- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus

Reported speech: indirect speech
Indirect speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech , the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
direct | indirect | reported clause | |
statement | ) I was tired. | -clause | |
question | . . | clause clause clause | |
command | . | -infinitive clause |
Indirect speech: reporting statements
Indirect reports of statements consist of a reporting clause and a that -clause. We often omit that , especially in informal situations:
The pilot commented that the weather had been extremely bad as the plane came in to land. (The pilot’s words were: ‘The weather was extremely bad as the plane came in to land.’ )
I told my wife I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday. ( that -clause without that ) (or I told my wife that I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday .)
Indirect speech: reporting questions
Reporting yes-no questions and alternative questions.
Indirect reports of yes-no questions and questions with or consist of a reporting clause and a reported clause introduced by if or whether . If is more common than whether . The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She asked if [S] [V] I was Scottish. (original yes-no question: ‘Are you Scottish?’ )
The waiter asked whether [S] we [V] wanted a table near the window. (original yes-no question: ‘Do you want a table near the window? )
He asked me if [S] [V] I had come by train or by bus. (original alternative question: ‘Did you come by train or by bus?’ )
Questions: yes-no questions ( Are you feeling cold? )
Reporting wh -questions
Indirect reports of wh -questions consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a wh -word ( who, what, when, where, why, how ). We don’t use a question mark:
He asked me what I wanted.
Not: He asked me what I wanted?
The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She wanted to know who [S] we [V] had invited to the party.
Not: … who had we invited …
Who , whom and what
In indirect questions with who, whom and what , the wh- word may be the subject or the object of the reported clause:
I asked them who came to meet them at the airport. ( who is the subject of came ; original question: ‘Who came to meet you at the airport?’ )
He wondered what the repairs would cost. ( what is the object of cost ; original question: ‘What will the repairs cost?’ )
She asked us what [S] we [V] were doing . (original question: ‘What are you doing?’ )
Not: She asked us what were we doing?
When , where , why and how
We also use statement word order (subject + verb) with when , where, why and how :
I asked her when [S] it [V] had happened (original question: ‘When did it happen?’ ).
Not: I asked her when had it happened?
I asked her where [S] the bus station [V] was . (original question: ‘Where is the bus station?’ )
Not: I asked her where was the bus station?
The teacher asked them how [S] they [V] wanted to do the activity . (original question: ‘How do you want to do the activity?’ )
Not: The teacher asked them how did they want to do the activity?
Questions: wh- questions
Indirect speech: reporting commands
Indirect reports of commands consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a to -infinitive:
The General ordered the troops to advance . (original command: ‘Advance!’ )
The chairperson told him to sit down and to stop interrupting . (original command: ‘Sit down and stop interrupting!’ )
We also use a to -infinitive clause in indirect reports with other verbs that mean wanting or getting people to do something, for example, advise, encourage, warn :
They advised me to wait till the following day. (original statement: ‘You should wait till the following day.’ )
The guard warned us not to enter the area. (original statement: ‘You must not enter the area.’ )
Verbs followed by a to -infinitive
Indirect speech: present simple reporting verb
We can use the reporting verb in the present simple in indirect speech if the original words are still true or relevant at the time of reporting, or if the report is of something someone often says or repeats:
Sheila says they’re closing the motorway tomorrow for repairs.
Henry tells me he’s thinking of getting married next year.
Rupert says dogs shouldn’t be allowed on the beach. (Rupert probably often repeats this statement.)
Newspaper headlines
We often use the present simple in newspaper headlines. It makes the reported speech more dramatic:
JUDGE TELLS REPORTER TO LEAVE COURTROOM
PRIME MINISTER SAYS FAMILIES ARE TOP PRIORITY IN TAX REFORM
Present simple ( I work )
Reported speech
Reported speech: direct speech
Indirect speech: past continuous reporting verb
In indirect speech, we can use the past continuous form of the reporting verb (usually say or tell ). This happens mostly in conversation, when the speaker wants to focus on the content of the report, usually because it is interesting news or important information, or because it is a new topic in the conversation:
Rory was telling me the big cinema in James Street is going to close down. Is that true?
Alex was saying that book sales have gone up a lot this year thanks to the Internet.
‘Backshift’ refers to the changes we make to the original verbs in indirect speech because time has passed between the moment of speaking and the time of the report.
direct speech | indirect speech |
| not very happy at work.’ | not very happy at work. |
| going home.’ | going home. |
| be late.’ | be late. |
| been working,’ she said. | . |
| to make her so angry?’ he asked. | to make her so angry. |
In these examples, the present ( am ) has become the past ( was ), the future ( will ) has become the future-in-the-past ( would ) and the past ( happened ) has become the past perfect ( had happened ). The tenses have ‘shifted’ or ‘moved back’ in time.
direct | indirect | |
present simple | → | past simple |
present continuous | → | past continuous |
present perfect simple | → | past perfect simple |
present perfect continuous | → | past perfect continuous |
past simple | → | past perfect simple |
past continuous | → | past perfect continuous |
future (will) | → | future-in-the-past (would) |
past perfect | ↔ | past perfect (no change) |
The past perfect does not shift back; it stays the same:
Direct speech | Indirect speech |
| already left. |
Modal verbs
Some, but not all, modal verbs ‘shift back’ in time and change in indirect speech.
direct speech | indirect speech | change | |
| be there,’ he promised. | be there. | becomes |
| need more money.’ I open it?’ she asked. | need more money. open it. | usually becomes in reported questions, becomes |
| see you at 2.30,’ he added. | see me at 2.30. | becomes |
| be back later,’ she said. wait in the hallway,’ he said. | be back later. wait in the hallway. | (possibility) becomes (permission) becomes |
| pay by 30th April.’ be awful to live in such a noisy place,’ she said. | pay by 30th April. be awful to live in such a noisy place. | (obligation) usually becomes (speculation) does not change |
| sell it for about 2,000 euros,’ he said. | sell it for about 2,000 euros. | no change |
| go there immediately,’ she said. | go there immediately. | no change |
| buy it if I had the money,’ he said. | buy it if he had the money. | no change |
| snow tonight,’ he warned. | snow that night. | no change |
| come till six o’clock,’ he said. | come till six o’clock. | no change |
We can use a perfect form with have + - ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past:
He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: ‘The noise might be the postman delivering letters.’ )
He said he would have helped us if we’d needed a volunteer. (original statement: ‘I’ll help you if you need a volunteer’ or ‘I’d help you if you needed a volunteer.’ )
Used to and ought to do not change in indirect speech:
She said she used to live in Oxford. (original statement: ‘I used to live in Oxford.’ )
The guard warned us that we ought to leave immediately. (original statement: ‘You ought to leave immediately.’ )
No backshift
We don’t need to change the tense in indirect speech if what a person said is still true or relevant or has not happened yet. This often happens when someone talks about the future, or when someone uses the present simple, present continuous or present perfect in their original words:
He told me his brother works for an Italian company. (It is still true that his brother works for an Italian company.)
She said she ’s getting married next year. (For the speakers, the time at the moment of speaking is ‘this year’.)
He said he ’s finished painting the door. (He probably said it just a short time ago.)
She promised she ’ll help us. (The promise applies to the future.)
Indirect speech: changes to pronouns
Changes to personal pronouns in indirect reports depend on whether the person reporting the speech and the person(s) who said the original words are the same or different.
direct | indirect | |
| don’t want to shock people,’ Tom said. | said he didn’t want to shock people. | different speakers ( changes to ) |
| ’ll look after Toby,’ I said. | said I would look after Toby. | same speaker (no change) |
| need to be here at nine o’clock,’ George told Beatrice. | told Beatrice she needed to be there at nine o’clock. | different speakers ( changes to ) |
| hope you will join us tonight,’ I said to James. | told James I hoped he would join us that night. | same speaker (no change to ; changes to ) |
Indirect speech: changes to adverbs and demonstratives
We often change demonstratives ( this, that ) and adverbs of time and place ( now, here, today , etc.) because indirect speech happens at a later time than the original speech, and perhaps in a different place.
direct speech | indirect speech |
| .’ | the next/following day. |
| this moment in time.’ | . |
| .” | . |
| ,’ the boy protested. | . |
Typical changes to demonstratives, adverbs and adverbial expressions
direct | indirect | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect speech: typical errors
The word order in indirect reports of wh- questions is the same as statement word order (subject + verb), not question word order:
She always asks me where [S] [V] I am going .
Not: She always asks me where am I going .
We don’t use a question mark when reporting wh- questions:
I asked him what he was doing.
Not: I asked him what he was doing?

Word of the Day
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
used at the end of words to mean "without

Putting a spanner in the works – Idioms in The Guernsey Literary and Potato Peel Pie Society

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
To add ${headword} to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Reported Speech
Perfect english grammar.

