about the data to an appendix. But both academic journal articles and policy papers share some things in common, for instance the necessity for clear writing, a well-organized structure, and the use of headings.
So what factors make up the genre of the academic journal article in sociology? While there is some flexibility, particularly for ethnographic work, academic journal articles tend to follow a fairly standard format. They begin with a “title page” that includes the article title (often witty and involving scholarly inside jokes, but more importantly clearly describing the content of the article); the authors’ names and institutional affiliations, an abstract , and sometimes keywords designed to help others find the article in databases. An abstract is a short summary of the article that appears both at the very beginning of the article and in search databases. Abstracts are designed to aid readers by giving them the opportunity to learn enough about an article that they can determine whether it is worth their time to read the complete text. They are written about the article, and thus not in the first person, and clearly summarize the research question, methodological approach, main findings, and often the implications of the research.
After the abstract comes an “introduction” of a page or two that details the research question, why it matters, and what approach the paper will take. This is followed by a literature review of about a quarter to a third the length of the entire paper. The literature review is often divided, with headings, into topical subsections, and is designed to provide a clear, thorough overview of the prior research literature on which a paper has built—including prior literature the new paper contradicts. At the end of the literature review it should be made clear what researchers know about the research topic and question, what they do not know, and what this new paper aims to do to address what is not known.
The next major section of the paper is the section that describes research design, data collection, and data analysis, often referred to as “research methods” or “methodology.” This section is an essential part of any written or oral presentation of your research. Here, you tell your readers or listeners “how you collected and interpreted your data” (Taylor, Bogdan, and DeVault 2016:215). Taylor, Bogdan, and DeVault suggest that the discussion of your research methods include the following:
- The particular approach to data collection used in the study;
- Any theoretical perspective(s) that shaped your data collection and analytical approach;
- When the study occurred, over how long, and where (concealing identifiable details as needed);
- A description of the setting and participants, including sampling and selection criteria (if an interview-based study, the number of participants should be clearly stated);
- The researcher’s perspective in carrying out the study, including relevant elements of their identity and standpoint, as well as their role (if any) in research settings; and
- The approach to analyzing the data.
After the methods section comes a section, variously titled but often called “data,” that takes readers through the analysis. This section is where the thick description narrative; the quotes, broken up by theme or topic, with their interpretation; the discussions of case studies; most data displays (other than perhaps those outlining a theoretical model or summarizing descriptive data about cases); and other similar material appears. The idea of the data section is to give readers the ability to see the data for themselves and to understand how this data supports the ultimate conclusions. Note that all tables and figures included in formal publications should be titled and numbered.
At the end of the paper come one or two summary sections, often called “discussion” and/or “conclusion.” If there is a separate discussion section, it will focus on exploring the overall themes and findings of the paper. The conclusion clearly and succinctly summarizes the findings and conclusions of the paper, the limitations of the research and analysis, any suggestions for future research building on the paper or addressing these limitations, and implications, be they for scholarship and theory or policy and practice.
After the end of the textual material in the paper comes the bibliography, typically called “works cited” or “references.” The references should appear in a consistent citation style—in sociology, we often use the American Sociological Association format (American Sociological Association 2019), but other formats may be used depending on where the piece will eventually be published. Care should be taken to ensure that in-text citations also reflect the chosen citation style. In some papers, there may be an appendix containing supplemental information such as a list of interview questions or an additional data visualization.
Note that when researchers give presentations to scholarly audiences, the presentations typically follow a format similar to that of scholarly papers, though given time limitations they are compressed. Abstracts and works cited are often not part of the presentation, though in-text citations are still used. The literature review presented will be shortened to only focus on the most important aspects of the prior literature, and only key examples from the discussion of data will be included. For long or complex papers, sometimes only one of several findings is the focus of the presentation. Of course, presentations for other audiences may be constructed differently, with greater attention to interesting elements of the data and findings as well as implications and less to the literature review and methods.
Concluding Your Work
After you have written a complete draft of the paper, be sure you take the time to revise and edit your work. There are several important strategies for revision. First, put your work away for a little while. Even waiting a day to revise is better than nothing, but it is best, if possible, to take much more time away from the text. This helps you forget what your writing looks like and makes it easier to find errors, mistakes, and omissions. Second, show your work to others. Ask them to read your work and critique it, pointing out places where the argument is weak, where you may have overlooked alternative explanations, where the writing could be improved, and what else you need to work on. Finally, read your work out loud to yourself (or, if you really need an audience, try reading to some stuffed animals). Reading out loud helps you catch wrong words, tricky sentences, and many other issues. But as important as revision is, try to avoid perfectionism in writing (Warren and Karner 2015). Writing can always be improved, no matter how much time you spend on it. Those improvements, however, have diminishing returns, and at some point the writing process needs to conclude so the writing can be shared with the world.
Of course, the main goal of writing up the results of a research project is to share with others. Thus, researchers should be considering how they intend to disseminate their results. What conferences might be appropriate? Where can the paper be submitted? Note that if you are an undergraduate student, there are a wide variety of journals that accept and publish research conducted by undergraduates. Some publish across disciplines, while others are specific to disciplines. Other work, such as reports, may be best disseminated by publication online on relevant organizational websites.
After a project is completed, be sure to take some time to organize your research materials and archive them for longer-term storage. Some Institutional Review Board (IRB) protocols require that original data, such as interview recordings, transcripts, and field notes, be preserved for a specific number of years in a protected (locked for paper or password-protected for digital) form and then destroyed, so be sure that your plans adhere to the IRB requirements. Be sure you keep any materials that might be relevant for future related research or for answering questions people may ask later about your project.
And then what? Well, then it is time to move on to your next research project. Research is a long-term endeavor, not a one-time-only activity. We build our skills and our expertise as we continue to pursue research. So keep at it.
- Find a short article that uses qualitative methods. The sociological magazine Contexts is a good place to find such pieces. Write an abstract of the article.
- Choose a sociological journal article on a topic you are interested in that uses some form of qualitative methods and is at least 20 pages long. Rewrite the article as a five-page research summary accessible to non-scholarly audiences.
- Choose a concept or idea you have learned in this course and write an explanation of it using the Up-Goer Five Text Editor ( https://www.splasho.com/upgoer5/ ), a website that restricts your writing to the 1,000 most common English words. What was this experience like? What did it teach you about communicating with people who have a more limited English-language vocabulary—and what did it teach you about the utility of having access to complex academic language?
- Select five or more sociological journal articles that all use the same basic type of qualitative methods (interviewing, ethnography, documents, or visual sociology). Using what you have learned about coding, code the methods sections of each article, and use your coding to figure out what is common in how such articles discuss their research design, data collection, and analysis methods.
- Return to an exercise you completed earlier in this course and revise your work. What did you change? How did revising impact the final product?
- Find a quote from the transcript of an interview, a social media post, or elsewhere that has not yet been interpreted or explained. Write a paragraph that includes the quote along with an explanation of its sociological meaning or significance.
The style or personality of a piece of writing, including such elements as tone, word choice, syntax, and rhythm.
A quotation, usually one of some length, which is set off from the main text by being indented on both sides rather than being placed in quotation marks.
A classification of written or artistic work based on form, content, and style.
A short summary of a text written from the perspective of a reader rather than from the perspective of an author.
Social Data Analysis Copyright © 2021 by Mikaila Mariel Lemonik Arthur is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Subscribe to journal Subscribe
- Get new issue alerts Get alerts
Secondary Logo
Journal logo.
Colleague's E-mail is Invalid
Your message has been successfully sent to your colleague.
Save my selection
Presentation of Results
Regehr, Glenn
The author gratefully acknowledges the extensive input and feedback for this chapter provided by Dr. Lorelei Lingard.

Full Text Access for Subscribers:
Individual subscribers.

Institutional Users
Not a subscriber.
You can read the full text of this article if you:
- + Favorites
- View in Gallery
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.17(12); 2021 Dec

Ten simple rules for effective presentation slides
Kristen m. naegle.
Biomedical Engineering and the Center for Public Health Genomics, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, Virginia, United States of America
Introduction
The “presentation slide” is the building block of all academic presentations, whether they are journal clubs, thesis committee meetings, short conference talks, or hour-long seminars. A slide is a single page projected on a screen, usually built on the premise of a title, body, and figures or tables and includes both what is shown and what is spoken about that slide. Multiple slides are strung together to tell the larger story of the presentation. While there have been excellent 10 simple rules on giving entire presentations [ 1 , 2 ], there was an absence in the fine details of how to design a slide for optimal effect—such as the design elements that allow slides to convey meaningful information, to keep the audience engaged and informed, and to deliver the information intended and in the time frame allowed. As all research presentations seek to teach, effective slide design borrows from the same principles as effective teaching, including the consideration of cognitive processing your audience is relying on to organize, process, and retain information. This is written for anyone who needs to prepare slides from any length scale and for most purposes of conveying research to broad audiences. The rules are broken into 3 primary areas. Rules 1 to 5 are about optimizing the scope of each slide. Rules 6 to 8 are about principles around designing elements of the slide. Rules 9 to 10 are about preparing for your presentation, with the slides as the central focus of that preparation.
Rule 1: Include only one idea per slide
Each slide should have one central objective to deliver—the main idea or question [ 3 – 5 ]. Often, this means breaking complex ideas down into manageable pieces (see Fig 1 , where “background” information has been split into 2 key concepts). In another example, if you are presenting a complex computational approach in a large flow diagram, introduce it in smaller units, building it up until you finish with the entire diagram. The progressive buildup of complex information means that audiences are prepared to understand the whole picture, once you have dedicated time to each of the parts. You can accomplish the buildup of components in several ways—for example, using presentation software to cover/uncover information. Personally, I choose to create separate slides for each piece of information content I introduce—where the final slide has the entire diagram, and I use cropping or a cover on duplicated slides that come before to hide what I’m not yet ready to include. I use this method in order to ensure that each slide in my deck truly presents one specific idea (the new content) and the amount of the new information on that slide can be described in 1 minute (Rule 2), but it comes with the trade-off—a change to the format of one of the slides in the series often means changes to all slides.

