Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List

Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Is College Worth It?
As economic outcomes for young adults with and without degrees have improved, americans hold mixed views on the value of college, table of contents.
- Labor force trends and economic outcomes for young adults
- Economic outcomes for young men
- Economic outcomes for young women
- Wealth trends for households headed by a young adult
- The importance of a four-year college degree
- Getting a high-paying job without a college degree
- Do Americans think their education prepared them for the workplace?
- Is college worth the cost?
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology
- Current Population Survey methodology
- Survey of Consumer Finances methodology

Pew Research Center conducted this study to better understand public views on the importance of a four-year college degree. The study also explores key trends in the economic outcomes of young adults among those who have and have not completed a four-year college degree.
The analysis in this report is based on three data sources. The labor force, earnings, hours, household income and poverty characteristics come from the U.S. Census Bureau’s Annual Social and Economic Supplement of the Current Population Survey. The findings on net worth are based on the Federal Reserve’s Survey of Consumer Finances.
The data on public views on the value of a college degree was collected as part of a Center survey of 5,203 U.S. adults conducted Nov. 27 to Dec. 3, 2023. Everyone who took part in the survey is a member of Pew Research Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. Address-based sampling ensures that nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for this report , along with responses, and the survey’s methodology .
Young adults refers to Americans ages 25 to 34.
Noncollege adults include those who have some college education as well as those who graduated from high school but did not attend college. Adults who have not completed high school are not included in the analysis of noncollege adults. About 6% of young adults have not completed high school. Trends in some labor market outcomes for those who have not finished high school are impacted by changes in the foreign-born share of the U.S. population. The Census data used in this analysis did not collect information on nativity before 1994.
Some college includes those with an associate degree and those who attended college but did not obtain a degree.
The some college or less population refers to adults who have some college education, those with a high school diploma only and those who did not graduate high school.
A full-time, full-year worker works at least 50 weeks per year and usually 35 hours a week or more.
The labor force includes all who are employed and those who are unemployed but looking for work.
The labor force participation rate is the share of a population that is in the labor force.
Young adults living independently refers to those who are not living in the home of either of their parents.
Household income is the sum of incomes received by all members of the household ages 15 and older. Income is the sum of earnings from work, capital income such as interest and dividends, rental income, retirement income, and transfer income (such as government assistance) before payments for such things as personal income taxes, Social Security and Medicare taxes, union dues, etc. Non-cash transfers such as food stamps, health benefits, subsidized housing and energy assistance are not included. As household income is pretax, it does not include stimulus payments or tax credits for earned income and children/dependent care.
Net worth, or wealth, is the difference between the value of what a household owns (assets) and what it owes (debts).
All references to party affiliation include those who lean toward that party. Republicans include those who identify as Republicans and those who say they lean toward the Republican Party. Democrats include those who identify as Democrats and those who say they lean toward the Democratic Party.
At a time when many Americans are questioning the value of a four-year college degree, economic outcomes for young adults without a degree are improving.
After decades of falling wages, young U.S. workers (ages 25 to 34) without a bachelor’s degree have seen their earnings increase over the past 10 years. Their overall wealth has gone up too, and fewer are living in poverty today.
Things have also improved for young college graduates over this period. As a result, the gap in earnings between young adults with and without a college degree has not narrowed.
The public has mixed views on the importance of having a college degree, and many have doubts about whether the cost is worth it, according to a new Pew Research Center survey.
- Only one-in-four U.S. adults say it’s extremely or very important to have a four-year college degree in order to get a well-paying job in today’s economy. About a third (35%) say a college degree is somewhat important, while 40% say it’s not too or not at all important.
- Roughly half (49%) say it’s less important to have a four-year college degree today in order to get a well-paying job than it was 20 years ago; 32% say it’s more important, and 17% say it’s about as important as it was 20 years ago.
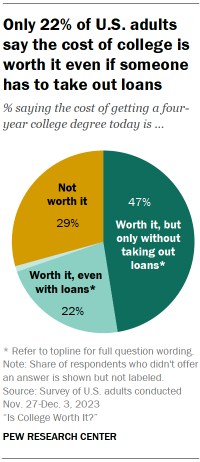
- Only 22% say the cost of getting a four-year college degree today is worth it even if someone has to take out loans. Some 47% say the cost is worth it only if someone doesn’t have to take out loans. And 29% say the cost is not worth it.
These findings come amid rising tuition costs and mounting student debt . Views on the cost of college differ by Americans’ level of education. But even among four-year college graduates, only about a third (32%) say college is worth the cost even if someone has to take out loans – though they are more likely than those without a degree to say this.
