Fix "local variable referenced before assignment" in Python


Introduction
If you're a Python developer, you've probably come across a variety of errors, like the "local variable referenced before assignment" error. This error can be a bit puzzling, especially for beginners and when it involves local/global variables.
Today, we'll explain this error, understand why it occurs, and see how you can fix it.
The "local variable referenced before assignment" Error
The "local variable referenced before assignment" error in Python is a common error that occurs when a local variable is referenced before it has been assigned a value. This error is a type of UnboundLocalError , which is raised when a local variable is referenced before it has been assigned in the local scope.
Here's a simple example:
Running this code will throw the "local variable 'x' referenced before assignment" error. This is because the variable x is referenced in the print(x) statement before it is assigned a value in the local scope of the foo function.
Even more confusing is when it involves global variables. For example, the following code also produces the error:
But wait, why does this also produce the error? Isn't x assigned before it's used in the say_hello function? The problem here is that x is a global variable when assigned "Hello ". However, in the say_hello function, it's a different local variable, which has not yet been assigned.
We'll see later in this Byte how you can fix these cases as well.
Fixing the Error: Initialization
One way to fix this error is to initialize the variable before using it. This ensures that the variable exists in the local scope before it is referenced.
Let's correct the error from our first example:
In this revised code, we initialize x with a value of 1 before printing it. Now, when you run the function, it will print 1 without any errors.
Fixing the Error: Global Keyword
Another way to fix this error, depending on your specific scenario, is by using the global keyword. This is especially useful when you want to use a global variable inside a function.
No spam ever. Unsubscribe anytime. Read our Privacy Policy.
Here's how:
In this snippet, we declare x as a global variable inside the function foo . This tells Python to look for x in the global scope, not the local one . Now, when you run the function, it will increment the global x by 1 and print 1 .
Similar Error: NameError
An error that's similar to the "local variable referenced before assignment" error is the NameError . This is raised when you try to use a variable or a function name that has not been defined yet.
Running this code will result in a NameError :
In this case, we're trying to print the value of y , but y has not been defined anywhere in the code. Hence, Python raises a NameError . This is similar in that we are trying to use an uninitialized/undefined variable, but the main difference is that we didn't try to initialize y anywhere else in our code.
Variable Scope in Python
Understanding the concept of variable scope can help avoid many common errors in Python, including the main error of interest in this Byte. But what exactly is variable scope?
In Python, variables have two types of scope - global and local. A variable declared inside a function is known as a local variable, while a variable declared outside a function is a global variable.
Consider this example:
In this code, x is a global variable, and y is a local variable. x can be accessed anywhere in the code, but y can only be accessed within my_function . Confusion surrounding this is one of the most common causes for the "variable referenced before assignment" error.
In this Byte, we've taken a look at the "local variable referenced before assignment" error and another similar error, NameError . We also delved into the concept of variable scope in Python, which is an important concept to understand to avoid these errors. If you're seeing one of these errors, check the scope of your variables and make sure they're being assigned before they're being used.
Monitor with Ping Bot
Reliable monitoring for your app, databases, infrastructure, and the vendors they rely on. Ping Bot is a powerful uptime and performance monitoring tool that helps notify you and resolve issues before they affect your customers.
© 2013- 2024 Stack Abuse. All rights reserved.

Top 2 Methods to Solve the ‘Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment’ Error in Python

Table of Contents
When working with Python, encountering the UnboundLocalError can be quite common, especially when dealing with variables that you intend to access globally within a function. This error typically occurs when a variable is referenced before it has been assigned a value within the local scope.
The Problem: Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment
Consider the following example:
Running the code above yields the error:
The critical point here is whether the variable test1 is recognized as global or local. In this case, Python reinterprets test1 as a local variable due to the attempted modification with += , which leads to confusion when it’s referenced before being assigned any value in the local scope.
So how can you resolve this issue effectively without passing test1 as an argument into test_func ? Let’s explore two main methods to approach this.
Method 1: Avoiding Globals
The best practice suggests minimizing the use of global variables. Instead of modifying a global variable directly, consider passing the variable to a function. Here’s how you could rewrite the example to avoid using a global variable entirely:
In this example, test_func takes a parameter x , performs the operation, and returns the modified value, allowing us to keep the variable scope clean.
Method 2: Declaring a Variable as Global
If modifying a global variable within a function is necessary, use the global keyword. Here’s how you can clarify that test1 should be treated as a global variable within test_func :
By using global test1 , you inform Python of your intention to operate on the global instance of test1 , thus eliminating the UnboundLocalError .