Top left: A background slide that describes the background material on a project from my lab. The slide was created using a PowerPoint Design Template, which had to be modified to increase default text sizes for this figure (i.e., the default text sizes are even worse than shown here). Bottom row: The 2 new slides that break up the content into 2 explicit ideas about the background, using a central graphic. In the first slide, the graphic is an explicit example of the SH2 domain of PI3-kinase interacting with a phosphorylation site (Y754) on the PDGFR to describe the important details of what an SH2 domain and phosphotyrosine ligand are and how they interact. I use that same graphic in the second slide to generalize all binding events and include redundant text to drive home the central message (a lot of possible interactions might occur in the human proteome, more than we can currently measure). Top right highlights which rules were used to move from the original slide to the new slide. Specific changes as highlighted by Rule 7 include increasing contrast by changing the background color, increasing font size, changing to sans serif fonts, and removing all capital text and underlining (using bold to draw attention). PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor.
Rule 2: Spend only 1 minute per slide
When you present your slide in the talk, it should take 1 minute or less to discuss. This rule is really helpful for planning purposes—a 20-minute presentation should have somewhere around 20 slides. Also, frequently giving your audience new information to feast on helps keep them engaged. During practice, if you find yourself spending more than a minute on a slide, there’s too much for that one slide—it’s time to break up the content into multiple slides or even remove information that is not wholly central to the story you are trying to tell. Reduce, reduce, reduce, until you get to a single message, clearly described, which takes less than 1 minute to present.
Rule 3: Make use of your heading
When each slide conveys only one message, use the heading of that slide to write exactly the message you are trying to deliver. Instead of titling the slide “Results,” try “CTNND1 is central to metastasis” or “False-positive rates are highly sample specific.” Use this landmark signpost to ensure that all the content on that slide is related exactly to the heading and only the heading. Think of the slide heading as the introductory or concluding sentence of a paragraph and the slide content the rest of the paragraph that supports the main point of the paragraph. An audience member should be able to follow along with you in the “paragraph” and come to the same conclusion sentence as your header at the end of the slide.
Rule 4: Include only essential points
While you are speaking, audience members’ eyes and minds will be wandering over your slide. If you have a comment, detail, or figure on a slide, have a plan to explicitly identify and talk about it. If you don’t think it’s important enough to spend time on, then don’t have it on your slide. This is especially important when faculty are present. I often tell students that thesis committee members are like cats: If you put a shiny bauble in front of them, they’ll go after it. Be sure to only put the shiny baubles on slides that you want them to focus on. Putting together a thesis meeting for only faculty is really an exercise in herding cats (if you have cats, you know this is no easy feat). Clear and concise slide design will go a long way in helping you corral those easily distracted faculty members.
Rule 5: Give credit, where credit is due
An exception to Rule 4 is to include proper citations or references to work on your slide. When adding citations, names of other researchers, or other types of credit, use a consistent style and method for adding this information to your slides. Your audience will then be able to easily partition this information from the other content. A common mistake people make is to think “I’ll add that reference later,” but I highly recommend you put the proper reference on the slide at the time you make it, before you forget where it came from. Finally, in certain kinds of presentations, credits can make it clear who did the work. For the faculty members heading labs, it is an effective way to connect your audience with the personnel in the lab who did the work, which is a great career booster for that person. For graduate students, it is an effective way to delineate your contribution to the work, especially in meetings where the goal is to establish your credentials for meeting the rigors of a PhD checkpoint.
Rule 6: Use graphics effectively
As a rule, you should almost never have slides that only contain text. Build your slides around good visualizations. It is a visual presentation after all, and as they say, a picture is worth a thousand words. However, on the flip side, don’t muddy the point of the slide by putting too many complex graphics on a single slide. A multipanel figure that you might include in a manuscript should often be broken into 1 panel per slide (see Rule 1 ). One way to ensure that you use the graphics effectively is to make a point to introduce the figure and its elements to the audience verbally, especially for data figures. For example, you might say the following: “This graph here shows the measured false-positive rate for an experiment and each point is a replicate of the experiment, the graph demonstrates …” If you have put too much on one slide to present in 1 minute (see Rule 2 ), then the complexity or number of the visualizations is too much for just one slide.
Rule 7: Design to avoid cognitive overload
The type of slide elements, the number of them, and how you present them all impact the ability for the audience to intake, organize, and remember the content. For example, a frequent mistake in slide design is to include full sentences, but reading and verbal processing use the same cognitive channels—therefore, an audience member can either read the slide, listen to you, or do some part of both (each poorly), as a result of cognitive overload [ 4 ]. The visual channel is separate, allowing images/videos to be processed with auditory information without cognitive overload [ 6 ] (Rule 6). As presentations are an exercise in listening, and not reading, do what you can to optimize the ability of the audience to listen. Use words sparingly as “guide posts” to you and the audience about major points of the slide. In fact, you can add short text fragments, redundant with the verbal component of the presentation, which has been shown to improve retention [ 7 ] (see Fig 1 for an example of redundant text that avoids cognitive overload). Be careful in the selection of a slide template to minimize accidentally adding elements that the audience must process, but are unimportant. David JP Phillips argues (and effectively demonstrates in his TEDx talk [ 5 ]) that the human brain can easily interpret 6 elements and more than that requires a 500% increase in human cognition load—so keep the total number of elements on the slide to 6 or less. Finally, in addition to the use of short text, white space, and the effective use of graphics/images, you can improve ease of cognitive processing further by considering color choices and font type and size. Here are a few suggestions for improving the experience for your audience, highlighting the importance of these elements for some specific groups:
- Use high contrast colors and simple backgrounds with low to no color—for persons with dyslexia or visual impairment.
- Use sans serif fonts and large font sizes (including figure legends), avoid italics, underlining (use bold font instead for emphasis), and all capital letters—for persons with dyslexia or visual impairment [ 8 ].
- Use color combinations and palettes that can be understood by those with different forms of color blindness [ 9 ]. There are excellent tools available to identify colors to use and ways to simulate your presentation or figures as they might be seen by a person with color blindness (easily found by a web search).
- In this increasing world of virtual presentation tools, consider practicing your talk with a closed captioning system capture your words. Use this to identify how to improve your speaking pace, volume, and annunciation to improve understanding by all members of your audience, but especially those with a hearing impairment.

Rule 8: Design the slide so that a distracted person gets the main takeaway
It is very difficult to stay focused on a presentation, especially if it is long or if it is part of a longer series of talks at a conference. Audience members may get distracted by an important email, or they may start dreaming of lunch. So, it’s important to look at your slide and ask “If they heard nothing I said, will they understand the key concept of this slide?” The other rules are set up to help with this, including clarity of the single point of the slide (Rule 1), titling it with a major conclusion (Rule 3), and the use of figures (Rule 6) and short text redundant to your verbal description (Rule 7). However, with each slide, step back and ask whether its main conclusion is conveyed, even if someone didn’t hear your accompanying dialog. Importantly, ask if the information on the slide is at the right level of abstraction. For example, do you have too many details about the experiment, which hides the conclusion of the experiment (i.e., breaking Rule 1)? If you are worried about not having enough details, keep a slide at the end of your slide deck (after your conclusions and acknowledgments) with the more detailed information that you can refer to during a question and answer period.
Rule 9: Iteratively improve slide design through practice
Well-designed slides that follow the first 8 rules are intended to help you deliver the message you intend and in the amount of time you intend to deliver it in. The best way to ensure that you nailed slide design for your presentation is to practice, typically a lot. The most important aspects of practicing a new presentation, with an eye toward slide design, are the following 2 key points: (1) practice to ensure that you hit, each time through, the most important points (for example, the text guide posts you left yourself and the title of the slide); and (2) practice to ensure that as you conclude the end of one slide, it leads directly to the next slide. Slide transitions, what you say as you end one slide and begin the next, are important to keeping the flow of the “story.” Practice is when I discover that the order of my presentation is poor or that I left myself too few guideposts to remember what was coming next. Additionally, during practice, the most frequent things I have to improve relate to Rule 2 (the slide takes too long to present, usually because I broke Rule 1, and I’m delivering too much information for one slide), Rule 4 (I have a nonessential detail on the slide), and Rule 5 (I forgot to give a key reference). The very best type of practice is in front of an audience (for example, your lab or peers), where, with fresh perspectives, they can help you identify places for improving slide content, design, and connections across the entirety of your talk.
Rule 10: Design to mitigate the impact of technical disasters
The real presentation almost never goes as we planned in our heads or during our practice. Maybe the speaker before you went over time and now you need to adjust. Maybe the computer the organizer is having you use won’t show your video. Maybe your internet is poor on the day you are giving a virtual presentation at a conference. Technical problems are routinely part of the practice of sharing your work through presentations. Hence, you can design your slides to limit the impact certain kinds of technical disasters create and also prepare alternate approaches. Here are just a few examples of the preparation you can do that will take you a long way toward avoiding a complete fiasco:
- Save your presentation as a PDF—if the version of Keynote or PowerPoint on a host computer cause issues, you still have a functional copy that has a higher guarantee of compatibility.
- In using videos, create a backup slide with screen shots of key results. For example, if I have a video of cell migration, I’ll be sure to have a copy of the start and end of the video, in case the video doesn’t play. Even if the video worked, you can pause on this backup slide and take the time to highlight the key results in words if someone could not see or understand the video.
- Avoid animations, such as figures or text that flash/fly-in/etc. Surveys suggest that no one likes movement in presentations [ 3 , 4 ]. There is likely a cognitive underpinning to the almost universal distaste of pointless animations that relates to the idea proposed by Kosslyn and colleagues that animations are salient perceptual units that captures direct attention [ 4 ]. Although perceptual salience can be used to draw attention to and improve retention of specific points, if you use this approach for unnecessary/unimportant things (like animation of your bullet point text, fly-ins of figures, etc.), then you will distract your audience from the important content. Finally, animations cause additional processing burdens for people with visual impairments [ 10 ] and create opportunities for technical disasters if the software on the host system is not compatible with your planned animation.
Conclusions
These rules are just a start in creating more engaging presentations that increase audience retention of your material. However, there are wonderful resources on continuing on the journey of becoming an amazing public speaker, which includes understanding the psychology and neuroscience behind human perception and learning. For example, as highlighted in Rule 7, David JP Phillips has a wonderful TEDx talk on the subject [ 5 ], and “PowerPoint presentation flaws and failures: A psychological analysis,” by Kosslyn and colleagues is deeply detailed about a number of aspects of human cognition and presentation style [ 4 ]. There are many books on the topic, including the popular “Presentation Zen” by Garr Reynolds [ 11 ]. Finally, although briefly touched on here, the visualization of data is an entire topic of its own that is worth perfecting for both written and oral presentations of work, with fantastic resources like Edward Tufte’s “The Visual Display of Quantitative Information” [ 12 ] or the article “Visualization of Biomedical Data” by O’Donoghue and colleagues [ 13 ].
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank the countless presenters, colleagues, students, and mentors from which I have learned a great deal from on effective presentations. Also, a thank you to the wonderful resources published by organizations on how to increase inclusivity. A special thanks to Dr. Jason Papin and Dr. Michael Guertin on early feedback of this editorial.
Funding Statement
The author received no specific funding for this work.
- Student Program
- Sign Up for Free