Four-year college graduates (58%) are much more likely than those without a college degree (26%) to say their education was extremely or very useful in giving them the skills and knowledge they needed to get a well-paying job. (This finding excludes the 9% of respondents who said this question did not apply to them.)
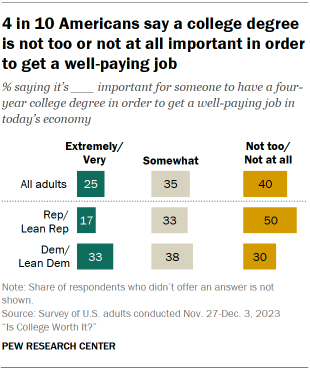
Views on the importance of college differ widely by partisanship. Republicans and Republican-leaning independents are more likely than Democrats and Democratic leaners to say:
- It’s not too or not at all important to have a four-year college degree in order to get a well-paying job (50% of Republicans vs. 30% of Democrats)
- A college degree is less important now than it was 20 years ago (57% vs. 43%)
- It’s extremely or very likely someone without a four-year college degree can get a well-paying job (42% vs. 26%)
At the same time that the public is expressing doubts about the value of college, a new Center analysis of government data finds young adults without a college degree are doing better on some key measures than they have in recent years.
A narrow majority of workers ages 25 to 34 do not have a four-year college degree (54% in 2023). Earnings for these young workers mostly trended downward from the mid-1970s until roughly a decade ago.
Outcomes have been especially poor for young men without a college degree. Other research has shown that this group saw falling labor force participation and sagging earnings starting in the early 1970s , but the last decade has marked a turning point.
This analysis looks at young men and young women separately because of their different experiences in the labor force.
Trends for young men
- Labor force participation: The share of young men without a college degree who were working or looking for work dropped steadily from 1970 until about 2014. Our new analysis suggests things have stabilized somewhat for this group over the past decade. Meanwhile, labor force participation among young men with a four-year degree has remained mostly flat.
- Full-time, full-year employment: The share of employed young men without a college degree who are working full time and year-round has varied somewhat over the years – trending downward during recessions. It’s risen significantly since the Great Recession of 2007-09, with the exception of a sharp dip in 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. For employed young men with a college degree, the share working full time, full year has remained more stable over the years.
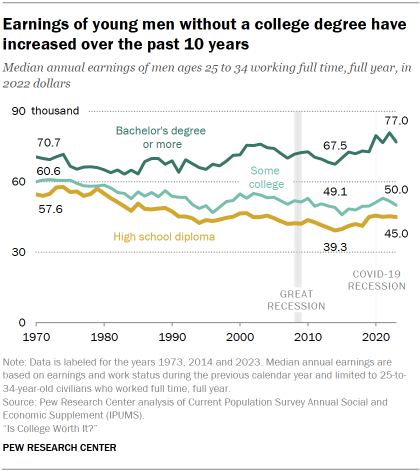
- Median annual earnings: Since 2014, earnings have risen for young men with some college education and for those whose highest attainment is a high school diploma. Even so, earnings for these groups remain below where they were in the early 1970s. Earnings for young men with a bachelor’s degree have also trended up, for the most part, over the past 10 years.
- Poverty: Among young men without a college degree who are living independently from their parents, the share in poverty has fallen significantly over the last decade. For example, 12% of young men with a high school diploma were living in poverty in 2023, down from a peak of 17% in 2011. The share of young men with a four-year college degree who are in poverty has also fallen and remains below that of noncollege young men.
Trends for young women
- Labor force participation: The shares of young women with and without a college degree in the labor force grew steadily from 1970 to about 1990. Among those without a college degree, the share fell after 2000, and the drop-off was especially sharp for young women with a high school diploma. Since 2014, labor force participation for both groups of young women has increased.
- Full-time, full-year employment: The shares of employed young women working full time and year-round, regardless of their educational attainment, have steadily increased over the decades. There was a decline during and after the Great Recession and again (briefly) in 2021 due to the pandemic. Today, the shares of women working full time, full year are the highest they’ve ever been across education levels.
