- Hard skills
- Soft skills
- Life skills
- People skills
- Social skills
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions

Problem-Solving Mastery: Your Roadmap to Effective Solutions
- Job Skills , Life skills , Soft skills

In today’s rapidly evolving world, problem-solving skills have become more critical. The ability to identify, analyze, and find effective solutions to complex challenges is highly valued across various domains, including education, business, and personal life. Problem-solving skills empower individuals to overcome obstacles, make informed decisions, and confidently navigate uncertain situations. They are key personal and professional success drivers, enabling individuals to adapt to change, innovate, and seize opportunities.
This article will delve into the essential steps for mastering problem-solving skills. We will explore the characteristics of effective problem solvers and highlight the step-by-step process they follow to tackle problems. From defining the problem and gathering information to evaluating solutions and implementing the chosen course of action, we will cover each stage in detail, providing valuable insights and practical strategies. Additionally, we will discuss various techniques and tools that can enhance problem-solving abilities and address common challenges individuals encounter. Whether you are a student, professional, or simply looking to enhance your problem-solving skills, this article will serve as a comprehensive guide to equip you with the necessary knowledge and techniques to become a proficient problem solver.
Understanding Problem Solving
A. definition of problem-solving.
Problem-solving is a fundamental skill applicable across diverse academic, professional, and personal contexts. It plays a crucial role in business, science, engineering, and everyday life, enabling individuals to overcome obstacles, achieve goals, and improve outcomes.
Here are some definitions with sources-
“Problem-solving is the cognitive process of identifying, analyzing, and resolving obstacles or difficulties encountered to achieve a desired goal or outcome.”
Source: – Simon, H. A. (1972). Theories of Bounded Rationality. Decision and Organization, 1(1), 161-176.
“Problem-solving refers to the systematic approach of finding solutions to challenges by utilizing logical thinking, analytical skills, and creativity.”
Source: – D’Zurilla, T. J., & Nezu, A. M. (2007). Problem-Solving Therapy: A Positive Approach to Clinical Intervention. Springer Publishing Company.
“Problem-solving is the cognitive process of identifying, analyzing, and overcoming obstacles through the application of problem-solving strategies, critical thinking , and decision-making skills.”
Source: – Fogler, H. S., LeBlanc, S. E., & Rizzo, E. (2020). Strategies for Creative Problem Solving. Pearson.
“Problem-solving involves the ability to define problems, generate potential solutions, evaluate alternatives, and implement the best course of action, resulting in effective decision making and successful resolution of challenges.”
Source: – Bransford, J. D., Brown, A. L., & Cocking, R. R. (2000). How People Learn: Brain, Mind, Experience, and School : Expanded Edition. National Academies Press.
B. The role of problem-solving in personal and professional life
The Role of Problem-Solving in Personal and Professional Life:
1. Personal Life:
a. Decision Making: Problem-solving is crucial in making informed decisions about personal matters, such as career choices, relationships, and financial planning.
b. Resolving Conflicts: Effective problem-solving skills help resolve conflicts and disputes, fostering healthier relationships and communication.
c. Adaptability: Problem-solving enables individuals to navigate life’s challenges and adapt to changing circumstances, enhancing personal growth and resilience.
d. Goal Achievement: By identifying obstacles and finding solutions, problem-solving helps individuals overcome barriers and progress towards achieving personal goals.
2. Professional Life:
a. Innovation and Creativity: Problem-solving is at the core of innovation, enabling individuals to identify opportunities, develop new ideas, and implement creative solutions.
b. Decision Making: Effective problem-solving skills aid in making sound business decisions, analyzing data, and evaluating options to achieve desired outcomes.
c. Troubleshooting and Crisis Management : Problem-solving is crucial in addressing workplace issues, identifying root causes, and implementing solutions to operational challenges and crises.
d. Collaboration and Teamwork: Problem-solving skills facilitate effective collaboration and teamwork, as individuals work together to analyze problems, generate ideas, and implement solutions.
e. Continuous Improvement: By identifying inefficiencies and finding better solutions, problem-solving drives continuous improvement in processes, products, and services.
f. Leadership: Strong problem-solving abilities are essential for effective leadership, as leaders navigate complex situations, inspire teams, and drive organizational success.
Overall, problem-solving is vital in personal and professional life, empowering individuals to overcome obstacles, make informed decisions, foster innovation, and achieve desired outcomes. It promotes adaptability, resilience, and growth, enhancing overall success and satisfaction in various aspects of life.

Characteristics of Effective Problem Solvers
Here are some Characteristics of Effective Problem Solvers:
1. Critical Thinking: Effective problem solvers possess strong critical thinking skills. They can analyze situations objectively, evaluate information, identify patterns, and make logical connections to understand the underlying causes of problems.
2. Analytical Skills: Effective problem solvers can break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable components. They can examine each component individually, identify relevant factors, and assess their interrelationships to understand the problem comprehensively.
3. Creativity and Innovative Thinking: Effective problem solvers think outside the box and are open to unconventional ideas and solutions. They approach problems creatively, seeking new perspectives, alternative approaches, and innovative solutions.
4. Persistence and Resilience: Effective problem solvers persevere when facing obstacles and setbacks. They are resilient and maintain a positive attitude, viewing challenges as opportunities for growth and learning rather than insurmountable barriers.
5. Adaptability and Flexibility: Effective problem solvers are adaptable and flexible in their thinking and approach. They are open to adjusting their strategies, considering different viewpoints, and embracing change as they navigate complex problem-solving situations.
6. Systems Thinking: Effective problem solvers consider the larger context and understand the interconnectedness of various factors. They can see how different elements within a system influence each other and recognize the ripple effects of their decisions and actions.
7. Collaboration and Communication: Effective problem solvers are skilled in collaboration and communication. They actively listen to others, seek input and feedback, and can articulate their thoughts and ideas clearly. They can work well in teams, leveraging diverse perspectives and expertise to find optimal solutions.
8. Decision Making: Effective problem solvers are proficient in decision-making . They gather relevant information, weigh different options, assess risks and benefits, and make informed choices based on a logical and rational evaluation process.
9. Continuous Learning: Effective problem solvers have a growth mindset and a thirst for knowledge. They actively seek opportunities to learn new skills, expand their knowledge base, and stay updated on industry trends and advancements.
10. Emotional Intelligence: Effective problem solvers possess emotional intelligence, allowing them to understand and manage their emotions and empathize with others. They can navigate interpersonal dynamics, handle conflicts constructively, and foster positive relationships while solving problems.
These characteristics collectively contribute to the effectiveness of problem solvers, enabling them to approach challenges with a systematic, innovative, and resilient mindset, ultimately leading to successful problem resolution and achieving desired outcomes.
The Problem-Solving Process
Here is The Problem-Solving Process Step by Step:
Step 1: Defining the Problem:
1. Identifying the root cause: To effectively solve a problem, it’s important to identify the underlying cause or causes. This involves digging deeper to understand the factors or circumstances that led to the problem’s occurrence.
2. Clarifying the desired outcome: Clearly defining the desired outcome provides a clear direction for problem-solving. It helps in setting goals and measuring the success of the solution.
Step 2: Gathering information and analyzing the situation:
1. Collecting relevant data and facts: Gathering relevant data and facts about the problem is crucial for making informed decisions. This involves collecting information from reliable sources, conducting surveys, interviews, or analyzing existing data.
2. Conducting research and seeking different perspectives: Researching the problem and seeking different perspectives allows for a comprehensive understanding of the situation. This may involve studying case studies, consulting experts, or getting insights from people who have faced similar challenges.
Step 3: Generating potential solutions:
1. Brainstorming techniques: Brainstorming involves generating many ideas without judgment. It encourages creativity and open-mindedness, allowing for the exploration of various solutions.
2. Considering multiple options: Considering multiple options helps in expanding the range of possibilities. It involves evaluating different approaches, strategies, or alternatives to find the most effective solution.
Step 4: Evaluating and selecting the best solution:
1. Assessing pros and cons: Evaluating the potential solutions involves assessing their advantages and disadvantages. This helps in understanding the potential benefits and drawbacks of each option.
2. Using decision-making tools and techniques: Decision-making tools and techniques, such as decision matrices, cost-benefit analysis, or SWOT analysis, can provide a structured approach to evaluating and comparing different solutions. They help in making an informed decision.
Step 5: Implementing the chosen solution:
1. Developing an action plan: A detailed action plan outlines the steps and tasks needed to implement the chosen solution. It includes setting deadlines, assigning responsibilities, and allocating necessary resources.
2. Overcoming potential obstacles: Anticipating potential obstacles and challenges helps develop contingency plans. By identifying potential barriers in advance, proactive measures can be taken to overcome them and ensure a smoother implementation process.
Step 6: Monitoring and evaluating the outcomes:
1. Assessing the solution’s effectiveness: Regularly monitoring and evaluating the outcomes of the implemented solution is crucial. This involves measuring the results against the desired outcome and assessing whether the solution effectively addresses the problem.
2. Making adjustments if necessary: If the desired outcomes are not achieved or new issues arise, it may be necessary to adjust the solution or implementation plan. This ensures continuous improvement and adaptability throughout the problem-solving process.
By following this step-by-step process, individuals and teams can approach problem-solving systematically and comprehensively, increasing the chances of finding effective solutions and achieving desired outcomes.