How to Create a Survey
How to turn survey results into a great presentation
How to present your survey results
Choose the best data to share, tell a story, adhere to common design rules, create an additional report.
You’ve launched your survey . The results are in. Now it’s time to make sense of them.
Creating a survey results presentation is one of the best ways to analyze your results and present them to stakeholders in a format that makes them clear and understandable.
It’s not as simple as copying and pasting everything into a PowerPoint presentation, though. Here’s how you can create an awesome survey results presentation.

Why you should turn survey results into a presentation
Not everyone is going to be willing to sift through all your survey responses and tease out the relevant findings. That’s why you need to succinctly summarize those findings and make them digestible for everyone. A survey results presentation is the perfect tool.
How to create a survey results presentation: Best practices
Before you rush to turn your responses into a presentation, take the time to acquaint yourself with the following best practices.
Not every insight you collect from your survey is going to be relevant to your target audience. So start by narrowing down your dataset to include only information that’s useful. Think about what you want your audience to take away from your presentation, and then choose your data accordingly.
If you really want to capture your audience’s attention, tell a story with your presentation. Rather than just show them the raw data, explain what the findings mean and why your audience should care.
Using subjective feedback from surveys can work well. While it’s helpful to show data that proves your point, using specific examples can make your presentations much more powerful, writes corporate trainer Dana Brownlee .
There are several design best practices you should follow, writes Shonna Waters, Ph.D. , vice president of strategic alliances and partnerships at professional coaching platform BetterUp. That includes using a minimalistic background, placing only your major points on each slide, and avoiding blocks of copy. “Keep the presentation stimulating and appealing without overwhelming your audience with bright colors or too much font,” Waters advises.
Not all of your survey findings will be suitable to include in your presentation, but they may still be essential for stakeholders. “If you’re presenting data to senior executives or business clients, you might want to prepare a full report on your findings,” writes Swetha Amaresan , senior marketing coordinator at Nickelodeon International. “You wouldn’t refer to this document during a presentation, but you might hand this to your audience to read through on their own time.”
Turn survey results into a presentation with Jotform Report Builder
If you’re worried about keeping track of all the best practices above, let Jotform’s Report Builder do the hard work for you. Jotform Report Builder automatically turns your Jotform survey responses into beautiful, professional reports.
Create the perfect report with a range of charts and tables. You can drag and drop design elements to suit your tastes. Don’t worry about having to update your presentation once it’s designed — presentations are updated automatically with each new form submission.
Just so you know
Automatically turn your survey responses into professional presentations with Jotform Report Builder .
How Jotform can make surveys easy
Whether you want to create a survey or turn your existing survey into a report, Jotform is the ideal tool. With over 800 free survey templates , it’s easy to get started.
You can tailor the survey to your needs, choosing the format that works best for you. That could be a classic survey where all questions are listed on a single page, or you may opt for Jotform Cards, where you ask one question per page.
If you want to dig deeper, you can use conditional logic to create an interactive survey that changes depending on each user’s response. Conditional logic improves the quality of answers from respondents while also improving the completion rate.
With Jotform, you never have to worry about privacy or security. All Jotform form data is protected with a 256-bit SSL connection and is compliant with the General Data Protection Regulation and the California Consumer Privacy Act. You can even add an optional feature that helps with HIPAA compliance if you’re creating a healthcare survey.
Thank you for helping improve the Jotform Blog. 🎉
RECOMMENDED ARTICLES

Parent survey questions: What to ask and why

7 important user experience survey questions you should ask

Top 15 employee pulse survey tools

80 survey question examples and when to use them

4 types of survey questions to engage your audience

How to write good survey questions

20 psychology survey questions to ask your clients

How to ask someone to take a survey via email
The 5 most powerful Bucket.io alternatives for 2024

Ethnicity survey questions: Benefits and examples

8 leading Survicate alternatives for customer feedback in 2024

Top survey topics and ideas

25 post-training survey questions to ask employees

Top 20 team collaboration survey questions

Survey report examples with informative visuals

How to use a survey dashboard effectively

4 tips for creating effective quantitative surveys

How to conduct an online survey

How to ask someone to fill out a survey

Top 21 brand survey questions

Key marketing survey questions to ask your audience

How many questions to include in an online survey

The 6 best customer satisfaction survey tools

21 website usability survey questions to ask your user

Peakon alternatives in 2024

One question at a time: The best strategy for a survey

Creating a fun survey: Topics and best practices

5 UX survey tools to help you create a winning user experience

What is a good survey response rate?

50 business survey questions to ask your customers

How to embed a survey in a website

How to calculate the Net Promoter Score® (NPS®)

What are ambiguous survey questions, and how do you avoid asking them?

30 examples of ranking survey questions

How to make Google Forms anonymous

Closed-ended questions: Definition and examples

How to send Mailchimp surveys easily

How to automate survey follow-up emails

The 3 best Checkbox Survey alternatives

How to do a poll in Slack

10 of the best StrawPoll alternatives

30 questions to ask in your membership survey

11 top survey incentive ideas

How to add a popup survey on your website

Qualitative vs quantitative questions: What you need to know

Top podcast survey questions to ask guests and listeners

How to use open-ended survey questions

Best training survey questions to evaluate effectiveness

Social media survey questions: Examples and best practices

How to create an anonymous survey for employees

What is the smiley face rating scale?

5 types of questionnaires

8 of the best WordPress survey plug-ins

Top 3 Key Survey alternatives in 2024

50 mental health survey questions to ask employees

Offline surveys: How to collect data anywhere

Lead generation surveys: Sample questions, tips, and benefits

How to create a survey in Microsoft Word

How to send a survey to your email list on AWeber

CRM survey benefits, best practices, and example questions
What you need to know about SurveyMonkey pricing

How to add a signature in SurveyMonkey

14 political survey questions to gauge public opinion

Basic product survey questions to ask customers

How to write unbiased survey questions

The 5 best Alchemer (formerly SurveyGizmo) alternatives

Real estate survey questions for buyers and sellers

Top diversity and inclusion questions to ask employees

A Guide to Creating the Perfect Survey Form

Webinar: How to use surveys and email marketing to gain key insights

How to create an NPS® survey email that gets results

Top 8 QuestionPro alternatives in 2024

Top 7 KwikSurveys alternatives in 2024
How to embed a survey in an email

What is a survey?

Top survey questions to ask kids

65+ e-commerce survey questions for valuable business insights

5 tips for creating great qualitative surveys
Survey rating scales 1-5: Understand your audience better
How to create a survey on Facebook

Qualtrics vs SurveyMonkey: Which should you choose?