Reported Statements
Here's how it works:
We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence:
- Direct speech: I like ice cream.
- Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
We don't need to change the tense, though probably we do need to change the 'person' from 'I' to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'. (As I'm sure you know, often, we can choose if we want to use 'that' or not in English. I've put it in brackets () to show that it's optional. It's exactly the same if you use 'that' or if you don't use 'that'.)
But , if the reporting verb is in the past tense, then usually we change the tenses in the reported speech:
- Reported speech: She said (that) she liked ice cream.
| present simple | I like ice cream | She said (that) she liked ice cream. |
| present continuous | I am living in London | She said (that) she was living in London. |
| past simple | I bought a car | She said (that) she had bought a car OR She said (that) she bought a car. |
| past continuous | I was walking along the street | She said (that) she had been walking along the street. |
| present perfect | I haven't seen Julie | She said (that) she hadn't seen Julie. |
| past perfect* | I had taken English lessons before | She said (that) she had taken English lessons before. |
| will | I'll see you later | She said (that) she would see me later. |
| would* | I would help, but... | She said (that) she would help but... |
| can | I can speak perfect English | She said (that) she could speak perfect English. |
| could* | I could swim when I was four | She said (that) she could swim when she was four. |
| shall | I shall come later | She said (that) she would come later. |
| should* | I should call my mother | She said (that) she should call her mother |
| might* | I might be late | She said (that) she might be late |
| must | I must study at the weekend | She said (that) she must study at the weekend OR She said she had to study at the weekend |
* doesn't change.
- Direct speech: The sky is blue.
- Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
Click here for a mixed tense exercise about practise reported statements. Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.
Reported Questions
So now you have no problem with making reported speech from positive and negative sentences. But how about questions?
- Direct speech: Where do you live?
- Reported speech: She asked me where I lived.
- Direct speech: Where is Julie?
- Reported speech: She asked me where Julie was.
| Where is the Post Office, please? | She asked me where the Post Office was. |
| What are you doing? | She asked me what I was doing. |
| Who was that fantastic man? | She asked me who that fantastic man had been. |
- Direct speech: Do you like chocolate?
- Reported speech: She asked me if I liked chocolate.
| Do you love me? | He asked me if I loved him. |
| Have you ever been to Mexico? | She asked me if I had ever been to Mexico. |
| Are you living here? | She asked me if I was living here. |
Click here to practise reported 'wh' questions. Click here to practise reported 'yes / no' questions. Reported Requests
There's more! What if someone asks you to do something (in a polite way)? For example:
- Direct speech: Close the window, please
- Or: Could you close the window please?
- Or: Would you mind closing the window please?
- Reported speech: She asked me to close the window.
| Please help me. | She asked me to help her. |
| Please don't smoke. | She asked me not to smoke. |
| Could you bring my book tonight? | She asked me to bring her book that night. |
| Could you pass the milk, please? | She asked me to pass the milk. |
| Would you mind coming early tomorrow? | She asked me to come early the next day. |
- Direct speech: Please don't be late.
- Reported speech: She asked us not to be late.
Reported Orders
- Direct speech: Sit down!
- Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
| Go to bed! | He told the child to go to bed. |
| Don't worry! | He told her not to worry. |
| Be on time! | He told me to be on time. |
| Don't smoke! | He told us not to smoke. |
- Click here for an exercise to practise reported requests and orders.
| now | then / at that time |
| today | yesterday / that day / Tuesday / the 27th of June |
| yesterday | the day before yesterday / the day before / Wednesday / the 5th of December |
| last night | the night before, Thursday night |
| last week | the week before / the previous week |
| tomorrow | today / the next day / the following day / Friday |
- Click here for an exercise about using 'say' and 'tell'.
- Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method
Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) in English – Summary
How to use reported speech.
If you have a sentence in Direct Speech, try to follow our 5 steps to put the sentence into Reported Speech..
- Define the type of the sentence (statement, questions, command)
- What tense is used in the introductory sentence?
- Do you have to change the person (pronoun)?
- Do you have to backshift the tenses?
- Do you have to change expressions of time and place?
1. Statements, Questions, Commands
Mind the type of sentences when you use Reported Speech. There is more detailed information on the following pages.
- Commands, Requests
2. The introductory sentence
If you use Reported Speech there are mostly two main differences.
The introductory sentence in Reported Speech can be in the Present or in the Past .
If the introductory sentences is in the Simple Present, there is no backshift of tenses.
Direct Speech:
- Susan, “ Mary work s in an office.”
Reported Speech:
- Introductory sentence in the Simple Present → Susan says (that)* Mary work s in an office.
- Introductory sentence in the Simple Past → Susan said (that)* Mary work ed in an office.
3. Change of persons/pronouns
If there is a pronoun in Direct Speech, it has possibly to be changed in Reported Speech, depending on the siutation.
- Direct Speech → Susan, “I work in an office.”
- Reported Speech → Susan said (that)* she worked in an office.
Here I is changed to she .
4. Backshift of tenses
If there is backshift of tenses in Reported Speech, the tenses are shifted the following way.
- Direct Speech → Peter, “ I work in the garden.”
- Reported Speech → Peter said (that)* he work ed in the garden.
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Simple forms | |
| Simple Present | Simple Past |
| Simple Past | Past Perfect |
| Present Perfect | |
| Past Perfect | |
| will | would |
| Progressive forms | |
| am/are/is | was/were |
| was/were | had been |
| has been | |
| had been | |
5. Conversion of expressions of time and place
If there is an expression of time/place in the sentence, it may be changed, depending on the situation.
- Direct Speech → Peter, “I worked in the garden yesterday .”
- Reported Speech → Peter said (that) he had worked in the garden the day before .
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| this evening | that evening |
| today/this day | that day |
| these days | those days |
| now | then |
| a week ago | a week before |
| last weekend | the weekend before / the previous weekend |
| next week | the following week |
| tomorrow | the next/following day |
| here | there |
6. Additional information
In some cases backshift of tenses is not necessary, e.g. when statements are still true. Backshift of tenses is never wrong.
- John, “My brother is at Leipzig university.”
- John said (that) his brother was at Leipzig university. or
- John said (that) his brother is at Leipzig university.
when you use general statements.
- Mandy, “The sun rises in the east.”
- Mandy said (that) the sun rose in the east. or
- Mandy said (that) the sun rises in the east.
* The word that is optional, that is the reason why we put it in brackets.
- You are here:
- Grammar Explanations
- Reported Speech
The Reported Speech

Table of Contents
What is reported speech.
Reported speech is also referred to as indirect speech or indirect discourse .
Before explaining how to report a discourse, let us first distinguish between direct speech and reported speech .
Direct speech vs reported speech
More examples:
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|
| She says: “I like tuna fish.” | She says that she likes tuna fish. |
| She said: “I’m visiting Paris next weekend.” | She said that she was visiting Paris the following weekend. |
| He asked Betty: “Do you like cheese?” | He wanted to know if Betty liked cheese. |
Different types of reported speech
A. reporting statements, 1- pronouns.
| Shifting back tense | Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|---|
| (no backshift) | “I poems.” | He that he poems. |
| (backshift) | “I poems | He that he poems. |
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| He said: “I happy” | He said that he happy |
| He said: “I for my keys” | He said that he for his keys |
| He said: “I New York last year” | He said that he New York the previous year. |
| He said: ” I here for a long time “ | He said that he there for a long time |
| He said: “They the work when I “ | He said that they the work when he “ |
| He said: “I football when the accident “ | He said that football when the accident |
| He said: “I football for two hours.” | He said that football for two hours |
| He said: “I a newspaper when the light “ | He said that he a newspaper when the light |
| He said: “I the door.” | He said that the door. |
| He said: “I a Mercedes if I rich” | He said that he a Mercedes if he rich |
3. Modal verbs
| Modal | Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|---|
| can | “I do it.” | He said that he do it. |
| may | “ I go out?” | He wanted to know if he go out. |
| must | “She apply for the job.” | He said that she apply for the job. |
| will | “They call you.” | He told her that they call her. |
4- Place, demonstratives, and time expressions
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|
| Time Expressions | |
| today | that day |
| now | then |
| yesterday | the day before |
| … days ago | … days before |
| last week | the week before/the previous week |
| next year | the following year/the next year/ the year after |
| tomorrow | the next day/the following day |
| Place | |
| here | there |
| Demonstratives | |
| this | that |
| these | those |
B. Reporting Questions
| Types of questions | Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|---|
| With question words (what, why, where, how…) | “Why don’t you speak English?” | He asked me why I didn’t speak English. |
| Without question words (yes or no questions) | “Do you speak English?” | He asked me whether/if I spoke English. |
C. Reporting requests/commands
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|
| “Nancy, do the exercise.” | He told Nancy to do the exercise. |
| “Nancy, give me your pen, please.” | He asked Nancy to give him her pen. |
| Tenses are not relevant for requests, simply use / + verb (infinitive without “to”) |
| For affirmative use + infinitive (without to) For negative requests, use + infinitive (without to). |
D. Other transformations
Main clauses connected with and/but, punctuation rules of the reported speech, can we omit that in the reported speech, list of reporting verbs.
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
|---|---|
| simple present | simple past |
| simple past | past perfect |
| present continuous | past continuous |
| past continuous | past perfect continuous |
| will | would |
| shall | should |
| may | might |
| can | could |
| must | had to |
Reported Speech – Rules, Examples
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
They say gossip is a natural part of human life. That’s why language has evolved to develop grammatical rules about the “he said” and “she said” statements. We call them reported speech.
Every time we use reported speech in English, we are talking about something said by someone else in the past. Thinking about it brings me back to high school, when reported speech was the main form of language!
Learn all about the definition, rules, and examples of reported speech as I go over everything. I also included a worksheet at the end of the article so you can test your knowledge of the topic.
What Does Reported Speech Mean?
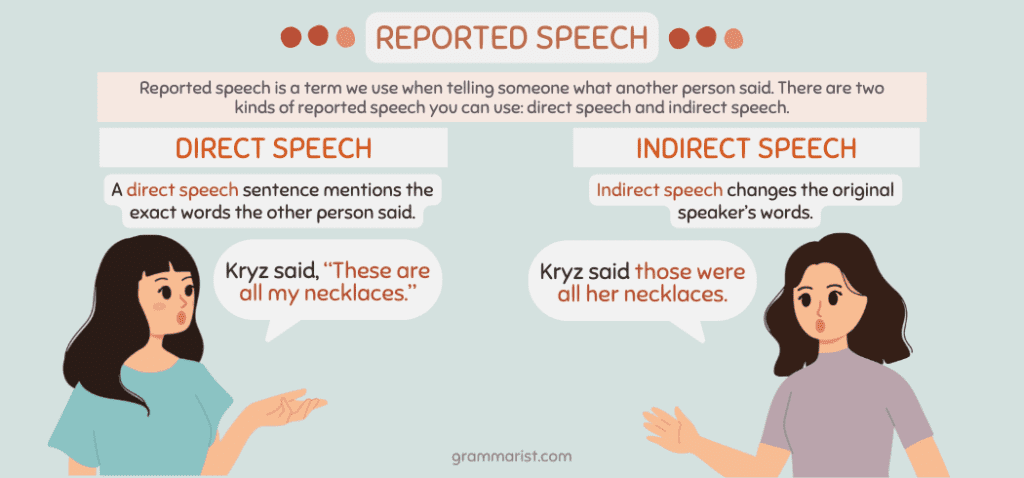
Reported speech is a term we use when telling someone what another person said. You can do this while speaking or writing.
There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I’ll break each down for you.
A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example:
- Kryz said, “These are all my necklaces.”
Indirect speech changes the original speaker’s words. For example:
- Kryz said those were all her necklaces.
When we tell someone what another individual said, we use reporting verbs like told, asked, convinced, persuaded, and said. We also change the first-person figure in the quotation into the third-person speaker.
Reported Speech Examples
We usually talk about the past every time we use reported speech. That’s because the time of speaking is already done. For example:
- Direct speech: The employer asked me, “Do you have experience with people in the corporate setting?”
Indirect speech: The employer asked me if I had experience with people in the corporate setting.
- Direct speech: “I’m working on my thesis,” I told James.
Indirect speech: I told James that I was working on my thesis.
Reported Speech Structure
A speech report has two parts: the reporting clause and the reported clause. Read the example below:
- Harry said, “You need to help me.”
The reporting clause here is William said. Meanwhile, the reported clause is the 2nd clause, which is I need your help.
What are the 4 Types of Reported Speech?
Aside from direct and indirect, reported speech can also be divided into four. The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative.
Reported Speech Rules
The rules for reported speech can be complex. But with enough practice, you’ll be able to master them all.
Choose Whether to Use That or If
The most common conjunction in reported speech is that. You can say, “My aunt says she’s outside,” or “My aunt says that she’s outside.”
Use if when you’re reporting a yes-no question. For example:
- Direct speech: “Are you coming with us?”
Indirect speech: She asked if she was coming with them.
Verb Tense Changes
Change the reporting verb into its past form if the statement is irrelevant now. Remember that some of these words are irregular verbs, meaning they don’t follow the typical -d or -ed pattern. For example:
- Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken.
Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken.
Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form.
Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting. This verb tense also works if the report is something someone would repeat. For example:
- Slater says they’re opening a restaurant soon.
- Maya says she likes dogs.
This rule proves that the choice of verb tense is not a black-and-white question. The reporter needs to analyze the context of the action.
Move the tense backward when the reporting verb is in the past tense. That means:
- Present simple becomes past simple.
- Present perfect becomes past perfect.
- Present continuous becomes past continuous.
- Past simple becomes past perfect.
- Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous.
Here are some examples:
- The singer has left the building. (present perfect)
He said that the singers had left the building. (past perfect)
- Her sister gave her new shows. (past simple)
- She said that her sister had given her new shoes. (past perfect)
If the original speaker is discussing the future, change the tense of the reporting verb into the past form. There’ll also be a change in the auxiliary verbs.
- Will or shall becomes would.
- Will be becomes would be.
- Will have been becomes would have been.
- Will have becomes would have.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I will be there in a moment.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would be there in a moment.
Do not change the verb tenses in indirect speech when the sentence has a time clause. This rule applies when the introductory verb is in the future, present, and present perfect. Here are other conditions where you must not change the tense:
- If the sentence is a fact or generally true.
- If the sentence’s verb is in the unreal past (using second or third conditional).
- If the original speaker reports something right away.
- Do not change had better, would, used to, could, might, etc.
Changes in Place and Time Reference
Changing the place and time adverb when using indirect speech is essential. For example, now becomes then and today becomes that day. Here are more transformations in adverbs of time and places.
- This – that.
- These – those.
- Now – then.
- Here – there.
- Tomorrow – the next/following day.
- Two weeks ago – two weeks before.
- Yesterday – the day before.
Here are some examples.
- Direct speech: “I am baking cookies now.”
Indirect speech: He said he was baking cookies then.
- Direct speech: “Myra went here yesterday.”
Indirect speech: She said Myra went there the day before.
- Direct speech: “I will go to the market tomorrow.”
Indirect speech: She said she would go to the market the next day.
Using Modals