Techniques and Strategies for Effective Problem Solving
Here are some Techniques and Strategies for Effective Problem Solving:
A. SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats):
SWOT analysis is a widely used technique for understanding a situation or organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses and the external opportunities and threats it faces. It involves identifying and analyzing these four factors to gain insights into the current state and potential future scenarios. One can effectively capitalize on opportunities and mitigate threats by understanding strengths and weaknesses.
B. Root cause analysis:
Root cause analysis is a technique used to identify the underlying cause or causes of a problem. It involves digging deeper into the problem to determine the fundamental reasons for its occurrence. By identifying and addressing the root cause, rather than just treating symptoms, one can prevent the problem from recurring and find long-term solutions.
C. Pareto analysis:
Pareto analysis, also known as the 80/20 rule, is a technique that helps prioritize tasks or issues based on their significance. It involves identifying the vital few (20%) contributing to the majority (80%) of the problem. One can achieve the greatest impact with limited resources by focusing efforts on addressing the most significant factors.
D. Six Thinking Hats technique:
The Six Thinking Hats technique, developed by Edward de Bono, is a method for approaching problem-solving from different perspectives. Each “hat” represents a different thinking mode or mindset, such as logical, creative, critical, etc. By consciously adopting these different perspectives, individuals or teams can explore different angles, consider various factors, and enhance problem-solving.
E. Design thinking approach:
The design thinking approach is a human-centered problem-solving methodology. It emphasizes empathy, collaboration, and experimentation to understand the user’s needs, ideate innovative solutions, and iterate through prototypes. It involves several stages, including empathizing with users, defining the problem, ideating potential solutions, prototyping, and testing. This approach encourages a creative and iterative problem-solving process that delivers solutions meeting user needs.
By utilizing these techniques and strategies for effective problem-solving, individuals and teams can enhance their problem-solving capabilities, think more critically and creatively, and arrive at comprehensive and innovative solutions to address various challenges.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Problem-Solving
Now we discuss how to overcome Common Challenges in Problem-Solving:
A. Emotional barriers and biases:
1. Self-awareness: Recognize and acknowledge your emotions and biases that may hinder the problem-solving process.
2. Objective perspective: Strive to approach problems with an open mind and consider alternative viewpoints.
3. Seek feedback: Involve others in problem-solving to gain diverse perspectives and challenge your biases.
B. Fear of failure and risk aversion:
1. Embrace a growth mindset: View failures as learning opportunities and be open to taking calculated risks.
2. Break problems into smaller steps: Breaking down complex problems into smaller, manageable tasks can help reduce the Fear of failure.
3. Experiment and iterate: Implement solutions in iterative stages, allowing for adjustments and learning from setbacks.
C. Lack of communication and collaboration:
1. Active listening: Listen attentively to others’ perspectives, fostering effective communication and understanding.
2. Encourage participation: Create a supportive environment where everyone feels comfortable contributing ideas and insights.
3. Foster teamwork: Promote collaboration and establish clear roles and responsibilities within problem-solving teams.
D. Ineffective time management:
1. Prioritize tasks: Identify the most critical aspects of the problem and allocate time accordingly.
2. Set deadlines and milestones: Establish specific deadlines for each step of the problem-solving process to stay on track.
3. Avoid distractions: Minimize interruptions and focus on the task by creating a conducive work environment.
By addressing these common problem-solving challenges, individuals and teams can enhance their problem-solving effectiveness and achieve better outcomes. Overcoming emotional barriers and biases, embracing risk-taking, fostering effective communication and collaboration, and managing time efficiently are key factors in successful problem-solving endeavors. By developing strategies to tackle these challenges, individuals can unlock their problem-solving potential and approach challenges with confidence and resilience.
Developing Problem-Solving Skills
Is it possible to develop problem-solving skills? Yes, it is possible. But How?
A. Continuous learning and skill development:
1. Stay curious: Cultivate a continuous learning mindset by seeking new knowledge, exploring different perspectives, and staying updated on industry trends.
2. Acquire relevant knowledge: Develop a solid foundation in the areas relevant to problem-solving, such as critical thinking, analytical skills, creativity, and decision-making.
3. Pursue professional development: Attend workshops, training programs, and online courses on problem-solving techniques and strategies.
B. Seeking feedback and reflection:
1. Welcome constructive criticism: Seek feedback from peers, mentors, or supervisors to gain insights into areas for improvement in your problem-solving approach.
2. Reflect on past experiences: Evaluate your problem-solving efforts, identify strengths and weaknesses, and learn from your successes and failures.
3. Develop self-awareness: Understand your thinking patterns, biases, and emotional reactions to improve your problem-solving skills.
C. Practicing problem-solving exercises and scenarios:
1. Solve puzzles and brain teasers: Engage in activities that challenge your problem-solving abilities, such as puzzles, riddles, or logic games.
2. Simulate problem-solving scenarios: Create hypothetical problem-solving situations and brainstorm potential solutions to enhance your critical thinking and decision-making skills.
3. Participate in group problem-solving activities: Collaborate with others in problem-solving exercises or workshops to foster teamwork and develop effective communication skills.
D. Engaging in real-life problem-solving experiences:
1. Embrace challenges: Seek opportunities to tackle real-world problems, whether at work, in personal projects, or community initiatives.
2. Apply problem-solving techniques: Utilize the problem-solving process and relevant strategies to address issues encountered in various aspects of life.
3. Learn from experiences: Reflect on your problem-solving approach in real-life situations, identify areas of improvement, and adjust your strategies accordingly.
Developing problem-solving skills is an ongoing process that requires continuous learning, practice, and application in both simulated and real-life scenarios. By investing time and effort in skill development, seeking feedback, reflecting on experiences, and engaging in problem-solving activities, individuals can strengthen their problem-solving abilities and effectively address complex challenges.
Applying Problem-Solving Skills in Different Areas
Now we will discuss Applying Problem-Solving Skills in Different Areas:
A. Problem-solving in the workplace:
Problem-solving skills are highly valuable in the workplace as they enable individuals to address challenges, make informed decisions, and contribute to organizational success. In a professional setting, problem-solving involves identifying and analyzing issues, generating effective solutions, and implementing them to achieve desired outcomes. It often requires collaboration, critical thinking, and creative problem-solving techniques. Effective problem-solving in the workplace can lead to increased productivity, improved teamwork, and innovation.
B. Problem-solving in personal relationships:
Problem-solving skills play a crucial role in maintaining healthy and constructive personal relationships. Conflicts and challenges are inevitable with family members, friends, or romantic partners. Applying problem-solving skills in personal relationships involves active listening, empathy, and open communication. It requires identifying and understanding the issues, finding common ground, and working towards mutually beneficial solutions. Problem-solving in personal relationships helps build trust, strengthen connections, and promote harmony.
C. Problem-solving in entrepreneurship:
Problem-solving is an essential skill for entrepreneurs, as it drives innovation and the ability to identify and seize opportunities. Entrepreneurs face various challenges, such as market competition, resource constraints, and changing customer needs. Applying problem-solving skills in entrepreneurship involves identifying market gaps, analyzing customer pain points, and developing innovative solutions. Entrepreneurs must be adaptable, resilient, and creative in finding solutions that address real-world problems and create customer value.
D. Problem-solving in everyday life:
Problem-solving skills are not limited to specific areas but are applicable in everyday life. From simple tasks to complex decisions, problem-solving helps navigate challenges efficiently. Everyday problem-solving involves assessing situations, setting goals, considering available resources, and making informed choices. It can range from troubleshooting technology issues to managing personal finances, resolving conflicts, or finding solutions to logistical problems. Developing problem-solving skills in everyday life leads to increased self-confidence, improved decision-making abilities, and overall personal effectiveness.
In all these areas, applying problem-solving skills enables individuals to approach challenges with a structured and analytical mindset, find practical solutions, and overcome obstacles effectively. It empowers individuals to think critically, adapt to changing circumstances, and positively contribute to various aspects of their lives.
Case Studies of Successful Problem Solving
Here are some Case Studies of Successful Problem Solving:
A. Real-life examples of problem-solving success stories:
1. NASA’s Apollo 13 Mission: The Apollo 13 mission faced a critical problem when an oxygen tank exploded, jeopardizing the lives of the astronauts. Through collaborative problem-solving, the NASA team on the ground and the astronauts in space worked together to develop innovative solutions, such as building a makeshift CO2 filter, conserving power, and navigating a safe return to Earth.
2. Apple’s iPhone Development: Apple faced the challenge of creating a revolutionary smartphone that combined multiple functions in a user-friendly design. Through rigorous problem-solving, Apple’s team developed groundbreaking solutions, such as the touch screen interface, intuitive user experience, and integration of various technologies, leading to the successful launch of the iPhone.
3. Toyota’s Lean Manufacturing System: Toyota encountered production inefficiencies and quality issues. By implementing problem-solving techniques, such as the Toyota Production System, the company focused on waste reduction, continuous improvement, and empowering employees to identify and solve problems. This increased productivity, improved quality, and a competitive advantage in the automotive industry.
B. Analysis of the problem-solving strategies employed:
1. Collaborative Problem-Solving: Successful problem-solving often involves collaboration among individuals or teams. Organizations can tackle complex challenges more effectively by leveraging diverse perspectives, knowledge, and skills.
2. Innovative Thinking: Problem-solving success stories often involve innovative thinking to address issues in novel ways. This may include exploring new technologies, challenging conventional wisdom, or adopting creative approaches that disrupt the status quo.
3. Systematic Approach: Effective problem-solving requires a systematic approach that involves defining the problem, gathering relevant information, analyzing options, and implementing solutions. This structured method provides a comprehensive understanding of the problem and helps identify the most appropriate action.
4. Continuous Improvement: Many successful problem-solving cases are committed to continuous improvement. Organizations embracing a learning and adaptability culture are better equipped to identify and solve problems efficiently, leading to long-term success.
5. Customer-Centric Solutions: Problem-solving strategies that prioritize understanding and meeting customer needs tend to yield successful outcomes. Organizations can develop solutions that deliver value and drive customer satisfaction by placing the customer at the center of problem-solving efforts.
Analyzing the problem-solving strategies employed in these case studies provides valuable insights into the approaches, techniques, and mindsets that contribute to successful problem resolution. It highlights the importance of collaboration, innovation, systematic thinking, continuous improvement, and customer focus in achieving positive outcomes.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, problem-solving skills are vital in various aspects of life, including personal, professional, and entrepreneurial endeavors. Through this article, we have explored the importance of problem-solving, its Definition, its role in different areas, characteristics of effective problem solvers, the problem-solving process, and techniques for effective problem-solving. We have also examined case studies of successful problem-solving and analyzed the strategies employed.
Recap of key points:
1. Problem-solving skills are crucial for personal, professional, and entrepreneurial success.
2. Effective problem solvers possess critical thinking, creativity, adaptability, and perseverance.
3. The problem-solving process involves defining the problem, gathering information, generating solutions, evaluating options, implementing the chosen solution, and monitoring outcomes.
4. Techniques like SWOT analysis, root cause analysis, Pareto analysis, Six Thinking Hats, and design thinking provide valuable frameworks for problem-solving.
As you have learned about the importance and various aspects of problem-solving, I encourage you to apply these skills in your own life. Problem-solving is not a mere intellectual exercise but a practical tool that can lead to personal growth, professional success, and positive societal contributions. Developing and honing your problem-solving abilities allows you to navigate challenges, make informed decisions, and find innovative solutions.
Embrace a continuous improvement mindset and a willingness to think outside the box. Seek opportunities to apply problem-solving skills in your relationships, workplace, entrepreneurial ventures, and everyday life. Remember that each challenge presents an opportunity for growth and learning. You can overcome obstacles and achieve desired outcomes by approaching problems with a structured and analytical mindset, considering multiple perspectives, and employing effective problem-solving techniques.
Incorporate problem-solving into your daily life and encourage others to do the same. By doing so, you contribute to a more proactive and solution-oriented society. Remember, problem-solving is a skill that can be developed and refined through practice and experience. So, take on challenges, embrace creativity, and be a proactive problem solver.
Start applying problem-solving skills today, and you will witness the positive impact it can have on your life and the lives of those around you.
Solution-Based Thinking: Top Traits of Great Problem Solvers
According to a Job Outlook 2017 survey of employers, the top three attributes sought most frequently in candidates are:
- Demonstration of strong teamwork (78 percent)
- Problem-solving skills (77.3 percent)
- Excellent written communication competency (75 percent)
At just over 77 percent, it’s evident that the act of problem-solving is a universal skill which applies to all positions within varying industries. We will all likely find ourselves tasked with some form of problem-solving at one time or another. Unfortunately, however, solution-based thinking doesn’t always come naturally to all of us.

First, however, let’s review why this quality is so widely valued in the job market.
Why do employers value problem-solvers?
1. problem solvers can handle any situation..
When these individuals are faced with a problem with no immediate solution in sight, they don’t panic immediately. Instead, they remain calm and figure out how they can solve the issue.
2. Problem solvers bring ideas and solutions to the table.
They do not wait to be told to do things. They make suggestions on how to improve workflow. They try to proactively shape their environment instead of accepting the present circumstances.
3. Problem solvers make the right decisions for an organization.
These individuals think analytically, therefore, it is easier for them to make the right decisions.
What are the common traits of good problem solvers?
1. problem solvers know what the problem is..
In many situations, they are able to identify specific or potential roadblocks before others do.
2. Problem solvers know when to apply simple or complex solutions.
Problems can come with all levels of complications. A good problem solver knows when to apply systematic and complex solutions to the issue or when to make use of shortcuts and find an easier route to the solution.
3. Problem solvers view problems as opportunities to grow.
Those with solution-based thinking often view problems as situations that will help them learn and improve upon their existing expertise.
4. Problem solvers think outside the box.
The act of trouble-shooting alone causes the mind to delve beyond what is most obvious. True problem-solvers are open to new ways of thinking and exploration toward solutions.
5. Problem solvers do not feel that they are always right.
Individuals who are focused on finding the right solution are more concerned with what is best for the present circumstance than proving themselves right (or someone else wrong, for that matter). They will also not be found bragging about being right (even if they are).
6. Problem solvers have well-developed social skills.
They connect well with people; both in person and online. This trait also helps them find solutions through other channels.
7. Problem solvers would rather prevent than intervene.
Solution-based thinkers know that the best way to be more productive in an organization is to prevent problems from developing in the first place. They are therefore, quite centered on quality and due-diligence.
8. Problem solvers explore all options.
They rarely rely upon a single solution to a problem. As trouble-shooters, they are always ready with a backup plan or a new angle toward handling the issue.
9. Problem solvers have reasonable expectations in specific situations.
They understand that several issues can often have a hand in one problem, requiring patience when it comes to isolating the issue at play. For this reason, they are aware that each problem should be approached with realistic expectations.
10. Problem solvers do not create more problems for other people.
The goal of a true problem solver is to discover solutions that will not harm or overly inconvenience others. They are aware that if they must apply a solution which may adversely affect their colleagues, the solution will be temporary and actions will be taken to reduce negative consequences for the rest of the company.
However, for those who may not be natural trouble-shooters at heart, here are some suggested steps toward improving your solution-based thinking and follow-through.
Steps to Problem Solving:
1. identify the problem..
Once you’ve identified the problem, try to figure out why and how it occurred.
2. Determine the criteria for your solution.
Before generating a solution, you must first define what you hope to achieve. For example, your solution must stay within a specific budget or time frame.
3. Create possible solutions.
Try to generate several possible ways to rectify the problem. Do not rely on a single solution. If the problem is complex, you may need to consult experts or perform further research on the subject.
4. Analyze each possible solution.
Analyze each potential solution alongside the criteria that you created. Create a table to make it easier for you to view which solution should be applied.
5. Choose the best solution.
Choose the solution that is most practical or most feasible.
6. Create an implementation plan.
You need to have a working strategy to implement your solution. This plan should also help track the plan’s ongoing success. Try to include time and cost estimates.
7. Document all information connected to your solution.
Make list of all information you’ve acquire from steps 1 through 6. Attempt to keep your findings to two pages or less for ease of reference.
8. Meet with your manager or supervisor.
Present your solution plan to your boss as you give him a copy of your document. Explain why you feel these are the best choices toward solution.

As we know, in order to stand out in the workplace, contribution is crucial. Managers and supervisors already face many day to day problems. When they know they have an employee who is ready to face and work through challenges, that individual is naturally valued by his or her superiors and by the organization as a whole.
Fred Coon, CEO
At SC&C we offer Career Analysis to help senior decision-makers from all walks of life identify strategies and tactics to increase their value-add employment potential.
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!

