👀 Turn any prompt into captivating visuals in seconds with our AI-powered design generator ✨ Try Piktochart AI!

Progress Report: How to Write, Structure, and Make Project Progress Visually Attractive

Picture this: Days or weeks into a project, your supervisor asks for a progress report.
Depending on your experience with writing progress reports, you might respond with readiness, anxiety, or confusion. Where do you begin? How do you know you’ve created a satisfactory or even amazing final report? Fear not—the expert team here at Piktochart is here to help.
In this progress reporting guide, we’ll not only give you top tips on how to write a successful report but additionally provide you with progress report templates and checklists to keep you focused on the important stuff. We begin, of course, with the all-important question anyone from a newbie to even a seasoned professional might have: “What is a progress report?”
Table of contents:
What is a progress report, why is a progress report important.
- How to write a progress report
- How to structure a progress report
- Free progress report templates you can edit right away
Progress report checklist
In case you prefer watching over reading, feel free to check out the video summary of this blog post:
A progress report is exactly what it sounds like—a document using simple and straightforward language that explains in detail what has been achieved and what else is needed for project completion. Essentially this document is a status update before the final report, outlining tasks completed by a team member, project manager, or team, along with what else needs to be done.
W hether you need to provide daily progress reports or even quarterly progress reports, this asset outlines the activities you’ve carried out, the tasks you’ve completed, and the milestones you’ve reached vis-à-vis your project plan .
Depending on the scope and complexity of the project, you might need to give a progress report weekly or monthly or for every 25% project milestone.
In terms of audience, a progress report is typically written for a supervisor, colleague, or client. Progress reports can be written from the perspective of one person as well as an entire team or department.
Throughout your career, you’re likely to be creating more reports than you can count (challenge for you: count them and find how many resources you’re using!).
Perhaps you find yourself spending more time crunching data and plugging numbers into graphs than actually working.
Reports don’t have to be as time-consuming as they often are. Progress report templates are time-savers! Get your free Piktochart account so you can follow along as we share more templates below.
We also tapped into the brilliance of Kevan Lee of Buffer in this interactive content experience to help you with your progress report projects.
Dive right in here, and learn some reporting hacks from Kevan .
Sometimes it might feel like writing about your progress in detail is redundant, especially when you’ve been regularly communicating with your supervisor, teammates, and client throughout the course of the project. Like any project manager, you probably think there are more important things to work on.
But this type of professional report is actually quite useful for several reasons.
1. It gets everyone on the same page
Each person who receives a copy of the report will know what has been accomplished and what is remaining. This prevents confusion about what has been or has yet to be done. Additionally, it provides proof and data about the respective project that can be cited and sourced if and when questions arise in the future.
2. Writing progress reports facilitates collaboration
This is especially important when different teams or departments work together. Knowing what another team is prioritizing helps prevent working in silos and also reduces task redundancy. Additionally, progress reporting helps a team identify areas where it can offer help or collaborate with others.
When teams can track progress on where other teams are on the project timeline, project managers get a better idea of the current status. They can reassign resources to make sure everyone is on track to hit the deadline for the current project, which can be tricky if you’re managing remote teams .
If you’d like to learn more about how you can work together with your team on a report, sign up for a free Piktochart account and try our online report maker .
3. It improves transparency and accountability by providing a paper trail
When you submit your report, you’ve placed on record that you’ve accomplished a task or explained why your results were different than expected. Once the document has been accepted, it becomes part of the project’s official documentation.
So, just in case someone accuses you in the future of failing to accomplish a task or not reporting a problem, you can point to the progress report as proof that you did so.
On the flip side, if your project ever gets nominated for an award, you can be sure validators will come seeking documents that explain how the entire thing was accomplished.
4. It improves project evaluation and review
Next time you plan for a project, your team can examine documents, including progress reports, of previous projects to find out what was done right, what went wrong, and what can be improved.
Previous reports can shed light on systemic issues, loopholes, and other causes of delay or failure—both internal and external—that must be avoided or resolved.
5. It provides insights for future planning
When the supervisor knows what tasks have been accomplished, he or she can focus on monitoring progress toward the next stages of the project.
When a report shows that delays have occurred, the supervisor is able to investigate the problems that hindered progress and take steps to prevent them from happening again in the future.
The supervisor will also be able to adjust the project timeline if absolutely needed or instruct teams to double down.
Ultimately, all the valuable insights from the project documentation can increase the chance of success for future projects.
Here is a progress report format example:

How to write progress report s
Have you ever found yourself stuck tapping your pen or staring at a blinking cursor, unable to begin writing?
Writer’s block is not an unusual experience when creating progress reports, especially for those whose jobs typically don’t involve drafting a long document or creating a formal report.
One reason people may find it difficult to write these reports is the thought that they’re not ‘writers.’ Yet, this is simply a negative mindset.
Reports don’t require sophisticated language—in fact, the simpler, the better.
Here are some writing tips on progress reporting:
“Piktochart is my go-to tool when I’m looking for a way to summarize data that is easy for our upper management to review. Piktochart provides me with the tools to display data in a creative, visually appealing way.” – Erica Barto, Selection, Testing & Assessment Specialist at Valero Energy Corporation Create a report, presentation, infographic, or other visuals online with Piktochart. You don’t need any graphic design experience to make professional visual content. Sign up for free .
1. Think of it as a Q&A
Before you start worrying about your reporting frequency and whether you should provide monthly reports or weekly reports, take a step back and focus on the purpose of the report itself.
In essence, the reporting process comes down to Q&A; you’re answering key questions about your progress. Imagine your manager, colleagues, or client asking you their most important questions, and you’re simply providing them with answers on the project status.
For example, let’s say that you’re organizing a weekend fair with food stalls and music and that you’re put in charge of food concessions.
The project plan might require you to have secured letters of intent (LOI) from at least 10 businesses by the end of the first month.
Your progress report would then outline the companies or entrepreneurs who have sent LOIs, including a description of their businesses and plans for their food stalls. If talks are in progress with other businesses that haven’t yet sent LOIs, you can include that and explain when they’re expected to send in their letters.
On the other hand, if you haven’t met your target, you’d have to explain why but also narrate the efforts you have exerted and the expected timeline for achieving the desired results.