If the direct speech contains a modal verb, make sure to change them accordingly.
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- Shall becomes should or would.
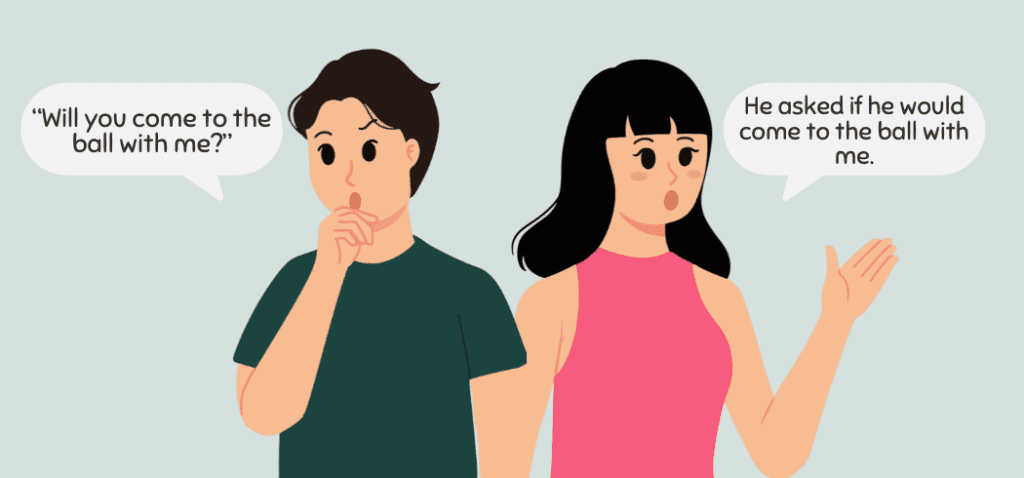
- Direct speech: “Will you come to the ball with me?”
Indirect speech: He asked if he would come to the ball with me.
- Direct speech: “Gina can inspect the room tomorrow because she’s free.”
Indirect speech: He said Gina could inspect the room the next day because she’s free.
However, sometimes, the modal verb should does not change grammatically. For example:
- Direct speech: “He should go to the park.”
Indirect speech: She said that he should go to the park.
Imperative Sentences
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please . Instead, say request or say. For example:
- “Please don’t interrupt the event,” said the host.
The host requested them not to interrupt the event.
- Jonah told her, “Be careful.”
- Jonah ordered her to be careful.
Reported Questions
When reporting a direct question, I would use verbs like inquire, wonder, ask, etc. Remember that we don’t use a question mark or exclamation mark for reports of questions. Below is an example I made of how to change question forms.
- Incorrect: He asked me where I live?
Correct: He asked me where I live.
Here’s another example. The first sentence uses direct speech in a present simple question form, while the second is the reported speech.
- Where do you live?
She asked me where I live.
Wrapping Up Reported Speech
My guide has shown you an explanation of reported statements in English. Do you have a better grasp on how to use it now?
Reported speech refers to something that someone else said. It contains a subject, reporting verb, and a reported cause.
Don’t forget my rules for using reported speech. Practice the correct verb tense, modal verbs, time expressions, and place references.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.

Reported Speech: Important Grammar Rules and Examples
Reported speech is a very common thing in the English language. We do it almost every day, in conversation and in writing. The problem is, sometimes there can be some confusion around the topic. So today we’ll take a look at reported speech: what it is, how to use it, and we’ll give some interactive exercises of reported speech too, so you can see how it looks in everyday conversations or writing.
Reported Speech
When we use reported speech, we are referring to something that was said either by ourselves or by someone else in the past. An example of this might be ‘he said that he was going shopping. This type of speech is used very frequently during both spoken and written examples of English and it is an important part of the language which any English student will find useful to learn. In this section, we are going to look at types of reported speech as well as how we can use it.
What is Reported Speech?
Reported speech is simply when we tell somebody what someone else said. You can do this in your writing, or in speech. Reported speech is very different from direct speech , which is when you show what somebody said in the exact way that they said it . In reported speech though, you do not need to quote somebody directly.
Instead, we use a reporting verb, such as ‘say’ or ‘ask’. These reporting verbs are used to report the speech to someone else. There are many different reporting verbs that can be used, and we’ll try to use different ones throughout this article to show you some examples, but you can always do some research too if you want to learn more examples for yourself.
In short, reported speech is the linguistic technique that we use to tell somebody what someone else’s direct speech was. In reported speech though, you may need to make certain changes to the grammar to make the sentence make sense. So, we’ll look at some grammar change examples below and highlight what needs to be changed.
Reported Speech Examples
When we use reported speech, we are usually talking about the past (because obviously, the person who spoke originally spoke in the past). The verbs therefore usually have to be in the past too.
For example :
- Direct speech: I’ve lost my umbrella .
- Reported speech: He said (that) he had lost his umbrella.
Reported Speech Rules
When changing from direct to indirect speech, you need to change the grammar in certain ways. In this section, we are going to be looking a little more closely at direct and indirect speech and how they are used.