The Seven Traits of Highly Effective Consulting Problem Solvers
The most valuable professionals and leaders aren’t just smart – they consistently demonstrate an ability to solve complex problems.
After spending over a decade in strategy consulting and advising hundreds of business leaders, I’ve noticed that traditional “intelligence” or subject matter expertise isn’t what sets great problem solvers apart.
Truly effective problem solvers exhibit specific traits that enable them to tackle challenges systematically and creatively.
In other articles, I’ve covered problem-solving approaches and processes .
Here, I’ll explore the characteristics and mindsets that great problem solvers have in common:
- curiosity and open-mindedness
- analytical thinking
- creativity and lateral thinking
- resilience and adaptability
- collaborative mindset
- systems thinking
- A bias for action
1. Curiosity and Open-mindedness
The best problem solvers share an insatiable curiosity about how things work. They must know why things are the way they are and how to potentially fix them. These people are obsessed with diagnosing root causes and not trusting the conventional wisdom of others. They let their curiosity guide them, even if it means questioning those in power.
I saw this first-hand when working with a consumer tech company struggling with user engagement. While most team members focused on obvious metrics like app usage and click-through rates, one analyst kept asking about user behaviors outside the app. Her questions about how people were using competing products and when they weren’t using our client’s app led to a breakthrough insight: users weren’t disengaged because of the product’s features, but because of how the app fit (or didn’t fit) into their daily routines. This discovery completely reframed the problem and led to a more effective solution.
This trait extends beyond just asking questions. Truly curious problem solvers:
- Resist jumping to conclusions, even when the answer seems obvious
- Actively seek out contradictory evidence to test their assumptions
- Show genuine interest in understanding different perspectives
- Approach familiar problems with fresh eyes
To help drive curiosity, at McKinsey , they try to turn any hypothesis into a question and then split teams into opposing camps that argue for the “right” answer. In these, “thesis/antithesis, or red team/blue team, sessions,” they:
divide a group into opposing teams that argue against the early answers—typically, more traditional conclusions that are more likely to come from a conventional pattern. Why is this solution better? Why not that one? We’ve found that better results come from embracing uncertainty.
Good problem solvers thrive in these sessions. Because they know that by remaining open to new ideas and possibilities, better answers usually emerge.
2. Analytical Thinking
Analytical thinking is the ability to break down complex issues into manageable components and identify patterns in data. It is essential for turning curiosity into actionable insights.
There is a reason that all consulting firms focus on analytical thinking in their recruiting process . Analytical mindsets allow problem solvers to navigate through complexity and arrive at data-driven solutions as efficiently as possible.
Whether you’re evaluating market entry opportunities, diagnosing falling sales, optimizing operations, or developing a new product strategy, you’ll need to:
- Break down complex problems into manageable components
- Identify patterns and relationships in seemingly unrelated data
- Question the quality and completeness of data
- Draw insights from both quantitative and qualitative information
- Balance detail with big-picture thinking
The best analytical thinkers don’t just crunch numbers – they know how to combine different types of analyses to build compelling arguments. On any given day, you might find yourself analyzing customer segments, building financial models, evaluating operational metrics, or synthesizing market research. The key is knowing which analytical tools to use when, and how to translate data into actionable insights.
3. Creativity and Lateral Thinking
While analytical skills help understand problems, creativity is what unlocks breakthrough solutions.
Blending insight and creativity often leads to breakthrough solutions that may not be apparent through conventional thinking alone. The best problem solvers can generate innovative solutions by thinking outside the box and connecting seemingly unrelated ideas.
Consider Airbnb’s creative solution to their early growth challenges. When they noticed their listings weren’t getting much traction, they could have followed the conventional path of increasing advertising spend. Instead, they identified that poor listing photos were hurting conversion rates. Their creative solution? They borrowed cameras and went door-to-door in New York, taking professional photos of listings themselves. This seemingly simple idea not only doubled their revenue in their target market but led to the development of a professional photography program that became a key differentiator for their platform.
Creative problem solvers consistently:
- Generate multiple potential solutions rather than fixating on one
- Draw inspiration from different industries and contexts
- Challenge conventional wisdom and “the way things have always been done”
- Combine existing ideas in novel ways
- Use analogies and metaphors to reframe problems
Creativity alone isn’t enough – the best problem solvers know how to persist when their initial creative solutions don’t work out.
4. Resilience and Adaptability
Problem-solving is rarely a linear process. It requires resilience in the face of setbacks and the flexibility to adjust course based on new information.
Consider how Netflix has demonstrated resilience and adaptability throughout its history. When faced with the rise of streaming technology that threatened their DVD-by-mail business, they didn’t just adapt their delivery method – they completely transformed their business model. They pivoted to streaming, then evolved again to become a content producer. Each transition required both resilience to weather significant challenges and the adaptability to embrace new ways of creating value.
Resilient problem solvers demonstrate these key attributes:
- View setbacks as learning opportunities rather than failures
- Remain calm and focused when faced with unexpected challenges
- Adjust their approach based on new information
- Maintain perspective during difficult situations
- Stay committed to finding solutions even when initial attempts fail
5. Collaborative Mindset
Complex problems rarely have simple solutions, and they’re seldom solved by individuals working alone. The best problem solvers recognize the value of diverse perspectives and know how to leverage collective expertise.
Consider any major business transformation – whether it’s developing a new product, entering a new market, or restructuring an organization. Success depends on bringing together different viewpoints and expertise. Engineers need to work with designers and finance teams with operations, and everyone needs to understand the customer perspective.
Strong collaborators consistently:
- Actively seek diverse perspectives
- Listen effectively and build on others’ ideas
- Share information and insights openly
- Navigate disagreements constructively
- Build alignment around solutions
- Give credit to others’ contributions
Importantly, effective collaboration isn’t just about agreement – it requires constructive disagreement. At McKinsey, they call this an “obligation to dissent.” But while leaders often say they are open to disagreement, their reactions tell a different story. As several McKinsey consultants write , “…their reactions often change when they actually get some. They may feel defensive. They may question their own judgment. They may resent having to take time to revisit the decision-making process.”
But disagreement or dissent is not a silver bullet. Many people struggle to give high-quality dissent. Good problem solvers know how to deal with this. At Amazon, for example, they have a principle called “disagree and commit” which means you can actually disagree but if the team decides its the right direction you move on and look to support the effort.
6. Systems Thinking
The ability to see the bigger picture – understanding how different elements interconnect and influence each other – is crucial for effective problem-solving. Systems thinkers recognize that most significant problems don’t exist in isolation.
Take climate change as an example of complex systems at work. When Tesla entered the automotive market, they understood that selling electric vehicles alone wouldn’t drive adoption. They had to think systematically about the entire transportation ecosystem: charging infrastructure, battery technology, consumer perceptions, and even energy generation. Their success came from addressing the system as a whole, not just one component.
Effective systems thinkers consistently:
- Consider second and third-order effects of potential solutions
- Identify connections between seemingly unrelated factors
- Think about long-term implications, not just quick fixes
- Recognize patterns and feedback loops
- Balance competing priorities across different parts of a system
Systems-based perspectives help ensure that solutions are sustainable and don’t create new problems while solving existing ones.
7. Bias for Action
While thorough analysis and systems thinking are crucial, effective problem solvers know when to move from analysis to action. And sometimes that means making decisions with imperfect information.
Amazon exemplifies this trait through their “Day 1” philosophy. Jeff Bezos has consistently emphasized the importance of making high-quality decisions quickly, even with incomplete information. Their ability to rapidly test new ideas – from Prime delivery to AWS – demonstrates how a bias for action, combined with careful analysis, can lead to breakthrough innovations.
Action-oriented problem solvers:
- Balance analysis with the need to move forward
- Break large solutions into testable components
- Learn and adjust based on real-world feedback
- Take calculated risks when appropriate
- Maintain momentum while remaining thoughtful
Bonus: The World is Always Changing, We Need Imagination
In her book about Marvin Bower , the spiritual godfather of McKinsey, Elizabeth Haas Edersheim shared a powerful quote about Bower’s perspective on problem-solving:
Einstein said that imagination was more important than knowledge. Today’s problems cannot be solved by thinking the way we thought when we created them. Coming from Einstein that’s quite a statement. Imagination is an important feature of the consultant. If he can’t imagine, there’s no use analyzing. And I’m afraid that we spend too much time analyzing and not enough on imagination. We can’t really shape things without imagination.
Do you have a toolkit for business problem solving? I created Think Like a Strategy Consultant as an online course to make the tools of strategy consultants accessible to driven professionals, executives, and consultants. This course teaches you how to synthesize information into compelling insights, structure your information in ways that help you solve problems, and develop presentations that resonate at the C-Level. Click here to learn more or if you are interested in getting started now, enroll in the self-paced version ($497) or hands-on coaching version ($997). Both versions include lifetime access and all future updates.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Get the Free Mini-Course
Learn to solve complex problems, write compellingly, and upgrade your thinking with our free mini-course.
Work With Us
Join 1,000+ professionals and students learning consulting skills and accelerating their careers
30% Off Everything
10 Characteristics of Good Problem Solvers
Professional psychologist, motivational writer
Good problem solvers are good thinkers. They have less drama and problems to begin with and don't get overly emotional when faced with a problem. They usually see problems as challenges and life experiences and try to stand above them, objectively.
Good problem solvers use a combination of intuition and logic to come up with their solutions. Intuition has more to do with the emotional and instinctive side of us and logic is more related to our cognition and thinking. Good problem solvers use both of these forces to get as much information as they can to come up with the best possible solution. In addition, they are reasonably open minded but logically skeptical.
Some of the general characteristics of good problem solvers are:
1. They don't need to be right all the time: They focus on finding the right solution rather than wanting to prove they are right at all costs.
2. They go beyond their own conditioning: They go beyond a fixated mind set and open up to new ways of thinking and can explore options.
3. They look for opportunity within the problem: They see problems as challenges and try to learn from them.
4. They know the difference between complex and simple thinking: They know when to do a systematic and complex thinking and when to go through short cuts and find an easy solution.
5. They have clear definition of what the problem is: They can specifically identity the problem.
6. They use the power of words to connect with people: They are socially well developed and find ways to connect with people and try to find happy-middle solutions.
7. They don't create problems for others: They understand that to have their problem solved they can't create problems for others. Good problems solvers who create fair solutions make a conscious effort not to harm others for a self-interest intention. They know such acts will have long term consequences even if the problem is temporarily solved.
8. They do prevention more than intervention: Good problem solvers have a number of skills to prevent problems from happening in the first place. They usually face less drama, conflict, and stressful situations since they have clear boundaries, don't let their rights violated and do not violate other people's rights. They are more of a positive thinker so naturally they are surrounded with more positivity and have more energy to be productive.
9. They explore their options: They see more than one solution to a problem and find new and productive ways to deal with new problems as they arise. They also have a backup plan if the first solution does not work and can ask for support and advise when needed.
We Need Your Support
Other news outlets have retreated behind paywalls. At HuffPost, we believe journalism should be free for everyone.
Would you help us provide essential information to our readers during this critical time? We can't do it without you.
Can't afford to contribute? Support HuffPost by creating a free account and log in while you read.
You've supported HuffPost before, and we'll be honest — we could use your help again . We view our mission to provide free, fair news as critically important in this crucial moment, and we can't do it without you.
Whether you give once or many more times, we appreciate your contribution to keeping our journalism free for all.
Whether you give just one more time or sign up again to contribute regularly, we appreciate you playing a part in keeping our journalism free for all.
Already contributed? Log in to hide these messages.
10. They have reasonable expectations: Good problem solvers have reasonable expectations as to what the solution would be. They understand that there are many elements effecting a situation and that idealistic ways of thinking and going about solving a problem will be counterproductive.
At the end, good problem solvers do not have too many irrational fears when dealing with problems. They can visualize the worst case scenario, work their way out of it and let go of the fear attached to it. Fear can make your logic and intuition shady and your decisions unproductive.
From Our Partner
More in wellness, more in life.

A Beginner’s Guide for Becoming a Better Problem Solver
How you think about a problem is more important than the problem itself. – Norman Vincent Peale
Three Methods of Thinking
Problem-solving, creative and critical thinking go hand-in-hand helping us to see the world from a number of different vantage points. Each of these ways of thinking strengthens our capacity to think flexibly and intelligently when faced with the unending problems that life throws our way.
This post will specifically focus on the process of problem-solving and how you can use it to break through life’s most difficult challenges. We will specifically explore the attitude, beliefs, habits, and qualities that are indispensable for effective problem-solving. We will also outline a primary problem-solving method that will help you to break down any obstacles that stand in your way. And to finish off we will look at some ongoing problem-solving tactics you can use to keep your mind focused and proactive when dealing with life’s daily challenges.
This article post is part of the Effective Thinking series of IQ Matrix maps that are designed to help you successfully deal with the problems and challenges confronting your reality. Topics within this series include:
• Part 1: Strategic Questions • Part 2: Creative Thinking • Part 3: Problem Solving • Part 4: Critical Thinking • Part 5: Six Thinking Hats
Indispensable Problem Solver Attributes
To become a great problem solver requires a little more than a set of effective problem-solving strategies. In fact, your ability to solve problem starts in your head at a psychological level.
If you do not take the time to fully condition your mind and prepare it for the act of problem-solving, then you will struggle to consistently adopt the daily behaviors and rituals that are required for effective problem-solving.
Within this section, we will identify the indispensable attributes required for problem-solving that you must learn to cultivate on a daily basis. If you fail to incorporate these qualities into your psyche, then you will struggle to apply the relevant problem-solving techniques and strategies discussed in this post.
A Problem Solver’s Attitude
A problem solver’s attitude determines how they consistently tackle problems on a daily basis. This attitude is evident in their thoughts, behaviors, and actions, and it is this attitude that helps build their resolve and shapes their character.
Let’s delve into the mind of an effective problem solver and identify some of the attitudes that are absolutely indispensable to their ongoing success:
“I will make sure to do things carefully.”
An effective problem solver always strives to work through their problems in a patient, meticulous and careful way. They fully understand that the care they give to a problem at the beginning will help them to realize better results in the future.
“This problem can be solved.”
An effective problem solver intuitively understands that any problem can and will be solved, given enough time, patience and meticulous careful attention.
“I must persist until a solution is reached.”
An effective problem solver knows that not all problems will be solved within the time frame they may have expected. However, they also understand that if they are persistent and resolute, that eventually a solution will be found.
“If I don’t solve it now, I will next time.”
An effective problem solver realizes that whatever cannot be solved now, will eventually be solved another time.
They fully understand that due to their current level of skill, knowledge, or simply due to circumstances out of their control, that a solution simply cannot be reached.
An effective problem solver will bide their time to acquire new information and knowledge, to develop and enhance their skill levels, and to gain insights from a variety of perspectives. They completely understand that eventually, the right solution will indeed come their way as long as they never give up.
“I am going to enjoy this process.”
An effective problem solver knows that unless they adopt a playful, curious and inquisitive attitude, that they will struggle to find appropriate solutions. They therefore always strive to find new and unique ways to enjoy the process of working their way through a problem.

