
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

3.4 Sampling Techniques in Quantitative Research
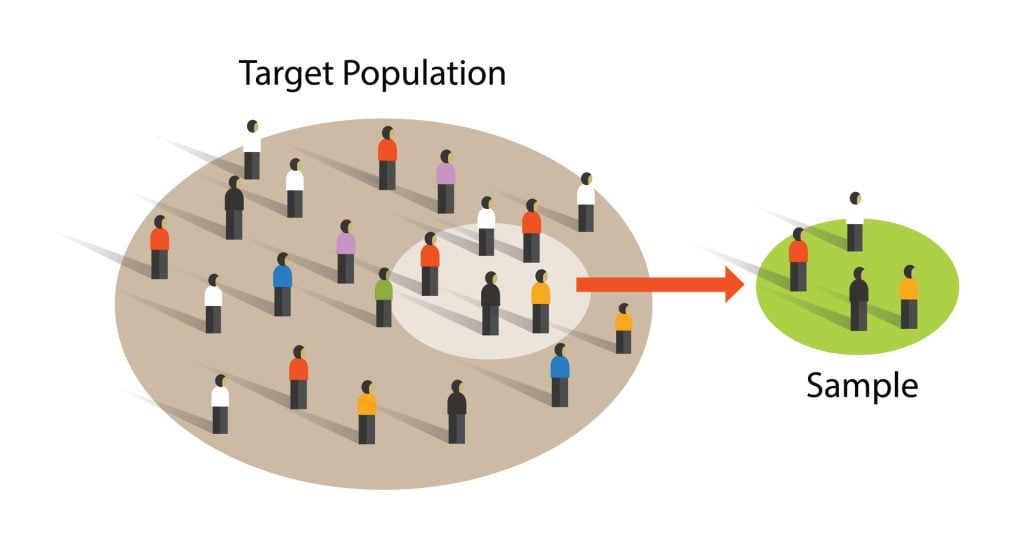
Target population.
The target population includes the people the researcher is interested in conducting the research and generalizing the findings on. 40 For example, if certain researchers are interested in vaccine-preventable diseases in children five years and younger in Australia. The target population will be all children aged 0–5 years residing in Australia. The actual population is a subset of the target population from which the sample is drawn, e.g. children aged 0–5 years living in the capital cities in Australia. The sample is the people chosen for the study from the actual population (Figure 3.9). The sampling process involves choosing people, and it is distinct from the sample. 40 In quantitative research, the sample must accurately reflect the target population, be free from bias in terms of selection, and be large enough to validate or reject the study hypothesis with statistical confidence and minimise random error. 2
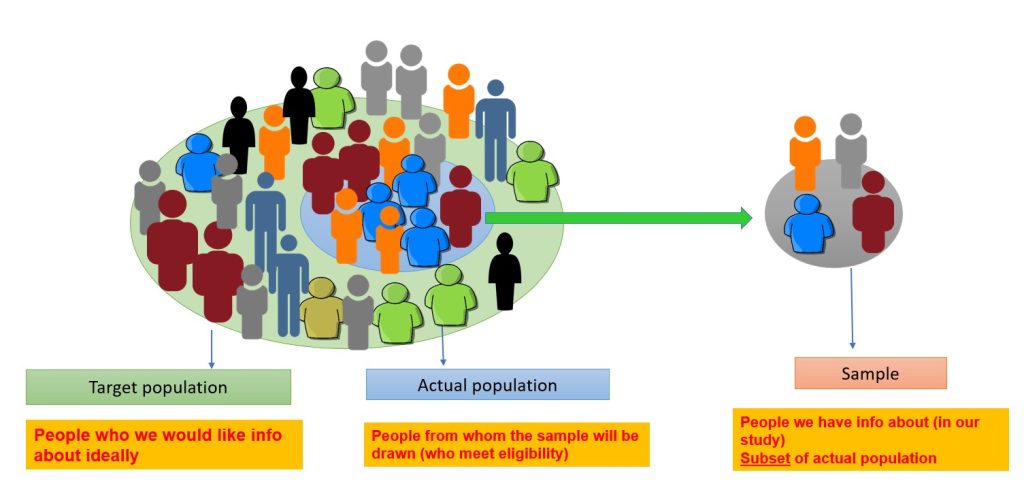
Sampling techniques
Sampling in quantitative research is a critical component that involves selecting a representative subset of individuals or cases from a larger population and often employs sampling techniques based on probability theory. 41 The goal of sampling is to obtain a sample that is large enough and representative of the target population. Examples of probability sampling techniques include simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, systematic random sampling and cluster sampling ( shown below ). 2 The key feature of probability techniques is that they involve randomization. There are two main characteristics of probability sampling. All individuals of a population are accessible to the researcher (theoretically), and there is an equal chance that each person in the population will be chosen to be part of the study sample. 41 While quantitative research often uses sampling techniques based on probability theory, some non-probability techniques may occasionally be utilised in healthcare research. 42 Non-probability sampling methods are commonly used in qualitative research. These include purposive, convenience, theoretical and snowballing and have been discussed in detail in chapter 4.
Sample size calculation
In order to enable comparisons with some level of established statistical confidence, quantitative research needs an acceptable sample size. 2 The sample size is the most crucial factor for reliability (reproducibility) in quantitative research. It is important for a study to be powered – the likelihood of identifying a difference if it exists in reality. 2 Small sample-sized studies are more likely to be underpowered, and results from small samples are more likely to be prone to random error. 2 The formula for sample size calculation varies with the study design and the research hypothesis. 2 There are numerous formulae for sample size calculations, but such details are beyond the scope of this book. For further readings, please consult the biostatistics textbook by Hirsch RP, 2021. 43 However, we will introduce a simple formula for calculating sample size for cross-sectional studies with prevalence as the outcome. 2
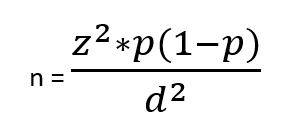
z is the statistical confidence; therefore, z = 1.96 translates to 95% confidence; z = 1.68 translates to 90% confidence
p = Expected prevalence (of health condition of interest)
d = Describes intended precision; d = 0.1 means that the estimate falls +/-10 percentage points of true prevalence with the considered confidence. (e.g. for a prevalence of 40% (0.4), if d=.1, then the estimate will fall between 30% and 50% (0.3 to 0.5).
Example: A district medical officer seeks to estimate the proportion of children in the district receiving appropriate childhood vaccinations. Assuming a simple random sample of a community is to be selected, how many children must be studied if the resulting estimate is to fall within 10% of the true proportion with 95% confidence? It is expected that approximately 50% of the children receive vaccinations
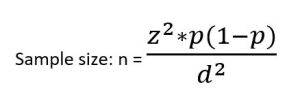
z = 1.96 (95% confidence)
d = 10% = 10/ 100 = 0.1 (estimate to fall within 10%)
p = 50% = 50/ 100 = 0.5
Now we can enter the values into the formula
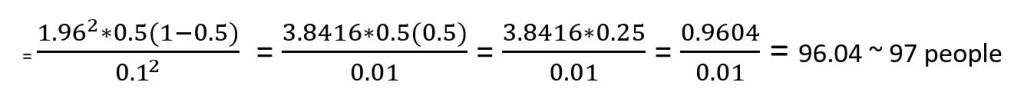
Given that people cannot be reported in decimal points, it is important to round up to the nearest whole number.
An Introduction to Research Methods for Undergraduate Health Profession Students Copyright © 2023 by Faith Alele and Bunmi Malau-Aduli is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Part I: Sampling, Data Collection, & Analysis in Quantitative Research
In this module, we will focus on how quantitative research collects and analyzes data, as well as methods for obtaining sample population.
- Levels of Measurement
- Reliability and Validity
- Population and Samples
- Common Data Collection Methods
- Data Analysis
- Statistical Significance versus Clinical Significance
Objectives:
- Describe levels of measurement
- Describe reliability and validity as applied to critical appraisal of research
- Differentiate methods of obtaining samples for population generalizability
- Describe common data collection methods in quantitative research
- Describe various data analysis methods in quantitative research
- Differentiate statistical significance versus clinical significance
Levels of measurement
Once researchers have collected their data (we will talk about data collection later in this module), they need methods to organize the data before they even start to think about statistical analyses. Statistical operations depend on a variable’s level of measurement. Think about this similarly to shuffling all of your bills in some type of organization before you pay them. With levels of measurement, we are precisely recording variables in a method to help organize them.
There are four levels of measurement:
Nominal: The data can only be categorized
Ordinal: The data can be categorized and ranked
Interval: The data can be categorized, ranked, and evenly spaced
Ratio: The data can be categorized, ranked, even spaced, and has a natural zero
Going from lowest to highest, the 4 levels of measurement are cumulative. This means that they each take on the properties of lower levels and add new properties.