Further Alternatives
While the two methods outlined above are the most straightforward solutions, you can also consider using classes to encapsulate your variables and methods, managing state more formally through object-oriented programming. Here’s a simple example:
This alternative approach provides a structured way to manage your variables, improving code readability and maintainability.
FAQs on Top 2 Methods to Solve the ‘Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment’ Error in Python
Q: what is unboundlocalerror in python, q: how can i avoid using global variables in python, q: does using the global keyword affect performance, q: what are the best practices for variable scope in python.
For additional resources on Python programming, you might find W3Schools Python Tutorials and Geeks for Geeks Python Programming useful.
Local variable referenced before assignment in Python
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024 Reading time · 4 min

# Local variable referenced before assignment in Python
The Python "UnboundLocalError: Local variable referenced before assignment" occurs when we reference a local variable before assigning a value to it in a function.
To solve the error, mark the variable as global in the function definition, e.g. global my_var .
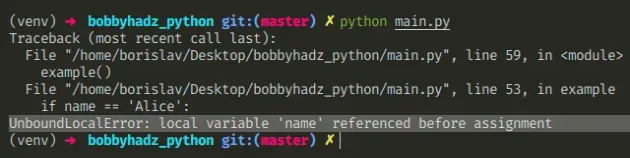
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
We assign a value to the name variable in the function.
# Mark the variable as global to solve the error
To solve the error, mark the variable as global in your function definition.
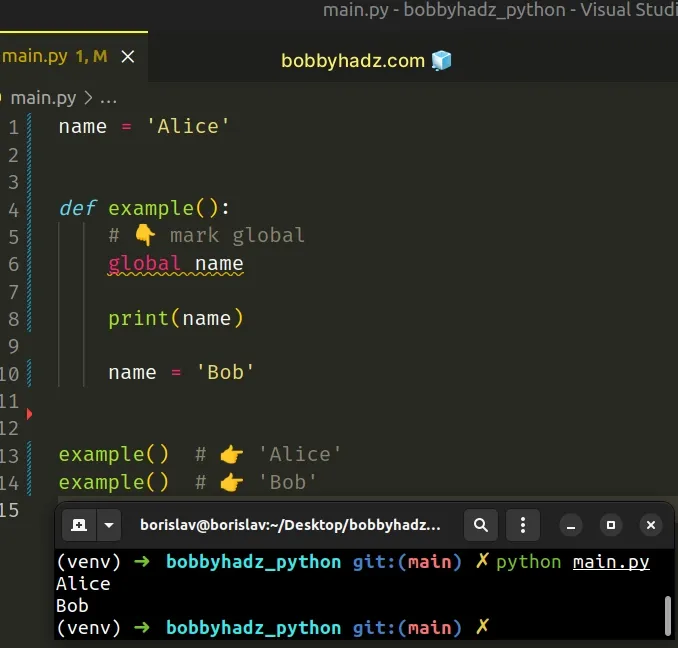
If a variable is assigned a value in a function's body, it is a local variable unless explicitly declared as global .