2 . Use simple and straightforward language
This doesn’t mean you can’t use technical jargon.
For example, if you’re in the construction business, you don’t have to avoid using terms like “tender” or “variation” or “risk management.”
But otherwise, speak plainly. Use clear and concise language.
One misconception in business writing is that complexity impresses. In truth, it only causes confusion. Fact is, being able to speak plainly about your subject indicates that you understand your subject matter inside out.
Let’s get specific. One thing that makes business documents dreary is the transformation of verbs into nouns—just like I did there.
If we had to rephrase that to keep the verb, we’d write, “transforming verbs into nouns.” It sounds simpler and gets to the point.

3 . Avoid using the passive voice where possible
Sometimes, you can’t avoid using the passive voice in formal documents that prohibit the first-person point-of-view. But when done well, it helps to make your progress reports more relatable.
Going back to the food concession example, a passive sentence would read: “Research on potential food concessionaires was carried out.”
To make that sentence active, give it an actor (which is the team in this case), as in: “The team researched on potential food concessionaires.”
4. Be specific
A study published in the Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience found that when you use concrete words, you tend to engage both the left and right parts of the brain, while the right region tends to remain unstimulated by abstract words.
While the jury is still out on exactly how word meanings are represented in the mind, we can agree that the phrase “a merry sound” doesn’t stir the imagination as much as “tinkling bells”.
“A hot day” doesn’t activate visual imagery as much as “a melting popsicle” does. When a reader’s mind is stimulated by words, it’s less likely to drift off.

Taking the previous example, “researched on potential food concessionaires” doesn’t evoke a visual image. Meanwhile, “built a list of 50 potential food concessionaires” is more concrete, especially when you add details of what food items might be sold.
5. Explain jargon if needed
This depends on who will be reading your progress reports, and if you’re using very specialized jargon that only members of your team would be familiar with.
For example, in a report written by a construction team addressed to the project manager , construction jargon could be used as the recipient obviously understands it.
6. Spell out acronyms when they first occur in the document
Don’t assume that every single person reading the report will understand all the acronyms you use without you spelling them out.
For instance, in construction work, SWMS should first be spelled out as “safe work method statement”. ‘Pre-starts’ should be spelled out as ‘pre-start checks’. So in your report, it would look like this: “safe work method statement (SWMS)”, then all subsequent references are free to just be SWMS.
7. Stick to facts
Avoid providing an opinion, unless it’s part of the project.
For instance, your task might be to analyze data and offer your interpretation and prediction. In that case, you can offer your speculation and point of view, as long as you have evidence to back you up.
8. Use graphics to supplement the text
Avoid writing down a long series of numbers in a sentence. Try using different types of graphs , tables or charts, especially when dealing with a series of numbers.
Here at Piktochart, we have many progress report templates, and the hiring progress report below is a great example.
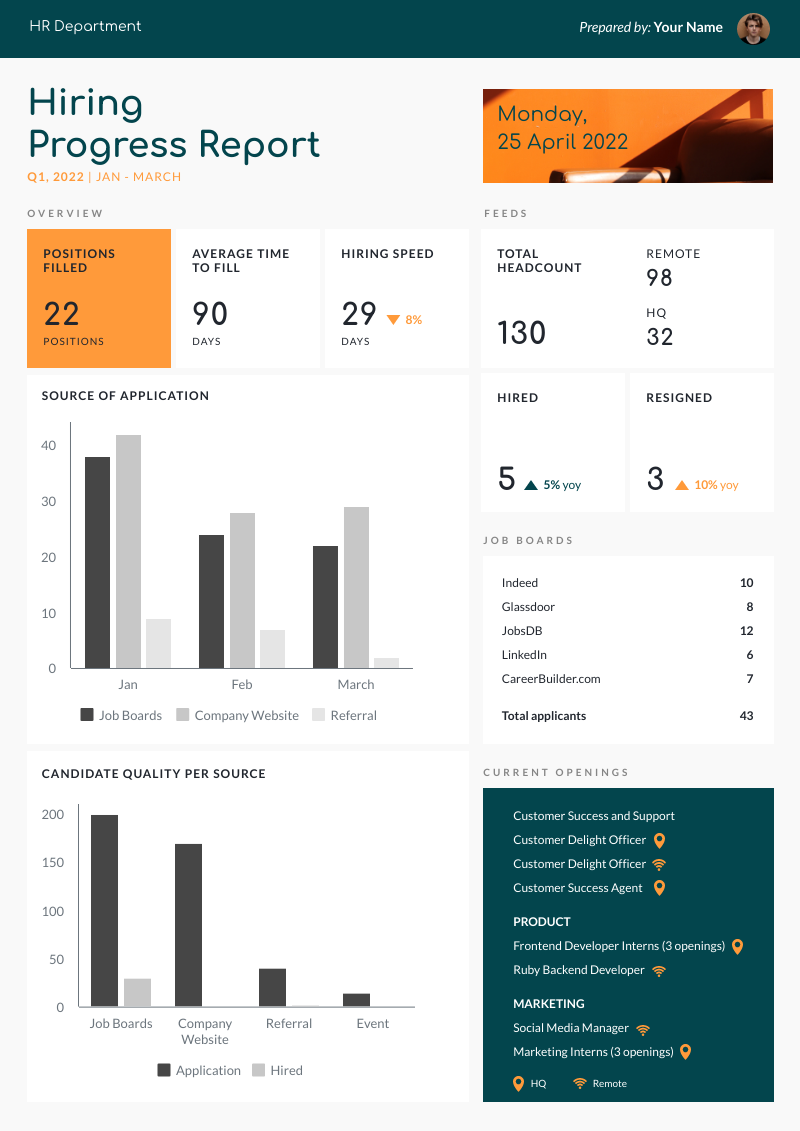
When using graphs or charts, try out several types to determine which ones best present your data. You might use a bar graph , pie chart , line graph , or even scatter plot . When doing so, though, spend time distinguishing different data sets from the others by using labels and colors.
Don’t worry if this sounds daunting—there are plenty of software that can help you visualize data , including the most basic examples, MS Excel and Numbers for Mac.
Feel you’ve got enough to information to get started? You can create a report in minutes with our AI report generator . Simply share your prompt on what type of report you want, and our AI tool will suggest several templates to choose from. You can pick the most appropriate one, then customize it in our editor.
How to structure progress report s
You may still be wondering about the exact process of how to write a progress report. Armed with all of these practical tips, how do you put the report together?
First, it depends on the type of report, as well as the intended reader. A progress report may be written daily, weekly, or monthly. It may be written for an individual or a team.
As you’ll see in the examples below, the main parts of a progress report are:
1. Introduction
This part provides an overview of the contents of the progress report. It’s best to write this after you’ve completed all the other parts of the report. That way, you’ll be able to provide an accurate summary.
Keep it short and simple. One or two paragraphs will do.
2. Accomplishments
Numbers and details are your friends, especially when writing this section of the progress report. The accomplishments you write should correspond to your goals.