Verb Tense Changes in Reported Speech

If the reporting verb is in the present tense, then very little needs to be done to the direct speech sentence to change it. Here’s an example.
- Direct speech: I like dogs.
- Reported speech: She says she likes dogs.
Here nothing really needed to be changed except the pronoun, because you are now talking about somebody else, so ‘I’ becomes ‘She’ or ‘He’. The tense is still the same because ‘says’ is the present tense version of the reporting verb. But what happens if the sentence needs to be changed to past tense?
Sometimes it is necessary to change the reporting verb into the past tense if what was said is no longer relevant, or was said sometime in the past. Here are the changes that would need to be made.
- Reported speech: She said she liked dogs.
As well as changing the pronouns here, we’ve had to change the tense of both the reporting verb and the verb. So, ‘says’ becomes ‘said’ and ‘like’ becomes ‘liked’.
When the reporting verb is in the past tense, verb tense forms usually need to change. The tenses generally move backward in this way:
- Present Simple Tense into Past Simple Tense
- Present Continuous Tense into Past Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Tense into Past Perfect Tense
- Past Simple Tense into Past Perfect Tense
- Past Continuous Tense into Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense (the tense remains unchanged)
If somebody is talking about what will happen in the future then, again, you will need to change the tense of the reporting verb.
- Direct speech: I shall leave in a moment.
- Reported speech: She said that she would leave in a moment.
Notice how ‘shall’ and “will” become ‘would’ here in order for it to make sense.
- Will into Would
- Will be into Would be
- Will have into Would have
- Will have been into Would have been
Modal verbs actually have a very interesting relationship with reported speech, so we’ll look at that below too.
Modal Verbs and Reported Speech
We’ve already covered modal verbs in another article, but it’s interesting to see how they are changed in reported speech.
- Can into Could
- Could (The verb remains unchanged)
- Have to into Had to
- Must into Must/Had to
- May into Might
- Might (The verb remains unchanged)
- Should (The verb remains unchanged)
Let’s take a look at some examples.
- Direct speech: Will I see you later?
- Reported speech: He asked if he would see me later.
In the direct speech example you can see the modal verb ‘will’ being used to ask a question. Notice how in reported speech the modal verb ‘will’ and the reporting verb ‘ask’ are both written in the past tense. So, ‘will’ becomes ‘would’ and ‘ask’ becomes ‘asked’. It’s important in reported speech to make sure that each part of the sentence is in the same tense.
Sometimes though, modal verbs do not need to change tense because they already read correctly. Here’s an example.
- Direct speech: I should go to the park.
- Reported speech: He told me he should go to the park.
Notice that nothing needed to be changed here to fit the past tense reporting verb ‘told’. ‘Should’ does not need to be changed grammatically for either sentence to make sense. But you will notice that because we decided to use the reporting verb ‘told’ instead of ‘said’, we had to include the pronoun ‘me’ for it to make sense.
- Reported speech: He told me he should go to the park.
- Reported speech: He said he should go to the park.
Both of these sentences make grammatical sense, because we added the pronoun ‘me’ after ‘told’ in the first sentence, but we didn’t after ‘said’ in the second one. Here is the incorrect versions so you can see why it doesn’t work grammatically:
- Incorrect reported speech: He told he should go to the park.
- Incorrect reported speech: He said me he should go to the park.
In order to make the top one make sense, we need to add ‘me’ like we did in the correct examples above. In order to make the second one make sense, we would either have to remove ‘me’ like we did in the correct one above, or we would have to add another word. So that it looked like this.
- Reported speech: He said to me he should go to the park.
The above sentence makes sense, but sometimes you have to watch your wording of certain things to make sure that you aren’t over-speaking/writing. This can be a problem if you are trying to get your point across quickly. You should always choose the option that is quickest to say/write because it sounds/looks better and you run less risk of making a grammatical mistake.
This guide could not possibly be extensive, because there are many grammar rules that need to be followed when reporting speech, but they vary wildly. The take-home message should really be that when reporting speech, it is important to think carefully about what you are going to say or write, so you know it makes sense. Hopefully, this guide served as a good starting point though, so you can identify reported speech now, and start to think about which grammar rules are applied.
Direct and Indirect Speech
Changes in time and place in reported speech.
Time and place references often have to change in Indirect Speech
- Now –> Then
- Today –> That day
- Here –> There
- This –> That
- Tomorrow –> The following day/ The next day/ The day after
- Next week –> The following week/ The next week/ The week after
- Yesterday –> The previous day/ The day before
- Last week –> The previous week/ The week before
- Ago –> Previously/ Before
- Tonight –> That night
No Change in Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
There is no change in verb tenses in Indirect Speech when:
- The introductory verb is in the Present, Present Perfect or Future .
- If the reported sentence deals with a fact or general truth .
- The reported sentence contains a time clause .
- The verb of the sentence is in the unreal past (the second or the third conditional ).
- The subjunctive stays unchanged in the subordinate clause .
- Had better , could , would , used to , should , might , ought to and mustn’t remain unchanged.
- If the speaker reports something immediately or soon after it was said .
Reporting Verbs in Indirect Speech
List of reporting verbs in reported speech.
- Tell, say, ask.
- Verb + that + clause : complain, deny, explain, exclaim, remark, promise, boast, inform somebody, claim, agree, suggest.
- Verb + to + infinitive : agree, offer, refuse, demand, threaten, promise, claim.
- Verb + indirect object + to + infinitive : advise, allow, beg, command, encourage, forbid, invite, want, instruct, permit, urge, order, remind, warn.
- Verb + “ing” form : admit (to), accuse somebody of, apologize for, boast about/ of, complain to somebody of, deny, insist on, suggest.
- Verb + how : explain to somebody.
Reported Questions in English
When you are changing a question from direct speech into indirect speech, you follow the same kinds of rules as for statements.
To report a question , we use verbs such as inquire, wonder, want to know, ask…
Reported Commands and Requests in English
Reported Orders, Commands, and Requests are formed using the to-infinitive and not to-infinitive.
The reporting verbs for the orders/ commands/ requests are order, shout, demand, warn, beg, command, tell, insist, beseech , threaten, implore, ask, propose, forbid…
When we change from direct to indirect speech, the pronoun and tense changes are also needed.
Reported Speech Video
- Latest Posts
- Active vs. Passive Voice Exercises – Active vs. Passive Voice Worksheet - December 25, 2023
- Phrase Exercises – Phrase Worksheet - December 23, 2023
- Sentence Exercises – Sentence Worksheet - December 23, 2023
Exercise on Reported Speech
Rewrite the sentences in reported speech. Change pronouns and time expressions where necessary.
- She said, "I am reading." → She said that
- They said, "We are busy." → They said that
- He said, "I know a better restaurant." → He said that
- She said, "I woke up early." → She said that
- He said, "I will ring her." → He said that
- They said, "We have just arrived." → They said that
- He said, "I will clean the car." → He said that
- She said, "I did not say that." → She said that
- She said, "I don't know where my shoes are." → She said that
- He said: "I won't tell anyone." → He said that
| |
Reported Speech – Free Exercise
Write the following sentences in indirect speech. Pay attention to backshift and the changes to pronouns, time, and place.
- Two weeks ago, he said, “I visited this museum last week.” → Two weeks ago, he said that . I → he simple past → past perfect this → that last …→ the … before
- She claimed, “I am the best for this job.” → She claimed that . I → she simple present→ simple past this→ that
- Last year, the minister said, “The crisis will be overcome next year.” → Last year, the minister said that . will → would next …→ the following …
- My riding teacher said, “Nobody has ever fallen off a horse here.” → My riding teacher said that . present perfect → past perfect here→ there
- Last month, the boss explained, “None of my co-workers has to work overtime now.” → Last month, the boss explained that . my → his/her simple present→ simple past now→ then
Rewrite the question sentences in indirect speech.
- She asked, “What did he say?” → She asked . The subject comes directly after the question word. simple past → past perfect
- He asked her, “Do you want to dance?” → He asked her . The subject comes directly after whether/if you → she simple present → simple past
- I asked him, “How old are you?” → I asked him . The subject comes directly after the question word + the corresponding adjective (how old) you→ he simple present → simple past
- The tourists asked me, “Can you show us the way?” → The tourists asked me . The subject comes directly after whether/if you→ I us→ them
- The shop assistant asked the woman, “Which jacket have you already tried on?” → The shop assistant asked the woman . The subject comes directly after the question word you→ she present perfect → past perfect
Rewrite the demands/requests in indirect speech.
- The passenger requested the taxi driver, “Stop the car.” → The passenger requested the taxi driver . to + same wording as in direct speech
- The mother told her son, “Don’t be so loud.” → The mother told her son . not to + same wording as in direct speech, but remove don’t
- The policeman told us, “Please keep moving.” → The policeman told us . to + same wording as in direct speech ( please can be left off)
- She told me, “Don’t worry.” → She told me . not to + same wording as in direct speech, but remove don’t
- The zookeeper told the children, “Don’t feed the animals.” → The zookeeper told the children . not to + same wording as in direct speech, but remove don’t
How good is your English?
Find out with Lingolia’s free grammar test
Take the test!
Maybe later
- English Grammar
- Reported Speech
Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how far you have understood the topic.

Table of Contents
Definition of reported speech, rules to be followed when using reported speech, table 1 – change of pronouns, table 2 – change of adverbs of place and adverbs of time, table 3 – change of tense, table 4 – change of modal verbs, tips to practise reported speech, examples of reported speech, check your understanding of reported speech, frequently asked questions on reported speech in english, what is reported speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message.
Now, take a look at the following dictionary definitions for a clearer idea of what it is.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
Reported speech is a little different from direct speech . As it has been discussed already, reported speech is used to tell what someone said and does not use the exact words of the speaker. Take a look at the following rules so that you can make use of reported speech effectively.
- The first thing you have to keep in mind is that you need not use any quotation marks as you are not using the exact words of the speaker.
- You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech.
| Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said) |
- You can use verbs like said, asked, requested, ordered, complained, exclaimed, screamed, told, etc. If you are just reporting a declarative sentence , you can use verbs like told, said, etc. followed by ‘that’ and end the sentence with a full stop . When you are reporting interrogative sentences, you can use the verbs – enquired, inquired, asked, etc. and remove the question mark . In case you are reporting imperative sentences , you can use verbs like requested, commanded, pleaded, ordered, etc. If you are reporting exclamatory sentences , you can use the verb exclaimed and remove the exclamation mark . Remember that the structure of the sentences also changes accordingly.
- Furthermore, keep in mind that the sentence structure , tense , pronouns , modal verbs , some specific adverbs of place and adverbs of time change when a sentence is transformed into indirect/reported speech.
Transforming Direct Speech into Reported Speech
As discussed earlier, when transforming a sentence from direct speech into reported speech, you will have to change the pronouns, tense and adverbs of time and place used by the speaker. Let us look at the following tables to see how they work.
| I | He, she |
| Me | Him, her |
| We | They |
| Us | Them |
| You | He, she, they |
| You | Him, her, them |
| My | His, her |
| Mine | His, hers |
| Our | Their |
| Ours | Theirs |
| Your | His, her, their |
| Yours | His, hers, theirs |
| This | That |
| These | Those |
| Here | There |
| Now | Then |
| Today | That day |
| Tomorrow | The next day / The following day |
| Yesterday | The previous day |
| Tonight | That night |
| Last week | The week before |
| Next week | The week after |
| Last month | The previous month |
| Next month | The following month |
| Last year | The previous year |
| Next year | The following year |
| Ago | Before |
| Thus | So |
| Simple Present Example: Preethi said, “I cook pasta.” | Simple Past Example: Preethi said that she cooked pasta. |
| Present Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I am cooking pasta.” | Past Continuous Example: Preethi said that she was cooking pasta. |
| Present Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I have cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Present Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I have been cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Simple Past Example: Preethi said, “I cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Past Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I was cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Past Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I had cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect (No change) Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I had been cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous (No change) Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Will | Would |
| May | Might |
| Can | Could |
| Shall | Should |
| Has/Have | Had |
Here are some tips you can follow to become a pro in using reported speech.
- Select a play, a drama or a short story with dialogues and try transforming the sentences in direct speech into reported speech.
- Write about an incident or speak about a day in your life using reported speech.
- Develop a story by following prompts or on your own using reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written. Check them out.
- Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl.
- Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations.
- Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were.
- The judges announced that the Warblers were the winners of the annual acapella competition.
- Binsha assured that she would reach Bangalore by 8 p.m.
- Kumar said that he had gone to the doctor the previous day.
- Lakshmi asked Teena if she would accompany her to the railway station.
- Jibin told me that he would help me out after lunch.
- The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
- Rahul said that he was drawing a caricature.
Transform the following sentences into reported speech by making the necessary changes.
1. Rachel said, “I have an interview tomorrow.”
2. Mahesh said, “What is he doing?”
3. Sherly said, “My daughter is playing the lead role in the skit.”
4. Dinesh said, “It is a wonderful movie!”
5. Suresh said, “My son is getting married next month.”
6. Preetha said, “Can you please help me with the invitations?”
7. Anna said, “I look forward to meeting you.”
8. The teacher said, “Make sure you complete the homework before tomorrow.”
9. Sylvester said, “I am not going to cry anymore.”
10. Jade said, “My sister is moving to Los Angeles.”
Now, find out if you have answered all of them correctly.
1. Rachel said that she had an interview the next day.
2. Mahesh asked what he was doing.
3. Sherly said that her daughter was playing the lead role in the skit.
4. Dinesh exclaimed that it was a wonderful movie.
5. Suresh said that his son was getting married the following month.
6. Preetha asked if I could help her with the invitations.
7. Anna said that she looked forward to meeting me.
8. The teacher told us to make sure we completed the homework before the next day.
9. Sylvester said that he was not going to cry anymore.
10. Jade said that his sister was moving to Los Angeles.
What is reported speech?
What is the definition of reported speech.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
What is the formula of reported speech?
You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech. Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said)
Give some examples of reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written.
| ENGLISH Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Reported Speech
Learn how to use reported speech in English. Reported speech is also known as indirect speech and is used to tell somebody else what another person said. Using reported speech in English can sometimes be difficult for non-native speakers as we (usually) change the verbs, pronouns and specific times.
Keep reading to understand how to use reported speech and download this free English lesson!