- A variable is nominal if the values could be interchanged (e.g. 1 = male, 2 = female OR 1 = female, 2 = male).
- A variable is ordinal if there is a quantitative ordering of values AND if there are a small number of values (e.g. excellent, good, fair, poor).
- A variable is usually considered interval if it is measured with a composite scale or test.
- A variable is ratio level if it makes sense to say that one value is twice as much as another (e.g. 100 mg is twice as much as 50 mg) (Polit & Beck, 2021).
Reliability and Validity as Applied to Critical Appraisal of Research
Reliability measures the ability of a measure to consistently measure the same way. Validity measures what it is supposed to measure. Do we have the need for both in research? Yes! If a variable is measured inaccurately, the data is useless. Let’s talk about why.
For example, let’s set out to measure blood glucose for our study. The validity is how well the measure can determine the blood glucose. If we used a blood pressure cuff to measure blood glucose, this would not be a valid measure. If we used a blood glucose meter, it would be a more valid measure. It does not stop there, however. What about the meter itself? Has it been calibrated? Are the correct sticks for the meter available? Are they expired? Does the meter have fresh batteries? Are the patient’s hands clean?
Reliability wants to know: Is the blood glucose meter measuring the same way, every time?
Validity is asking, “Does the meter measure what it is supposed to measure?” Construct validity: Does the test measure the concept that it’s intended to measure? Content validity: Is the test fully representative of what it aims to measure? Face validity: Does the content of the test appear to be suitable to its aims?
Leibold, 2020
Obtaining Samples for Population Generalizability
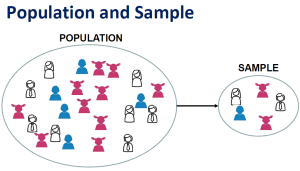
In quantitative research, a population is the entire group that the researcher wants to draw conclusions about.
A sample is the specific group that the researcher will actually collect data from. A sample is always a much smaller group of people than the total size of the population. For example, if we wanted to investigate heart failure, there would be no possible way to measure every single human with heart failure. Therefore, researchers will attempt to select a sample of that large population which would most likely reflect (AKA: be a representative sample) the larger population of those with heart failure. Remember, in quantitative research, the results should be generalizable to the population studied.
There is a lot of confusion with students (and even some researchers!) when they refer to “ random assignment” versus “ random sampling ”. Random assignment is a signature of a true experiment. This means that if participants are not truly randomly assigned to intervention groups, then it is not a true experiment. Remember, random sampling is a technique used to select individuals from a larger population to be included in a study. The key characteristic of random sampling is that every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. Random assignment is a process used in experimental research to assign participants to different groups or conditions (e.g., treatment vs. control) in a way that each participant has an equal chance of being placed in any group.
A researcher will specify population characteristics through eligibility criteria. This means that they consider which characteristics to include ( inclusion criteria ) and which characteristics to exclude ( exclusion criteria ).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria are essential for defining who is eligible to participate in a study. Establishing inclusion and exclusion criteria for study participants is a standard, required practice when designing high-quality research protocols. Inclusion criteria are defined as the key features of the target population that the investigators will use to answer their research question (Boswell & Cannon, 2022). Typical inclusion criteria include demographic, clinical, and geographic characteristics.
For example, what might be your criteria for including someone from participation? Are any criteria based on age, gender, race, ethnicity, sexual orientation, origin, type and stage of disease, the subject’s previous treatment history, and the presence or absence (as in the case of the “healthy” or “control” subject) of other medical, psychosocial, or emotional conditions? If so, justify. For example, if you are doing a study on pregnant persons, will you exclude men (most likely, you will)? If you exclude men, even if it seems obvious, this needs to be determined and stated.
- Inclusion Criteria : These are the characteristics that participants must have to be included in the study. Inclusion criteria help ensure that the sample is relevant to the research question and that the findings will be applicable to the population of interest. For example, in a study on diabetic patients, inclusion criteria might include being diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes and being over the age of 18.
- Exclusion Criteria : These are the characteristics that disqualify potential participants from the study. Exclusion criteria are used to remove individuals who might confound the results or who do not fit the study’s focus. Continuing the example above, exclusion criteria might include pregnant patients or other chronic conditions that could interfere with the study outcomes.
For example, if we were studying chemotherapy in breast cancer subjects, we might specify:
- Inclusion Criteria: Postmenopausal women between the ages of 45 and 75 who have been diagnosed with Stage II breast cancer.
- Exclusion Criteria: Abnormal renal function tests since we are studying a combination of drugs that may be nephrotoxic. Renal function tests are to be performed to evaluate renal function and the threshold values that would disqualify the prospective subject is serum creatinine above 1.9 mg/dl.
Sampling Designs:
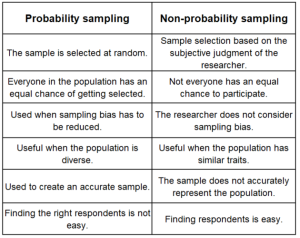
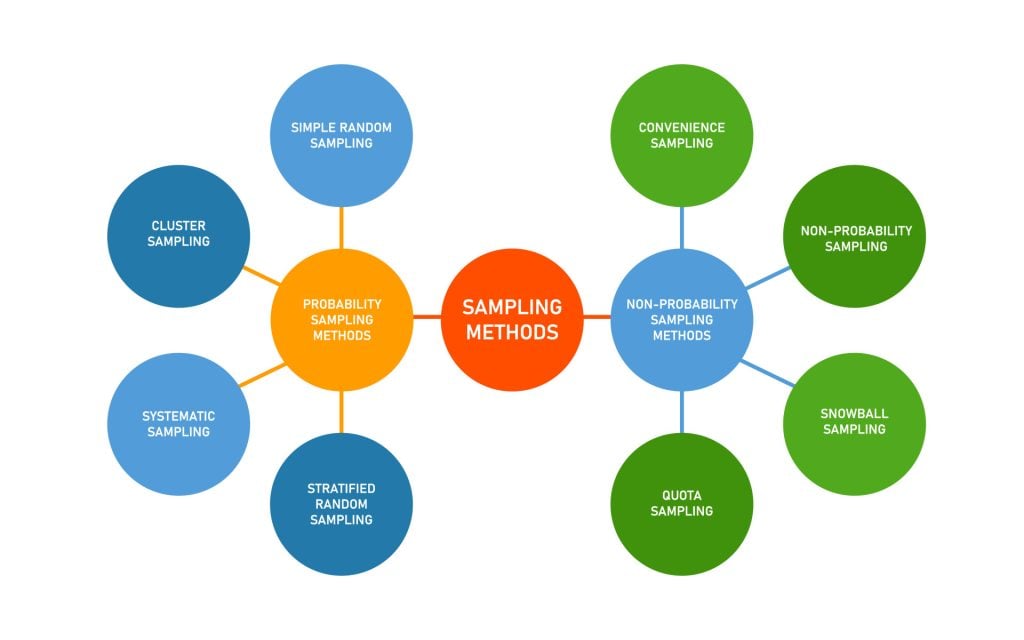