What were your goals for the period covered by the report?
This could be a goal for the day, week, month, or quarter. On the other hand, it could be a team goal, too.
Be concrete when writing goals. For instance:

Avoid providing too much detailed information. The simpler this section is, the easier it is for stakeholders and the project team to see the project priorities.
4. Roadblocks
Explain what situations, if any, prevented you from achieving your goals, or may have hindered the project’s progress.
But don’t stop there. Be proactive and present an action plan and timeline for resolving the roadblocks. Include details, such as funds, materials, and human resources you may need to implement the solution.
Progress reporting templates you can edit right away
To guide you better, here are progress report template examples that are visually attractive and highly readable.
These templates are available if you sign up for a free Piktochart account . Once you log in, use any of the templates below and edit the elements and text to make it your own.
1. Daily progress report s
A daily progress report includes your goals for the day, as well as your accomplishments the previous day. It also explains challenges encountered in performing tasks and achieving goals.
Another section under the daily report is ‘lessons learned’. These need to be directly related to the day’s tasks and challenges, as well as to the previous day’s accomplishments.
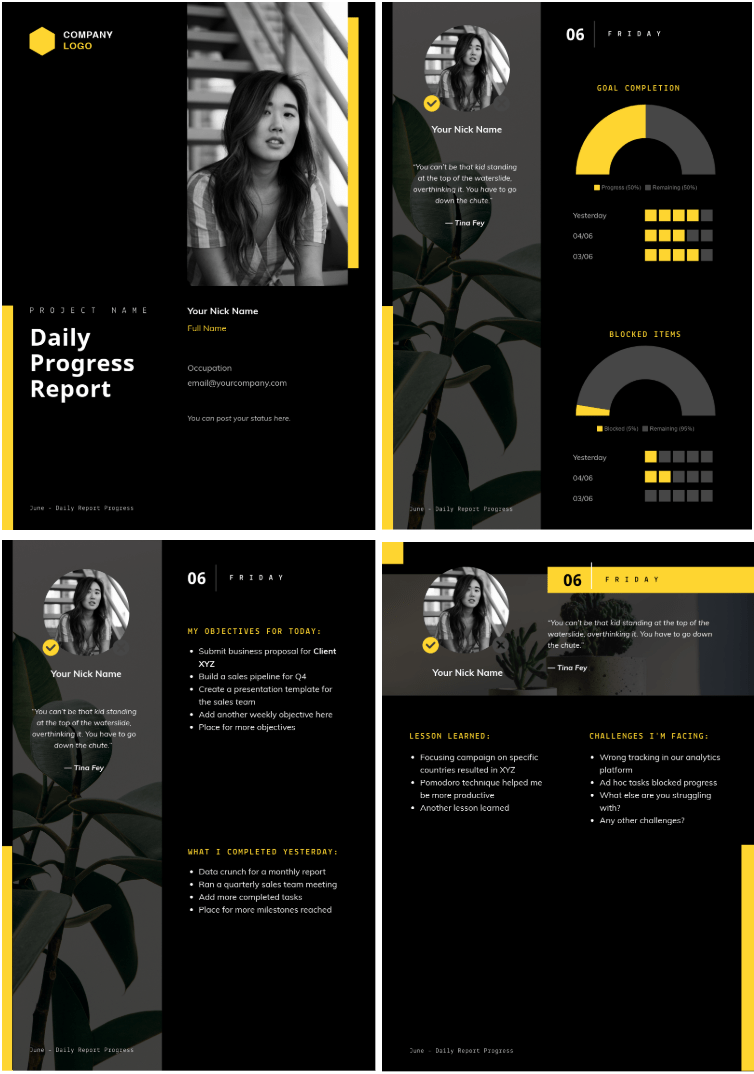
2. Weekly progress report
Weekly progress reports provide a week-by-week breakdown of what has been accomplished and what tasks remain to be completed.
Just like a daily report, a weekly progress report may include challenges and lessons learned. Examples are included in the templates below.
To get a better idea of this, let’s go back to the events example:
- Many potential vendors were attending a week-long industry convention; couldn’t book meetings.
- Potential vendors didn’t read the entire email.