Let’s study reported speech !
Reported speech vs. direct speech.
When we want to tell somebody else what another person said, we can use either direct speech or reported speech .
When we use d irect speech, we use the same words but use quotation marks, “_”. For example:
Scott said, “I am coming to work. I will be late because there is a lot of traffic now.”
When we use r eported speech, we usually change the verbs, specific times, and pronouns. For example:
Scott said that he was coming to work. He said that he would be late because there was a lot of traffic at that time.
How do we use reported speech ?
Since reported speech is usually talking about the past, we usually change the verbs into the past. It is always necessary to change the verbs when the action has finished or is untrue.
We do not always change the verbs. When you are reporting an action that is still current or true, it is not necessary to change the verb tense. For example:
How old are you? “ I am twenty-seven years old .” She said she is twenty-seven years old.
We usually follow the rules below. When we are reporting speech, we are usually talking about the past; therefore, we change the verbs into the past.
|
|
“I eat pizza.” | He said (that) he ate pizza. |
“I am eating pizza.” | He said (that) he was eating pizza. |
“I will eat pizza.” | He said (that) he would eat pizza. |
“I am going to eat pizza.” | He said (that) he was going to eat pizza. |
When we are reporting past actions, it is not always necessary to change the verb tense. We can usually leave the verbs in the same tense and just change the pronouns. However, we sometimes need to use the to clarify the time order of events. the never changes in . | |
“I ate pizza.” “I ate pizza, so I am not hungry.” | He said (that) he ate pizza. He said (that) he had eaten pizza, so he wasn’t hungry.” |
“I was eating pizza.” “I was eating pizza when she called.” | He said (that) he was eating pizza. He said (that) he had been eating pizza when she called. |
Reporting Questions
We use a special form when we report questions:
WH-Questions:
Where is + Tom’s house ? He asked where Tom’s house + was.
Where does Tom live? He asked where Tom lived.
Yes/No Questions:
Does Tom live in Miami? She asked if Tom lived in Miami.
Is Tom happy? She asked if Tom was happy.
Say vs. Tell
Say Something
June: “I love English .”
June said (that) she loved English.
Tell Someone Something
June: “I love English.”
June told me (that) she loved English.
Modal Verbs and Reported Speech
Must, might, could, would, should , and ought to stay the same in re ported s peech . We usually change may to might .
Infinitives and Reported Speech
Infinitives stay the same in reported speech:
“ I am going to the store to buy milk.” He said he was going to the store to buy milk.
We also use infinitives when reporting orders and commands, especially when using tell .
“ Do your homework. Don’t use a dictionary!!” He told me to do to my homework and not to use a dictionary.
Reporting Suggestions
When we are reporting another speakers suggestions, we can use a special form with suggest, recommend, or propose .
SUGGEST/ RECOMMEND/PROPOSE + (*THAT) + SUBJECT PRONOUN + **V1
SUGGEST/ RECOMMEND/PROPOSE + V1 + ING
“I think you should visit Viscaya.” → He suggested we visit Viscaya. He suggested visiting Viscaya.
“Try to get there early to get good seats.” → He recommended we get there early to get good seats.
*That is often omitted in speech.
**The verb is always in the base form. We do not use third person.
Reporting Statements
A reported statement begins with an introductory clause and is followed by the ‘information’ clause. The speaker may choose different words, but the meaning remains unchanged. Some formal words to introduce a reported statement or response are: declared, stated, informed, responded, replied, etc.
“I don’t agree with these new rules. I am not going to accept this change!” → He declared that he was in disagreement with the new rules and stated that he would not accept the changes.
Free English Lesson PDF Download
Reported Speech ~ Exercises and Practice
A. Change each direct speech example into the reported speech . The first one has been done for you.
- Michelle said, “I love my Chihuahua, Daisy.”
Michelle said that she loved her Chihuahua, Daisy.
2. Republicans said, “We don’t support Obama’s plan to raise taxes.”
__________________________________________________________.
3.With her mouth full, Sarah said, “I am eating mashed potatoes.”
4. John Lee said, “This year, I will not pay my taxes.”
5. Lebron said, “I am going to win the championship next year.”
6. Patty said, “I can’t stomach another hamburger. I ate one yesterday.”
B. Rewrite the sentences/questions below using reported / indirect speech . Always change the tense, even though it is not always necessary. You can use ‘said’, ‘told me’ , or ‘asked’ .
1. Sarah: “I am in the shower right now.”
_____________________________________________________________________________
2. John: “I dropped my son off at school this morning.”
3. Samuel: “I am going to the beach with my sister this afternoon.”
4. John: “Jessica will call you later.”
5. The girls: “Who does John live with?”
6. Our classmate: “Did we have any homework last night?”
7. Sarah: “I am moving to Tokyo because I want to learn Japanese.”
8. John: “Why do you have an umbrella?”
9. The students: “Our teacher can’t find her books anywhere.”
10. Sarah and Jillian: “Is John British?”
11. Steve: “I’m going to the beach so that I can play volleyball.”
__________________________________________________________________________________
12. Ann: “Where is the bathroom?”
13. My parents: “What are you going to do with your life?”
14. Sarah: “I ate breakfast before I came to school.”
C. Your friend Megan is very nosy (she always wants to know what’s going on) so she constantly asks questions about your life and the lives of your friends. Rewrite her questions using the reported questions form. The first one has been done for you .
1. Why do you date Ryan?
She asked me why I dated Ryan.
2. How much money do you make at your new job?
________________________________________________________________________________
3. Does Ryan think I’m pretty?
4. Where is your favorite restaurant?
5. Do I look good in these jeans?
6. Can I borrow some twenty bucks?
D. Your American grandfather is telling you about how things used to be. Using the reported speech , tell your friends what he said.
“In the 1930s, people were very poor. They ate watery soup and hard bread. Many people lost their jobs. To make matters worse, a horrible drought ruined most of the farmland in the American midwest. People went to California to look for a better life. They picked strawberries in the hot California sun.”
Did you download this lesson? If not, don’t forget to download this free English lesson.
If you have any questions about English grammar, please contact us via email us or just comment below. I hope this lesson helped you understand how to use reported speech in English.
Click here to subscribe to our newsletter! #TurnYourLanguageOn
Do you need to improve your English? See the locations of our English language schools in the United States.

Take our FREE Proficiency Test and
Discover your English Proficiency Level!

Proud partners with National Geographic Learning

Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Type | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ajs_anonymous_id | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| ajs_group_id | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| ajs_user_id | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| centerVisitorId | persistent | 7981 years | Description unavailable. |
| fr | persistent | 3 months | Description unavailable. |
| hblid | persistent | 2 years | Description unavailable. |
| NID | persistent | 6 months | Description unavailable. |
| olfsk | persistent | 2 years | Description unavailable. |
| test_cookie | persistent | 15 minutes | Description unavailable. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | persistent | 1 hour | Description unavailable. |
| wcsid | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| wordpress_test_cookie | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| _fbp | persistent | 2 hours | Description unavailable. |
| _ga | persistent | 2 year | Description unavailable. |
| _gat | session | 1 minute | Description unavailable. |
| _gid | persistent | 1 day | Description unavailable. |
| _hjIncludedInSample | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| _ok | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| _okbk | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| _okdetect | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| _oklv | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
| __cfduid | persistent | 1 year | Description unavailable. |
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
Reported Speech in English
“Reported speech” might sound fancy, but it isn’t that complicated.
It’s just how you talk about what someone said.
Luckily, it’s pretty simple to learn the basics in English, beginning with the two types of reported speech: direct (reporting the exact words someone said) and indirect (reporting what someone said without using their exact words ).
Read this post to learn how to report speech, with tips and tricks for each, plenty of examples and a resources section that tells you about real world resources you can use to practice reporting speech.
How to Report Direct Speech
How to report indirect speech, reporting questions in indirect speech, verb tenses in indirect reported speech, simple present, present continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, simple past, past continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, simple future, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, authentic resources for practicing reported speech, novels and short stories, native english videos, celebrity profiles.
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Direct speech refers to the exact words that a person says. You can “report” direct speech in a few different ways.
To see how this works, let’s pretend that I (Elisabeth) told some people that I liked green onions.
Here are some different ways that those people could explain what I said:
Direct speech: “I like green onions,” Elisabeth said.
- Thousands of learner friendly videos (especially beginners)
- Handpicked, organized, and annotated by FluentU's experts
- Integrated into courses for beginners

Direct speech: “I like green onions,” she told me. — In this sentence, we replace my name (Elisabeth) with the pronoun she.
In all of these examples, the part that was said is between quotation marks and is followed by a noun (“she” or “Elisabeth”) and a verb. Each of these verbs (“to say,” “to tell [someone],” “to explain”) are ways to describe someone talking. You can use any verb that refers to speech in this way.
You can also put the noun and verb before what was said.
Direct speech: Elisabeth said, “I like spaghetti.”
The example above would be much more likely to be said out loud than the first set of examples.
Here’s a conversation that might happen between two people:
- Interactive subtitles: click any word to see detailed examples and explanations
- Slow down or loop the tricky parts
- Show or hide subtitles
- Review words with our powerful learning engine
1: Did you ask her if she liked coffee?
2: Yeah, I asked her.
1: What did she say?
2. She said, “Yeah, I like coffee.” ( Direct speech )
Usually, reporting of direct speech is something you see in writing. It doesn’t happen as often when people are talking to each other.
Direct reported speech often happens in the past. However, there are all kinds of stories, including journalism pieces, profiles and fiction, where you might see speech reported in the present as well.
This is sometimes done when the author of the piece wants you to feel that you’re experiencing events in the present moment.
- Learn words in the context of sentences
- Swipe left or right to see more examples from other videos
- Go beyond just a superficial understanding

For example, a profile of Kristen Stewart in Vanity Fair has a funny moment that describes how the actress isn’t a very good swimmer:
Direct speech: “I don’t want to enter the water, ever,” she says. “If everyone’s going in the ocean, I’m like, no.”
Here, the speech is reported as though it’s in the present tense (“she says”) instead of in the past (“she said”).
In writing of all kinds, direct reported speech is often split into two or more parts, as it is above.
Here’s an example from Lewis Carroll’s “ Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland ,” where the speech is even more split up:
Direct speech: “I won’t indeed!” said Alice, in a great hurry to change the subject of conversation. “Are you—are you fond—of—of dogs?” The Mouse did not answer, so Alice went on eagerly: “There is such a nice little dog near our house I should like to show you!”
Reporting indirect speech is what happens when you explain what someone said without using their exact words.
- FluentU builds you up, so you can build sentences on your own
- Start with multiple-choice questions and advance through sentence building to producing your own output
- Go from understanding to speaking in a natural progression.
Let’s start with an example of direct reported speech like those used above.
Direct speech: Elisabeth said, “I like coffee.”
As indirect reported speech, it looks like this:
Indirect speech: Elisabeth said she liked coffee.
You can see that the subject (“I”) has been changed to “she,” to show who is being spoken about. If I’m reporting the direct speech of someone else, and this person says “I,” I’d repeat their sentence exactly as they said it. If I’m reporting this person’s speech indirectly to someone else, however, I’d speak about them in the third person—using “she,” “he” or “they.”
You may also notice that the tense changes here: If “I like coffee” is what she said, this can become “She liked coffee” in indirect speech.
- Images, examples, video examples, and tips
- Covering all the tricky edge cases, eg.: phrases, idioms, collocations, and separable verbs
- No reliance on volunteers or open source dictionaries
- 100,000+ hours spent by FluentU's team to create and maintain
However, you might just as often hear someone say something like, “She said she likes coffee.” Since people’s likes and preferences tend to change over time and not right away, it makes sense to keep them in the present tense.
Indirect speech often uses the word “that” before what was said:
Indirect speech: She said that she liked coffee.
There’s no real difference between “She said she liked coffee” and “She said that she liked coffee.” However, using “that” can help make the different parts of the sentence clearer.
Let’s look at a few other examples:
Indirect speech: I said I was going outside today.