Top 9 Qualaroo alternatives in 2024

63 insightful hotel survey questions

SurveyLegend alternatives in 2024

Survicate vs SurveyMonkey: Comparing online survey platforms

Cybersecurity questionnaires: How to assess online threats

How to conduct a pricing survey: Questions to ask

How to avoid survey fatigue

6 effective ways to find survey participants

How to get the most out of Peakon surveys

Survey data collection: 5 best practices

How to write a survey introduction (plus examples)

14 best SurveyMonkey alternatives in 2024

Pre-sales surveys: How to focus on your best leads

How to set up and send a Constant Contact survey

42 questions to ask in a depression survey

How to create an employee pulse survey

20 pre-training survey questions for a professional development course

Yes-or-no questions in online forms and surveys
Send Comment :
How to Present Survey Results in PowerPoint (3 Insanely Quick Shortcuts)

Mikel Resaba

Struggling with presenting survey results in PowerPoint? Not sure how to present survey results in PowerPoint in ways that are easy and quick? It’s a common challenge: turning a spreadsheet of numbers into a compelling visual story. Before we delve into solutions, let’s address the core issues:
- Audiences can easily get overwhelmed by raw data.
- Essential insights often get buried in charts and graphs.
- Keeping the presentation interactive and engaging is not straightforward.
Now, how can we overcome these obstacles and captivate our audience? The answer lies in a combination of innovative tools and presentation techniques, which we will explore next.
How to Present Survey Results in PowerPoint: Quick Suggestions
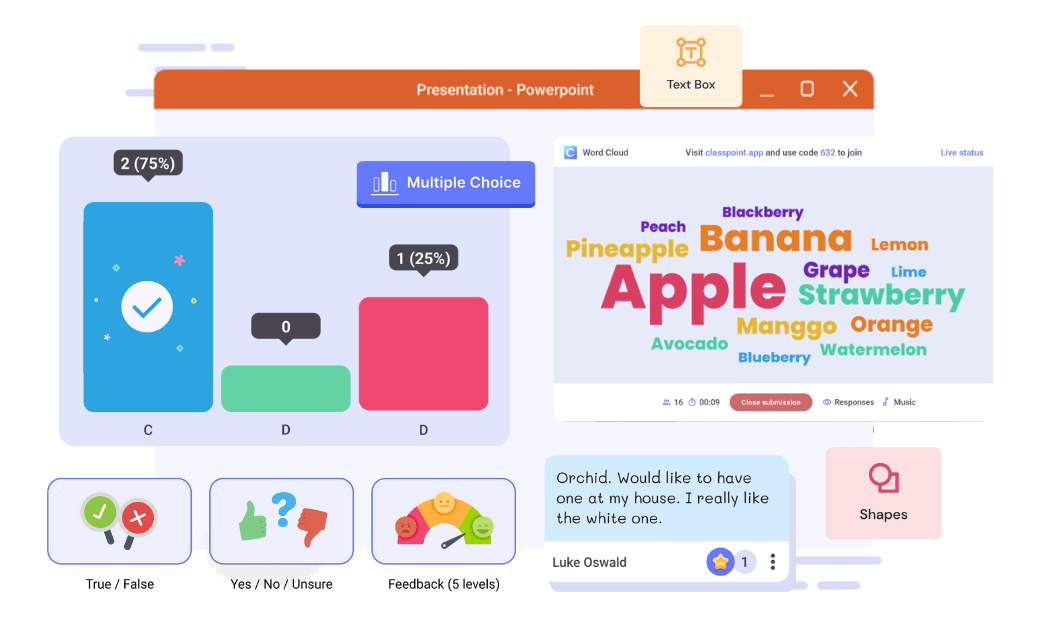
- ClassPoint Quick Poll : Run live polling in PowerPoint and display the survey results instantly to your audience.
- Infographics and Data Visualization: Utilize infographics to make complex data more understandable. Tools like PowerPoint’s built-in chart and graph features can help you create visually appealing representations of your survey results.
- Interactive PowerPoint Slides : Incorporate interactive elements like hyperlinks, triggered animations, or embedded videos to make your presentation more engaging. These features can illustrate your survey findings in a dynamic way.
- Storytelling with Data: Use a narrative structure to present your survey results. This involves setting up a storyline where data points are introduced as part of a larger narrative, making the presentation more relatable and memorable.
- Comparative Analysis: If your survey results are comparative in nature, use side-by-side comparisons, before-and-after snapshots, or trend analyzes to depict changes or contrasts effectively.
- Animated Charts and Graphs: Animations can be a powerful tool in highlighting specific parts of your data. Animated bar charts, pie charts, or line graphs can draw attention to key findings in your survey.
3 Insanely Quick and Easy Ways on How to Present Survey Results in PowerPoint !
Presenting survey results effectively requires more than just sharing data; it involves storytelling, visual impact, and audience engagement. Whether you’re an educator, a business professional, or a researcher, the way you present your findings can significantly influence your audience’s understanding and reaction.
Today we are sharing with you 3 insanely quick and easy shortcuts to present survey results in PowerPoint 👇
1. ClassPoint Quick Poll
The first and more effortless method of presenting survey results in PowerPoint is through running a live poll in PowerPoint , then displaying the results instantly while presenting. This method combines conducting a live poll and presenting the survey result into one seamless act.
Here’s how you can do it 👇👇
- Step 1 : Install the ClassPoint add-in for PowerPoint.
- Step 2 : Launch any presentation slides and enter slide show mode.
- Step 3 : Click on “Quick Poll” on the ClassPoint tab at the bottom of your screen and choose from three poll types: true or false, yes or no, and agree or disagree to launch the poll.
- Step 4 : Audience can join your poll at classpoint.app and the poll and survey results will be immediately displayed on your slide.
Benefits of ClassPoint Quick Poll
- Ease of Use: ClassPoint’s Quick Poll integrates seamlessly with PowerPoint, allowing for instant poll creation without the need for external apps or tools.
- Diverse Poll Types: Choose from True/False, Yes/No/Unsure, Feedback polls, and Custom polls to suit the nature of your survey data.
- Real-Time Engagement: Engage your audience by receiving immediate responses, making your presentation dynamic and interactive.
2. Presenting Survey Results Using Charts
The traditional way.
Charts provide a clear and concise way to present your survey data. PowerPoint’s array of chart options allows you to tailor your data presentation to your audience’s needs.
Here’s a quick step-by-step guide:
- Step 1 : Select the data for your chart.
- Step 2 : Go to the ‘Insert’ tab in PowerPoint and choose ‘Chart’.
- Step 3 : Pick the chart type that best represents your data.
- Step 4 : Customize the chart’s design and format it to fit your presentation style.
- Step 5 : Insert the chart into your presentation and use it to tell the story behind your data.
The Pro Way: Using PowerPoint SmartArt
- Step 1 : Type your data as texts or bullet points in PowerPoint.
- Step 2 : Navigate to PowerPoint ribbon and select ‘Convert to Smart Art’.
- Step 3 : Next, choose the desired chart or graph.
Alternatively, you can also select ‘Smart Art’ under the ‘Insert’ and select from a range of pre-designed charts or graphs, then insert the survey data accordingly.
3. Presenting Survey Results Using Animations
Animations can bring your data presentation to life. With PowerPoint’s animation features, you can take your survey result presentation up a notch. There are many ways you can animate your charts, but in this article, we will be sharing with you a cool way of animating your survey results in the style of a donut chart:
- Step 1 : Add the shape ‘Arc’ to your PowerPoint slides.
- Step 2 : At the settings panel, change the ‘Cap Type’ to ‘Round’, and adjust the width to your liking.
- Step 3 : Select the “Wheel” animation effect from your PowerPoint ribbon.
- Step 4 : (Optional): Add an ellipse at the tip of the wheel to make the animation more seamless.
FAQs on How to Present Survey Results in PowerPoint
When it comes to presenting survey results in PowerPoint, several questions often arise. This FAQ section aims to address some of the most common inquiries, providing clear and concise answers to help enhance your presentation skills.
How can I make my survey results stand out in a presentation?
To make survey results stand out, use a mix of visual aids like charts, graphs, and infographics. Tailor the design to your audience and ensure that the key findings are highlighted clearly and concisely.
What are some effective ways to keep my audience engaged during the presentation?
Engage your audience by incorporating interactive elements like live polls, quizzes, or Q&A sessions. Also, use storytelling techniques to weave your data into a compelling narrative.
Can I use animations effectively in presenting survey data?
Yes, animations can be used effectively to draw attention to specific data points. However, use them sparingly to avoid distracting from the main message.
Is it important to customize PowerPoint templates for survey presentations?
Customizing PowerPoint templates helps in aligning the design with your presentation’s theme and makes your data more accessible and understandable to the audience.
Elevate Your Presentations Today: Embrace ClassPoint’s Quick Poll
Ready to revolutionize how you present survey results? Embrace the power of C lassPoint’s Quick Poll to make your presentations more interactive and insightful. Here’s how you can get started:
- Experiment with different poll types to find what best suits your audience.
- Analyze the results in real-time for a more dynamic presentation.
- Use the feedback to refine your approach and content.
About Mikel Resaba
Try classpoint for free.
All-in-one teaching and student engagement in PowerPoint.
Supercharge your PowerPoint. Start today.
800,000+ people like you use ClassPoint to boost student engagement in PowerPoint presentations.
- Data Visualizations
- Most Recent
- Presentations
- Infographics
- Forms and Surveys
- Video & Animation
- Case Studies
- Design for Business
- Digital Marketing
- Design Inspiration
- Visual Thinking
- Product Updates
- Visme Webinars
- Artificial Intelligence
How to Analyze and Present Survey Results
Written by: Orana Velarde

Are your survey results sitting in a file on your computer waiting to be analyzed? Or maybe there’s a stack of filled out forms somewhere in your office?
It’s time to get that survey data ready to present to stakeholders or members of your team.
Visme has all the tools you need to visualize your survey data in a report , infographic, printable document or an online, interactive design.
In this article, we’ll help you understand what a survey is and how to conduct one. We’ll also show you how to analyze survey data and present it with visuals.
Let’s get started.
Jump to the Section You Want
What is a survey, the 4 best tools for creating surveys, how to analyze survey results, how to present survey results with visme.
A survey is a study that involves asking a group of people all the same questions. It’s a research activity that aims to collect data about a particular topic.
A survey usually consists of at least one question and can be as long as tens of questions. The length of your survey depends on the nature of the research.
Surveys can be categorized into three main types:
- Cross-sectional. This survey is of a small section of a larger population within a small time frame. These are usually short and easy to answer quickly.
- Longitudinal. These are for collecting survey data over a longer period of time to learn about a shift or transformation in opinion or thought about a particular topic. The people surveyed are the same every time.
- Retrospective. In this case, the survey includes questions about events that happened in the past.
When it comes to survey results, your data can be either qualitative or quantitative.
- Quantitative. This data is collected from close-ended questions. These can be numerical answers, or yes and no answers. Quantitative surveys are easier to analyze and chart because of their nature.
- Qualitative. This data is collected from open-ended questions. Qualitative surveys usually ask participants their opinion about a particular topic. The answers can be harder to analyze and chart, as they need to be grouped and simplified first.
The survey results infographic below is from a quantitative survey where participants simply chose their favorites from a list. Customize it to use for your own data.