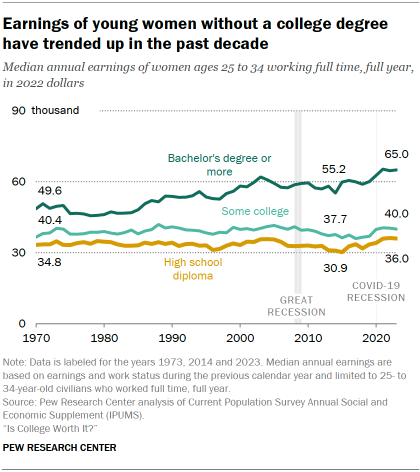
- Median annual earnings: Median earnings for young women without a college degree were relatively flat from 1970 until about a decade ago. These women did not experience the steady decline in earnings that noncollege young men did over this period. By contrast, earnings have grown over the decades for young women with a college degree. In the past 10 years, earnings for women both with and without a college degree have risen.
- Poverty: As is the case for young men without a college degree, the share of noncollege young women living in poverty has fallen substantially over the past decade. In 2014, 31% of women with a high school diploma who lived independently from their parents were in poverty. By 2023, that share had fallen to 21%. Young women with a college degree remain much less likely to be in poverty than their counterparts with less education.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Business & Workplace
- Economic Conditions
- Higher Education
- Income & Wages
- Recessions & Recoveries
- Student Loans
U.S. women are outpacing men in college completion, including in every major racial and ethnic group
A look at historically black colleges and universities in the u.s., 5 facts about student loans, half of latinas say hispanic women’s situation has improved in the past decade and expect more gains, from businesses and banks to colleges and churches: americans’ views of u.s. institutions, most popular, report materials.
901 E St. NW, Suite 300 Washington, DC 20004 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan, nonadvocacy fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It does not take policy positions. The Center conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, computational social science research and other data-driven research. Pew Research Center is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts , its primary funder.
© 2024 Pew Research Center

Importance of College Education: Why it is Important to go to College
You are approaching high school graduation and wondering what’s in store next. Sure, the thought of going straight into the workforce to immediately generate an income sounds exciting. But have you considered furthering your studies to expand your earning potential within today’s economy? While higher education may easily be one of the largest expenses you will face in your lifetime, attending college provides opportunities for graduates that may not be as widespread for those without a university degree.
Did You Know? : According to the U.S. Department of Education college graduates with a bachelor’s degree typically earn 66 percent more than those with only a high school diploma, and are also far less likely to face unemployment.

Why Consider Going to College?
The biggest advantage of going to college is the gateway to increased opportunity. We aren’t just talking about more work opportunities after graduation, but also the endless possibilities of making new connections that may become of value to you for life, the benefits of gaining knowledge , the encouragement of discovering new passions, and so much more!
Make Valuable Connections
Attending college gives you the opportunity to meet new people of different backgrounds with unique interests, increasing your chances of connecting with people in your potential career field. Knowing the right people can take you far in life! You never know who is going to help you land your dream job, or connect you with the right person who will.
Some ways you can expand your network in college is by becoming a part of clubs that align with your interests, playing sports, or volunteering for an organization. Joining a sorority or a fraternity is also a surefire way to meet some close friends for many. You could even pick up an internship or part-time job on or off-campus, and meet people that way as well. Learning from someone more established is also a fantastic way to test the waters in a field of interest, and in that sense, get to know yourself better!
Exercise the Mind
Students pursuing higher education are presented with the opportunity to read books and listen to lectures of top experts in their fields. As a result, they gain advanced knowledge in areas that interest them most. This stimulation encourages individuals to think critically, question concepts, and explore new ideas, which allow for additional growth and development. Generally, college graduates have an edge in the job market over those who have just come out of high school. In recent years, seniors have also been going back to college to exercise their minds and to learn from new opportunities to help them as they grow older.
Open Up to More Job Opportunities
Finally, most people pursuing a college degree look forward to promising job prospects after graduating. The good news is that many recruiters in the United States now look for candidates that have experienced higher education. We have shifted from a manufacturing-based economy to a knowledge-based economy, which makes having a college education especially important these days. Regardless of what career field plan to commit to, you will likely benefit from going to college!
Get Well-Rounded
By experiencing things like being a part of a club, participating in a group study, taking a variety of courses, and continually enhancing your work ethic, you innately get to know yourself as an individual better.
More often than not, those entering their twenties without a clue on what they want to do for a living will develop a better sense of their “calling” after taking different classes that were not offered in high school. Some examples of such courses may include psychology, communications, sociology, business, and computer science, to name a few.
Many higher education students are also living away from home for the first time, and that independence and freedom allows them to try things they didn’t feel totally comfortable doing in their high school years. New discoveries could lead to new passions and potential career paths after college!
With the global economy becoming increasingly competitive, going to college is a smart way to give yourself the best chance at landing a stable, well-paying job. Gain a wealth of knowledge and experience that you would never receive if you decided to skip higher education. You’ll be surprised at how much personal development you will experience, too!