Indirect speech: They told me that they wanted to order pizza.
Indirect speech: He mentioned it was raining.
Indirect speech: She said that her father was coming over for dinner.
You can see an example of reporting indirect speech in the funny video “ Cell Phone Crashing .” In this video, a traveler in an airport sits down next to another traveler talking on his cell phone. The first traveler pretends to be talking to someone on his phone, but he appears to be responding to the second traveler’s conversation, which leads to this exchange:
Woman: “Are you answering what I’m saying?”
Man “No, no… I’m on the phone with somebody, sorry. I don’t mean to be rude.” (Direct speech)
Woman: “What was that?”
Man: “I just said I was on the phone with somebody.” (Indirect speech)
When reporting questions in indirect speech, you can use words like “whether” or “if” with verbs that show questioning, such as “to ask” or “to wonder.”
Direct speech: She asked, “Is that a new restaurant?”
Indirect speech: She asked if that was a new restaurant.
In any case where you’re reporting a question, you can say that someone was “wondering” or “wanted to know” something. Notice that these verbs don’t directly show that someone asked a question. They don’t describe an action that happened at a single point in time. But you can usually assume that someone was wondering or wanted to know what they asked.
Indirect speech: She was wondering if that was a new restaurant.
Indirect speech: She wanted to know whether that was a new restaurant.
It can be tricky to know how to use tenses when reporting indirect speech. Let’s break it down, tense by tense.
Sometimes, indirect speech “ backshifts ,” or moves one tense further back into the past. We already saw this in the example from above:
Direct speech: She said, “I like coffee.”
Indirect speech: She said she liked coffee.
Also as mentioned above, backshifting doesn’t always happen. This might seem confusing, but it isn’t that difficult to understand once you start using reported speech regularly.
What tense you use in indirect reported speech often just depends on when what you’re reporting happened or was true.
Let’s look at some examples of how direct speech in certain tenses commonly changes (or doesn’t) when it’s reported as indirect speech.
To learn about all the English tenses (or for a quick review), check out this post .
Direct speech: I said, “I play video games.”
Indirect speech: I said that I played video games (simple past) or I said that I play video games (simple present).
Backshifting into the past or staying in the present here can change the meaning slightly. If you use the first example, it’s unclear whether or not you still play video games; all we know is that you said you played them in the past.
If you use the second example, though, you probably still play video games (unless you were lying for some reason).
However, the difference in meaning is so small, you can use either one and you won’t have a problem.
Direct speech: I said, “I’m playing video games.”
Indirect speech: I said that I was playing video games (past continuous) or I said that I’m playing video games (present continuous).
In this case, you’d likely use the first example if you were telling a story about something that happened in the past.
You could use the second example to repeat or stress what you just said. For example:
Hey, want to go for a walk?
Direct speech: No, I’m playing video games.
But it’s such a nice day!
Indirect speech: I said that I’m playing video games!
Direct speech: Marie said, “I have read that book.”
Indirect speech: Marie said that she had read that book (past perfect) or Marie said that she has read that book (present perfect).
The past perfect is used a lot in writing and other kinds of narration. This is because it helps point out an exact moment in time when something was true.
The past perfect isn’t quite as useful in conversation, where people are usually more interested in what’s true now. So, in a lot of cases, people would use the second example above when speaking.
Direct speech: She said, “I have been watching that show.”
Indirect speech: She said that she had been watching that show (past perfect continuous) or She said that she has been watching that show (present perfect continuous).
These examples are similar to the others above. You could use the first example whether or not this person was still watching the show, but if you used the second example, it’d probably seem like you either knew or guessed that she was still watching it.
Direct speech: You told me, “I charged my phone.”
Indirect speech: You told me that you had charged your phone (past perfect) or You told me that you charged your phone (simple past).
Here, most people would probably just use the second example, because it’s simpler, and gets across the same meaning.
Direct speech: You told me, “I was charging my phone.”
Indirect speech: You told me that you had been charging your phone (past perfect continuous) or You told me that you were charging your phone (past continuous).
Here, the difference is between whether you had been charging your phone before or were charging your phone at the time. However, a lot of people would still use the second example in either situation.
Direct speech: They explained, “We had bathed the cat on Wednesday.”
Indirect speech: They explained that they had bathed the cat on Wednesday. (past perfect)
Once we start reporting the past perfect tenses, we don’t backshift because there are no tenses to backshift to.
So in this case, it’s simple. The tense stays exactly as is. However, many people might simplify even more and use the simple past, saying, “They explained that they bathed the cat on Wednesday.”
Direct speech: They said, “The cat had been going outside and getting dirty for a long time!”
Indirect speech: They said that the cat had been going outside and getting dirty for a long time. (past perfect continuous)
Again, we don’t shift the tense back here; we leave it like it is. And again, a lot of people would report this speech as, “They said the cat was going outside and getting dirty for a long time.” It’s just a simpler way to say almost the same thing.
Direct speech: I told you, “I will be here no matter what.”
Indirect speech: I told you that I would be here no matter what. (present conditional)
At this point, we don’t just have to think about tenses, but grammatical mood, too. However, the idea is still pretty simple. We use the conditional (with “would”) to show that at the time the words were spoken, the future was uncertain.
In this case, you could also say, “I told you that I will be here no matter what,” but only if you “being here” is still something that you expect to happen in the future.
What matters here is what’s intended. Since this example shows a person reporting their own speech, it’s more likely that they’d want to stress the truth of their own intention, and so they might be more likely to use “will” than “would.”
But if you were reporting someone else’s words, you might be more likely to say something like, “She told me that she would be here no matter what.”
Direct speech: I said, “I’ll be waiting for your call.”
Indirect speech: I said that I would be waiting for your call. (conditional continuous)
These are similar to the above examples, but apply to a continuous or ongoing action.
Direct speech: She said, “I will have learned a lot about myself.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would have learned a lot about herself (conditional perfect) or She said that she will have learned a lot about herself (future perfect).
In this case, using the conditional (as in the first example) suggests that maybe a certain event didn’t happen, or something didn’t turn out as expected.
However, that might not always be the case, especially if this was a sentence that was written in an article or a work of fiction. The second example, however, suggests that the future that’s being talked about still hasn’t happened yet.
Direct speech: She said, “By next Tuesday, I will have been staying inside every day for the past month.”
Indirect speech: She said that by next Tuesday, she would have been staying inside every day for the past month (perfect continuous conditional) or She said that by next Tuesday, she will have been staying inside every day for the past month (past perfect continuous).
Again, in this case, the first example might suggest that the event didn’t happen. Maybe the person didn’t stay inside until next Tuesday! However, this could also just be a way of explaining that at the time she said this in the past, it was uncertain whether she really would stay inside for as long as she thought.
The second example, on the other hand, would only be used if next Tuesday hadn’t happened yet.
Let’s take a look at where you can find resources for practicing reporting speech in the real world.
One of the most common uses for reported speech is in fiction. You’ll find plenty of reported speech in novels and short stories . Look for books that have long sections of text with dialogue marked by quotation marks (“…”). Once you understand the different kinds of reported speech, you can look for it in your reading and use it in your own writing.
Writing your own stories is a great way to get even better at understanding reported speech.
One of the best ways to practice any aspect of English is to watch native English videos. By watching English speakers use the language, you can understand how reported speech is used in real world situations.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Try FluentU for FREE!
Celebrity profiles, which you can find in print magazines and online, can help you find and practice reported speech, too. Celebrity profiles are stories that focus on a famous person. They often include some kind of interview. The writer will usually spend some time describing the person and then mention things that they say; this is when they use reported speech.
Because many of these profiles are written in the present tense, they can help you get used to the basics of reported speech without having to worry too much about different verb tenses.
While the above may seem really complicated, it isn’t that difficult to start using reported speech.
Mastering it may be a little difficult, but the truth is that many, many people who speak English as a first language struggle with it, too!
Reported speech is flexible, and even if you make mistakes, there’s a good chance that no one will notice.
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe


100 Reported Speech Examples: How To Change Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of communicating what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. For example, if your friend said, “ I am going to the store ,” in reported speech, you might convey this as, “ My friend said he was going to the store. ” Reported speech is common in both spoken and written language, especially in storytelling, news reporting, and everyday conversations.
Reported Speech: Changing Pronouns
Pronouns are usually changed to match the perspective of the person reporting the speech. For example, “I” in direct speech may become “he” or “she” in reported speech, depending on the context. Here are some example sentences:
Reported Speech: Reporting Verbs
Reported speech: tense shifts.
When converting direct speech into reported speech, the verb tense is often shifted back one step in time. This is known as the “backshift” of tenses. It’s essential to adjust the tense to reflect the time elapsed between the original speech and the reporting. Here are some examples to illustrate how different tenses in direct speech are transformed in reported speech:
Reported Speech: Changing Time and Place References
Reported speech: question format.
When converting questions from direct speech into reported speech, the format changes significantly. Unlike statements, questions require rephrasing into a statement format and often involve the use of introductory verbs like ‘asked’ or ‘inquired’. Here are some examples to demonstrate how questions in direct speech are converted into statements in reported speech:
Reported Speech: Omitting Quotation Marks
Reported speech quiz.
Transformation of Sentence: Direct & Indirect Speech
A direct speech can be transformed into an indirect speech and vice versa using a suitable reporting verb and a linker depending on the sentence. Let’s have an example first.
Direct Speech
| Tina | said | “Are you busy now?” |
Indirect Speech
| Tina | asked | whether | I was busy then. |
List of Reporting verbs and linkers (list 1)
| Said, told | That | |
| 1. Yes-no question 2. Wh-question | Asked, wanted to know, enquired | If / whether |
| Asked, wanted to know, enquired | wh-word | |
| 1. Without ‘Let’ 2. With ‘Let’ | Told, ordered, advised, requested, asked | to / not to |
| Suggested, proposed | that | |
| Wished, prayed | that | |
| Exclaimed in joy / sorrow / wonder / fear / disgust etc. | that |
Verbs of Reported speech (if the reporting verb is in past tense) (list 2) Direct speech → Indirect speech Am / is / are → was / were Was / were → had been Has / have → had Had → had had Shall / will → would Can → could May → might Must, should → must, should Verb1 → verb2 Verb2 → had + verb3
Change of time and place expressions in past tense (list 3) now → then ago → before today → that day yesterday → the previous day tomorrow → the next day last night → the previous night here → there this → that these → those
Narration change of Assertive sentence
Narration change of interrogative sentence, narration change of imperative sentence, narration change of optative sentence, narration change of exclamatory sentence, narration change of vocatives, narration change of question tag.
We serve cookies on this site to offer, protect and improve our services. KNOW MORE OK

- Reported Speech
Reported Speech: Whenever you are quoting someone else’s words , you use two kinds of speeches – Direct or Indirect speech . In this chapter, we will learn all about Direct and Indirect speech and how to convert one into another.
Suggested Videos
Reported speech- how does it work.