Lessons Learned
- Consider industry events when planning a timeline for contacting clients
- Introductory emails must be short and have readable formatting

3. Monthly progress report ing
A monthly report is necessary for projects with longer durations. The report may provide both monthly and quarterly data on project progress.

4. Team progress report s
Team progress reports provide information on both team and individual milestones and progress status. Now this one is more complicated, simply because it involves several people who may have worked on different tasks.
It’s not enough to just let one person make the report. Of course, one person can do the typing, but everyone must provide input and feedback.
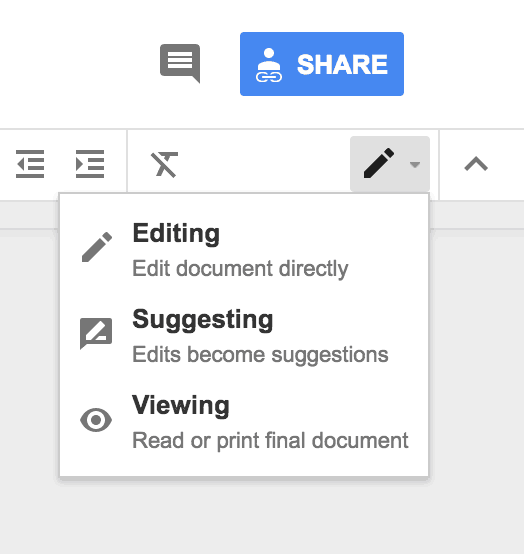
One way to keep a record of different team members’ input is to keep track of edits they have made.
To do this, simply enable tracking of changes on a Word document, or on Pages for Mac users. When working on a collaborative tool like Google Docs , click the pencil icon on the top-right part of the window, and choose “Edits become suggestions” on the drop-down menu. Here’s what that looks like:
On the other hand, team members can insert comments or questions. Again, you can do this easily on a Word document, as well as on software that let you comment on shared documents, like Google Docs and Piktochart .
Here’s what it looks like in Piktochart (learn more about this feature in our guide to annotated comments for teams ):
Here’s one example of Piktochart’s many team project report templates .
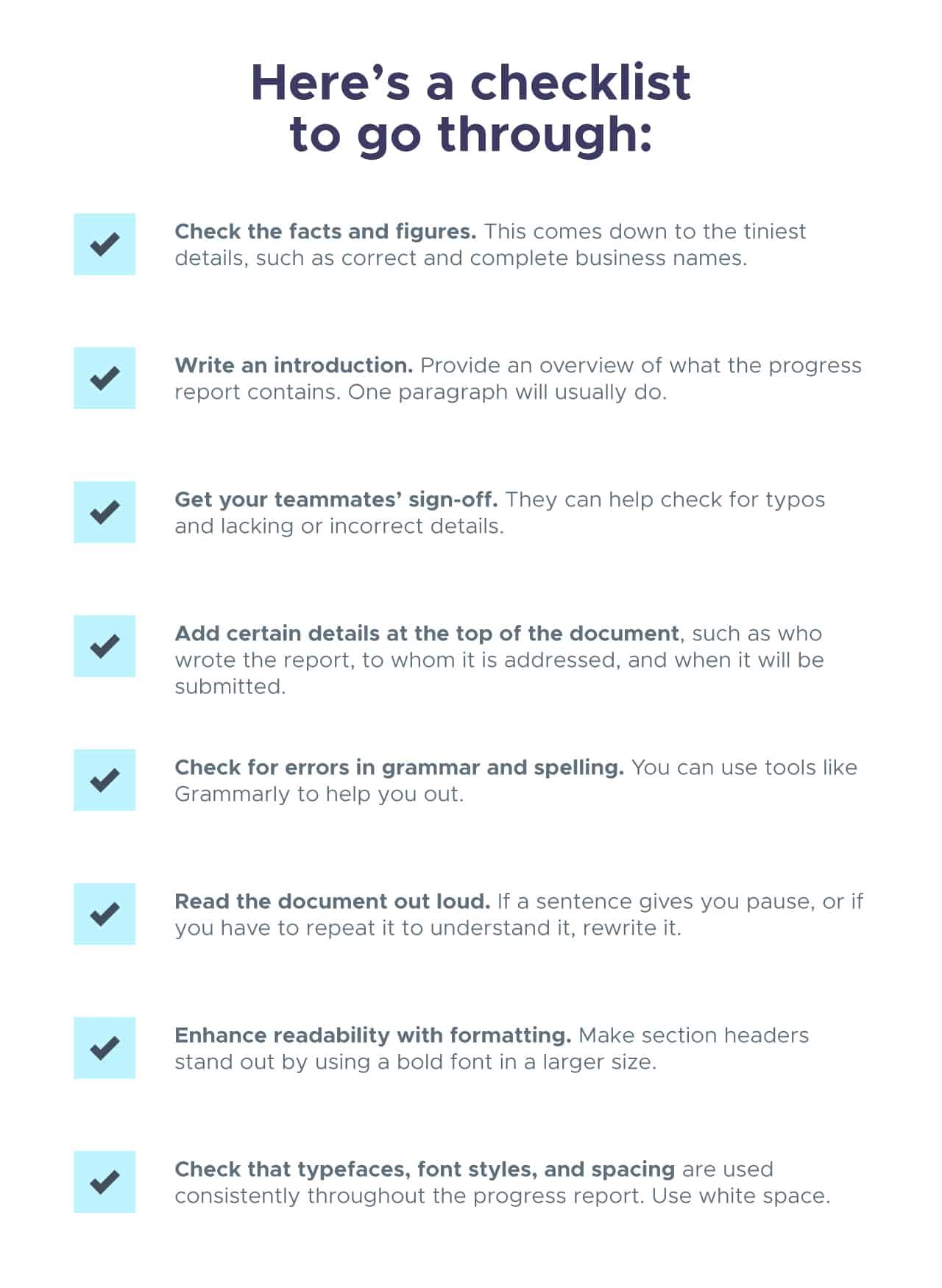
One last thing… You’ve finally finished typing up your report—breathe a sigh of relief, but don’t hit ‘send’ just yet.
Go over it at least once (better to do it more than once, especially if it’s a team report). Re-read the article, edit the content as needed, then ask a teammate to proofread with a fresh pair of eyes.
Other Posts