# Local variables shadow global ones with the same name
You could reference the global name variable from inside the function but if you assign a value to the variable in the function's body, the local variable shadows the global one.
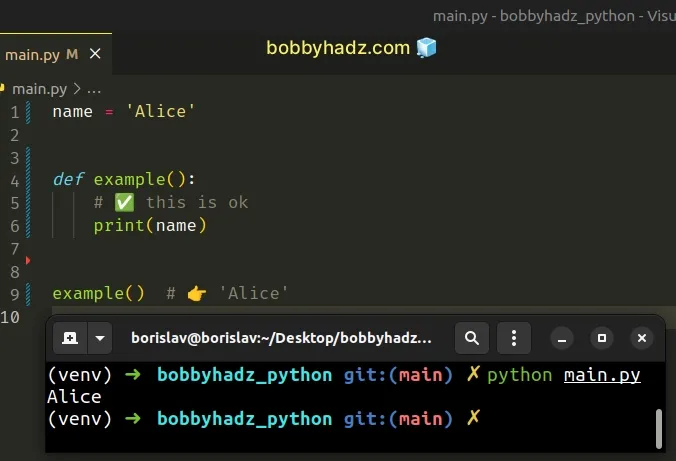
Accessing the name variable in the function is perfectly fine.
On the other hand, variables declared in a function cannot be accessed from the global scope.
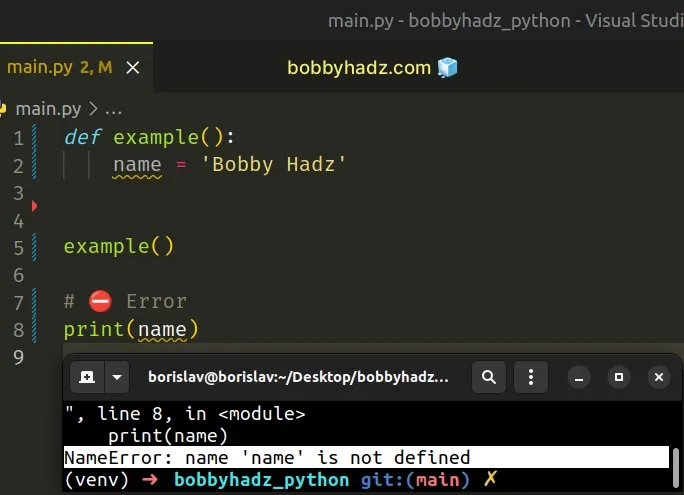
The name variable is declared in the function, so trying to access it from outside causes an error.
Make sure you don't try to access the variable before using the global keyword, otherwise, you'd get the SyntaxError: name 'X' is used prior to global declaration error.
# Returning a value from the function instead
An alternative solution to using the global keyword is to return a value from the function and use the value to reassign the global variable.
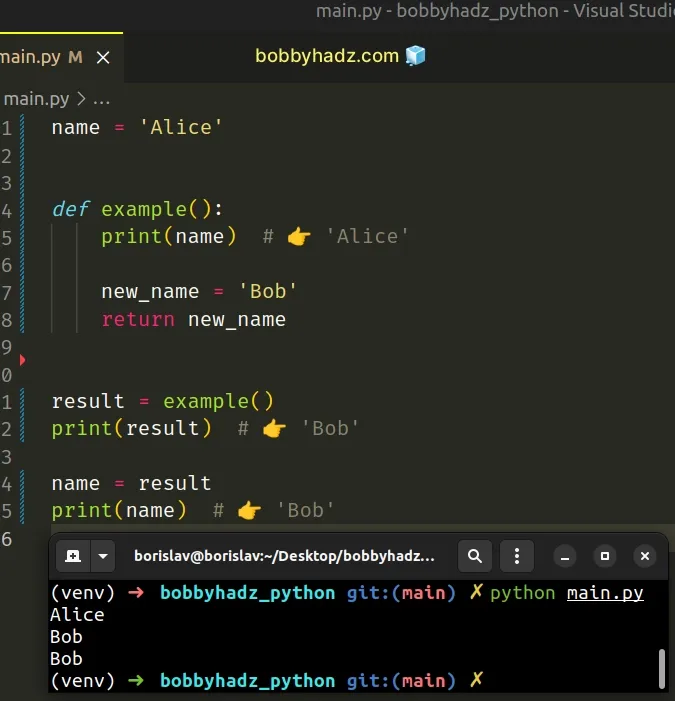
We simply return the value that we eventually use to assign to the name global variable.
# Passing the global variable as an argument to the function
You should also consider passing the global variable as an argument to the function.
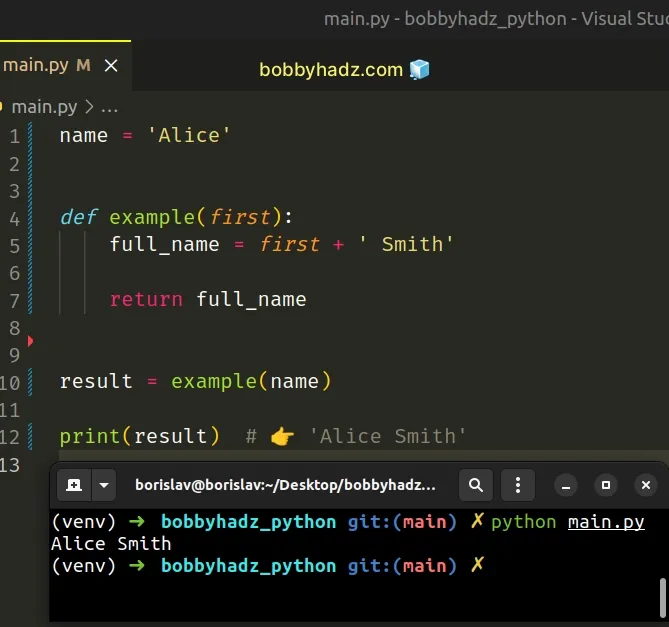
We passed the name global variable as an argument to the function.
If we assign a value to a variable in a function, the variable is assumed to be local unless explicitly declared as global .
# Assigning a value to a local variable from an outer scope
If you have a nested function and are trying to assign a value to the local variables from the outer function, use the nonlocal keyword.
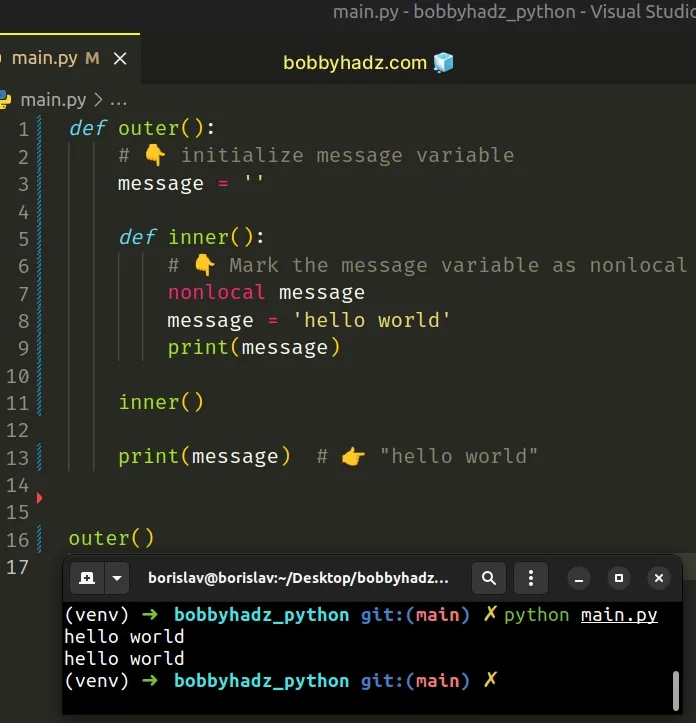
The nonlocal keyword allows us to work with the local variables of enclosing functions.