There are two broad classes of sampling in quantitative research: Probability and nonprobability sampling.
Probability sampling : As the name implies, probability sampling means that each eligible individual has a random chance (same probability) of being selected to participate in the study.
There are three types of probability sampling:
Simple random sampling : Every eligible participant is randomly selected (e.g. drawing from a hat).
Stratified random sampling : Eligible population is first divided into two or more strata (categories) from which randomization occurs (e.g. pollution levels selected from restaurants, bars with ordinances of state laws, and bars with no ordinances).
Systematic sampling : Involves the selection of every __ th eligible participant from a list (e.g. every 9 th person).
Nonprobability sampling : In nonprobability sampling, eligible participants are selected using a subjective (non-random) method.
There are four types of nonprobability sampling:
Convenience sampling : Participants are selected for inclusion in the sample because they are the easiest for the researcher to access. This can be due to geographical proximity, availability at a given time, or willingness to participate in the research.
Quota sampling : Participants are from a very tailored sample that’s in proportion to some characteristic or trait of a population. For example, the researcher could divide a population by the state they live in, income or education level, or sex. The population is divided into groups (also called strata) and samples are taken from each group to meet a quota.
Purposive sampling : A group of non-probability sampling techniques in which units are selected because they have characteristics that the researcher needs in their sample. In other words, units are selected “on purpose” in purposive sampling.
Snowball sampling: Existing study participants recruit future participants from their acquaintances or networks. It is often used in studies where the population is hard to reach.
And, a 5th type: Consecutive sampling : A sampling technique in which every subject meeting the criteria of inclusion is selected until the required sample size is achieved. Consecutive sampling is defined as a nonprobability technique where samples are picked at the ease of a researcher more like convenience sampling, only with a slight variation. Here, the researcher selects a sample or group of people, conducts research over a period, collects results, and then moves on to another sample.
The goal in sampling is that it is a representative sample that is similar to the larger population. A representative sample should resemble the population in key demographic, behavioral, or other relevant characteristics. This ensures that the findings from the sample can be extrapolated to the population. The sample must be large enough to capture the diversity of the population and minimize sampling error (the difference between the sample results and the actual population parameters). A small sample might not adequately represent the population, especially in terms of its variability. To create a representative sample, the selection process must be unbiased, meaning that no specific group is more or less likely to be included than others. Bias in the selection process can lead to an unrepresentative sample, which will distort the study results.
Common Data Collection Methods in Quantitative Research
There are various methods that researchers use to collect data for their studies. For nurse researchers, existing records are an important data source. Researchers need to decide if they will collect new data or use existing data. There is also a wealth of clinical data that can be used for non-research purposed to help answer clinical questions.
Let’s look at some general data collection methods and data sources in quantitative research.
Existing data could include medical records, school records, corporate diaries, letters, meeting minutes, and photographs. These are easy to obtain do not require participation from those being studied.
Collecting new data:
Let’s go over a few methods in which researcher can collect new data. These usually requires participation from those being studied.
Self-reports can be obtained via interviews or questionnaires . Closed-ended questions can be asked (“Within the past 6 months, were you ever a member of a fitness gym?” Yes/No) or open-ended questions such as “Why did you decide to join a fitness gym?” Important to remember (this sometimes throws students off) is that conducting interviews and questionnaires does not mean it is qualitative in nature! Do not let that throw you off in assessing whether a published article is quantitative or qualitative. The nature of the questions, however, may help to determine the type of research (quantitative or qualitative), as qualitative questions deal with ascertaining a very organic collection of people’s experiences in open-ended questions.
Advantages of questionnaires (compared to interviews):
- Questionnaires are less costly and are advantageous for geographically dispersed samples.
- Questionnaires offer the possibility of anonymity, which may be crucial in obtaining information about certain opinions or traits.
Advances of interviews (compared to questionnaires):
- Higher response rates
- Some people cannot fill out a questionnaire.
- Opportunities to clarify questions or to determine comprehension
- Opportunity to collect supplementary data through observation
Psychosocial scales are often utilized within questionnaires or interviews. These can help to obtain attitudes, perceptions, and psychological traits.
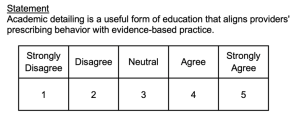
Likert Scales :
- Consist of several declarative statements ( items ) expressing viewpoints
- Responses are on an agree/disagree continuum (usually five or seven response options).
- Responses to items are summed to compute a total scale score.
Visual Analog Scale:
- Used to measure subjective experiences (e.g., pain, nausea)
- Measurements are on a straight line measuring 100 mm.
- End points labeled as extreme limits of sensation