A Problem Solver’s Beliefs
An effective problem solver has a set of indispensable beliefs and convictions that direct and propels their thoughts, actions, and daily behaviors. These beliefs are so deeply ingrained in their psyche that it would take the force and willpower of the entire world to shake these feeling of certainty.
Beliefs are opinions that we have about things, ourselves, others and the world around us that are injected with an undeniable sense of certainty.
Let’s now take a look at a handful of beliefs that are critical for effective problem solving:
“There is no failure, only feedback.”
An effective problem solver believes that outcomes bring with them no failure, but rather only feedback. This feedback must be used as a source of knowledge, insight, and inspiration to help enhance the decision-making process.
“There is a way to make this work.”
An effective problem solver believes that there is always a way to make things work. They may not see the solution at this very moment, however with a little persistence they wholeheartedly believe that they will eventually reach a satisfactory outcome.
“Choice is better than no choice.”
An effective problem solver believes that it is better to have more choices than to be limited by the choices that one has. As such, they always strive to expand the possibilities, to expand the opportunities and avenues for answers — allowing for as many choices as possible to further their understanding of the problem.
“Success can be modeled.”
An effective problem solver believes that successful problem solving can be modeled. As such, they consistently seek out other people who have successfully overcome similar problems and they attempt to model their thinking, decisions, and actions in a meticulous way. This helps them to overcome the obstacles and challenges in their own life.
“Curiosity expands opportunities and possibilities.”
An effective problem solver believes that one must be curious at all times if one desires to spot the opportunities and possibilities that lie along one’s path.
Curiosity is an endearing characteristic that helps expand creativity, intelligence and one’s ability to think under pressure.
A Problem Solver’s Habits
An effective problem solver has a set of daily habits and rituals. These habits assist them to think more effectively and proactively about the problems and challenges they are confronted with.
Let’s take a look at three habitual thinking patterns that are indispensable for effective problem solving:
Deep Probing
An effective problem solver cultivates the habit of deep-probing. This involves the process of meticulous thinking, which takes into account all angles and perspectives about a problem — making sure that nothing is left to chance.
They fully realize that through a process of simple deduction that they will be better able to work their way through the problem in a more effective and efficient way.
The habit of deep probing can be compared to the simple act of peeling layers off an onion. Each layer that the problem solver peels allows them to dig deeper into the heart of the problem, and thusly closer to the inevitable solution.
Associating with the Past
An effective problem solver realizes that any new piece of information can effectively be associated with past memories, experiences, and learnings, to further their problem-solving ability.
Recognizing Patterns
An effective problem solver effortlessly recognizes patterns within every problem or circumstance.
Everything within our Universe is built upon patterns and rhythmic dances that create the events and circumstances of our lives. In fact, these same patterns cause and create our life’s problems and circumstances.
By identifying and learning to understand these patterns, effective problem solvers are able to decipher clues that will lead them to reliable solutions and answers.
When attempting to identify patterns look for similarities, differences, rhythms, errors, future scenarios and trends that the problem is bringing to light.
A Problem Solver’s Characteristics
An effective problem solver can easily be distinguished from others by the key personality characteristics that naturally help them to break down boundaries and attain the heights of logical and constructive thought.
The characteristics presented below are the primary traits we must cultivate within our own personalities if we seek to successfully overcome the problems and challenges that are confronting our daily lives.
An effective problem solver understands that many problems will never fully be solved if a risk isn’t involved.
A risk may mean overcoming a fear, thinking outside-the-box, or simply making the tough decisions that at the moment may seem uncertain and unclear.
Problem solvers are risk takers who believe that intelligent risk-taking will enable them to reach effective solutions to the challenges confronting their daily reality.
An effective problem solver is persistent in thought, decision, and action. They clearly understand that there are a means and way around any problem, fully believing that as long as they persist and persevere that they will always find an angle that will help them obtain a desired outcome.
Enthusiastic
An effective problem solver displays passion and enthusiasm at all times. These two qualities provide them with the energy and motivation they need to help them overcome the toughest of challenges.
An effective problem solver is meticulous with every step they take moving towards their desired outcomes.
This thoroughness allows them to work through their problems step-by-step — taking into account all angles and perspectives.
Adaptable and Flexible
An effective problem solver is constantly vigilant and aware of constantly changing circumstances. They clearly understand that problems can shift and change at a moments notice, and as a result, they must adapt their approach accordingly.
It is only through flexibility-of-thought that they are able to work through their problems in an efficient and effective way.
Open Minded
An effective problem solver is always humbly open minded to other people’s opinions and perspectives. They clearly understand that they do have all the answers and that others may indeed have alternative views that will help them to see things from new and unique perspectives. This likewise helps open the doors to new understandings that would not otherwise have been available to them.
Lighthearted
An effective problem solver approaches their daily challenges in a light-hearted and playful manner. They fully realize the overwhelming power that problems can have on their psyche. To counteract this, they approach each problem in a playful and light-hearted way — helping them to find solutions and answers where others only see overwhelm and distress.
An effective problem solver is proactive. They understand, they just have to keep moving forward and continue to take proactive action no matter how uncertain events or circumstances may seem at any specific moment in time.
The opposite of being proactive is being reactive . When we are reactive we become easily overwhelmed by the events and circumstances of our lives because we fail to take control of our emotional responses.
An effective problem solver is a curious thinker .
Curiosity naturally leads to a plethora of questions that need to be answered. Once answered, they can evolve into a myriad of solutions that will help you to attain your desired goals and objectives far more quickly.
Non-Conforming
An effective problem solver does not conform to the standards and norms of mainstream society. Instead, they think out of the box and break the rules in order to attain their desired outcomes.
The Primary Problem Solving Method
There are many problem-solving techniques and strategies that we could present here. However, there is essentially only one primary problem-solving method that will help you to structure and break down a problem step-by-step from the beginning to the very end. To view an advanced version of this problem-solving method, please check out the Visual Thinking Path .
Within this section, we will work our way through a six-step primary problem-solving method.
By consciously learning to apply each of these steps/phases into your problem-solving regime, you will proactively take control of your daily decision-making process.
The Preparation Phase
This phase helps you to identify, define and decipher an overall picture and understanding of the problem that is currently confronting your reality.
As you progress through this phase, it is important to gain as much clarity about your problem as possible from absolutely every angle and perspective. Any assumptions or misunderstandings here could very well sabotage your ability to reach an effective solution. Therefore be very careful to clarify everything clearly and meticulously.
Identify the Problem
Your first step is to always clearly identify the problem that is confronting your reality. Many people fail to do this correctly, and as a result, they discover that what they thought was a problem is, in fact, a mistaken assumption that now requires a dramatically different approach.
Define Problem in Writing
Once you have identified the problem, your next step is to clearly define it on paper. It is only through the process of writing our thoughts down on paper that we attain the clarity we need to effectively deal with the challenges that stand in our way.
Question the Problem
To further clarify and expand your understanding about this problem, it is recommended that you ask yourself a set of open-ended questions that will help you to define the problem from a variety of angles and perspectives.
The questions you should be asking yourself must be focused on the What? When? Where? Why? Who? and How? of the problem under question.
Undertaking this process with meticulous attention will open new insights and understandings that will help you as you move through this problem-solving strategy.
It is important to understand that you are not seeking solutions or answers here but rather gathering insights about the problem from as many different angles and perspectives you can identify.
Here are a few questions to get you started:
What is the actual problem that is impeding my progress? When did this problem occur? Where did this problem first appear? Why is this problem impeding my progress? Who is involved in this problem? How is this problem influencing other areas of my life?
Determine Possible Causes
Once you have clarified the problem, your next step is to identify the possible causes that may have triggered these outcomes.
Again during this stage, you must continue asking What? When? Where? Why? Who? and How? questions.
What could be the potential causes of this problem? When did these causes originate? Where did these causes originate? Why did these causes originate? Who could have triggered this problem? How does all this help me with identifying the causes of this problem?
Reframe the Problem
Once you have identified and defined the causes of the problem, it is important to open your mind to alternative perspectives.
At this stage, you are not yet seeking answers or solutions but rather opening your mind to different perspectives that will help you to understand the problem from a variety of angles.
Here are a few reframing questions to get you started:
How might other people perceive this problem? How would I perceive this problem if I was to look back on it 12 months from this day? What if I was completely detached from this problem and its outcomes. How would I now perceive it? What has to be true for this to be a problem?
Define Desired Outcomes
Finally, you must gain clarity by defining the desired outcomes you would like to attain from successfully working your way through this problem.
These outcomes will help direct your mind towards solutions as you progressively move through the remaining phases.
The strategy you use to achieve this outcome isn’t important at this stage. The only thing that matters is that you clarify on paper the end objective or goal you would like to achieve.

The Generation Phase
This phase allows for free association and exploration of wild and crazy ideas that must not be judged, criticized or condemned for any reason.
The greater flexibility of thought you incorporate into this phase, the more effective the later phases will become.
It is important throughout this phase that you literally overwhelm your brain with as many solutions as possible. The greater the variety of solutions and strategies you come up with, the more insightful and effective the Incubation Phase will become.
Recall Past Learning, Experiences and Mistakes
Recalling your past life experiences will help you to gain a better perspective on your current predicament.
Many people constantly need to deal with the same ongoing problems because they simply fail to learn from their past experience and mistakes.
It is only through a process of self-reflection and understanding that we will gain the necessary insights to move through our current problems efficiently and effectively.
Keep in mind that any past experience — even if not directly related to your current problems — could potentially help you find the solutions you are after.
Explore Strategies and Solutions
Having brought your past learnings and mistakes into the present, you are now ready to brainstorm solutions and strategies that will help you to successfully overcome the challenge confronting your current reality.
While brainstorming it’s important not judge or criticize your solutions. Your thinking must flow effectively and efficiently from one idea to the next like water gently trickling off a leaf. All you are doing is generating possible and potential solutions that will help to expand your thinking and awareness about the problem you are currently experiencing.
You can lightly consider the drawbacks and obstacles that may be attached to each of your solutions, however primarily spend your time on the benefits of each strategy and how it could potentially lead you to the outcome you outlined within the Preparation Phase.
As a final thought, keep in mind that the how isn’t important here. Instead, it is the what that matters.
The Incubation Phase
This could very well be called the Resting Phase .
Your goal here is to simply allow the solutions and ideas you came up with during the Generation Phase to harvest and grow within the recesses of your mind without ridicule or judgment.
The key here is to separate your mind from the problem so completely that it simply becomes irrelevant and insignificant.
Flowers cannot sprout and grow if weeds are dominating your thought process.
Indulge in Brainstorming Naps
Brainstorming naps are short 15 to 30-minute breaks you take throughout your day where you close your eyes and open yourself up to potential solutions.
Before you take these brainstorming naps, it is important that you partake in a good 30 to 45 minutes of intense thought and self-reflection about possible solutions to your problem.
As you lie back in a comfortable position and close your eyes, ask yourself the following questions:
How can I solve this problem in the most effective and efficient way? What must I do to attain my desired outcome?
Once your questions have been asked, simply settle down and observe your thoughts as though you are watching clouds drifting across the sky. Within these visual images, you may very well find the answers you are after.
Sleep on Problem
Simply put your problem to rest and go to sleep.
As you are nodding off, pose yourself insightful questions that will stimulate the thought process and encourage your brain to search for answers.
When you awaken the next morning, immediately reflect on your thoughts and dreams — they may hold the answers you have been searching for.
Change Your Environment to Improve Incubation
Stepping out into nature or simply into an inspiring and energetic environment will separate you from your problem and help you to think more effectively about potential solutions. However, since we are in the Incubation Phase, it is important to simply let go of the process of intense meticulous thinking. Instead, enjoy your surroundings and the answers you are after will eventually reveal themselves to you. And just in case, have a piece of paper and pen ready to write down inspiring solutions as they come your way.
Evolution Phase
Now that your ideas have had a chance to incubate within the recesses of your mind, you are now ready to take your thinking to the next level — becoming your worst and best critic.
Your goal throughout the Evolution Phase is to break down and clarify all your potential solutions progressively and meticulously allowing for deep insights and all round perspectives.
The more thorough you are while undertaking this process, the fewer problems you will face throughout the Implementation Phase that follows.
Prioritize and Evaluate Solutions
Collate all the solutions you brought forward throughout the Generation and Incubation Phases and evaluate them accordingly.
Evaluate the viability of these solutions by looking at them from a variety of different angles and perspectives. Also, take into account the time and energy you have available that will allow you to bring these solutions into the real world.
Once completed, prioritize your solutions to help you better decipher which ones could best assist you in overcoming your problems most effectively.
Speculate Potential Future Outcomes and Negative Consequences
Future-pace each solution and see it clearly helping you overcome your problem.
Identify the possible drawbacks, weaknesses, strengths and potential opportunities that may result.
The greater clarity you gain here, the easier it will be to settle on an ideal and clear-cut solution to your problem.
Settle on Solutions
Having accumulated a thorough and comprehensive list of solutions throughout the Generation and Incubation Phases, and having outlined the possible consequences of each of these outcomes, you are now ready to select one primary desirable solution that will help you overcome your problem in the most effective and efficient manner.
Take everything into consideration and decide which solution will best help you to achieve your desired outcome.
Implementation Phase
Your goal throughout the Implementation Phase is to progressively and meticulously work through the solution to your problem in a step-by-step manner using a process of logical decision making and action. You are basically bringing everything you have thought about and outlined on paper into reality.
Many people will struggle to get through this stage successfully because of the dreaded procrastination bug. Be sure that you don’t fall into this dirty trap. 🙁
Clarify Your Personal Vision of Outcome on Paper
Having settled on your ideal solution to this problem, take some time now to clarify this vision on paper.
Clarify the Personal Resources at Your Disposal
Identify the support, skills, knowledge, and tools you currently have at your disposal that will help you to successfully overcome this problem. These are your resources . If you find that you are lacking in some of these areas, then you may need to regroup and update your skills or knowledge to help you deal with this problem more effectively. Or you may simply need to obtain the help and support of a new group of people who can guide you through this problem in a more proactive and efficient way.
Create Three Alternative Plans of Action
Now that you have the necessary skills, knowledge, support, and tools you need to overcome this problem successfully, your next step is to draw up your plan of action.
As previously discussed, it is important to be flexible with your actions and to take into consideration all the drawbacks and potential pitfalls of these steps.
In order to minimize the possibilities of getting stuck, it is critical that you outline three alternative plans of action. If Plan A works out, then that’s great. However, if it fails miserably, then you still have Plan B and C at your disposal.
Set Clear Defined Deadlines for these Actions
Clear and defined deadlines will motivate you into action while providing you with a time sensitive objective to work towards.
Take Action Committing Yourself to the Result

The Learning Phase
This is an important phase that is very often overlooked. It will help you to clarify your thoughts, including the methods and strategies you used throughout the problem-solving process.
The learnings you gather from self-reflection will provide you with indispensable insights that will put your problem-solving methods in perspectives — improving the effectiveness and efficiency of your approach as you tackle similar challenges in the future.
Monitor Your Outcomes
As you progress along your journey towards implementing your solution, pay attention to the outcomes that result from every thought you make and every decision and action you take. This awareness will help you to better understand your personal traits and tendencies, which will likewise assist you with improving your problem-solving methods in the future.
Reflect on the Problem Solving Process
Once you have successfully overcome your problem, spend some time thinking and reflecting on the problem-solving process.
Here are some questions to get you started:
What did I do well, and what am I proud of about the way I conducted myself throughout this process? What problem solving traits did I cultivate and bring to the forefront throughout this process? What problem solving traits did I neglect? What mistakes did I make as I worked my way through this problem? What have I learned from these experiences? What could I have done better… more effectively and efficiently? How can I use these learnings and experiences to further my problem solving abilities in the future?
For a more advanced look at this problem-solving method, please check out the Visual Thinking Path .