Graphic Design Trends 2025: 9 Key Predictions and Practical Applications

What Color is Vermilion? Its Meaning, Code & Combinations

What Color is Amaranth? Its Meaning, Code & Combinations

Progress Report: What is it & How to Write it? (Steps & Format)
Want to create a progress report to highlight the project’s achievements? No worries, we have got you covered! Read on…
A quick question – on a scale of 1 to 10, how important is it to regularly keep track and provide project updates to your supervisors, colleagues, or clients? The answer is 12! Simply, because nobody likes being left in the dark!
For any project in a company, people around it need to be well-informed about the project status, the research being done by the project team, their decisions, and the scope for improvement. These updates are an integral part of project management and ensure that every team member is operating efficiently with their goals being met on time.
One way to showcase the status of your project and keep track of it is to write a powerful progress report!
In fact, the American Society for Training and Development shows that having a specific place to check your progress increases the probability of meeting a goal by 95%.
Progress reports are a great place for project managers to inform and engage their supervisors, clients, or associates, about the progress they have made on a project over a certain period.
If executed well, progress reports provide a quick overview of how things are humming along, offering valuable insights to increase productivity, provide the necessary guidance, and quickly solve emerging difficulties.
However, writing a progress report can be a little daunting, especially, when you have a diverse team and various sub-projects to manage. Well, don’t fret! We’re going to fix that. In this blog post, we’ll teach you everything about progress reports, why they are important, and how you can write one that will make everyone say ‘wow’!
What is the Progress Report? (Definition)
A progress report is a document that explains in detail how much progress you have made towards the completion of your ongoing project.
A progress report is a management tool used in all types of organizations, that outlines the tasks completed, activities carried out, and target achieved vis-à-vis your project plan.
In a progress report, you explain any or all of the following:
- The amount of work complete?
- What part of the work is currently in progress?
- The problems or unexpected things that have occurred?
- What work is pending?
- How the project is going in general?
Read more: How To Write An Impressive Project Proposal?