Surveys are conducted in different ways, depending on the needs of the surveyor and proximity of participants. While some surveys are conducted face-to-face, others are carried out via telephone, or self-administered digitally or on paper.
Surveys can be conducted for lots of different reasons, such as:
- Market research for businesses and brands
- Election polls or intended participation
- Customer satisfaction and/or suggestions
- User research for UX design
- Brand tracking studies
- And much more…
To conduct a successful survey, you need the right tools. For face-to-face surveys, you’ll need a group of people who will visit participants, enough printed survey copies or a way to record spoken answers.
For telephone surveys, you’ll need a group of people who can call participants over the phone. You’ll also need a computer program or printed survey question forms where the surveyor can record the data.
For online surveys, you can use a number of different tools. Below are our favorites:
- Typeform. Create a Typeform directly on their website or right inside your Visme dashboard. To collect and analyze the survey data from a Typeform, download it as an Excel or CSV file. For more than 20 answers, connect the Google Sheets integration to your Typeform.
- Google Forms. Collecting survey data in a Google Form is easy. The answers are instantly added to a spreadsheet that you can then further analyze and present with Visme later.
- SurveyMonkey. Creating a survey in SurveyMonkey isn’t just easy, they also offer data analysis tools for your results like filtering and grouping. Furthermore, Survey Monkey offers simple presenting tools for your data. You can also download the results as a CSV or Excel file like with many other tools, and then present visually with Visme.
- Stripo. With this tool, you can create a survey directly in an email and save all your results to analyze. Get an example of what your survey email could look like.
How to Create a Typeform Survey With Visme
With Visme, not only can you present your survey results, you can also create a survey! With our Typeform integration, creating a survey in a Visme project is as easy as inserting a new chart.
- Step 1: Create an area for your Typeform — a new block, slide or section — and click on the Apps button on the left tools panel.
- Step 2: Click on the Typeform button to connect your Typeform account.
- Step 3: Once you’ve signed in to your Typeform account, you can import any Typeform that you’ve previously created as long as it's not private or unpublished.
When you present survey data results with visuals, the trends and conclusions are easier and faster to understand.
But before you can do that, you’ll first need to analyze your results. The analysis process depends on the type of survey conducted and how the data was collected.
For example, simple online quantitative surveys can be fed directly to a spreadsheet, while qualitative surveys conducted face-to-face will need considerably more data entry work.
According to Thematic , these are the 5 steps you need to follow for best analysis results.

As you can see, the analysis starts even before creating the survey. This helps make sure that you are asking the right questions.
The data must then be organized into a filterable spreadsheet or table. The most common survey software available for analysis work is Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets.
To analyze more complex data , another great tool is Tableau — a powerful analysis and visualization tool. In fact, for large survey data, we suggest you use a mix of Tableau visualizations embedded into your Visme project along with our signature data widgets.
Now that we’ve looked at all the steps involved in conducting a survey, collecting data and analyzing it, let’s find out how to present your survey results with visuals.
Presenting survey results visually makes it easier to spot trends, arrive at conclusions and put the data to practical use. It’s essential to know how to present data to share insights with stakeholders and team members to get your message across.
You can easily make your survey data look beautiful with the help of Visme’s graph maker, data widgets and powerful integrations.
Check out the video below to learn more about how you can customize data and present it using data visualization tools in Visme.

Aside from data visualization, Visme lets you create interactive reports, presentations, infographics and other designs to help you better present survey results.
To give you more ideas, here are 9 unique ways to present survey results in Visme.
1. Create a Presentation
While many times you’ll put together a document, one-pager or infographic to visualize survey results, sometimes a presentation is the perfect format.
Create a survey presentation like the one below to share your findings with your team.
2. Create a Report
A multi-page report is a great way to print out a hard copy of your survey results, and formally share it with your team, management or stakeholders.
Here’s a survey report template in Visme you can customize.