Ongoing Problem Solving Tactics
Becoming an effective problem solver requires an ongoing process of conscious thought and action that opens new doors of opportunity to the solutions and answers you are after.
The solutions and answers you are after will be difficult to attain if you only apply the primary problem-solving method sporadically. Instead, you must consciously instill into your psyche habitual patterns of behavior that are consistent and aligned with a problem solver’s mentality.
Becoming an effective problem solver is not a part-time career, it is rather a full-time process that eventually becomes second nature.
Within this section, we will explore a number of effective ongoing problem-solving tactics you can use consistently throughout your day to keep your mind primed and ready for any challenge that may come your way.
Mindset Oriented Tactics
The following is a list of mindset oriented problem-solving tactics you can use on a consistent basis to keep your mind primed and ready for the challenges that come your way:
Visualize Your Desired Outcomes
It is said that we can only achieve our goals and objectives if we are able to clearly visualize them first in our minds-eye.
That which we are unable to visualize, we will likewise not be able to comprehend and realize within our physical reality.
When we were babies our motor skills developed over time through a process of observation and visualization. Only once we were able to successfully visualize in our minds-eye the process of picking-up physical objects, were we able to bring that same ability successfully into our physical reality. Given this, do you see how important it is to spend time visualizing your outcomes and the possible scenarios and strategies you will use to overcome your problems effectively?
Ask Questions Searching for Solutions
Questions are the keys that will unlock doors of opportunity and answers to even the most pressing of problems.
If you ask the ideal solution focused question , you will receive the right answers to help move you forward through your challenges in the most effective and efficient way.
Always See Opportunities for New Learnings
Problem-solving is essentially built upon the concept of opportunity-spotting.
Effective problem solvers don’t actually see problems as others do. Instead, they see only opportunities for new learnings, insights, and understandings that will help them to keep moving forward towards the attainment of their goals and objectives.
You must train your mind to look at every event or circumstance as an opportunity for you to become and grow to your full potential.
The challenges you face in life are there for a reason to help you attain your highest potential as a human being. See these problems as opportunities and you will move through them more effectively and swiftly than ever before.
Think Critically
By thinking critically about every problem and circumstance in your life, you will break down the walls of the assumption that tend to trap the mind within unhelpful thinking habits.
Think Creatively
Whereas problem-solving is very structured and logical, creativity , on the other hand, is unstructured and imaginative.
These two forms of effective thinking are in many ways tied together and will work in conjunction to help you break through the obstacles standing in your way.
Think is Solitude
In order to think more effectively about the problems in our lives, we must first clear the clutter from our heads.
This process begins when we remove ourselves from the physical distractions that could impede our thinking ability.
Within solitude, you will find peace, harmony and a sense of connection with your body, spirit, and mind. This will help release built-up tension while opening up the channels to intuitive, creative and logical thought — helping you to overcome your problems with far greater ease.
Let Go of Fears
Your fears will rob you of the ability to think effectively and problematically.
Effective problem solvers don’t allow their fears to control their thoughts, decisions, and actions. Instead, they usurp their fears and focus on the pleasures that will bring them the outcomes they desire to experience within their lives.
Let Go of Judgments and Criticisms
Effective problem solving requires us to let go of ill-fated judgments and criticisms.
The ideal solution can only be reached if we take time to harvest and cultivate it within the recesses of our minds for an extended period of time. This process thusly requires us to let go of the Devil’s Advocate role and milk our ideas for all their worth.
It is only towards the end of the problem-solving process that the Devil’s Advocate card should be played.
Let Go of Biases and Assumptions
For the same reason as mentioned above, we must let go of all biases and assumptions that may hold us back from successfully finding a solution to the problem at hand. This is often easier said than done because in many instances our assumptions and biases naturally color our understanding of reality.
If we mistakenly assume something, then we may redirect our thoughts, decisions, and actions down paths that we did not want to tread.
The solution is to ask insightful and carefully structured questions that will help us to break down the biases and assumptions we are holding onto at any one moment in time.
Allow for Fantasizing
Fantasizing can be an effective form of creative problem-solving.
Take time each and every day to remove yourself from physical reality and fantasize about creating a perfect life where everything you imagine becomes your reality.
This process will help to loosen your mind, and may very well open the doors to a set of insightful ideas that will assist you in overcoming your problems more effectively.
Allow for Playfulness
Playfulness is another endearing quality that you must cultivate every single day.
Perceive each and every problem as an intriguing game that you must win at all costs. Play this game, have fun, and enjoy the experience to its fullest.
Allow for Idea Incubation
No idea will fully evolve and grow to its fullest potential if you fail to incubate it within the recesses of your mind for a period of time.
Sometimes brilliant ideas can come to us quite effortlessly. As a result, our excitement takes over and we immediately take action in an attempt to bring the idea into physical reality. However, later we realize that the idea was incomplete or simply didn’t work as expected.
In instances such as these, it is easy to get disheartened. Our idea was great, but for some reason, it just didn’t evolve because little did we realize at the time, that this iceberg-idea was only the tip of a much larger, complete and comprehensive thought-pattern that was never brought to the surface .
In such instances, we must learn from this experience and take time to incubate our ideas as we move forward into the future.
Explore Funny and Foolish Ideas
No idea should ever be ruled out. Every idea is valid and useful no matter how foolish, crazy or funny it might seem on the surface. In fact, some of the most foolish ideas have indeed earned people millions and others billions of dollars. For this very reason, it’s critical that you never discount any idea until you have taken it through the entire problem-solving cycle discussed within this post.

Explore Alternative Perspectives Using Lenses
Lenses are a form of creative problem solving that will help you to expand your understanding and awareness of your circumstances from a variety of unique and interesting perspectives.
Each lens will help you to see the problem from a new point-of-view — assisting you with identifying creative solutions you may not have thought of before.
The following list presents you with just a few lenses you can use to help trigger creative solutions to your problems:
Childhood Lens
Look at your problem from the perspective of an inquisitive and curious child.
See your problem as an innocent circumstance that isn’t tinged with pre-conceived biases or assumptions .
Ask yourself seemingly foolish, funny and creative questions that open new ways of thinking about mundane circumstances and problems.
How would a child approach this problem? What kinds of questions would they ask?
Athlete’s Lens
Look at your problem from the perspective of a motivated and determined athlete.
See your problem as a mountain that you will tame and conquer .
Ask yourself questions that will help you to persist and persevere — effectively expanding the possibilities of your solutions.
How would an athlete approach this problem? What kinds of questions would they ask?
Artist’s Lens
Look at your problem from the perspective of a creative and imaginative thinker.
See your problem as a work of art that progressively takes shape .
Ask yourself questions built around metaphors , stories, visual concepts and ideas that will provide you with a unique perspective on your problem.
How would an artist approach this problem? What kinds of questions would they ask?
Scientist or Inventor’s Lens
Look at your problem from the perspective of an analytical scientist or crazy inventor.
See your problem as an experiment that you must test and perfect .
Ask yourself questions that are built upon logical thought and experimentation.
How would a scientist or crazy inventor approach this problem? What kinds of questions would they ask?
Politician’s Lens
Look at your problem from the perspective of a confident, confronting and ambitious politician.
See your problem as a political campaign that you must win at all costs .
Ask yourself questions that help you poke holes in your problem, thus bringing its weaknesses to the forefront — much like what politicians do to their opponents during television debates.
How would a politician approach this problem? What kinds of questions would they ask?
Action Oriented Tactics
The following is a list of action-oriented problem-solving tactics you can use on a consistent basis to keep your mind primed and ready for the challenges that come your way:
Persistently Write Out Questions
Questions are the keys that will bring forth the answers and solutions to your problems.
Sit down for 30 minutes per day with two sheets of paper and a pen. Now, write out your problem in a question format on top of both sheets. Next, take your 1st sheet of paper and spend 15 minutes writing out as many questions as you can think of that will help expand your understanding and awareness of this problem. Finally, when your 15 minutes is up, take out the 2nd sheet of paper and write out as many solutions as you can think of that will answer the questions you posed on the 1st sheet of paper.
By undertaking this process consistently each and every day, you will develop a problem-solving knack that will help you breakthrough any obstacle standing in your way.
Read Broadly
Sometimes the answers to our problems can come from the most unexpected sources.
Keep your problem in mind as you read a book, magazine or newspaper and observe your brain in overdrive searching for new pieces of information that it can associate with old memories and experiences.
Within every piece of information you read, the pictures you see, and the sounds you listen to, lies the solution to your problem . This awareness will get you halfway to your answer. However, you must be fully committed to lifelong learning.
Update Your Skills and Knowledge
Our problems can only overwhelm us when we feel incapable of dealing with them in an effective and timely manner. The solution for this is to update specific skills and knowledge (pertaining to the problem) that will allow you to better handle and manage these types of challenges in the future.
Use Positive Language
A pessimist will naturally have a very difficult time finding solutions to even the simplest of problems. On the other hand, an optimistic realist who uses positive language will bring forth a great array of solutions that will further expand their thinking and creative potential.
Use Concept Maps and Mind Maps
Mind maps are extraordinary problem-solving tools that will allow you to easily brainstorm effective and creative ideas.
Mind Maps mimic our brain’s natural capacity to think, manage and organize large chunks of information in an efficient way. They will help you to put your problem into perspective while giving birth to new connections and associations that may not have been evident before.
Use Diagrams
Because our brains think in pictures and not words, it just makes sense that diagrams would help us conceptualize our ideas in a much more creative way.
You may be surprised with the insights you will gather from simply drawing up your problem and solutions in a diagrammatic picture format.
Create and Use a Problem Solving System
Finally, it is important to understand that our problems will never evaporate completely. Such is life, that it constantly and continuously tests our resolve in order to help us grow and achieve our most desired goals and objectives.
Those people who don’t seem to experience any problems in life have simply mastered the illusion of hiding their problems from others. They have learned methods that help them manage their problems using a potentially unconscious systematization process.
Every time you successfully work through your problems, it is important to draw up a systematic management plan that will help you to deal with these types of problems in a more effective and efficient way in the future.
Visit Brian Tracy’s website to learn more about his personal development and business courses, books, and programs.
Concluding Thoughts
It has been said that…
It’s not what happens to us that determines our fate, it’s rather what we do with what happens that shapes our destiny.
The problems and challenges that confront our everyday reality are drawn to us for a reason and purpose — teaching us life lessons that help us grow and attain new levels of insight, awareness and understanding.
Without problems we would never grow, we would never mature, we would never fully develop, and we would never experience the joy and satisfaction of attaining our most inspiring goals and objectives .
Yes, problems are indeed blessings in disguise for some, while for others they become steppingstones for misery, stress, mayhem, and dissatisfaction. These people just don’t get it…
Time to Assimilate these Concepts

GET THIS MAP
Did you gain value from this article? Is it important that you know and understand this topic? Would you like to optimize how you think about this topic? Would you like a method for applying these ideas to your life?
If you answered yes to any of these questions, then I’m confident you will gain tremendous value from using the accompanying IQ Matrix for coaching or self-coaching purposes. This mind map provides you with a quick visual overview of the article you just read. The branches, interlinking ideas, and images model how the brain thinks and processes information. It’s kind of like implanting a thought into your brain – an upgrade of sorts that optimizes how you think about these concepts and ideas. 🙂
Recommended IQ Matrix Bundles

If you’re intrigued by the idea of using mind maps for self-improvement then I would like to invite you to become an IQ Matrix Member.
If you’re new to mind mapping or just want to check things out, then register for the Free 12 Month Membership Program . There you will gain access to over 90 mind maps, visual tools, and resources valued at over $500.
If, on the other hand, you want access to an ever-growing library of 100s of visual tools and resources, then check out our Premium Membership Packages . These packages provide you with the ultimate visual reference library for all your personal development needs.

Gain More Knowledge…
Here are some additional links and resources that will help you learn more about this topic:
- The Art of Complex Problem Solving @ iDiagram
- Einstein’s Secret to Amazing Problem Solving @ Litemind
- 16 Practical Tips for Solving Your Problems More Easily @ Positivity Blog
- 10 Timeless Lessons on Better Thinking @ Life Optimizer
- Your Guide to Get Spinning in the Idea Tornado @ Think Simple Now
- How to Find Creative Solutions to Non-Creative Problems @ Scott H Young
- Problem Solving Toolkit – 33 Tricks to Answer Tough Problems @ Scott H Young
- Solve Tough Problems by Using Lenses @ Scott H Young
- Square Watermelon Problem Solving @ Dumb Little Man
- The Best Way to Solve a Problem: Give Up @ Paid to Exist

About The Author
Adam Sicinski
Start typing and press enter to search.
- Book a Demo
Struggling to overcome challenges in your life? We all face problems, big and small, on a regular basis.
So how do you tackle them effectively? What are some key problem-solving strategies and skills that can guide you?
Effective problem-solving requires breaking issues down logically, generating solutions creatively, weighing choices critically, and adapting plans flexibly based on outcomes. Useful strategies range from leveraging past solutions that have worked to visualizing problems through diagrams. Core skills include analytical abilities, innovative thinking, and collaboration.
Want to improve your problem-solving skills? Keep reading to find out 17 effective problem-solving strategies, key skills, common obstacles to watch for, and tips on improving your overall problem-solving skills.
Key Takeaways:
- Effective problem-solving requires breaking down issues logically, generating multiple solutions creatively, weighing choices critically, and adapting plans based on outcomes.
- Useful problem-solving strategies range from leveraging past solutions to brainstorming with groups to visualizing problems through diagrams and models.
- Core skills include analytical abilities, innovative thinking, decision-making, and team collaboration to solve problems.
- Common obstacles include fear of failure, information gaps, fixed mindsets, confirmation bias, and groupthink.
- Boosting problem-solving skills involves learning from experts, actively practicing, soliciting feedback, and analyzing others’ success.
- Onethread’s project management capabilities align with effective problem-solving tenets – facilitating structured solutions, tracking progress, and capturing lessons learned.
What Is Problem-Solving?
Problem-solving is the process of understanding an issue, situation, or challenge that needs to be addressed and then systematically working through possible solutions to arrive at the best outcome.
It involves critical thinking, analysis, logic, creativity, research, planning, reflection, and patience in order to overcome obstacles and find effective answers to complex questions or problems.
The ultimate goal is to implement the chosen solution successfully.
What Are Problem-Solving Strategies?
Problem-solving strategies are like frameworks or methodologies that help us solve tricky puzzles or problems we face in the workplace, at home, or with friends.
Imagine you have a big jigsaw puzzle. One strategy might be to start with the corner pieces. Another could be looking for pieces with the same colors.
Just like in puzzles, in real life, we use different plans or steps to find solutions to problems. These strategies help us think clearly, make good choices, and find the best answers without getting too stressed or giving up.
Why Is It Important To Know Different Problem-Solving Strategies?
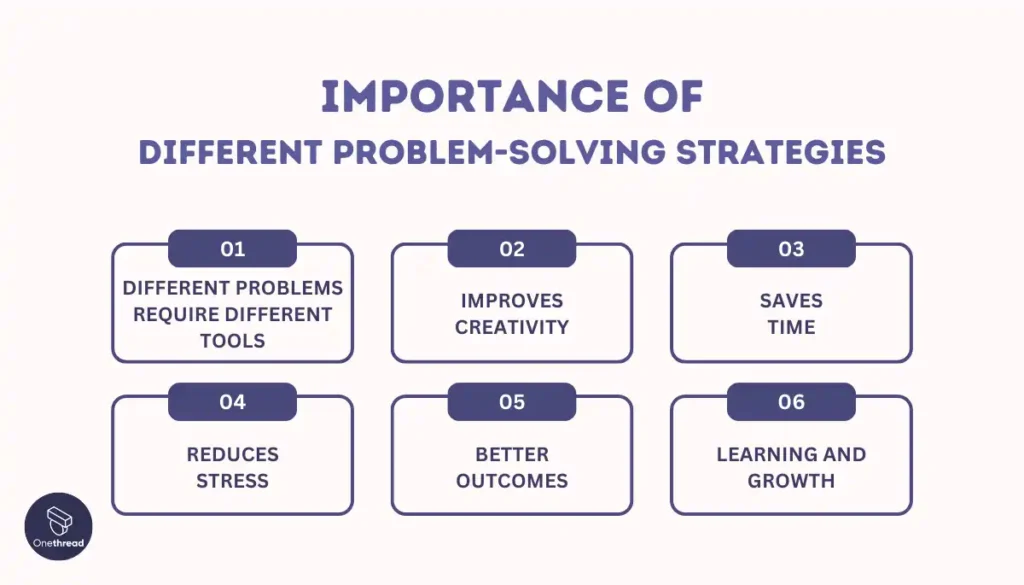
Knowing different problem-solving strategies is important because different types of problems often require different approaches to solve them effectively. Having a variety of strategies to choose from allows you to select the best method for the specific problem you are trying to solve.
This improves your ability to analyze issues thoroughly, develop solutions creatively, and tackle problems from multiple angles. Knowing multiple strategies also aids in overcoming roadblocks if your initial approach is not working.
Here are some reasons why you need to know different problem-solving strategies:
- Different Problems Require Different Tools: Just like you can’t use a hammer to fix everything, some problems need specific strategies to solve them.
- Improves Creativity: Knowing various strategies helps you think outside the box and come up with creative solutions.
- Saves Time: With the right strategy, you can solve problems faster instead of trying things that don’t work.
- Reduces Stress: When you know how to tackle a problem, it feels less scary and you feel more confident.
- Better Outcomes: Using the right strategy can lead to better solutions, making things work out better in the end.
- Learning and Growth: Each time you solve a problem, you learn something new, which makes you smarter and better at solving future problems.
Knowing different ways to solve problems helps you tackle anything that comes your way, making life a bit easier and more fun!
17 Effective Problem-Solving Strategies
Effective problem-solving strategies include breaking the problem into smaller parts, brainstorming multiple solutions, evaluating the pros and cons of each, and choosing the most viable option.
Critical thinking and creativity are essential in developing innovative solutions. Collaboration with others can also provide diverse perspectives and ideas.
By applying these strategies, you can tackle complex issues more effectively.
Now, consider a challenge you’re dealing with. Which strategy could help you find a solution? Here we will discuss key problem strategies in detail.
1. Use a Past Solution That Worked