Why are Progress Reports Important?
No project manager wakes up thinking “ I wish I could make reports for my supervisor and team all day” ! We get it. Writing progress reports are not very fun.
However, you know that writing progress reports are part of the deal. Progressive reporting demands talking with your team or client to understand the goals and showcase the information that closely relates to the said goals.
Whether the report is about updating the investors, marketing performance, or resource management. These reports let everyone see what’s going well and what isn’t.
It also assists managers to see the overall success or failure of projects. Furthermore, progress reports help to:
1. Make Information Transparent
The glue that holds together any relationship is visibility and transparency. A well-defined progress report directly presents how your work affects the project’s bottom line and showcases the rights and wrongs!
By adding transparency to your project plan, you can build an unmatched level of credibility and trust with your team and clients.
2. Encourage Constant Interaction
Creating and discussing progress reports results in constant communication and keeps everyone in the loop. Being in constant contact with others on a weekly or monthly basis ensures a clear understanding of roles and responsibilities.
3. Improve Project Evaluation and Review
Previous progress reports will help you in clarifying loopholes, and systemic issues, and examine documents to find out what went wrong, what can be done right, and which area needs improvement.
4. Provides Insight for Future Planning
When a progress report shows all the delays that have occurred, the supervisor or a project manager can monitor and investigate the issue that hindered progress and take additional steps to prevent them from happening in the future.
Read more: How to Write Project Reports that ‘Wow’ Your Clients?
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Progress Report
Step 1: understand the purpose.
Before you dive into writing your progress report, take a moment to understand its purpose. Who are you writing this for? What information do they need from you?
Knowing the audience and their needs will guide the entire structure of your report. Here are some questions to consider:
- Who will be reading this report? Is it your manager, a team of stakeholders, or a client?
- What decisions will they be making based on your report? Are they looking for a green light to move forward, or do they need to allocate resources?
- What level of detail do they expect? Do they need a broad overview, or will they be diving deep into specific tasks?
By understanding the purpose of your report, you can tailor the content to provide the most relevant and useful information for your audience. This will ensure your report is clear, concise, and achieves its desired outcome.
For example, if you’re reporting to your manager on a small project you’re leading, they might just need a quick update on completed tasks and any upcoming deadlines. On the other hand, a progress report for a client on a large-scale project might require a more detailed breakdown of achievements, challenges, and future plans.
Once you understand the purpose and who you’re writing for, you can move on to step two: choosing the right format for your progress report.
Step 2: Choose the Right Format
You’ve identified the purpose of your progress report (Step 1), now it’s time to pick the best outfit for it – the format! Just like you wouldn’t wear pajamas to a job interview, the format should suit the situation and your audience.
Here are some common formats for progress reports, along with when they might be most appropriate:
- Memo: This is a concise and professional way to update someone within your organization, like a supervisor or colleague. Memos are ideal for shorter reports (1-4 pages) that focus on key achievements and next steps.
- Letter: Similar to a memo, a letter works well for brief, semi-formal reports. This could be used for external audiences, such as a client or a funding agency.
- Formal Report: For lengthier projects with complex details, a formal report is the way to go. This format allows for in-depth sections on completed work, ongoing tasks, and future plans. It might also include charts, graphs, or tables to present data.
- Presentation: If your progress report needs to be visually engaging or you’ll be presenting it to a group, consider a slide deck. Slides are great for highlighting key points and using visuals to support your information.
Step 3: Start with a Title and Date
Every good report needs a clear title and date. Here’s why these are important and how to write them effectively:
- Think Signpost: Imagine your report is a signpost on a road trip. The title should be clear and concise, telling the reader exactly what the report is about.
- Focus on Content: Instead of a generic title like “Progress Report,” be specific! For example, if your report is on a marketing campaign, a good title could be “Social Media Marketing Campaign Progress Report – July 2024.”
- Keep it Short and Sweet: A long title can be overwhelming. Aim for 10-15 words that accurately represent the project and timeframe.
- Freshness Matters: The date helps the reader understand how recent the information in the report is.
- Specify the Reporting Period: If your report covers a specific timeframe, include those dates in the title or a subtitle. Example: “Social Media Marketing Campaign Progress Report – July 1st to July 15th, 2024”
Step 4: Provide an Introduction
The introduction of your progress report is like shaking hands for the first time – it creates a good first impression and sets the tone for the rest of the document. Here’s how to write a strong introduction:
- Start with the basics: Briefly mention the project name and the reporting period (e.g., weekly, monthly). You can also state who the report is submitted to (e.g., supervisor, client).
- Hook your reader: Briefly state the overall progress made on the project. Are you on track? Did you encounter any major roadblocks? This gives the reader a quick understanding of where things stand.
- Set the context: Provide a one-sentence reminder of the project’s goals. This refreshes the reader’s memory on what you’re trying to achieve.
Here’s an example to illustrate these points:
Project: Website Redesign – Progress Report (Week 3)
This report provides an update on the website redesign project for the period of July 7th to July 13th, 2024. We’ve made significant progress this week, completing the design for the homepage and starting development on core functionalities. The overall project remains on schedule to launch by the targeted date of August 1st.