Observational Methods include the observation method of data collection involves seeing people in a certain setting or place at a specific time and day. Essentially, researchers study the behavior of the individuals or surroundings in which they are analyzing. This can be controlled, spontaneous, or participant-based research .
When a researcher utilizes a defined procedure for observing individuals or the environment, this is known as structured observation. When individuals are observed in their natural environment, this is known as naturalistic observation. In participant observation, the researcher immerses himself or herself in the environment and becomes a member of the group being observed.
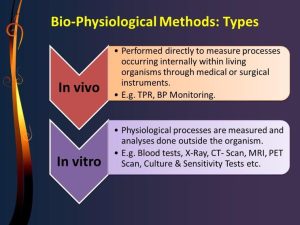
Biophysiologic Measures are defined as ‘those physiological and physical variables that require specialized technical instruments and equipment for their measurement’. Biophysiological measures are the most common instruments for collecting data in medical science studies. To collect valid and reliable data, it is critical to apply these measures appropriately.
- In vivo refers to when research or work is done with or within an entire, living organism. Examples can include studies in animal models or human clinical trials.
- In vitro is used to describe work that’s performed outside of a living organism. This usually involves isolated tissues, organs, or cells.
Let’s watch a video about Sampling and Data Collection that I made a couple of years ago.

Sampling Methods & Strategies 101
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Kerryn Warren (PhD) | January 2023

I f you’re new to research, sooner or later you’re bound to wander into the intimidating world of sampling methods and strategies. If you find yourself on this page, chances are you’re feeling a little overwhelmed or confused. Fear not – in this post we’ll unpack sampling in straightforward language , along with loads of examples .
Overview: Sampling Methods & Strategies
- What is sampling in a research context?
- The two overarching approaches
Simple random sampling
Stratified random sampling, cluster sampling, systematic sampling, purposive sampling, convenience sampling, snowball sampling.
- How to choose the right sampling method
What (exactly) is sampling?
At the simplest level, sampling (within a research context) is the process of selecting a subset of participants from a larger group . For example, if your research involved assessing US consumers’ perceptions about a particular brand of laundry detergent, you wouldn’t be able to collect data from every single person that uses laundry detergent (good luck with that!) – but you could potentially collect data from a smaller subset of this group.
In technical terms, the larger group is referred to as the population , and the subset (the group you’ll actually engage with in your research) is called the sample . Put another way, you can look at the population as a full cake and the sample as a single slice of that cake. In an ideal world, you’d want your sample to be perfectly representative of the population, as that would allow you to generalise your findings to the entire population. In other words, you’d want to cut a perfect cross-sectional slice of cake, such that the slice reflects every layer of the cake in perfect proportion.
Achieving a truly representative sample is, unfortunately, a little trickier than slicing a cake, as there are many practical challenges and obstacles to achieving this in a real-world setting. Thankfully though, you don’t always need to have a perfectly representative sample – it all depends on the specific research aims of each study – so don’t stress yourself out about that just yet!
With the concept of sampling broadly defined, let’s look at the different approaches to sampling to get a better understanding of what it all looks like in practice.