This strategy involves looking back at previous similar problems you have faced and the solutions that were effective in solving them.
It is useful when you are facing a problem that is very similar to something you have already solved. The main benefit is that you don’t have to come up with a brand new solution – you already know the method that worked before will likely work again.
However, the limitation is that the current problem may have some unique aspects or differences that mean your old solution is not fully applicable.
The ideal process is to thoroughly analyze the new challenge, identify the key similarities and differences versus the past case, adapt the old solution as needed to align with the current context, and then pilot it carefully before full implementation.
An example is using the same negotiation tactics from purchasing your previous home when putting in an offer on a new house. Key terms would be adjusted but overall it can save significant time versus developing a brand new strategy.
2. Brainstorm Solutions

This involves gathering a group of people together to generate as many potential solutions to a problem as possible.
It is effective when you need creative ideas to solve a complex or challenging issue. By getting input from multiple people with diverse perspectives, you increase the likelihood of finding an innovative solution.
The main limitation is that brainstorming sessions can sometimes turn into unproductive gripe sessions or discussions rather than focusing on productive ideation —so they need to be properly facilitated.
The key to an effective brainstorming session is setting some basic ground rules upfront and having an experienced facilitator guide the discussion. Rules often include encouraging wild ideas, avoiding criticism of ideas during the ideation phase, and building on others’ ideas.
For instance, a struggling startup might hold a session where ideas for turnaround plans are generated and then formalized with financials and metrics.
3. Work Backward from the Solution

This technique involves envisioning that the problem has already been solved and then working step-by-step backward toward the current state.
This strategy is particularly helpful for long-term, multi-step problems. By starting from the imagined solution and identifying all the steps required to reach it, you can systematically determine the actions needed. It lets you tackle a big hairy problem through smaller, reversible steps.
A limitation is that this approach may not be possible if you cannot accurately envision the solution state to start with.
The approach helps drive logical systematic thinking for complex problem-solving, but should still be combined with creative brainstorming of alternative scenarios and solutions.
An example is planning for an event – you would imagine the successful event occurring, then determine the tasks needed the week before, two weeks before, etc. all the way back to the present.
4. Use the Kipling Method
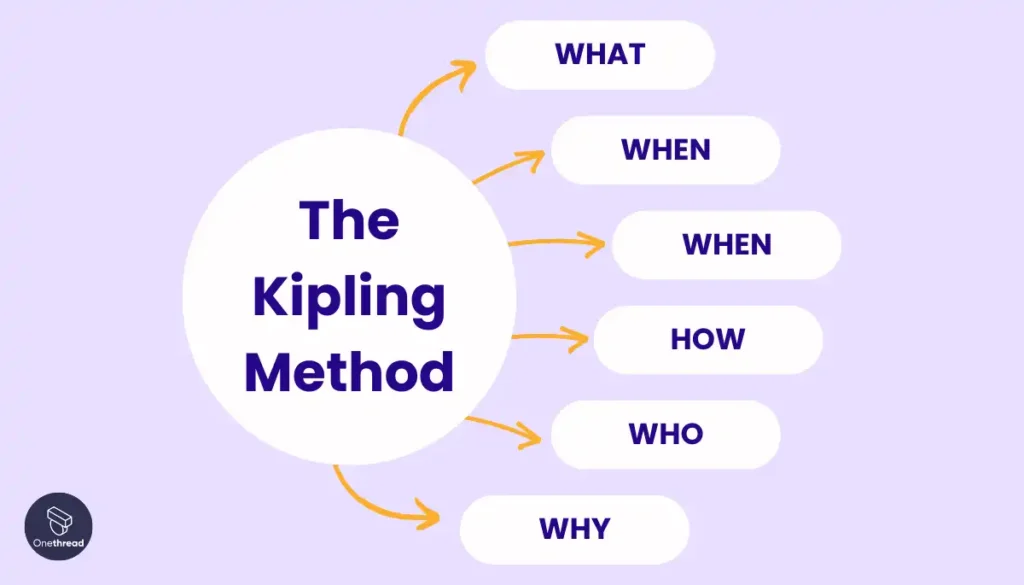
This method, named after author Rudyard Kipling, provides a framework for thoroughly analyzing a problem before jumping into solutions.
It consists of answering six fundamental questions: What, Where, When, How, Who, and Why about the challenge. Clearly defining these core elements of the problem sets the stage for generating targeted solutions.
The Kipling method enables a deep understanding of problem parameters and root causes before solution identification. By jumping to brainstorm solutions too early, critical information can be missed or the problem is loosely defined, reducing solution quality.
Answering the six fundamental questions illuminates all angles of the issue. This takes time but pays dividends in generating optimal solutions later tuned precisely to the true underlying problem.
The limitation is that meticulously working through numerous questions before addressing solutions can slow progress.
The best approach blends structured problem decomposition techniques like the Kipling method with spurring innovative solution ideation from a diverse team.
An example is using this technique after a technical process failure – the team would systematically detail What failed, Where/When did it fail, How it failed (sequence of events), Who was involved, and Why it likely failed before exploring preventative solutions.
5. Try Different Solutions Until One Works (Trial and Error)

This technique involves attempting various potential solutions sequentially until finding one that successfully solves the problem.
Trial and error works best when facing a concrete, bounded challenge with clear solution criteria and a small number of discrete options to try. By methodically testing solutions, you can determine the faulty component.
A limitation is that it can be time-intensive if the working solution set is large.
The key is limiting the variable set first. For technical problems, this boundary is inherent and each element can be iteratively tested. But for business issues, artificial constraints may be required – setting decision rules upfront to reduce options before testing.
Furthermore, hypothesis-driven experimentation is far superior to blind trial and error – have logic for why Option A may outperform Option B.
Examples include fixing printer jams by testing different paper tray and cable configurations or resolving website errors by tweaking CSS/HTML line-by-line until the code functions properly.
6. Use Proven Formulas or Frameworks (Heuristics)
Heuristics refers to applying existing problem-solving formulas or frameworks rather than addressing issues completely from scratch.
This allows leveraging established best practices rather than reinventing the wheel each time.
It is effective when facing recurrent, common challenges where proven structured approaches exist.
However, heuristics may force-fit solutions to non-standard problems.
For example, a cost-benefit analysis can be used instead of custom weighting schemes to analyze potential process improvements.
Onethread allows teams to define, save, and replicate configurable project templates so proven workflows can be reliably applied across problems with some consistency rather than fully custom one-off approaches each time.
Try One thread
Experience One thread full potential, with all its features unlocked. Sign up now to start your 14-day free trial!
7. Trust Your Instincts (Insight Problem-Solving)

Insight is a problem-solving technique that involves waiting patiently for an unexpected “aha moment” when the solution pops into your mind.
It works well for personal challenges that require intuitive realizations over calculated logic. The unconscious mind makes connections leading to flashes of insight when relaxing or doing mundane tasks unrelated to the actual problem.
Benefits include out-of-the-box creative solutions. However, the limitations are that insights can’t be forced and may never come at all if too complex. Critical analysis is still required after initial insights.
A real-life example would be a writer struggling with how to end a novel. Despite extensive brainstorming, they feel stuck. Eventually while gardening one day, a perfect unexpected plot twist sparks an ideal conclusion. However, once written they still carefully review if the ending flows logically from the rest of the story.
8. Reverse Engineer the Problem

This approach involves deconstructing a problem in reverse sequential order from the current undesirable outcome back to the initial root causes.
By mapping the chain of events backward, you can identify the origin of where things went wrong and establish the critical junctures for solving it moving ahead. Reverse engineering provides diagnostic clarity on multi-step problems.
However, the limitation is that it focuses heavily on autopsying the past versus innovating improved future solutions.
An example is tracing back from a server outage, through the cascade of infrastructure failures that led to it finally terminating at the initial script error that triggered the crisis. This root cause would then inform the preventative measure.
9. Break Down Obstacles Between Current and Goal State (Means-End Analysis)

This technique defines the current problem state and the desired end goal state, then systematically identifies obstacles in the way of getting from one to the other.
By mapping the barriers or gaps, you can then develop solutions to address each one. This methodically connects the problem to solutions.
A limitation is that some obstacles may be unknown upfront and only emerge later.
For example, you can list down all the steps required for a new product launch – current state through production, marketing, sales, distribution, etc. to full launch (goal state) – to highlight where resource constraints or other blocks exist so they can be addressed.
Onethread allows dividing big-picture projects into discrete, manageable phases, milestones, and tasks to simplify execution just as problems can be decomposed into more achievable components. Features like dependency mapping further reinforce interconnections.
Using Onethread’s issues and subtasks feature, messy problems can be decomposed into manageable chunks.
10. Ask “Why” Five Times to Identify the Root Cause (The 5 Whys)

This technique involves asking “Why did this problem occur?” and then responding with an answer that is again met with asking “Why?” This process repeats five times until the root cause is revealed.
Continually asking why digs deeper from surface symptoms to underlying systemic issues.
It is effective for getting to the source of problems originating from human error or process breakdowns.
However, some complex issues may have multiple tangled root causes not solvable through this approach alone.
An example is a retail store experiencing a sudden decline in customers. Successively asking why five times may trace an initial drop to parking challenges, stemming from a city construction project – the true starting point to address.
11. Evaluate Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT Analysis)

This involves analyzing a problem or proposed solution by categorizing internal and external factors into a 2×2 matrix: Strengths, Weaknesses as the internal rows; Opportunities and Threats as the external columns.
Systematically identifying these elements provides balanced insight to evaluate options and risks. It is impactful when evaluating alternative solutions or developing strategy amid complexity or uncertainty.
The key benefit of SWOT analysis is enabling multi-dimensional thinking when rationally evaluating options. Rather than getting anchored on just the upsides or the existing way of operating, it urges a systematic assessment through four different lenses:
- Internal Strengths: Our core competencies/advantages able to deliver success
- Internal Weaknesses: Gaps/vulnerabilities we need to manage
- External Opportunities: Ways we can differentiate/drive additional value
- External Threats: Risks we must navigate or mitigate
Multiperspective analysis provides the needed holistic view of the balanced risk vs. reward equation for strategic decision making amid uncertainty.
However, SWOT can feel restrictive if not tailored and evolved for different issue types.
Teams should view SWOT analysis as a starting point, augmenting it further for distinct scenarios.
An example is performing a SWOT analysis on whether a small business should expand into a new market – evaluating internal capabilities to execute vs. risks in the external competitive and demand environment to inform the growth decision with eyes wide open.
12. Compare Current vs Expected Performance (Gap Analysis)