Had we not used the nonlocal statement, the call to the print() function would have returned an empty string.
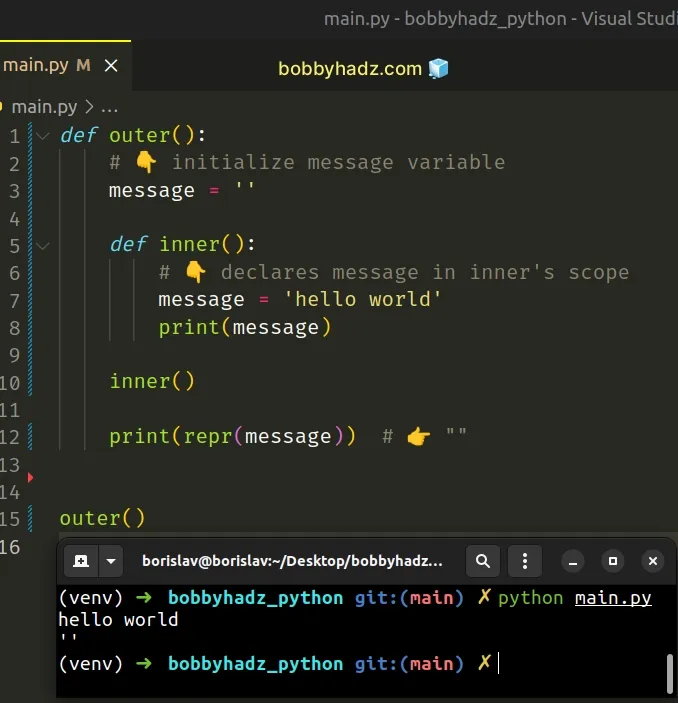
Printing the message variable on the last line of the function shows an empty string because the inner() function has its own scope.
Changing the value of the variable in the inner scope is not possible unless we use the nonlocal keyword.
Instead, the message variable in the inner function simply shadows the variable with the same name from the outer scope.
# Discussion
As shown in this section of the documentation, when you assign a value to a variable inside a function, the variable:
- Becomes local to the scope.
- Shadows any variables from the outer scope that have the same name.
The last line in the example function assigns a value to the name variable, marking it as a local variable and shadowing the name variable from the outer scope.
At the time the print(name) line runs, the name variable is not yet initialized, which causes the error.
The most intuitive way to solve the error is to use the global keyword.
The global keyword is used to indicate to Python that we are actually modifying the value of the name variable from the outer scope.
- If a variable is only referenced inside a function, it is implicitly global.
- If a variable is assigned a value inside a function's body, it is assumed to be local, unless explicitly marked as global .
If you want to read more about why this error occurs, check out [this section] ( this section ) of the docs.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- SyntaxError: name 'X' is used prior to global declaration

Borislav Hadzhiev
Web Developer

Copyright © 2024 Borislav Hadzhiev

IMAGES
VIDEO