You can also share interactive versions of your report online using Visme. After you finish designing your survey results report, simply hit publish to generate a shareable URL.
3. Add a Chart or Graph
The best way to present survey results is with a chart or graph. The type of chart you choose depends on the nature of your data. Below, we’ll take a look at two common types of charts you can use to visualize and present your survey data.
Bar graphs.
If you had a smaller survey and really want to visualize one main result, this bar graph survey results template is the perfect solution.
Insert your own information so you can quickly visualize the largest bars, giving you more insight into your audience.
Pie charts.
To visualize parts of a whole, a pie chart can really help to differentiate the answers that your audience gave. Look to see which responses were most popular to help you make more informed choices for your brand.
4. Visualize Text With Icons
Incorporating some of your survey questions into your report helps your audience understand your results better. Take it a step further by adding relevant icons to help visualize those questions.
Customize this template with your survey information before presenting it to your team.
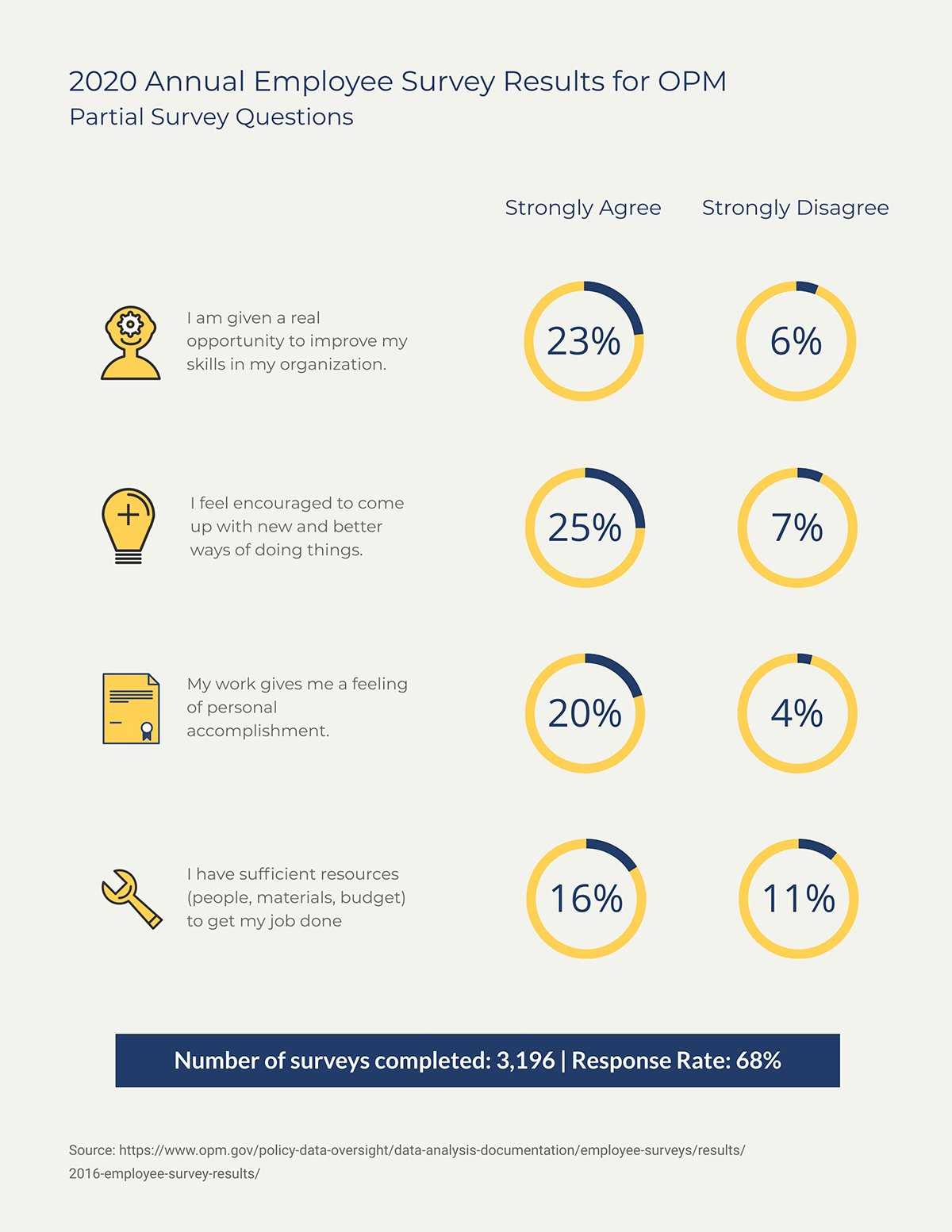
5. Use Pictographs
Another great way to use icons in your survey results report is with pictographs, or icon arrays. Pictographs use symbols like icons and shapes to convey meaning.
Use icon arrays to visualize sections of a whole. For example, you can use icons of people to visualize population data. Need to visualize the difference between cat lovers and dog lovers? Use an array with cat icons in different colors.
Here’s an example of a survey results report that uses pictographs to visualize psychographic data among a population.
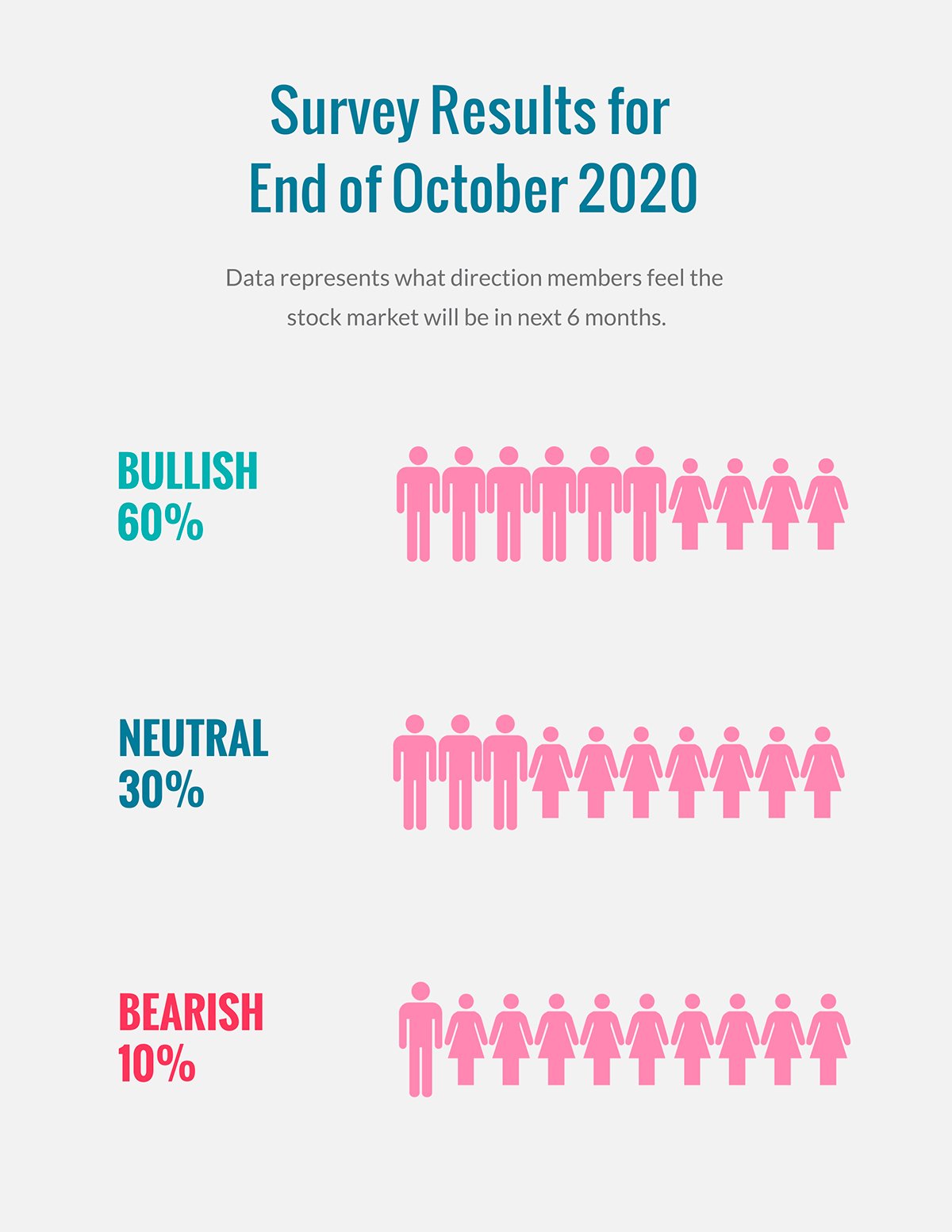
6. Create an Interactive Map
One more way to present survey results is with maps. This is a great solution for visualizing geographic data. In Visme, you have several options to help you create interactive maps:
- Choose between the world, regions, countries and states.
- Use the eye icons to hide or show different sections.
- Color code the sections as you wish.
- Make sections interactive by adding popups and hover effects.
7. Incorporate Creative Graphics
Get creative showcasing your results by adding graphics and illustrations that help represent your data. In the template below, we’ve used a human body to help visualize the survey results.
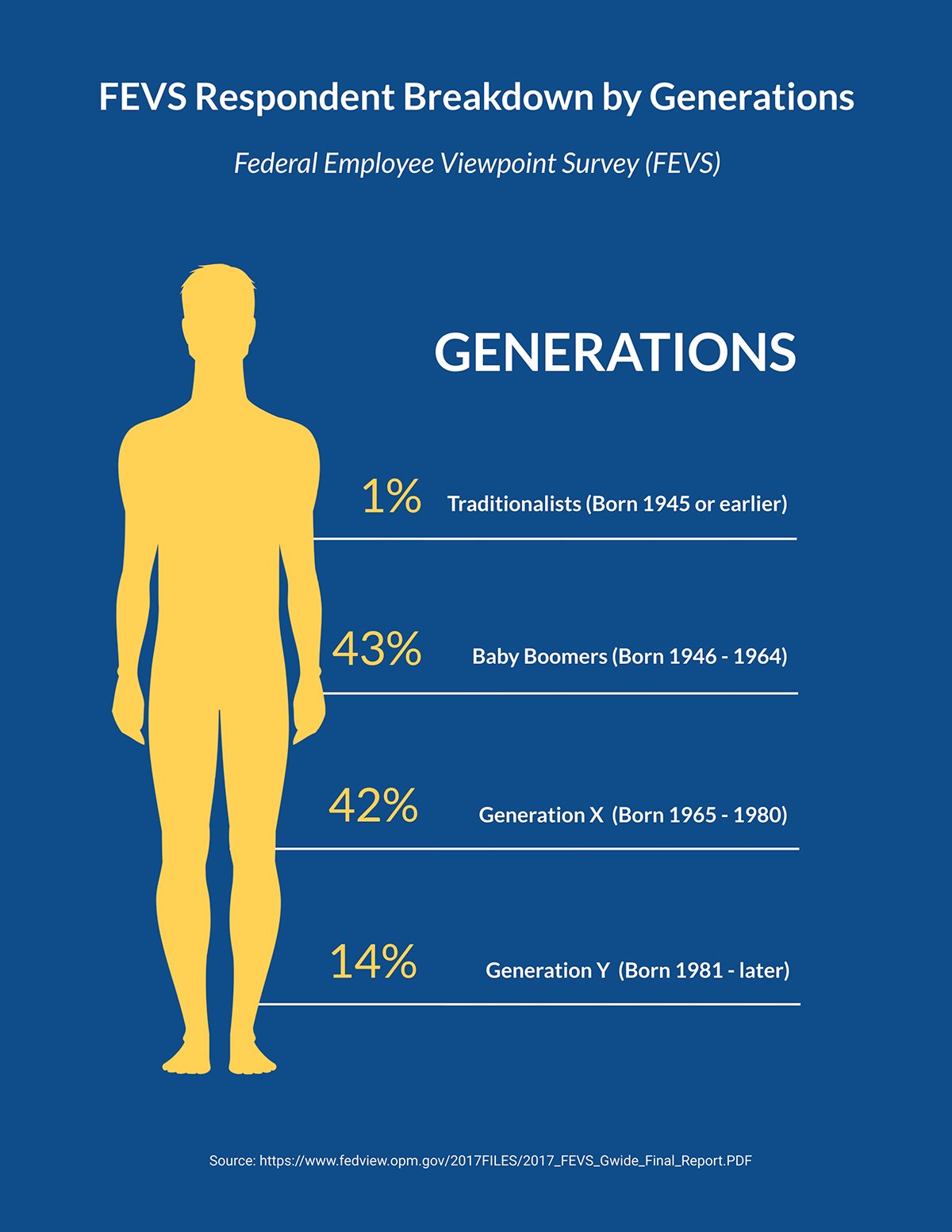
8. Use Multiple Data Widgets
If you want to show your survey results data in a snackable format, try using data widgets. These are perfect for showing percentages and quantitative comparisons in many different styles.
The best way to use them is to visualize one question of the survey at a time. For example, use one widget for the percentage of yes answers and another for the no answers.
In this template, you can easily customize multiple widgets to visualize different kinds of results and responses.
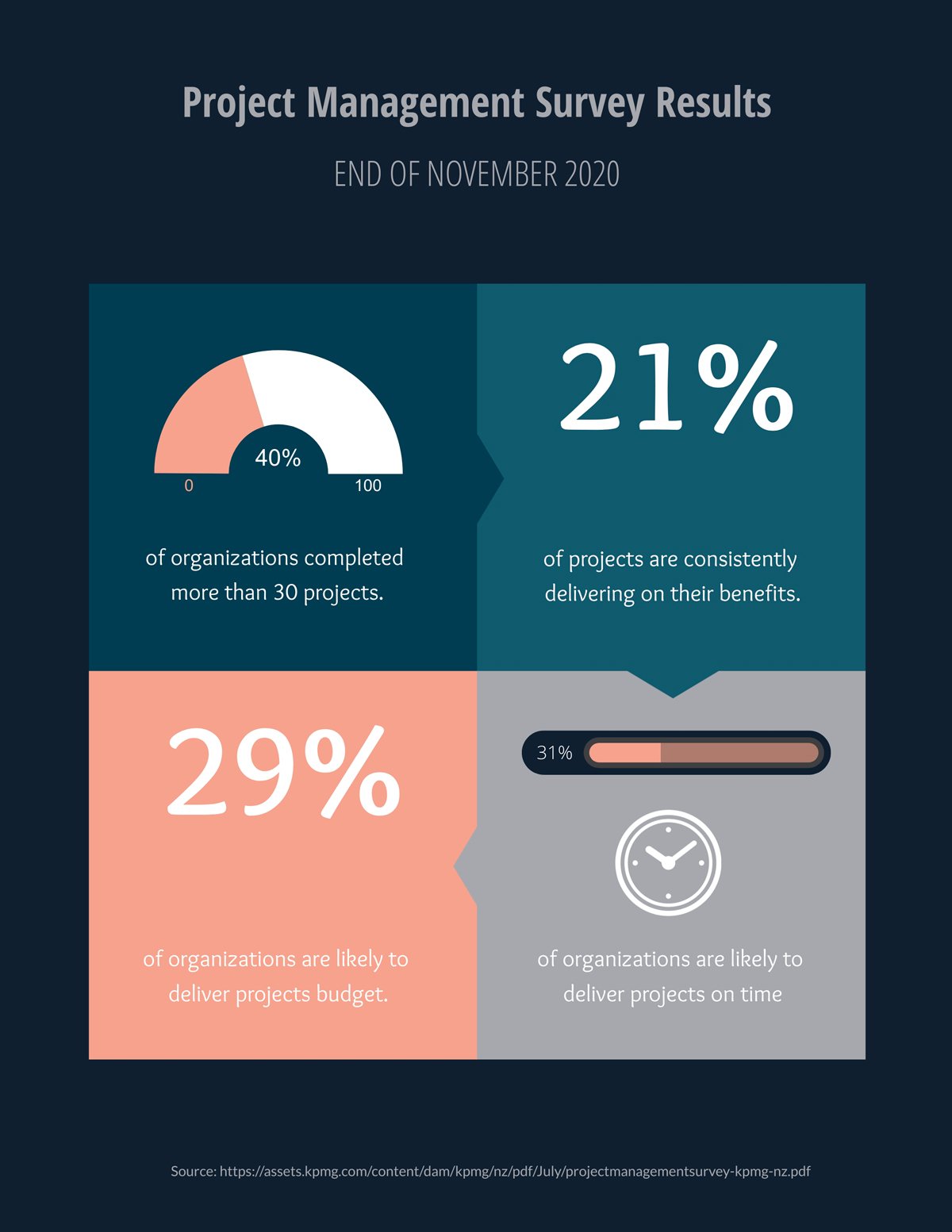
9. Embed Tableau Visualizations
Last but not least, you have the third-party embed option. With this tool, you can embed any Tableau visualization into a Visme project.
This is a great option if your data is more complex, or if you are a Tableau user who just wants to create better presentations with Visme.
To embed a Tableau into Visme, open the Media tab on the left-hand sidebar, then click on Embed Online Content. From the drop-down, select HTML.
Copy and paste the HTML from your Tableau visualization and paste it into Visme. Now your Tableau is part of a complete survey results report made with Visme!
Ready to Visualize and Present Your Survey Results?
To get started with visualizing your survey results, log in to your Visme account and choose one of the survey results templates.
If you don’t have a Visme account, creating one is easy and free . Simply register with your email and you’re good to go. Leave a comment below if you have any questions!
Create beautiful charts, graphs and data visualizations with ease.