This technique involves comparing the current state of performance, output, or results to the desired or expected levels to highlight shortfalls.
By quantifying the gaps, you can identify problem areas and prioritize address solutions.
Gap analysis is based on the simple principle – “you can’t improve what you don’t measure.” It enables facts-driven problem diagnosis by highlighting delta to goals, not just vague dissatisfaction that something seems wrong. And measurement immediately suggests improvement opportunities – address the biggest gaps first.
This data orientation also supports ROI analysis on fixing issues – the return from closing larger gaps outweighs narrowly targeting smaller performance deficiencies.
However, the approach is only effective if robust standards and metrics exist as the benchmark to evaluate against. Organizations should invest upfront in establishing performance frameworks.
Furthermore, while numbers are invaluable, the human context behind problems should not be ignored – quantitative versus qualitative gap assessment is optimally blended.
For example, if usage declines are noted during software gap analysis, this could be used as a signal to improve user experience through design.
13. Observe Processes from the Frontline (Gemba Walk)
A Gemba walk involves going to the actual place where work is done, directly observing the process, engaging with employees, and finding areas for improvement.
By experiencing firsthand rather than solely reviewing abstract reports, practical problems and ideas emerge.
The limitation is Gemba walks provide anecdotes not statistically significant data. It complements but does not replace comprehensive performance measurement.
An example is a factory manager inspecting the production line to spot jam areas based on direct reality rather than relying on throughput dashboards alone back in her office. Frontline insights prove invaluable.
14. Analyze Competitive Forces (Porter’s Five Forces)
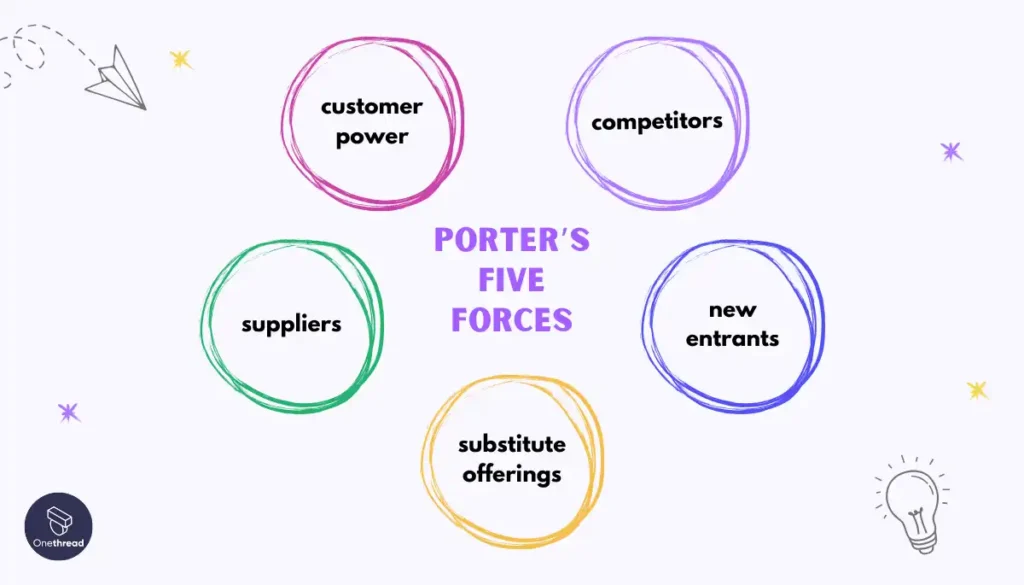
This involves assessing the marketplace around a problem or business situation via five key factors: competitors, new entrants, substitute offerings, suppliers, and customer power.
Evaluating these forces illuminates risks and opportunities for strategy development and issue resolution. It is effective for understanding dynamic external threats and opportunities when operating in a contested space.
However, over-indexing on only external factors can overlook the internal capabilities needed to execute solutions.
A startup CEO, for example, may analyze market entry barriers, whitespace opportunities, and disruption risks across these five forces to shape new product rollout strategies and marketing approaches.
15. Think from Different Perspectives (Six Thinking Hats)
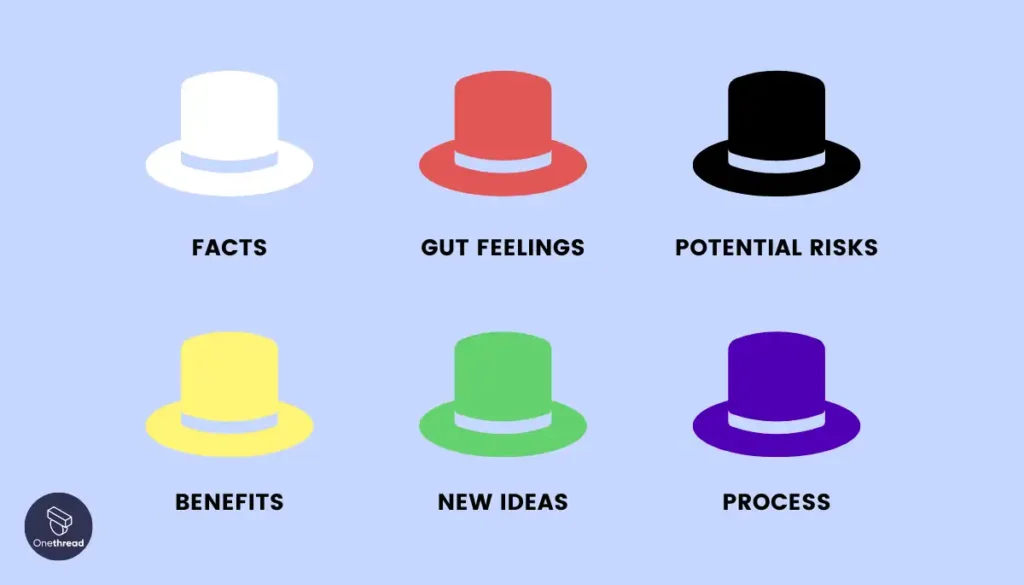
The Six Thinking Hats is a technique developed by Edward de Bono that encourages people to think about a problem from six different perspectives, each represented by a colored “thinking hat.”
The key benefit of this strategy is that it pushes team members to move outside their usual thinking style and consider new angles. This brings more diverse ideas and solutions to the table.
It works best for complex problems that require innovative solutions and when a team is stuck in an unproductive debate. The structured framework keeps the conversation flowing in a positive direction.
Limitations are that it requires training on the method itself and may feel unnatural at first. Team dynamics can also influence success – some members may dominate certain “hats” while others remain quiet.
A real-life example is a software company debating whether to build a new feature. The white hat focuses on facts, red on gut feelings, black on potential risks, yellow on benefits, green on new ideas, and blue on process. This exposes more balanced perspectives before deciding.
Onethread centralizes diverse stakeholder communication onto one platform, ensuring all voices are incorporated when evaluating project tradeoffs, just as problem-solving should consider multifaceted solutions.
16. Visualize the Problem (Draw it Out)
Drawing out a problem involves creating visual representations like diagrams, flowcharts, and maps to work through challenging issues.
This strategy is helpful when dealing with complex situations with lots of interconnected components. The visuals simplify the complexity so you can thoroughly understand the problem and all its nuances.
Key benefits are that it allows more stakeholders to get on the same page regarding root causes and it sparks new creative solutions as connections are made visually.
However, simple problems with few variables don’t require extensive diagrams. Additionally, some challenges are so multidimensional that fully capturing every aspect is difficult.
A real-life example would be mapping out all the possible causes leading to decreased client satisfaction at a law firm. An intricate fishbone diagram with branches for issues like service delivery, technology, facilities, culture, and vendor partnerships allows the team to trace problems back to their origins and brainstorm targeted fixes.
17. Follow a Step-by-Step Procedure (Algorithms)

An algorithm is a predefined step-by-step process that is guaranteed to produce the correct solution if implemented properly.
Using algorithms is effective when facing problems that have clear, binary right and wrong answers. Algorithms work for mathematical calculations, computer code, manufacturing assembly lines, and scientific experiments.
Key benefits are consistency, accuracy, and efficiency. However, they require extensive upfront development and only apply to scenarios with strict parameters. Additionally, human error can lead to mistakes.
For example, crew members of fast food chains like McDonald’s follow specific algorithms for food prep – from grill times to ingredient amounts in sandwiches, to order fulfillment procedures. This ensures uniform quality and service across all locations. However, if a step is missed, errors occur.
The Problem-Solving Process
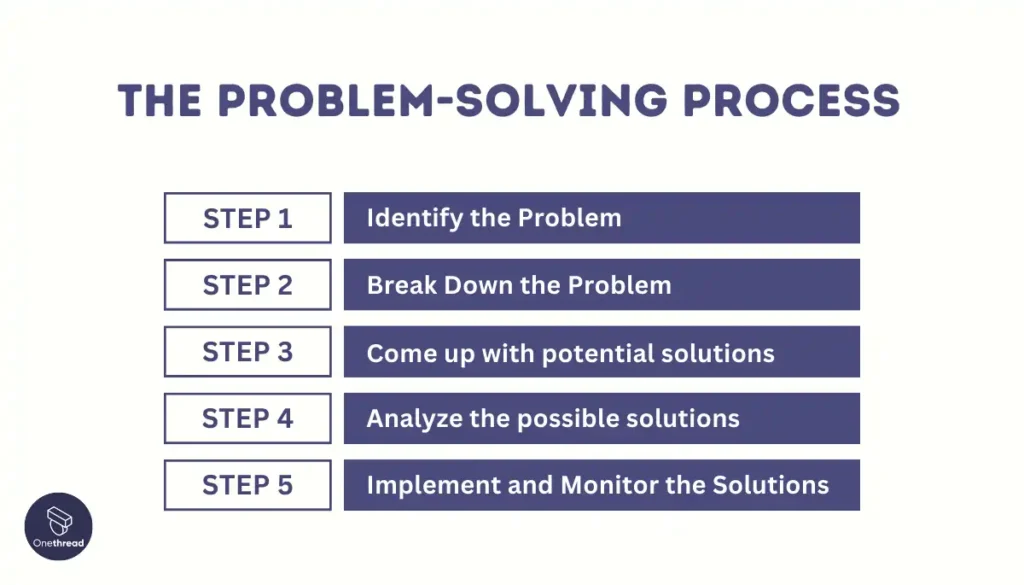
The problem-solving process typically includes defining the issue, analyzing details, creating solutions, weighing choices, acting, and reviewing results.
In the above, we have discussed several problem-solving strategies. For every problem-solving strategy, you have to follow these processes. Here’s a detailed step-by-step process of effective problem-solving:
Step 1: Identify the Problem
The problem-solving process starts with identifying the problem. This step involves understanding the issue’s nature, its scope, and its impact. Once the problem is clearly defined, it sets the foundation for finding effective solutions.
Identifying the problem is crucial. It means figuring out exactly what needs fixing. This involves looking at the situation closely, understanding what’s wrong, and knowing how it affects things. It’s about asking the right questions to get a clear picture of the issue.
This step is important because it guides the rest of the problem-solving process. Without a clear understanding of the problem, finding a solution is much harder. It’s like diagnosing an illness before treating it. Once the problem is identified accurately, you can move on to exploring possible solutions and deciding on the best course of action.
Step 2: Break Down the Problem
Breaking down the problem is a key step in the problem-solving process. It involves dividing the main issue into smaller, more manageable parts. This makes it easier to understand and tackle each component one by one.
After identifying the problem, the next step is to break it down. This means splitting the big issue into smaller pieces. It’s like solving a puzzle by handling one piece at a time.
By doing this, you can focus on each part without feeling overwhelmed. It also helps in identifying the root causes of the problem. Breaking down the problem allows for a clearer analysis and makes finding solutions more straightforward.
Each smaller problem can be addressed individually, leading to an effective resolution of the overall issue. This approach not only simplifies complex problems but also aids in developing a systematic plan to solve them.
Step 3: Come up with potential solutions
Coming up with potential solutions is the third step in the problem-solving process. It involves brainstorming various options to address the problem, considering creativity and feasibility to find the best approach.
After breaking down the problem, it’s time to think of ways to solve it. This stage is about brainstorming different solutions. You look at the smaller issues you’ve identified and start thinking of ways to fix them. This is where creativity comes in.
You want to come up with as many ideas as possible, no matter how out-of-the-box they seem. It’s important to consider all options and evaluate their pros and cons. This process allows you to gather a range of possible solutions.
Later, you can narrow these down to the most practical and effective ones. This step is crucial because it sets the stage for deciding on the best solution to implement. It’s about being open-minded and innovative to tackle the problem effectively.
Step 4: Analyze the possible solutions
Analyzing the possible solutions is the fourth step in the problem-solving process. It involves evaluating each proposed solution’s advantages and disadvantages to determine the most effective and feasible option.
After coming up with potential solutions, the next step is to analyze them. This means looking closely at each idea to see how well it solves the problem. You weigh the pros and cons of every solution.
Consider factors like cost, time, resources, and potential outcomes. This analysis helps in understanding the implications of each option. It’s about being critical and objective, ensuring that the chosen solution is not only effective but also practical.
This step is vital because it guides you towards making an informed decision. It involves comparing the solutions against each other and selecting the one that best addresses the problem.
By thoroughly analyzing the options, you can move forward with confidence, knowing you’ve chosen the best path to solve the issue.
Step 5: Implement and Monitor the Solutions
Implementing and monitoring the solutions is the final step in the problem-solving process. It involves putting the chosen solution into action and observing its effectiveness, making adjustments as necessary.
Once you’ve selected the best solution, it’s time to put it into practice. This step is about action. You implement the chosen solution and then keep an eye on how it works. Monitoring is crucial because it tells you if the solution is solving the problem as expected.
If things don’t go as planned, you may need to make some changes. This could mean tweaking the current solution or trying a different one. The goal is to ensure the problem is fully resolved.
This step is critical because it involves real-world application. It’s not just about planning; it’s about doing and adjusting based on results. By effectively implementing and monitoring the solutions, you can achieve the desired outcome and solve the problem successfully.
Why This Process is Important
Following a defined process to solve problems is important because it provides a systematic, structured approach instead of a haphazard one. Having clear steps guides logical thinking, analysis, and decision-making to increase effectiveness. Key reasons it helps are:
- Clear Direction: This process gives you a clear path to follow, which can make solving problems less overwhelming.
- Better Solutions: Thoughtful analysis of root causes, iterative testing of solutions, and learning orientation lead to addressing the heart of issues rather than just symptoms.
- Saves Time and Energy: Instead of guessing or trying random things, this process helps you find a solution more efficiently.
- Improves Skills: The more you use this process, the better you get at solving problems. It’s like practicing a sport. The more you practice, the better you play.
- Maximizes collaboration: Involving various stakeholders in the process enables broader inputs. Their communication and coordination are streamlined through organized brainstorming and evaluation.
- Provides consistency: Standard methodology across problems enables building institutional problem-solving capabilities over time. Patterns emerge on effective techniques to apply to different situations.
The problem-solving process is a powerful tool that can help us tackle any challenge we face. By following these steps, we can find solutions that work and learn important skills along the way.
Key Skills for Efficient Problem Solving

Efficient problem-solving requires breaking down issues logically, evaluating options, and implementing practical solutions.
Key skills include critical thinking to understand root causes, creativity to brainstorm innovative ideas, communication abilities to collaborate with others, and decision-making to select the best way forward. Staying adaptable, reflecting on outcomes, and applying lessons learned are also essential.
With practice, these capacities will lead to increased personal and team effectiveness in systematically addressing any problem.
Let’s explore the powers you need to become a problem-solving hero!
Critical Thinking and Analytical Skills
Critical thinking and analytical skills are vital for efficient problem-solving as they enable individuals to objectively evaluate information, identify key issues, and generate effective solutions.
These skills facilitate a deeper understanding of problems, leading to logical, well-reasoned decisions. By systematically breaking down complex issues and considering various perspectives, individuals can develop more innovative and practical solutions, enhancing their problem-solving effectiveness.
Communication Skills
Effective communication skills are essential for efficient problem-solving as they facilitate clear sharing of information, ensuring all team members understand the problem and proposed solutions.
These skills enable individuals to articulate issues, listen actively, and collaborate effectively, fostering a productive environment where diverse ideas can be exchanged and refined. By enhancing mutual understanding, communication skills contribute significantly to identifying and implementing the most viable solutions.
Decision-Making
Strong decision-making skills are crucial for efficient problem-solving, as they enable individuals to choose the best course of action from multiple alternatives.
These skills involve evaluating the potential outcomes of different solutions, considering the risks and benefits, and making informed choices. Effective decision-making leads to the implementation of solutions that are likely to resolve problems effectively, ensuring resources are used efficiently and goals are achieved.
Planning and Prioritization
Planning and prioritization are key for efficient problem-solving, ensuring resources are allocated effectively to address the most critical issues first. This approach helps in organizing tasks according to their urgency and impact, streamlining efforts towards achieving the desired outcome efficiently.
Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence enhances problem-solving by allowing individuals to manage emotions, understand others, and navigate social complexities. It fosters a positive, collaborative environment, essential for generating creative solutions and making informed, empathetic decisions.
Leadership skills drive efficient problem-solving by inspiring and guiding teams toward common goals. Effective leaders motivate their teams, foster innovation, and navigate challenges, ensuring collective efforts are focused and productive in addressing problems.
Time Management
Time management is crucial in problem-solving, enabling individuals to allocate appropriate time to each task. By efficiently managing time, one can ensure that critical problems are addressed promptly without neglecting other responsibilities.
Data Analysis
Data analysis skills are essential for problem-solving, as they enable individuals to sift through data, identify trends, and extract actionable insights. This analytical approach supports evidence-based decision-making, leading to more accurate and effective solutions.
Research Skills
Research skills are vital for efficient problem-solving, allowing individuals to gather relevant information, explore various solutions, and understand the problem’s context. This thorough exploration aids in developing well-informed, innovative solutions.
Becoming a great problem solver takes practice, but with these skills, you’re on your way to becoming a problem-solving hero.
How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills?