Whenever you report a speech there’s a reporting verb used like “say” or “tell”. For example:
Direct speech: I love to play football .
Reported speech: She said that she loves to play football. (Note 1 : Assume a gender if not mentioned already. Note 2: Using “that” is optional. This sentence could also have been written as “She said she loves to play football.”)
The tense doesn’t have to be changed in this case of reported speech. But of the reporting verb is in the past tense , we do change the tense of the sentence.
Browse more Topics under Transformation Sentences
- Active and Passive Voice
- Parts of Speech
- Types of Sentences
Reported speech- Play of the tenses:
| Simple present | simple past |
| present continous | past continuous |
| simple past | past perfect |
| past continuous | past perfect continuous |
| present perfect tense | past perfect tense |
| past perfect tense | past perfect tense |
Learn more about Parts of Speech here in detail
This is a summary table that will be crystal clear to you as you read further. Just come back to this table after this section and use this as a summary table:
| Simple present | I like to swim in the ocean | She said she liked to swim in the ocean | Simpe past |
| Simple present | I live in New Orleans | He said he lived in New Orleans | Simpe past |
| Past simple | I went to school in the morning | She said she had gone to school that morning | Past perfect |
| Present continuous | I was going to the Himalayas | He said he was going to the Himalayas | Past continuous |
| Past continuous | I was walking near the beach | She said that she had been walking near the beach | past perfect continuous |
| Present perfect | I have caught a few fishes | She said she had caught a few fishes | past perfect |
| Past perfect | I had trekked the Himalayas this time last year | He said he had trekked the Himalayas this time last year | Past perfect |
Some word transitions from direct to reported speech that will come in handy:
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- would stays would
- should stays should
- must stays must or had to(matter of choice)
- shall becomes should
Exception : A present tense in direct speech may not become a past tense in the reported speech if it’s a fact or something generic we are talking about in the sentence. For example-
Direct speech: The sun rises from the East.
Reported speech: She said that the sun rises/rose from the East.
Reported speech- Handling questions:
What happens when the sentence we are trying to report was actually a question? That’s something we are going to deal with in this section. Reported questions- It’s quite interesting. let’s get into it:
Well the good news is that the tense change you learnt above stays the same in reported speech for questions. The only difference is that when you report a question, you no more report it in the form of a question but in the form of a statement. For example:
Direct speech: Where do you want to eat?
Reported speech: She asked me where I wanted to eat.
Notice how the question mark is gone from the reported speech. The reported speech is a statement now. Keep that in mind as you read further.
Remember the tense change? Let’s apply that to a few questions now.
| Are you going to my house? | She asked me if I was going to her house. |
| Where were you going? | He asked me where I was going. |
| Where have you been? | She asked me where had i been. |
Now these are questions that have wordy answers to them. What about the questions that has yes/no answers to them? In these type of questions just add “if” before asking the question. For example:
- Direct speech: Would you like to eat some cupcakes?
- Reported speech: He asked me if i would like to eat some cupcakes.
- Direct speech: Have you ever seen the Van Gogh paintings?
- Reported speech: She asked me if I had ever seen the Van Gogh paintings.
- Direct speech: Are you eating your vegetables?
- Reported speech: She asked if I was eating my vegetables.
Reported speech- Reported requests:
Well not all questions require answers. Some questions are polite requests. Remember? Could you please try to remember? And then there are request statements. Let’s see how do we convert these into reported speech.
Reported request = ask me + to + verb or requested me + to +verb
Just add this rule to your reported speech and you have what is called a reported request.
| Could you please shut the door? | She asked me to shut the door. |
| Can you please help me? | She requested me to help her. |
Reported speech- Reported orders:
Well, not everyone is going to be polite. Sometimes, we get orders. Now how will you report them? Unlike the request, the reporting verb isn’t ask but told or tell. Also, when in orders, sometimes subjects are omitted but while reporting we have to revive the subjects. Let’s see a few examples:
- Direct speech: Sit down!
- Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
- Direct speech: don’t worry!
- Reported speech: She told me not to worry.
Reported speech- Time transitions:
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
| now | then / at that time |
| today | yesterday / that day / Tuesday / the 27th of June |
| yesterday | the day before yesterday / the day before / Wednesday / the 5th of December |
| last night | the night before, Thursday night |
| last week | the week before / the previous week |
| tomorrow | today / the next day / the following day / Friday |
With that, you have everything it takes to understand reported speech. you are all se to change the direct to reported speech. Go ahead and try a few examples. All the best!
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Transformation of Sentences
- Active and Passive voice
37 responses to “Active and Passive voice”
Simple but very nice explanation and helpfull too.
What is the voice change of ” I have endeavoured to understand the fundamental truths.”
ENDEAVOUR HAS BEEN MADE BY ME TO UNDERSTAND THE FUNDAMENTAL TRUTH.
The fundamental truths have been endeavoured to be understood by me
The fundamental truths to understand had been endeavoured by him
The fundamental truths have endeavoured to be understood by me
The fundamental truths has been understood endeavoured to by me
How to change the voice for the following sentence – the books will be received by tomorrow
By whom? We need a subject. If the subject was for example “The library”, then the sentence in active voice would read “The library will receive the books by tomorrow”.
You will receive the books by tomorrow.
Tomorrow you will receive the book
You will receive the books (by) tomorrow.
Someone will receive the books by tomorrow
Tomorrow will be receive the books
HE WILL RECEIVE THE BOOKS BY TOMORROW.
By tomorrow the books will be received.
By tomorrow, you will receive the books
Tomorrow received the book
Change this “take right and turn left” into passive voice
Let the right be taken amd left be turned
‘amd’ is “and” 😅
You are advised to take right and turn left
Very helpful information thanks
Very well explained all basics that can lead to gain further knowledge very easily
What is in this box change into passive
what is the voice change of,” some people think nuclear is the best, because it doesnt add to global warming “….
Brilliant stuff!! – Rishabh
A kite was made by Ravi . What is the active form of this statement???
how to change into passive this sentence “when they were shifting the patient to the I.C.U.,he died
change into passive voice this sentence “when they were shifting the patient to I.C.U.,he died .
May you tell us tense conversion in voice.
Sentences without action like…. Jim is a doctor . Is it active or passive and if any how would you decide without having a main verb ?
It is named after the name of its principal tree ‘sundari'(passive)
how can ocean be object 🙄???
They made a bag
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