Does College Matter?
College does matter and is absolutely worth it - if you choose a program that matches your career goals, graduate on time, and avoid too much debt.
Almost every job that leads to a promising career, with good pay and benefits, requires education or training beyond high school. For most high-paying professional jobs, that means a four-year college degree.
At the same time, career training or short-term educational programs for a growing number of technical fields can pay off, too.
For many, the question is: college or trade school?
Is college worth the cost?
If you stick with your studies and graduate in a reasonable time, college is worth the cost. The vast majority of college graduates are better off financially than their peers who didn’t complete college. College degrees are still in high demand from employers, and completing college is a strong sign that you’re ready for high-skilled work.
The key is finding a school where you’re likely to graduate and finish with low or modest debt. The national average is about $29,400 , which most graduates are able to pay off because their degree helped them earn a well-paying job. You can find detailed information about college graduation rates, the real cost of college over time, and how potential earnings vary by career field at bigfuture.org. And you can give yourself the opportunity to save time and money toward a degree while you’re in high school by scoring a 3 or higher on an AP Exam to earn college credit .
Students can get into trouble when they don’t graduate, or when they take on significant debt before they’re able to finish. Many college students don’t graduate on time, which makes a degree more expensive. Or they don’t finish at all, which means they don’t get the benefit of higher earnings.
Finishing college is the single most important thing you can do to make it affordable. Students who leave college without graduating are the most likely to have trouble with debt and future employment. As many as 4 in 10 students who start a 4-year degree program don’t finish in 6 years. Colleges with more resources, like generous financial aid funding, good counselors, and mentoring programs, typically have a better track record of graduating their students on time and with low debt.
What about career or technical training?
There are valuable training and credential options available, but there are also a lot of expensive programs that don’t add much to your résumé. It’s important to know what kind of training is most valuable for your planned career field.
Specific training programs in fields like construction, manufacturing, and healthcare can lead to immediate job opportunities and above-average pay. Job training credentials offered by community colleges, often in partnership with local employers, are some of the highest-rated programs.
Some larger tech companies like IBM, Google, and Apple will accept proof of specific coding or data analytics skills for entry-level jobs. However, they still normally require college degrees for higher-level positions.
Building a long-term career—taking on more responsibility, managing other people, earning more money—is often easier for those with both a college degree and industry-specific credentials. Employers usually see a college degree as meaning you have a set of flexible skills, like critical thinking and communication. Industry-specific credentials are a sign that you have hard skills like coding or database management.
Together, they make a stronger case that you’re ready for skilled work than either alone. Unless you have a very clear sense of your dream job and its required training programs, it’s generally better to pursue both college and industry credentials.
Should I go to college?
Thinking clearly about your goals and college options can help you make the right choice. Feeling confident about your next step after high school, whether that’s college or a high-value career path, will set you up for success.
Many variables affect your life and career, and it’s impossible to plan and predict all of them. It’s most important to find a field that genuinely interests you, then get all the valuable education and training you can in that field. Here are some tips on how to be successful after high school:
- Take classes in college or through a training program.
- Pursue internships with companies or organizations that can give you experience in your chosen field.
- Cultivate mentors who have built careers that interest you and ask how they did it.
You’re much more likely to complete a worthwhile degree or training program if you’re working toward a life and a job you’ll love. Focus on the future you want and be open to different options for getting there.
Find the right college for you.
Related articles.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
College Education amid COVID-19. As many colleges went online or to a hybrid online and in-person model during the COVID-19 (coronavirus) pandemic, colleges overall saw a significant fall 2020 enrollment drop. Undergraduate enrollment fell 3.6% (about 560,000 students) from fall 2019.
The public has mixed views on the importance of having a college degree, and many have doubts about whether the cost is worth it, according to a new Pew Research Center survey. Only one-in-four U.S. adults say it’s extremely or very important to have a four-year college degree in order to get a well-paying job in today’s economy.
Learn how college education can help you earn more, make connections, exercise your mind, and discover your passions. Find out the facts and figures on college graduates' income, unemployment, and career prospects.
The Postsecondary Value Commission, supported by the Gates Foundation, aims to define, measure, and act on the value of college education for all students. Learn how the commission proposes to address the inequities in higher education and the challenges of COVID-19.
College can lead to a promising career, higher pay, and lower debt if you choose a program that matches your goals and graduate on time. Learn how to find a college that suits you, avoid expensive and low-value programs, and get industry-specific credentials.
While college isn’t right for everyone, higher education is linked to many positive benefits. See why you should go to college if you can. For some students, going to college is a...