Trusted by leading brands
Recommended content for you:
Create Stunning Content!
Design visual brand experiences for your business whether you are a seasoned designer or a total novice.
About the Author
Orana is a multi-faceted creative. She is a content writer, artist, and designer. She travels the world with her family and is currently in Istanbul. Find out more about her work at oranavelarde.com
Your current User-Agent string appears to be from an automated process, if this is incorrect, please click this link:
We use cookies
This website uses cookies to provide better user experience and user's session management. By continuing visiting this website you consent the use of these cookies.
ChartExpo Survey

How to Prepare a Survey Results Presentation?
Data insights are the backbone of any survey results presentation.
People want data before making a decision. But they want it in a form that’s appealing to their emotions.
So, how do you serve data in a compelling and easy-to-understand form?
Let’s imagine you’ve just gathered survey responses. But you’re stuck in the trenches. You don’t know how to turn these responses into compelling data stories.
How do you jump over this obstacle?
Survey responses are complex and may have textual and numerical data. This requires you to change your strategy during the analysis phase.
We recommend you try these charts, namely:
CSAT Score Bar Chart
Customer satisfaction chart, likert scale chart.
These survey-based charts and graphs are tailor-made specifically to help extract in-depth insights into your survey responses.
Yes, you read that right.
Excel lacks ready-to-go, easy-to-read, and insightful survey results presentation graphs.
We’re not recommending you dispose of your Microsoft Excel.
Installing third-party apps (add-ins) to access ready-made and easy-to-decode survey results presentation charts.
In this blog, you’ll learn:
Table of Content:
Video tutorials: survey results presentation, what are the survey results, presenting survey results using charts, how to present survey results, survey results presentation example, how to display survey results: best practices, faqs on how to present survey results, survey results presentation in excel.
Survey Results Presentation in Google Sheets
Survey Results Presentation in Power BI
Definition: Survey results are the information collected from target respondents.
This data is usually about a specific topic to conduct research.
You have multiple methods at your disposal if your goal is to gather survey results for further analysis.
You can use a diverse number of mediums to gather feedback and opinions from the desired sample of your niche market.
Seasoned data visualization experts use freemium tools like Google Forms and Microsoft Forms to collect survey data faster.
These tools are free, easy to use, and, most importantly, shareable via email, social media, or website embeds.
Once you have gathered responses, what’s the next step?
This is what we seek to address in this blog.
In the coming section, we’ll address the following question: what are the best graphs to use for survey results?
Some of the tested and recommended charts for visualizing survey data include the following:
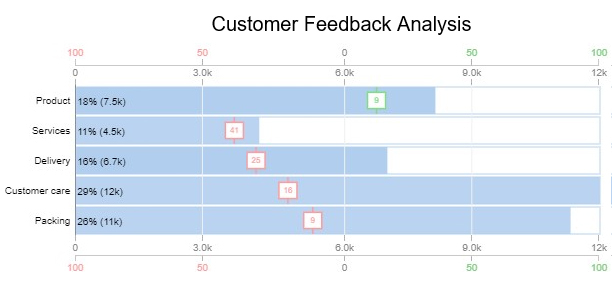
A CSAT Score Bar Chart is one of the survey results presentation-oriented visualizations you can use to display insights into your data.
The chart shows a Net Promoter Score – a customer experience-based metric.
The resulting insights are displayed along a Y-axis between -100 and +100. Use this graph to measure your customers’ level of loyalty.
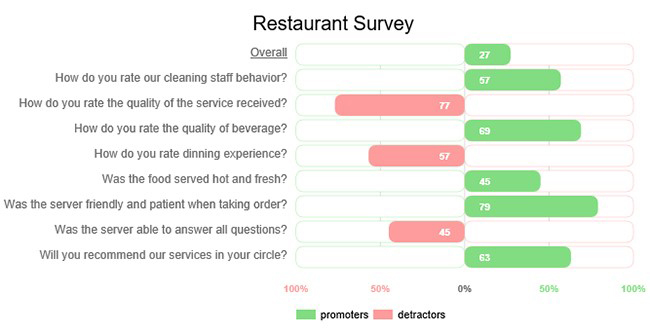
A Customer Satisfaction Chart is a survey result presentation-based graph you can use to display insights into close-ended questionnaire data.
The visualization shows the respondents agree or disagree with topics related to your brand. The easy-to-interpret chart is segmented into red and green, representing YES and NO.
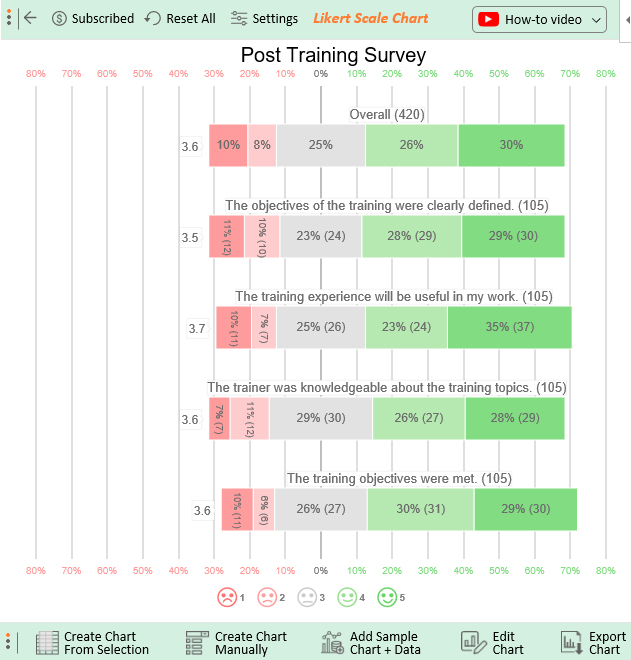
A Likert Chart is one of the survey results presentation-based visualizations you can use to showcase insights into the sentiments of your target respondents.
This psychometric scale-based visualization is best suited for displaying insights into survey data.
There are many Likert scale types, depending on agreement/disagreement levels. For instance, a 7-point Likert Scale Chart has up to 7 options for each question.
In the coming section, we’ll show you how to present survey results using the Likert Scale.
Also, we’ll unveil to you the tested and recommended add-in you can install in Excel to access survey result presentation-based visualizations, such as Likert and CSAT Score Bar Charts.
You don’t want to miss this.
Excel is one of the popular tools of visualization among business owners, offering various options such as the Mosaic plot to help analyze and present data effectively.
However, it lacks ready-made survey results presentation-based visualizations, such as the Likert Scale.
We’re not advising you to do away with Excel.
There’s an amazingly affordable tool that comes as an add-in you can easily install in Excel to access ready-to-go and easy-to-read survey results presentation-based visualizations, such as Likert.
The tool is called ChartExpo.
ChartExpo is an add-in you can easily install in your Excel to access ready-made and visually appealing survey results presentation-based visualizations, such as CSAT Score Bar Charts.
ChartExpo’s Features and Benefits
- You can turn overwhelming tables and spreadsheets into ready-made and visually stunning charts with just a few clicks.
- ChartExpo has a 7-day trial, which is free. So, if you’re unsatisfied with the data visualization add-in within a week, you can easily opt out within minutes.
- You have unlimited freedom to customize your charts and graphs according to your preferences.
In the coming section, we’ll show you how to install ChartExpo and visualize your data using easy-to-follow steps.
Let’s get started.
In this section, we’ll show you how to visualize your survey responses using a Likert Scale (one of the tested and proven survey result presentation visualizations).
Let’s get on with it.
| The objectives of the training were clearly defined. | 1 | 12 |
| The objectives of the training were clearly defined. | 2 | 10 |
| The objectives of the training were clearly defined. | 3 | 24 |
| The objectives of the training were clearly defined. | 4 | 29 |
| The objectives of the training were clearly defined. | 5 | 30 |
| The training experience will be useful in my work. | 1 | 11 |
| The training experience will be useful in my work. | 2 | 7 |
| The training experience will be useful in my work. | 3 | 26 |
| The training experience will be useful in my work. | 4 | 24 |
| The training experience will be useful in my work. | 5 | 37 |
| The trainer was knowledgeable about the training topics. | 1 | 7 |
| The trainer was knowledgeable about the training topics. | 2 | 12 |
| The trainer was knowledgeable about the training topics. | 3 | 30 |
| The trainer was knowledgeable about the training topics. | 4 | 27 |
| The trainer was knowledgeable about the training topics. | 5 | 29 |
| The training objectives were met. | 1 | 11 |
| The training objectives were met. | 2 | 6 |
| The training objectives were met. | 3 | 27 |
| The training objectives were met. | 4 | 31 |
| The training objectives were met. | 5 | 30 |
To get started with ChartExpo in Excel, follow the steps below:
- Open your Excel desktop application.
- Open the worksheet and click the Insert button to access the My Apps option.
- Click the Insert button to initiate the ChartExpo engine.
- Click on the Likert Scale Chart icon to get started.
- Highlight your data and click the Create Chart From Selection button, as shown.
- Check out the final chart below.
- Choose the Right Chart Type: Select a chart that best represents your data, such as bar charts for comparing categories or pie charts for showing proportions.
- Simplify the Data: Summarize key findings and group similar responses to make the data easier to interpret.
- Use Clear Labels and Titles: Ensure all charts have descriptive titles and labels that accurately explain the data.
- Color Coding: Use consistent and distinct colors to differentiate between data points without overwhelming the viewer.
- Highlight Key Insights: Use annotations or bold colors to emphasize the most important findings directly on the chart.
What do you mean by survey data?
Survey data is the information collected from target respondents.
You have multiple methods at your disposal if your goal is to gather survey data for further analysis.
You can use diverse mediums to gather feedback and opinions from the desired sample of your niche market.
What is the primary purpose of the survey?
Surveys can help you gauge the representativeness of your target market’s views and opinions.
When done well, they provide reliable insights into people’s opinions and sentiments that can be used to make crucial decisions.
Visualize survey responses using charts and graphs, such as the CSAT Score Bar and Likert Charts.