The two overarching sampling approaches
At the highest level, there are two approaches to sampling: probability sampling and non-probability sampling . Within each of these, there are a variety of sampling methods , which we’ll explore a little later.
Probability sampling involves selecting participants (or any unit of interest) on a statistically random basis , which is why it’s also called “random sampling”. In other words, the selection of each individual participant is based on a pre-determined process (not the discretion of the researcher). As a result, this approach achieves a random sample.
Probability-based sampling methods are most commonly used in quantitative research , especially when it’s important to achieve a representative sample that allows the researcher to generalise their findings.
Non-probability sampling , on the other hand, refers to sampling methods in which the selection of participants is not statistically random . In other words, the selection of individual participants is based on the discretion and judgment of the researcher, rather than on a pre-determined process.
Non-probability sampling methods are commonly used in qualitative research , where the richness and depth of the data are more important than the generalisability of the findings.
If that all sounds a little too conceptual and fluffy, don’t worry. Let’s take a look at some actual sampling methods to make it more tangible.
Need a helping hand?
Probability-based sampling methods
First, we’ll look at four common probability-based (random) sampling methods:
Importantly, this is not a comprehensive list of all the probability sampling methods – these are just four of the most common ones. So, if you’re interested in adopting a probability-based sampling approach, be sure to explore all the options.
Simple random sampling involves selecting participants in a completely random fashion , where each participant has an equal chance of being selected. Basically, this sampling method is the equivalent of pulling names out of a hat , except that you can do it digitally. For example, if you had a list of 500 people, you could use a random number generator to draw a list of 50 numbers (each number, reflecting a participant) and then use that dataset as your sample.
Thanks to its simplicity, simple random sampling is easy to implement , and as a consequence, is typically quite cheap and efficient . Given that the selection process is completely random, the results can be generalised fairly reliably. However, this also means it can hide the impact of large subgroups within the data, which can result in minority subgroups having little representation in the results – if any at all. To address this, one needs to take a slightly different approach, which we’ll look at next.
Stratified random sampling is similar to simple random sampling, but it kicks things up a notch. As the name suggests, stratified sampling involves selecting participants randomly , but from within certain pre-defined subgroups (i.e., strata) that share a common trait . For example, you might divide the population into strata based on gender, ethnicity, age range or level of education, and then select randomly from each group.
The benefit of this sampling method is that it gives you more control over the impact of large subgroups (strata) within the population. For example, if a population comprises 80% males and 20% females, you may want to “balance” this skew out by selecting a random sample from an equal number of males and females. This would, of course, reduce the representativeness of the sample, but it would allow you to identify differences between subgroups. So, depending on your research aims, the stratified approach could work well.

Next on the list is cluster sampling. As the name suggests, this sampling method involves sampling from naturally occurring, mutually exclusive clusters within a population – for example, area codes within a city or cities within a country. Once the clusters are defined, a set of clusters are randomly selected and then a set of participants are randomly selected from each cluster.
Now, you’re probably wondering, “how is cluster sampling different from stratified random sampling?”. Well, let’s look at the previous example where each cluster reflects an area code in a given city.
With cluster sampling, you would collect data from clusters of participants in a handful of area codes (let’s say 5 neighbourhoods). Conversely, with stratified random sampling, you would need to collect data from all over the city (i.e., many more neighbourhoods). You’d still achieve the same sample size either way (let’s say 200 people, for example), but with stratified sampling, you’d need to do a lot more running around, as participants would be scattered across a vast geographic area. As a result, cluster sampling is often the more practical and economical option.
If that all sounds a little mind-bending, you can use the following general rule of thumb. If a population is relatively homogeneous , cluster sampling will often be adequate. Conversely, if a population is quite heterogeneous (i.e., diverse), stratified sampling will generally be more appropriate.
The last probability sampling method we’ll look at is systematic sampling. This method simply involves selecting participants at a set interval , starting from a random point .
For example, if you have a list of students that reflects the population of a university, you could systematically sample that population by selecting participants at an interval of 8 . In other words, you would randomly select a starting point – let’s say student number 40 – followed by student 48, 56, 64, etc.
What’s important with systematic sampling is that the population list you select from needs to be randomly ordered . If there are underlying patterns in the list (for example, if the list is ordered by gender, IQ, age, etc.), this will result in a non-random sample, which would defeat the purpose of adopting this sampling method. Of course, you could safeguard against this by “shuffling” your population list using a random number generator or similar tool.

Non-probability-based sampling methods
Right, now that we’ve looked at a few probability-based sampling methods, let’s look at three non-probability methods :
Again, this is not an exhaustive list of all possible sampling methods, so be sure to explore further if you’re interested in adopting a non-probability sampling approach.
First up, we’ve got purposive sampling – also known as judgment , selective or subjective sampling. Again, the name provides some clues, as this method involves the researcher selecting participants using his or her own judgement , based on the purpose of the study (i.e., the research aims).
For example, suppose your research aims were to understand the perceptions of hyper-loyal customers of a particular retail store. In that case, you could use your judgement to engage with frequent shoppers, as well as rare or occasional shoppers, to understand what judgements drive the two behavioural extremes .
Purposive sampling is often used in studies where the aim is to gather information from a small population (especially rare or hard-to-find populations), as it allows the researcher to target specific individuals who have unique knowledge or experience . Naturally, this sampling method is quite prone to researcher bias and judgement error, and it’s unlikely to produce generalisable results, so it’s best suited to studies where the aim is to go deep rather than broad .