This introduction quickly establishes the context, highlights progress, and assures the reader things are moving forward. By following these steps, you can write a clear and informative introduction that sets the stage for a successful progress report.
Step 5: Detail the Work Completed
This section is where you get to showcase your hard work! You’ll explain all the tasks you successfully crossed off your list during the reporting period. Here are some pointers to make this part informative and impressive:
- Get Specific: Skip vague statements like “made some progress.” Clearly state which tasks are done and what the results were. Instead of “Worked on the marketing campaign,” try “Finished designing the social media campaign graphics and wrote the draft for the email newsletter.”
- Use Numbers to Show Off: Did you write 5 blog posts? Chat with 10 potential customers? Mention specific numbers to brag about the amount of work you completed.
- Highlight Results, Not Just Actions: Being busy isn’t the same as being productive. Focus on the concrete achievements from your finished tasks. Did your research paper get the green light? Did the website update lead to a jump in traffic?
- Organize for Easy Reading: If you tackled a bunch of different tasks, group them in a logical way. This could be by project stage, department, or any other way that makes sense for your work.
Step 6: Discuss Work in Progress
Now that you’ve covered completed tasks, it’s time to shine a light on what you’re currently working on. This section informs the reader about your ongoing efforts and sets expectations for the next reporting period.
Here’s how to approach this section effectively:
- Clearly identify ongoing tasks: List the specific tasks you’re actively working on. Briefly explain what stage they’re in and what progress has been made so far.
- Focus on significant tasks: Don’t overwhelm the reader with every tiny detail. Prioritize the most important ongoing tasks that are crucial for the project’s progress.
- Mention the estimated completion date: For each ongoing task, provide a realistic timeframe for its completion. This helps the reader understand your work schedule and anticipate upcoming milestones.
Let’s say you’re writing a progress report on a website development project. In the “Work in Progress” section, you might mention that you’re currently finalizing the design for the product page. You can then add that you’re expecting to complete the design by the end of next week and move on to development in the following reporting period.
Step 7: Outline Future Tasks
We’ve explored the completed tasks and the ongoing ones. Now, let’s turn our attention to the future! This section of your progress report focuses on outlining the upcoming tasks. Here, the goal is to provide a clear roadmap of what’s next.
By outlining future tasks, you achieve several things. First, it gives your reader a transparent picture of what’s coming down the pipeline. This demonstrates your organization and showcases a well-defined plan for moving forward. Second, you can prioritize tasks, highlighting which ones are most critical and need to be tackled first. Finally, if possible, including estimated timelines for key tasks helps manage expectations and identify any potential roadblocks before they arise.
So, how do you effectively outline future tasks? Here’s the key: avoid simply listing every single thing that needs to be done. Instead, break the remaining work into manageable chunks. Think of it like creating smaller, achievable milestones. Use strong action verbs to describe each task. For instance, instead of saying “Develop marketing materials,” a stronger approach would be “Write and finalize marketing brochures by August 1st.”
If your project involves multiple people, assigning ownership for each future task is a great practice. This ensures everyone is clear on their specific roles and deadlines, fostering accountability and a smooth workflow.
Step 8: Highlight Issues and Solutions
No project operates flawlessly throughout its course. This section allows you to acknowledge any obstacles or challenges you faced while working on the project during the reporting period. Here, transparency and honesty are key. However, the focus should be on solutions, not dwelling on the problems themselves.
Here’s how to approach this step effectively:
First, provide a concise description of the issue you encountered. This could involve anything from a delay in receiving materials to a specific technical hurdle that proved more difficult than initially anticipated.
Next, explain the impact of the issue. Did it affect the established timeline? Did it necessitate additional resources that weren’t previously planned for?
Most importantly, showcase your problem-solving skills. Explain the steps you took to address the issue. Perhaps you found an alternative supplier who could provide the materials faster. Maybe you adjusted your approach to the technical challenge and found a workaround.
Step 9: Provide a Conclusion
The conclusion of your progress report acts like a closing statement. It’s your chance to summarize the key takeaways from the entire report and ensure the reader has a clear understanding of the project’s current status. Here’s how to craft a strong conclusion:
Start by briefly reminding the reader of the project’s overall goals. This helps connect the dots and reminds everyone what you’re trying to achieve. Briefly highlight the most important milestones reached during this reporting period. Did you complete a crucial task or achieve a significant breakthrough? Mention these accomplishments to showcase progress made.
Next, outline the upcoming tasks for the next reporting period. This gives the reader a sense of direction and keeps everyone informed about what’s coming next. Remember to maintain a positive and professional tone throughout the conclusion. Emphasize your commitment to moving the project forward and achieving the desired results.
The conclusion should be short and to the point. Aim for a single, well-written paragraph that effectively summarizes the report’s key points. By following these steps, you can write a conclusion that leaves a lasting impression and keeps your stakeholders informed and engaged with the project’s progress.
Read more: Business Report: What is it & How to Write it? (Steps & Format)
Creating a Progress Report that Stands Out with Bit.ai !
If you are planning to show a progress report that looks exactly like any other bland report, chances are your readers are just going to skim it along the way or won’t read it at all.