party, and ick (1) the correct indirect speech for the Palten says, “I have won the match." a. Palten says that he has won the matc b. Palten says that he had won the matc c. Palten said that he had won the matc d. Palten said that I had won the match.
b. Palten says he had won the match
Related Questions
I will make brainliest pls help me! Which pair of lines from lift every voice and sing best supports the answer above? A. Lift every voice and sing, / Till earth and Heaven ring," B. ''Have not our weary feet / Come to the place for which our fathers sighed? C. ''Out from the gloomy past, till now we stand at last / Where the white gleam of our bright star is cast ." D. Shadowed beneath Thy hand, may we forever stand / True to our God, true to our native land." I will make brainliest pls help me! Which pair of lines from lift every voice and sing best supports the answer above? A. Lift every voice and sing, / Till earth and Heaven ring," B. ''Have not our weary feet / Come to the place for which our fathers sighed? C. ''Out from the gloomy past, till now we stand at last / Where the white gleam of our bright star is cast ." D. Shadowed beneath Thy hand, may we forever stand / True to our God, true to our native land."I will make brainliest pls help me! Which pair of lines from lift every voice and sing best supports the answer above? A. Lift every voice and sing, / Till earth and Heaven ring," B. ''Have not our weary feet / Come to the place for which our fathers sighed? C. ''Out from the gloomy past, till now we stand at last / Where the white gleam of our bright star is cast ." D. Shadowed beneath Thy hand, may we forever stand / True to our God, true to our native land."
"Facing the rising sun of our new day begun
Let us march on till victory is won.",
Explanation:
Explanation: Hope this helps you :)
Reword these sentences into one sentence. Tornadoes can pick up trees while they spin. Tornadoes can rip off roofs while they spin.
Thanks for the next couple of days. The comments for your help. I have been a while. I have been a while. I
I speak without a mouth and hear without ears. I have no body, but I come alive with wind. What am I?
An echo is my answer.
have a great day
God bless you
This random day based on the idiom, "No rhyme or reason," recognizes words that have no rhyme and encourages activities performed without a reason. Name another popular idiom and write about what you think it means.
Lets begin with the definition of an idiom:
An idiom is a widely used saying or expression that contains a figurative meaning that is different from the phrase's literal meaning. For example, if you say you're feeling “under the weather,” you don't literally mean that you're standing underneath the rain.
To me "under the weather" means not feeling well, my assumption being that the rain is the symbolism for sadness.
In this part you need to apply your knowledge on what academic language is. Rewrite the given sentences by observing the characteristics of an academic language. Use the space provided for your answer. 1. Parenting is a 24/7 job. 2. The cookery class is cooking up something big and elegant. 3. The task on writing a book can't be done successfully if you don't burn the midnight oil. 4. The viewers had this feeling of excitement after watching the romcom Thai movie 5. The employees are asked to report for work ASAP
Rewriting the given sentences will give us:
Rewriting a sentence or an essay means improving the said sentence by making some adequate changes that otherwise would have made the original sentence inferior.
Academic writing has to do with using formal words to communicate in a formal setting. The use of colloquial words, unnecessary abbreviations and slangs are discouraged.
Read more here:
https://brainly.com/question/24221458
We have ____________education on Thursday. A. physician B. physically C. physics D. physical
We have physical education on Thursday.
I said to them, "Can you help these boys?" into indirect speech
A offers: B responds: a seat on a bus positively
OFFERS A SEAT ON A BUS POSITIVELY
Use the word deposit in a complete sentence.
1 : to place for or as if for safekeeping I deposited money in the bank.
2 : to give as a pledge that a purchase will be made or a service used He deposited ten dollars on a new bicycle.
3 : to lay down : put He deposited his books on the table.
4 : to let fall or sink Layers of mud were deposited by flood waters.
5: The woman stopped by the bank to deposit her paycheck in her account.
6:She hurried to the library to deposit her books in dropbox so that she wouldn't get late fees.
Mark me as brainliest please
What is the role of raw materials in business?
Raw material is used for making other things
Raw materials like steel , wood and paper can be used to make other things like Bottles , Plastic bags and food holders
i need help please!!!
put i don't know
the teacher my just say it's ok
If you spoke a foreign language you ___ a better job. a. could get b. could have get c. can get d. got
If you spoke a foreign language you can get a better job.
Hope this helps you .
Based on the text what is the five second rule?
write essay on your use of internet?
The internet can help me in different ways like helping me with school when i really need it. The internet can also help by helping get updated on the big news and weather. I also use it to listen to music to get me through the day.
i just said what usually i do for the internet
Help me plsssssssssssssssss
1. The noisier the parties got, the more the neighbors complained.
2. The longer you stay up, the more tired you get the next day.
3. The more fun you have, the more memories you have.
4. The warmer the weather gets, the better I feel.
. Yesterday, after school, I went over to my friend Grayson’s house. As we approached the front door, his mom reminded him to warn me about their dog. Grayson whispered, “Just don’t be scared. Let him sniff you. He is a big, scary-looking dog. He will sniff you. Don’t freak out. Stay calm. Whatever you do, do NOT run or he will go after you.” I took a deep breath…1. What can you infer about Grayson’s dog? 10 points a. His dog is a sweet, friendly dog. b. His dog might chase people if they run off. c. His dog pees on the furniture.
when was William shakespeare born
in April 1564. The exact date of his birth is not recorded, but it is most often celebrated around the world on 23 April.
he was born on 1564 April
Imagine waking up one day to find no Internet, libraries, and cell phones. Newspapers, magazines, radio stations and TV channels have also disappeared. 1. How would you be informed of anything? 2. What ways would you have to communicate with one another? 3. How would you share information and communicate news and events? 4. How would it affect the way you live? 5. What would you personally miss most in such a situation?
I would be informed by a family member such as my mother because she'd be the first one up to find out. I would communicate with someone in person. I should share information by sending letters by mail. It would affect the way I live cause If I had no internet how would I find out what's been going on in the world, same as radio stations and TV. If there were no libraries how would I be able to read the books I love? If i had no cell phone how would I be able to speak to my friends and what if my house was on fire? I wouldn't been able to call the firemen nor police. Newspapers are NEWS PAPERS. I would miss the celebrity drama in that situation. and music
William slaughtered the goat and shared the meat with his neighbours. what type of sentences is it complex, compound or simple sentence
It is a compound sentence.
Compound sentences can be easily identified by the use of the conjunction 'and'.
What knowledge did the Prince share with the Demon? (The Demon with the Matted hair)
On hearing what the Brahmans had to say, they gave him the name of the Prince of the Five Weapons, sword, spear, bow, battle-axe, and shield.
On his way he came to a forest inhabited by the Demon with the Matted Hair.
ashu1233456 anyone know him please answer
Answer: No I do not
Explanation: sorry
Which is the most effective piece of evidence to support the claim that adolescents who exercise daily are healthier than those who are inactive? Adolescents who exercise daily have stronger muscles, higher levels of respiratory fitness, and lower levels of body fat. There are three categories of exercise that adolescents should partake in: aerobic, muscle-strengthening, and bone-strengthening. Spending too much time on the couch watching television can have negative consequences for adolescents. Adolescents enjoy different types of activities, such as dance, martial arts, or team sports.
Adolescents who exercise daily have stronger muscles, higher levels of respiratory fitness, and lower levels of body fat.
This answer goes in depth on why adolescents who exercise are generally healthier while the others do not.
Adolescence is the period of growth and development that occurs between childhood and maturity , an adolescent is someone between the ages of 10 and 19.
Regular physical activity can help children and adolescents improve their cardiorespiratory fitness, grow strong bones and muscles , control their weight , minimize anxiety and depression symptoms, and lower their chance of acquiring health issues .
Exercise is beneficial to our hearts, bones , muscles, weight, and sleep . Maintaining a healthy level of fitness can even help you live a longer and healthier life . We will benefit more from exercise if it becomes a daily habit rather than a once-in-a-while burst of intense effort .
Thus, Option A is the correct option for Adolescence .
For more information about Adolescence refer to the link:
https://brainly.com/question/9506316
Write an argumentative essay of 350 words of the topic given below. "Do you think it is possible for celebrities to have private lives?"
Hope this helps
How the idea was born? and other corporations. Marketers share their project ideas on the platform, both the marketer and the creator will establish a scope, milestones and payment structure
What is technical writing?
technical writing is a writing or drafting technical communication used in technical and occupational fields
Answer: Writing or drafting technical communication used in technical and occupational fields, such as computers hardware and software, engineering, robotics, etc.
Can someone please help contact ducky
Hey sorry havent been on in a bit.
Answer:ducky read this
Think of a brand you own or want to own. What do you think their advertising is trying to communicate to consumers?
Newspaper. Newspaper advertising can promote your business to a wide range of customers. ...
Magazine. Advertising in a specialist magazine can reach your target market quickly and easily. ...
Television. ...
Directories. ...
Outdoor and transit. ...
Direct mail, catalogues and leaflets. ...
Imagine that you are Myna, and you have a friend called Natasha. Your teacher gets to know from her colleagues that your friend Natasha has copied in the exam and asks you whether it is a rumor when you know that Natasha copied in the exam. Create a dialogue between yourself and your teacher. Please send the answer ASAP
Answer: ugh Explanation:yamete
john can reach the top op the board because he's tall
The question is incomplete...Please send the full question
In paragraph 17, the author describes America as “dream-y.” How does this word choice impact the meaning of the text? Cite other evidence from the text in your answer.
The choice of this word shows that the image that America transmits seems real , but it is illusory and hides truths that are not so beautiful.
Although you have not shown the text to which this question refers, we can see from questions similar to yours that you are referring to "Hollywood Dreams of Wealth, Youth, and Beauty."
In this text, the author shows that:
Thus, when the author uses the word "dream-y" he shows how the image we have of America is something mounted and superficial , like a dream , but which holds a more sober and ugly truth , which we cannot fully see.
More information on the link:
https://brainly.com/question/18955355?referrer=searchResults
Hollywood movies portray the American Dream as an attractive reality that every person who lives in America can attain.
"Hollywood Dreams of Wealth, Youth, and Beauty" is an article written by reporter Bob Mondello. In this article he talk about how Hollywood has managed to picture the American Dream easy to achieve, when it is not that easy.
The passage:
He begins his article by asserting that "Tinseltown (or Hollywood) didn't invent the American Dream..." But, Hollywood, did managed to picturize this dream in their movies. These movies would portray that the American Dream can be easily achieved through hard-work, by dressing good, etc while in reality not everyone is able to make it, 'even the folks who aren't making it onscreen are still movie stars.'
So, the connection that author tries to make in this article is that Hollywood has portrayed the American Dream easily achievable and attractive when in reality it is not.
Which transitions are used to summarize or conclude?
Here is a small list of words that can help you transition to the summary part of your work!
finally, in a word, in brief, briefly, in conclusion, in the end, in the final analysis, on the whole, thus, to conclude, to summarize, in sum, to sum up, in summary

COMMENTS
Reported speech: indirect speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Learn how to use reported speech with clear explanations and lots of exercises. Perfect English Grammar helps you master grammar skills.
How to use Reported Speech If you have a sentence in Direct Speech, try to follow our 5 steps to put the sentence into Reported Speech..
In English grammar, we use reported speech to say what another person has said. In reported speech, we change the tense and pronouns to show that some time has passed. Learn all about reported speech in English with Lingolia, then test your knowledge in the interactive exercises.
Reported speech is also referred to as indirect speech or indirect discourse. Before explaining how to report a discourse, let us first distinguish between direct speech and reported speech.
Aside from direct and indirect, reported speech can also be divided into four. The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative.
In reported speech though, you may need to make certain changes to the grammar to make the sentence make sense. So, we'll look at some grammar change examples below and highlight what needs to be changed.
backshift Rewrite the sentences in reported speech. Change pronouns and time expressions where necessary.
Exercises Write the following sentences in indirect speech. Pay attention to backshift and the changes to pronouns, time, and place.
Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how ...
a clause has meaning by itself (often it can be a full sentence) 1. Reporting verbswith the same structure as say: rep. verb + clause. *agree *promise *suggest complain *admit explain mention *claim. Direct Speech Reported Speech. "Why don't you go cycling in the countryside tomorrow," Ellen said.
Reported speech is also known as indirect speech and is used to tell somebody else what another person said. Using reported speech in English can sometimes be difficult for non-native speakers as we (usually) change the verbs, pronouns and specific times. Keep reading to understand how to use reported speech and download this free English lesson!
Learn to master reported speech in English! "Reported speech" means talking about the things that other people have said. Read this post to learn about direct and indirect reported speech in English. Reported speech is an essential skill for gossiping, chatting with friends and keeping up with the news.
Rewrite the direct speech as reported speech to complete the sentences. Use contractions where possible.
Reported speech can be quite challenging for English language learners because in order to change direct speech into reported speech, one must change the perspective and tense of what was said by the original speaker or writer. In this guide, we will explain in detail how to change direct speech into indirect speech and provide lots of examples of reported speech to help you understand. Here ...
Exercises: 1 2 3. Indirect speech - reported speech. Exercise 1. Choose the correct form to complete the sentences below. 1 'I work in a bank.' ⇒ He said that he in a bank. 2 'I am working today.' ⇒ She told us she that day. 3 'I've been ill for a couple of weeks.' ⇒ He told me he for a couple of weeks.
A direct speech can be transformed into an indirect speech and vice versa using a suitable reporting verb and a linker depending on the sentence. Let's have an example first.
B. Indirect or Reported Speech Reported speech is commonly used in speaking and writing. It is important to note that most verb tenses will change from direct to reported speech. The chart on the next page shows the most common verb and modal changes.
The landlady said to the student, "You must keep your room clean !". The landlady said to the student that he/she had to keep his / her room clean. Mr Simmons told Harry, "Don't smoke in my car!". Mr Simmons told Harry not to smoke in his car. He asked me, "Do you want to be famous?".
Reported Speech Reported Speech: Whenever you are quoting someone else's words, you use two kinds of speeches - Direct or Indirect speech. In this chapter, we will learn all about Direct and Indirect speech and how to convert one into another.
The rewritten sentences are he said he had slept when Mary called him, Anna complained her dog had been sick, and the teacher said I was always late.. What is the difference between direct and indirect speech? In the direct speech, the words of another person are reported using quotations.On the other hand, in indirect speech, the information is reported without quotations and due to this some ...
In this part you need to apply your knowledge on what academic language is. Rewrite the given sentences by observing the characteristics of an academic language. Use the space provided for your answer. 1. Parenting is a 24/7 job. 2. The cookery class is cooking up something big and elegant. 3.