Next up, we have convenience sampling. As the name suggests, with this method, participants are selected based on their availability or accessibility . In other words, the sample is selected based on how convenient it is for the researcher to access it, as opposed to using a defined and objective process.
Naturally, convenience sampling provides a quick and easy way to gather data, as the sample is selected based on the individuals who are readily available or willing to participate. This makes it an attractive option if you’re particularly tight on resources and/or time. However, as you’d expect, this sampling method is unlikely to produce a representative sample and will of course be vulnerable to researcher bias , so it’s important to approach it with caution.
Last but not least, we have the snowball sampling method. This method relies on referrals from initial participants to recruit additional participants. In other words, the initial subjects form the first (small) snowball and each additional subject recruited through referral is added to the snowball, making it larger as it rolls along .
Snowball sampling is often used in research contexts where it’s difficult to identify and access a particular population. For example, people with a rare medical condition or members of an exclusive group. It can also be useful in cases where the research topic is sensitive or taboo and people are unlikely to open up unless they’re referred by someone they trust.
Simply put, snowball sampling is ideal for research that involves reaching hard-to-access populations . But, keep in mind that, once again, it’s a sampling method that’s highly prone to researcher bias and is unlikely to produce a representative sample. So, make sure that it aligns with your research aims and questions before adopting this method.
How to choose a sampling method
Now that we’ve looked at a few popular sampling methods (both probability and non-probability based), the obvious question is, “ how do I choose the right sampling method for my study?”. When selecting a sampling method for your research project, you’ll need to consider two important factors: your research aims and your resources .
As with all research design and methodology choices, your sampling approach needs to be guided by and aligned with your research aims, objectives and research questions – in other words, your golden thread. Specifically, you need to consider whether your research aims are primarily concerned with producing generalisable findings (in which case, you’ll likely opt for a probability-based sampling method) or with achieving rich , deep insights (in which case, a non-probability-based approach could be more practical). Typically, quantitative studies lean toward the former, while qualitative studies aim for the latter, so be sure to consider your broader methodology as well.
The second factor you need to consider is your resources and, more generally, the practical constraints at play. If, for example, you have easy, free access to a large sample at your workplace or university and a healthy budget to help you attract participants, that will open up multiple options in terms of sampling methods. Conversely, if you’re cash-strapped, short on time and don’t have unfettered access to your population of interest, you may be restricted to convenience or referral-based methods.
In short, be ready for trade-offs – you won’t always be able to utilise the “perfect” sampling method for your study, and that’s okay. Much like all the other methodological choices you’ll make as part of your study, you’ll often need to compromise and accept practical trade-offs when it comes to sampling. Don’t let this get you down though – as long as your sampling choice is well explained and justified, and the limitations of your approach are clearly articulated, you’ll be on the right track.

Let’s recap…
In this post, we’ve covered the basics of sampling within the context of a typical research project.
- Sampling refers to the process of defining a subgroup (sample) from the larger group of interest (population).
- The two overarching approaches to sampling are probability sampling (random) and non-probability sampling .
- Common probability-based sampling methods include simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, cluster sampling and systematic sampling.
- Common non-probability-based sampling methods include purposive sampling, convenience sampling and snowball sampling.
- When choosing a sampling method, you need to consider your research aims , objectives and questions, as well as your resources and other practical constraints .
If you’d like to see an example of a sampling strategy in action, be sure to check out our research methodology chapter sample .
Last but not least, if you need hands-on help with your sampling (or any other aspect of your research), take a look at our 1-on-1 coaching service , where we guide you through each step of the research process, at your own pace.

You Might Also Like:

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Dissertation While Working: A How-To Guide
Struggling to balance your dissertation with a full-time job and family? Learn practical strategies to achieve success.

How To Review & Understand Academic Literature Quickly
Learn how to fast-track your literature review by reading with intention and clarity. Dr E and Amy Murdock explain how.

Dissertation Writing Services: Far Worse Than You Think
Thinking about using a dissertation or thesis writing service? You might want to reconsider that move. Here’s what you need to know.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
Excellent and helpful. Best site to get a full understanding of Research methodology. I’m nolonger as “clueless “..😉
Excellent and helpful for junior researcher!
Grad Coach tutorials are excellent – I recommend them to everyone doing research. I will be working with a sample of imprisoned women and now have a much clearer idea concerning sampling. Thank you to all at Grad Coach for generously sharing your expertise with students.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
- En español – ExME
- Em português – EME

What are sampling methods and how do you choose the best one?
Posted on 18th November 2020 by Mohamed Khalifa

This tutorial will introduce sampling methods and potential sampling errors to avoid when conducting medical research.
Introduction to sampling methods
Examples of different sampling methods, choosing the best sampling method.
It is important to understand why we sample the population; for example, studies are built to investigate the relationships between risk factors and disease. In other words, we want to find out if this is a true association, while still aiming for the minimum risk for errors such as: chance, bias or confounding .
However, it would not be feasible to experiment on the whole population, we would need to take a good sample and aim to reduce the risk of having errors by proper sampling technique.
What is a sampling frame?
A sampling frame is a record of the target population containing all participants of interest. In other words, it is a list from which we can extract a sample.
What makes a good sample?
A good sample should be a representative subset of the population we are interested in studying, therefore, with each participant having equal chance of being randomly selected into the study.
We could choose a sampling method based on whether we want to account for sampling bias; a random sampling method is often preferred over a non-random method for this reason. Random sampling examples include: simple, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling. Non-random sampling methods are liable to bias, and common examples include: convenience, purposive, snowballing, and quota sampling. For the purposes of this blog we will be focusing on random sampling methods .
Example: We want to conduct an experimental trial in a small population such as: employees in a company, or students in a college. We include everyone in a list and use a random number generator to select the participants
Advantages: Generalisable results possible, random sampling, the sampling frame is the whole population, every participant has an equal probability of being selected
Disadvantages: Less precise than stratified method, less representative than the systematic method