People want data before deciding. But they want it in a form that’s appealing to their emotions.
How do you serve data in a compelling and easy-to-understand form?
Assume you’ve just gathered survey responses. But you’re stuck in the trenches. You don’t know how to turn these responses into compelling data stories.
Survey responses are complex and may have qualitative and numerical data. This requires you to change your strategy during the analysis phase.
We recommend you try these charts, namely CSAT Score Bar, Customer Satisfaction, and Likert Scale Charts.
These survey-based charts and graphs are tailor-made to help extract in-depth insights into your responses.
Net Promoter, NPS, NPS Prism and many other terms related to NPS are registered trademarks of Bain & Company Inc., Satmetrix Systems Inc., and Fred Reichheld.
How much did you enjoy this article?

Related articles
How to Update a Chart in Excel for Clearer Insights?
Learn process of how to update a chart in Excel for effective analysis. Ensure your data is accurate and up-to-date with these practical steps and best practices.
What are HEDIS Measures: Overview and Guide
Delve into what HEDIS measures are, how they evaluate health plan performance, improve quality, and support transparency in healthcare delivery for patients.
Quality of Care Measures in Healthcare: A Complete Guide
Uncover the role of Quality of Care Measures in Healthcare in ensuring patient safety and satisfaction. Our analysis highlights key practices for better outcomes.
Population Pyramid Types with Real-World Examples
Uncover types of population pyramids and their impact on understanding demographic changes. Learn how expansive, constrictive, & stationary pyramids differ.
Balanced Scorecard: What is It, Uses, & Implementation
Explore Balanced Scorecard's role in aligning organizational activities with strategic goals, enhancing decision-making, and measuring performance effectively.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Written Presentation of Results. Once you've gone through the process of doing communication research - using a quantitative, qualitative, or critical/rhetorical methodological approach - the final step is to communicate it.. The major style manuals (the APA Manual, the MLA Handbook, and Turabian) are very helpful in documenting the structure of writing a study, and are highly recommended ...
Typically, evaluation reports include the results of the evaluation ("What"), interpretation of results ("So What"), and recommendations for continuing and improving the educational activity ("Now What"). How evaluation findings are communicated directly influences how stakeholders understand and react to the data and ultimately ...
What Are Effective Presentation Skills (and How to Improve ...
What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
How to Make a Successful Research Presentation
Here is a great way to synthesize and summarize your results in a way that will help your audience easily process what the results mean and then make a sound decision based on those results. How to Present Your Results and Get Recommendations Implemented. Focus on the Objective as the Burning Issue. In the first thirty seconds of your ...
A key component of scientific research is presenting research results to the scientific community. Research results are presented in three main formats: oral presentation; poster presentation; written paper. LS-LAMP participants give oral presentations and turn in written papers.
7.1 Sections of the Presentation. When preparing your slides, you need to ensure that you have a clear roadmap. You have a limited time to explain the context of your study, your results, and the main takeaways. Thus, you need to be organized and efficient when deciding what material will be included in the slides.
The results section is the core of a research paper where the study data and analyses are presented in an organized, uncluttered manner such that the reader can easily understand and interpret the findings. It is often embellished with self-explanatory tables and figures which assist in presenting data in addition to the text.
Here are a few best practices: Your results should always be written in the past tense. While the length of this section depends on how much data you collected and analyzed, it should be written as concisely as possible. Only include results that are directly relevant to answering your research questions.
A scientific paper is a written report that contains a presentation of the results of original scientific research. Its format is defined by centuries-old tradition of writing, the editorial ...
Indeed, disseminating the results is an essential part of the research process. By sharing your results with others, whether in written form as scholarly paper or an applied report or in some alternative format like an oral presentation, an infographic, or a video, you ensure that your findings become part of the ongoing conversation of ...
The Results section of a research paper lays out the body of evidence collected within the context of the study to support the conclusions and generalizations that are presented in the Discussion section. To be effective in supporting conclusions, the study results and their relation to the research questions and discussion points must be clear ...
The "presentation slide" is the building block of all academic presentations, whether they are journal clubs, thesis committee meetings, short conference talks, or hour-long seminars. ... Instead of titling the slide "Results," try "CTNND1 is central to metastasis" or "False-positive rates are highly sample specific." Use this ...
In a quantitative dissertation or capstone you will be presenting your results. You may present your results with or without a discussion explaining what those results mean. You will want to consult your chair to make sure you are following the approach. preferred by your chair. Thus, your chapter 4 may include the following: Introduction. Results.
Results may be presented in a number of ways, including via graphs, tables or other visual media or through detailed written description. The nature of your research will dictate the best forum through which to present. However, presentation of results is only part of the story you need to tell. A discussion of your results is where the ...
How to turn survey results into a great presentation
1. Using charts for survey results presentation at one glance. A chart or graph is a visual presentation of data. The major goal of using charts is to display your assessment or survey results in a meaningful way. Good charts convey information easily and quickly to the audience, whereas a bad chart leaves you confused.
Reporting Research Results in APA Style | Tips & Examples
Reporting the results of a program evaluation must explicitly consider how to: Align the results with the original evaluation questions and stakeholders' inputs. Make it actionable: evaluations are conducted to inform decisions. Adapt report to stakeholder audience and present using multiple formats and media.
Step 1: Install the ClassPoint add-in for PowerPoint. Step 2: Launch any presentation slides and enter slide show mode. Step 3: Click on "Quick Poll" on the ClassPoint tab at the bottom of your screen and choose from three poll types: true or false, yes or no, and agree or disagree to launch the poll. Step 4: Audience can join your poll at ...
1. Create a Presentation. While many times you'll put together a document, one-pager or infographic to visualize survey results, sometimes a presentation is the perfect format. Create a survey presentation like the one below to share your findings with your team. 1 / 8.
Invite collaborators: Share the presentation with your team members by sending them a link or inviting them directly through the software. Work together in real time: Once your team members have access, they can start editing the slide presentation simultaneously.Use the built-in chat and comment features to communicate and provide feedback in real time.
A Likert Chart is one of the survey results presentation-based visualizations you can use to showcase insights into the sentiments of your target respondents.. This psychometric scale-based visualization is best suited for displaying insights into survey data. There are many Likert scale types, depending on agreement/disagreement levels.
The results chapter or section simply and objectively reports what you found, without speculating on why you found these results. The discussion interprets the meaning of the results, puts them in context, and explains why they matter. In qualitative research, results and discussion are sometimes combined. But in quantitative research, it's ...
First as tragedy, then as farce. Same tournament; same umpire. New players; new court; new call. Same outcome: tennis shooting itself in the foot.