Improving your problem-solving skills can make you a master at overcoming challenges. Learn from experts, practice regularly, welcome feedback, try new methods, experiment, and study others’ success to become better.
Learning from Experts
Improving problem-solving skills by learning from experts involves seeking mentorship, attending workshops, and studying case studies. Experts provide insights and techniques that refine your approach, enhancing your ability to tackle complex problems effectively.
To enhance your problem-solving skills, learning from experts can be incredibly beneficial. Engaging with mentors, participating in specialized workshops, and analyzing case studies from seasoned professionals can offer valuable perspectives and strategies.
Experts share their experiences, mistakes, and successes, providing practical knowledge that can be applied to your own problem-solving process. This exposure not only broadens your understanding but also introduces you to diverse methods and approaches, enabling you to tackle challenges more efficiently and creatively.
Improving problem-solving skills through practice involves tackling a variety of challenges regularly. This hands-on approach helps in refining techniques and strategies, making you more adept at identifying and solving problems efficiently.
One of the most effective ways to enhance your problem-solving skills is through consistent practice. By engaging with different types of problems on a regular basis, you develop a deeper understanding of various strategies and how they can be applied.
This hands-on experience allows you to experiment with different approaches, learn from mistakes, and build confidence in your ability to tackle challenges.
Regular practice not only sharpens your analytical and critical thinking skills but also encourages adaptability and innovation, key components of effective problem-solving.
Openness to Feedback
Being open to feedback is like unlocking a secret level in a game. It helps you boost your problem-solving skills. Improving problem-solving skills through openness to feedback involves actively seeking and constructively responding to critiques.
This receptivity enables you to refine your strategies and approaches based on insights from others, leading to more effective solutions.
Learning New Approaches and Methodologies
Learning new approaches and methodologies is like adding new tools to your toolbox. It makes you a smarter problem-solver. Enhancing problem-solving skills by learning new approaches and methodologies involves staying updated with the latest trends and techniques in your field.
This continuous learning expands your toolkit, enabling innovative solutions and a fresh perspective on challenges.
Experimentation
Experimentation is like being a scientist of your own problems. It’s a powerful way to improve your problem-solving skills. Boosting problem-solving skills through experimentation means trying out different solutions to see what works best. This trial-and-error approach fosters creativity and can lead to unique solutions that wouldn’t have been considered otherwise.
Analyzing Competitors’ Success
Analyzing competitors’ success is like being a detective. It’s a smart way to boost your problem-solving skills. Improving problem-solving skills by analyzing competitors’ success involves studying their strategies and outcomes. Understanding what worked for them can provide valuable insights and inspire effective solutions for your own challenges.
Challenges in Problem-Solving
Facing obstacles when solving problems is common. Recognizing these barriers, like fear of failure or lack of information, helps us find ways around them for better solutions.
Fear of Failure
Fear of failure is like a big, scary monster that stops us from solving problems. It’s a challenge many face. Because being afraid of making mistakes can make us too scared to try new solutions.
How can we overcome this? First, understand that it’s okay to fail. Failure is not the opposite of success; it’s part of learning. Every time we fail, we discover one more way not to solve a problem, getting us closer to the right solution. Treat each attempt like an experiment. It’s not about failing; it’s about testing and learning.
Lack of Information
Lack of information is like trying to solve a puzzle with missing pieces. It’s a big challenge in problem-solving. Because without all the necessary details, finding a solution is much harder.
How can we fix this? Start by gathering as much information as you can. Ask questions, do research, or talk to experts. Think of yourself as a detective looking for clues. The more information you collect, the clearer the picture becomes. Then, use what you’ve learned to think of solutions.
Fixed Mindset
A fixed mindset is like being stuck in quicksand; it makes solving problems harder. It means thinking you can’t improve or learn new ways to solve issues.
How can we change this? First, believe that you can grow and learn from challenges. Think of your brain as a muscle that gets stronger every time you use it. When you face a problem, instead of saying “I can’t do this,” try thinking, “I can’t do this yet.” Look for lessons in every challenge and celebrate small wins.
Everyone starts somewhere, and mistakes are just steps on the path to getting better. By shifting to a growth mindset, you’ll see problems as opportunities to grow. Keep trying, keep learning, and your problem-solving skills will soar!
Jumping to Conclusions
Jumping to conclusions is like trying to finish a race before it starts. It’s a challenge in problem-solving. That means making a decision too quickly without looking at all the facts.
How can we avoid this? First, take a deep breath and slow down. Think about the problem like a puzzle. You need to see all the pieces before you know where they go. Ask questions, gather information, and consider different possibilities. Don’t choose the first solution that comes to mind. Instead, compare a few options.
Feeling Overwhelmed
Feeling overwhelmed is like being buried under a mountain of puzzles. It’s a big challenge in problem-solving. When we’re overwhelmed, everything seems too hard to handle.
How can we deal with this? Start by taking a step back. Breathe deeply and focus on one thing at a time. Break the big problem into smaller pieces, like sorting puzzle pieces by color. Tackle each small piece one by one. It’s also okay to ask for help. Sometimes, talking to someone else can give you a new perspective.
Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias is like wearing glasses that only let you see what you want to see. It’s a challenge in problem-solving. Because it makes us focus only on information that agrees with what we already believe, ignoring anything that doesn’t.
How can we overcome this? First, be aware that you might be doing it. It’s like checking if your glasses are on right. Then, purposely look for information that challenges your views. It’s like trying on a different pair of glasses to see a new perspective. Ask questions and listen to answers, even if they don’t fit what you thought before.
Groupthink is like everyone in a group deciding to wear the same outfit without asking why. It’s a challenge in problem-solving. It means making decisions just because everyone else agrees, without really thinking it through.
How can we avoid this? First, encourage everyone in the group to share their ideas, even if they’re different. It’s like inviting everyone to show their unique style of clothes.
Listen to all opinions and discuss them. It’s okay to disagree; it helps us think of better solutions. Also, sometimes, ask someone outside the group for their thoughts. They might see something everyone in the group missed.
Overcoming obstacles in problem-solving requires patience, openness, and a willingness to learn from mistakes. By recognizing these barriers, we can develop strategies to navigate around them, leading to more effective and creative solutions.
What are the most common problem-solving techniques?
The most common techniques include brainstorming, the 5 Whys, mind mapping, SWOT analysis, and using algorithms or heuristics. Each approach has its strengths, suitable for different types of problems.
What’s the best problem-solving strategy for every situation?
There’s no one-size-fits-all strategy. The best approach depends on the problem’s complexity, available resources, and time constraints. Combining multiple techniques often yields the best results.
How can I improve my problem-solving skills?
Improve your problem-solving skills by practicing regularly, learning from experts, staying open to feedback, and continuously updating your knowledge on new approaches and methodologies.
Are there any tools or resources to help with problem-solving?
Yes, tools like mind mapping software, online courses on critical thinking, and books on problem-solving techniques can be very helpful. Joining forums or groups focused on problem-solving can also provide support and insights.
What are some common mistakes people make when solving problems?
Common mistakes include jumping to conclusions without fully understanding the problem, ignoring valuable feedback, sticking to familiar solutions without considering alternatives, and not breaking down complex problems into manageable parts.
Final Words
Mastering problem-solving strategies equips us with the tools to tackle challenges across all areas of life. By understanding and applying these techniques, embracing a growth mindset, and learning from both successes and obstacles, we can transform problems into opportunities for growth. Continuously improving these skills ensures we’re prepared to face and solve future challenges more effectively.

Let's Get Started with Onethread
Onethread empowers you to plan, organise, and track projects with ease, ensuring you meet deadlines, allocate resources efficiently, and keep progress transparent.
By subscribing you agree to our Privacy Policy .
Giving modern marketing teams superpowers with short links that stand out.
- Live Product Demo
© Copyright 2023 Onethread, Inc
- Live Online Training
- Upcoming seminars
- ENDORSED PROGRAMMES from The Institute of Leadership
- In-house Seminars
- Strategic Performance Management
- Internal Expert and Consultant Retainer Scheme
- Personal Coaching
- Business Strategy and Development
- Human Resources Management
- Production, Operations and Materials Management
- Quality, Environmental, Health and Safety Management
- Conicon Blog
- Our clients
- Photo gallery
Problem Solving: The 10 characteristics that stand out in Problem Solvers
Effective problem solving is now among the most popular skills around the world.
Every day it turns out that most people can’t handle problems/crises that come either personal or professional!
At the same time, it’s an issue where decision-making people need training, so they don’t make jerky moves because of panic.
Effective problem solving is finding solutions to problems (internally – externally) using the right methods and tools – in essence to find ways to solve any problem that comes quickly and effectively
Below you will see the 10 characteristics that stand out in Problem Solvers:
1. They don’t waste their time proving they’re right – they focus on the solution.
2. They come out of their box and find ideas to explore their choices (they don’t think the same way – they shift their thinking)
3. They see opportunities through the problem and don’t over-think the problem all the time to feel better.
4. They know the difference between simple thinking and complexity (most people have complicated thinking because they are influenced by external factors such as media, society etc.)
5. They make clear exactly what is a problem – without being directly affected by their own perception which is not objective.
6. They use communication (power of words) to communicate with the world – rather than intimidate it.
7. They do not cause problems to others to solve their own (characteristic of most people)
8. They prefer prevention rather than intervention (if there were conditions for prevention it wouldn’t swell things so much)
9. Τhey search for their options (with different ways of thinking and have a problem management team)
10. They have reasonable expectations and know all the scenarios of each choice (good, neutral and bad)
Surely now that you have seen them you realize that there are very few people who have these characteristics!
Also these people know the 4 simplest steps for Problem Solving:
1. Specify the problem (what is really the problem – and not focus on the symptoms of the problem)
2. Create alternatives (for all scenarios, good, neutral and bad)
3. Evaluation and selection of alternatives (always based on the impact of each solution)
4. Implementation of Solutions (if it doesn’t work they always have a Plan B
The only thing that is certain is that problem solving is not innate in individuals. It needs training and friction with the subject!
Most remember the importance of this skill when it’s already too late!
Do you have these characteristics?
Christofi Vasiliki Communication, Soft Skills NAMA Certified Anger Management Specialist, PR Specialist Trainer and Coach
Do you feel that communication is a two-way process in your organization?
View Results
How we can Contribute?
Contact us here to find out what we can do for you or your business.
Testimonials
Conicon ltd.
Leading professional training and management consulting firm based in Limassol, Cyprus.
Privacy policy
This website use cookies, please read our Privacy policy .
- LIVE ONLINE TRAINING
- Endorsed programs
- Conicon team

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
ZFCO Problem Solving Study (2021) Zenger Folkman. 1. They get it done right away.In other studies comparing men and women leaders, we have found that this competency consistently shows the most ...
Here are some Characteristics of Effective Problem Solvers: 1. Critical Thinking: Effective problem solvers possess strong critical thinking skills. ... It often requires collaboration, critical thinking, and creative problem-solving techniques. Effective problem-solving in the workplace can lead to increased productivity, improved teamwork ...
Steps to Problem Solving: 1. Identify the problem. Once you've identified the problem, try to figure out why and how it occurred. 2. Determine the criteria for your solution. Before generating a solution, you must first define what you hope to achieve. For example, your solution must stay within a specific budget or time frame. 3.
Truly effective problem solvers exhibit specific traits that enable them to tackle challenges systematically and creatively. In other articles, I've covered problem-solving approaches and processes. Here, I'll explore the characteristics and mindsets that great problem solvers have in common: curiosity and open-mindedness; analytical thinking
10. They have reasonable expectations: Good problem solvers have reasonable expectations as to what the solution would be. They understand that there are many elements effecting a situation and that idealistic ways of thinking and going about solving a problem will be counterproductive.
A Problem Solver's Characteristics. An effective problem solver can easily be distinguished from others by the key personality characteristics that naturally help them to break down boundaries and attain the heights of logical and constructive thought. ... Effective problem solving requires us to let go of ill-fated judgments and criticisms.
17 Effective Problem-Solving Strategies. Effective problem-solving strategies include breaking the problem into smaller parts, brainstorming multiple solutions, evaluating the pros and cons of each, and choosing the most viable option. Critical thinking and creativity are essential in developing innovative solutions.
Effective problem solving is finding solutions to problems (internally - externally) using the right methods and tools - in essence to find ways to solve any problem that comes quickly and effectively . Below you will see the 10 characteristics that stand out in Problem Solvers: 1.
Both methodologies provide a structured, team-based problem-solving approach that guides individuals through a comprehensive and systematic process of identifying, analysing, and resolving problems in an effective and efficient manner. Step 1 - Define the Problem. The definition of the problem is the first step in effective problem solving.
In this article, we'll look at problem-solving, its importance, and ten tips and strategies to become a better problem-solver. What is Problem-Solving? (Definition) Problem-solving is the process of breaking down challenges to find solutions. Typically it is a four-stage process of 1) identifying an issue, 2) establishing a plan, 3) executing ...