Example: Every nth patient entering the out-patient clinic is selected and included in our sample
Advantages: More feasible than simple or stratified methods, sampling frame is not always required
Disadvantages: Generalisability may decrease if baseline characteristics repeat across every nth participant

Example: We have a big population (a city) and we want to ensure representativeness of all groups with a pre-determined characteristic such as: age groups, ethnic origin, and gender
Advantages: Inclusive of strata (subgroups), reliable and generalisable results
Disadvantages: Does not work well with multiple variables

Example: 10 schools have the same number of students across the county. We can randomly select 3 out of 10 schools as our clusters
Advantages: Readily doable with most budgets, does not require a sampling frame
Disadvantages: Results may not be reliable nor generalisable

How can you identify sampling errors?
Non-random selection increases the probability of sampling (selection) bias if the sample does not represent the population we want to study. We could avoid this by random sampling and ensuring representativeness of our sample with regards to sample size.
An inadequate sample size decreases the confidence in our results as we may think there is no significant difference when actually there is. This type two error results from having a small sample size, or from participants dropping out of the sample.
In medical research of disease, if we select people with certain diseases while strictly excluding participants with other co-morbidities, we run the risk of diagnostic purity bias where important sub-groups of the population are not represented.
Furthermore, measurement bias may occur during re-collection of risk factors by participants (recall bias) or assessment of outcome where people who live longer are associated with treatment success, when in fact people who died were not included in the sample or data analysis (survivors bias).
By following the steps below we could choose the best sampling method for our study in an orderly fashion.
Research objectiveness
Firstly, a refined research question and goal would help us define our population of interest. If our calculated sample size is small then it would be easier to get a random sample. If, however, the sample size is large, then we should check if our budget and resources can handle a random sampling method.
Sampling frame availability
Secondly, we need to check for availability of a sampling frame (Simple), if not, could we make a list of our own (Stratified). If neither option is possible, we could still use other random sampling methods, for instance, systematic or cluster sampling.
Study design
Moreover, we could consider the prevalence of the topic (exposure or outcome) in the population, and what would be the suitable study design. In addition, checking if our target population is widely varied in its baseline characteristics. For example, a population with large ethnic subgroups could best be studied using a stratified sampling method.
Random sampling
Finally, the best sampling method is always the one that could best answer our research question while also allowing for others to make use of our results (generalisability of results). When we cannot afford a random sampling method, we can always choose from the non-random sampling methods.
To sum up, we now understand that choosing between random or non-random sampling methods is multifactorial. We might often be tempted to choose a convenience sample from the start, but that would not only decrease precision of our results, and would make us miss out on producing research that is more robust and reliable.
References (pdf)
Mohamed Khalifa
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
No Comments on What are sampling methods and how do you choose the best one?
Thank you for this overview. A concise approach for research.
really helps! am an ecology student preparing to write my lab report for sampling.
I learned a lot to the given presentation.. It’s very comprehensive… Thanks for sharing…
Very informative and useful for my study. Thank you
Oversimplified info on sampling methods. Probabilistic of the sampling and sampling of samples by chance does rest solely on the random methods. Factors such as the random visits or presentation of the potential participants at clinics or sites could be sufficiently random in nature and should be used for the sake of efficiency and feasibility. Nevertheless, this approach has to be taken only after careful thoughts. Representativeness of the study samples have to be checked at the end or during reporting by comparing it to the published larger studies or register of some kind in/from the local population.
Thank you so much Mr.mohamed very useful and informative article
Subscribe to our newsletter
You will receive our monthly newsletter and free access to Trip Premium.
Related Articles

How to read a funnel plot
This blog introduces you to funnel plots, guiding you through how to read them and what may cause them to look asymmetrical.

Internal and external validity: what are they and how do they differ?
Is this study valid? Can I trust this study’s methods and design? Can I apply the results of this study to other contexts? Learn more about internal and external validity in research to help you answer these questions when you next look at a paper.

Cluster Randomized Trials: Concepts
This blog summarizes the concepts of cluster randomization, and the logistical and statistical considerations while designing a cluster randomized controlled trial.
Sampling Methods In Research: Types, Techniques, & Examples
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Sampling methods in psychology refer to strategies used to select a subset of individuals (a sample) from a larger population, to study and draw inferences about the entire population. Common methods include random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and convenience sampling. Proper sampling ensures representative, generalizable, and valid research results.
- Sampling : the process of selecting a representative group from the population under study.
- Target population : the total group of individuals from which the sample might be drawn.
- Sample: a subset of individuals selected from a larger population for study or investigation. Those included in the sample are termed “participants.”
- Generalizability : the ability to apply research findings from a sample to the broader target population, contingent on the sample being representative of that population.
For instance, if the advert for volunteers is published in the New York Times, this limits how much the study’s findings can be generalized to the whole population, because NYT readers may not represent the entire population in certain respects (e.g., politically, socio-economically).
The Purpose of Sampling
We are interested in learning about large groups of people with something in common in psychological research. We call the group interested in studying our “target population.”
In some types of research, the target population might be as broad as all humans. Still, in other types of research, the target population might be a smaller group, such as teenagers, preschool children, or people who misuse drugs.
Studying every person in a target population is more or less impossible. Hence, psychologists select a sample or sub-group of the population that is likely to be representative of the target population we are interested in.
This is important because we want to generalize from the sample to the target population. The more representative the sample, the more confident the researcher can be that the results can be generalized to the target population.
One of the problems that can occur when selecting a sample from a target population is sampling bias. Sampling bias refers to situations where the sample does not reflect the characteristics of the target population.
Many psychology studies have a biased sample because they have used an opportunity sample that comprises university students as their participants (e.g., Asch ).
OK, so you’ve thought up this brilliant psychological study and designed it perfectly. But who will you try it out on, and how will you select your participants?
There are various sampling methods. The one chosen will depend on a number of factors (such as time, money, etc.).
Random Sampling
Random sampling is a type of probability sampling where everyone in the entire target population has an equal chance of being selected.
This is similar to the national lottery. If the “population” is everyone who bought a lottery ticket, then everyone has an equal chance of winning the lottery (assuming they all have one ticket each).
Random samples require naming or numbering the target population and then using some raffle method to choose those to make up the sample. Random samples are the best method of selecting your sample from the population of interest.
- The advantages are that your sample should represent the target population and eliminate sampling bias.
- The disadvantage is that it is very difficult to achieve (i.e., time, effort, and money).
Stratified Sampling
During stratified sampling , the researcher identifies the different types of people that make up the target population and works out the proportions needed for the sample to be representative.
A list is made of each variable (e.g., IQ, gender, etc.) that might have an effect on the research. For example, if we are interested in the money spent on books by undergraduates, then the main subject studied may be an important variable.
For example, students studying English Literature may spend more money on books than engineering students, so if we use a large percentage of English students or engineering students, our results will not be accurate.
We have to determine the relative percentage of each group at a university, e.g., Engineering 10%, Social Sciences 15%, English 20%, Sciences 25%, Languages 10%, Law 5%, and Medicine 15%. The sample must then contain all these groups in the same proportion as the target population (university students).
- The disadvantage of stratified sampling is that gathering such a sample would be extremely time-consuming and difficult to do. This method is rarely used in Psychology.
- However, the advantage is that the sample should be highly representative of the target population, and therefore we can generalize from the results obtained.
Opportunity Sampling
Opportunity sampling is a method in which participants are chosen based on their ease of availability and proximity to the researcher, rather than using random or systematic criteria. It’s a type of convenience sampling .
An opportunity sample is obtained by asking members of the population of interest if they would participate in your research. An example would be selecting a sample of students from those coming out of the library.
- This is a quick and easy way of choosing participants (advantage)
- It may not provide a representative sample and could be biased (disadvantage).
Systematic Sampling
Systematic sampling is a method where every nth individual is selected from a list or sequence to form a sample, ensuring even and regular intervals between chosen subjects.
Participants are systematically selected (i.e., orderly/logical) from the target population, like every nth participant on a list of names.
To take a systematic sample, you list all the population members and then decide upon a sample you would like. By dividing the number of people in the population by the number of people you want in your sample, you get a number we will call n.
If you take every nth name, you will get a systematic sample of the correct size. If, for example, you wanted to sample 150 children from a school of 1,500, you would take every 10th name.
- The advantage of this method is that it should provide a representative sample.
Sample size
The sample size is a critical factor in determining the reliability and validity of a study’s findings. While increasing the sample size can enhance the generalizability of results, it’s also essential to balance practical considerations, such as resource constraints and diminishing returns from ever-larger samples.
Reliability and Validity
Reliability refers to the consistency and reproducibility of research findings across different occasions, researchers, or instruments. A small sample size may lead to inconsistent results due to increased susceptibility to random error or the influence of outliers. In contrast, a larger sample minimizes these errors, promoting more reliable results.
Validity pertains to the accuracy and truthfulness of research findings. For a study to be valid, it should accurately measure what it intends to do. A small, unrepresentative sample can compromise external validity, meaning the results don’t generalize well to the larger population. A larger sample captures more variability, ensuring that specific subgroups or anomalies don’t overly influence results.
Practical Considerations
Resource Constraints : Larger samples demand more time, money, and resources. Data collection becomes more extensive, data analysis more complex, and logistics more challenging.
Diminishing Returns : While increasing the sample size generally leads to improved accuracy and precision, there’s a point where adding more participants yields only marginal benefits. For instance, going from 50 to 500 participants might significantly boost a study’s robustness, but jumping from 10,000 to 10,500 might not offer a comparable advantage, especially considering the added costs.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Sampling in quantitative research is a critical component that involves selecting a representative subset of individuals or cases from a larger population and often employs sampling techniques based on probability theory. 41 The goal of sampling is to obtain a sample that is large enough and representative of the target population.
There are two primary types of sampling methods that you can use in your research: Probability sampling involves random selection, allowing you to make strong statistical inferences about the whole group. Non-probability sampling involves non-random selection based on convenience or other criteria, allowing you to easily collect data.
Researchers focus on the specific techniques that will yield highly representative samples (i.e., samples that are very much like the population). Quantitative researchers tend to use a type of sampling based on theories of probability from mathematics, called probability sampling.
Part I: Sampling, Data Collection, & Analysis in Quantitative Research. In this module, we will focus on how quantitative research collects and analyzes data, as well as methods for obtaining sample population. Levels of Measurement. Reliability and Validity. Population and Samples.
Probability-based sampling methods are most commonly used in quantitative research, especially when it’s important to achieve a representative sample that allows the researcher to generalise their findings.
This blog introduces sampling methods, with examples, and potential sampling errors to avoid when we are conducting medical research.
Sampling methods in psychology refer to strategies used to select a subset of individuals (a sample) from a larger population, to study and draw inferences about the entire population. Common methods include random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and convenience sampling.
In quantitative research, collecting data from an entire population of a study is impractical in many instances. It squanders resources like time and money which can be minimized by choosing suitable sampling techniques between probability and non-probability methods.
This article reviews probability and non-probability sampling methods, lists and defines specific sampling techniques, and provides pros and cons for consideration. In addition, issues related to sampling methods are described to highlight potential problems.
The chapter suggests selecting sampling techniques should be guided by research objectives, study scope, and availability of sampling frame rather than looking at the nature of sampling techniques.