Well, to lure your reader’s attention and proudly display the work you have done on the project, you have to make the progress report irresistibly compelling!
How about awesome visuals, accompanied by quality content that could grab the reader’s interest and encourage them to read the whole thing? No doubt, everybody likes reading something easy to grasp and visually stunning!
Luckily, we have got the perfect tool for you that will provide a reading experience like never before and bring your grey-scale progress reports to come alive! A solution like Bit.ai
Bit is a new-age cloud-based document collaboration tool that helps teams create, share, manage, and track interactive workplace documents.
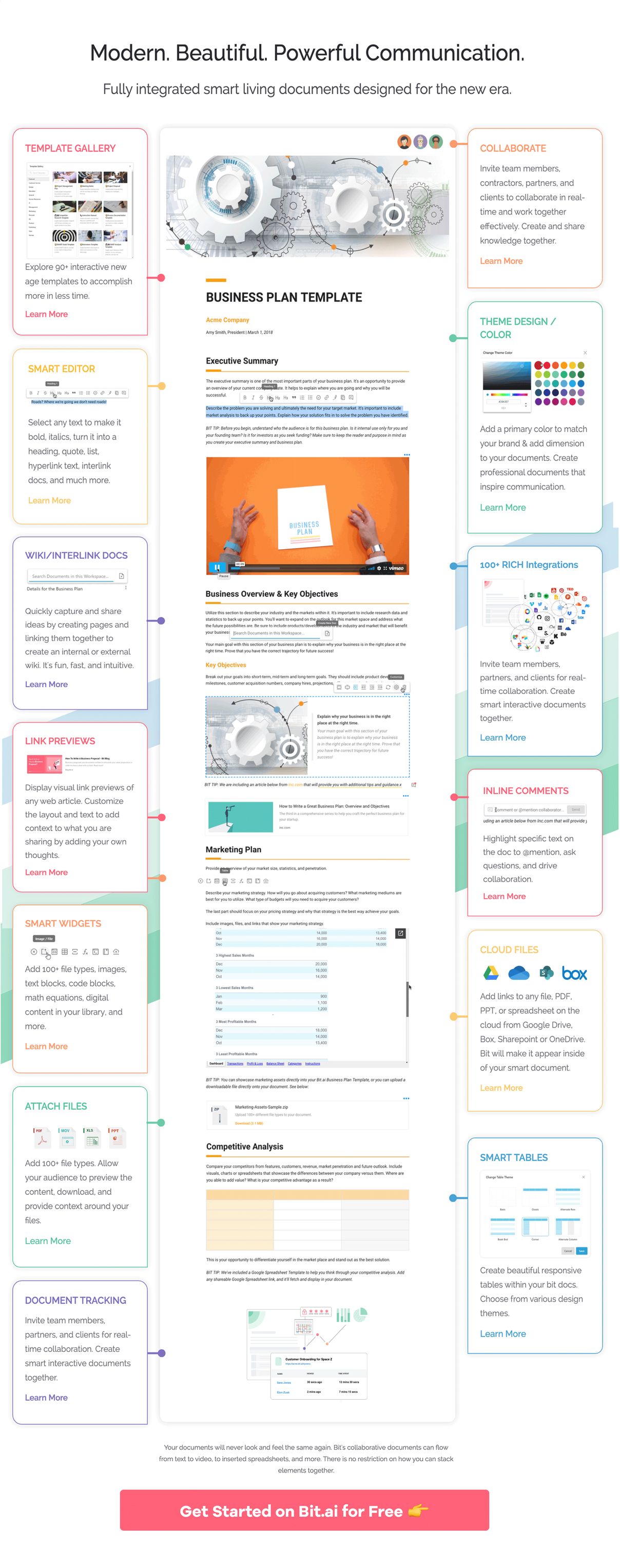
Bit helps you make sure your reports are more than just plain bland text and images. Thus, apart from allowing multiple users to collaborate on reports, Bit also allows users to share any sort of rich media like campaign video, tables, charts, One Drive files, Excel Spreadsheets, GIFs, Tweets, Pinterest boards, etc. Anything on the internet with a link can be shared and Bit will automatically turn it into visual content.
Bit has a very minimal design aesthetic which makes every design element pop, awesome readability, and rich features that will prevent collaborators from messing up any documents and help them rethink the way they work!
Besides writing progress reports, you can easily create other beautiful documents like the statement of work , project documentation, operational plan , roadmap, project charter , etc. in a common workplace for other team members to collaborate, document, share their knowledge, brainstorm ideas, store digital assets, and innovate together.
The best part is that this knowledge is safely secured in your workspaces and can be shared (or kept private) with anyone in your organization or the public!
All-in-all Bit is like Google Docs on steroids! So, no more settling for those boring text editors when you have an excessively robust solution to walk you through!
Still, not sure how Bit can help you create that perfect progress report to woo your readers? Let’s see some more of Bit’s awesome capabilities!
Key Benefits of Creating Your Progress Reports on Bit.ai
Simple, clean UI: Bit has a very minimal design aesthetic to it, allowing a newbie to quickly get on board with the platform. Even though the platform is feature-rich, it does a great job as to not overwhelm a new user and provides a systematic approach to work.
Organization of information: Information is often scattered in cloud storage apps, emails, Slack channels, and more. Bit brings all your information in one place by allowing you to organize information in workspaces and folders. Bring all your documents, media files, and other important company data in one place.
Brand consistency: Focus on the content and let Bit help you with the design and formatting. Bit documents are completely responsive and look great on all devices. With amazing templates and themes, Bit docs provide you with the type of brand and design consistency that is unheard of in the documentation industry
Smart search: Bit has very robust search functionality that allows anyone to search and find their documents swiftly. You can search workspaces, folders, document titles, and the content inside of documents with Bit’s rich-text search.
Media integrations: Companies use an average of 34 SaaS apps! No wonder why most of our time is spent hopping from one app to the next, looking for information. This is why Bit.ai integrates with over 100+ popular applications (YouTube, Typeform, LucidChart, Loom, Google Drive, etc) to help teams weave information in their documents beyond just text and images.
Multiple ways of sharing : Bit documents can be shared in three different states :
- Live state : A live state meaning that all changes that you make to the document will update in real-time. If you are sharing your documents with clients, partners, or customers they will always get your most up-to-date changes.
- Embeds : You can embed Bit documents on any website or blog. Bit docs are fully responsive and render perfectly on your website.
- Tracking : You can track your documents and gather real-time insights to understand how users interact with your content. See how much time users spend viewing documents, scroll ratio, user information, and more.
Our team at bit.ai has created a few more templates to make your business processes more efficient. Make sure to check them out before you go, y our team might need them!
- Training Manual Template
- Brainstorming Template
- Meeting Minutes Template
- Employee Handbook Template
- Transition Plan Template
- Customer Service Training Manual Template
- Employee Contract Template
- Performance Improvement Plan Template
A well-defined progress report is like the pulse of a project! It determines your relationship with your readers, highlights all the updates- big or small, and keeps everyone on the same page. Remember, depending on the complexity and scope of the project, you might need to share your progress report on a weekly or monthly basis for better efficiency!
Once you follow all the steps that are mentioned above, your reports are surely going to feel like a breeze of fresh air to your readers, making you look credible and professional. So what are you waiting for?
Do you write such reports in your organization, if yes, which tool do you use? Let us know in the comments below or tweet us @bit_ai
Further reads:
- Technical Report: What is it & How to Write it? (Steps & Structure Included)
- 11 Amazing Goal Tracking Apps and Tools! (Free & Paid)
- 7 Types of Reports Your Business Certainly Needs!
- Performance Report: What is it & How to Create it? (Steps Included)
- Formal Reports: What are they & How to Create them!
- KPI Report: What it is & How to Create a Perfect One?
- How to Write a Project Charter Document?

Document Creation: 12 Dos and Don'ts to Keep in Mind!
10 Best Apps for Writing a Book!

Related posts
Scope of work: what is it & how to create it (template included), portfolio: what is it & how to create an impressive one, how to write a case study (with template), query letter: what is it & how to create it, the best way to organize all of your work and get rid of chaos, 15 free online notepads you need to check out this year.

About Bit.ai
Bit.ai is the essential next-gen workplace and document collaboration platform. that helps teams share knowledge by connecting any type of digital content. With this intuitive, cloud-based solution, anyone can work visually and collaborate in real-time while creating internal notes, team projects, knowledge bases, client-facing content, and more.
The smartest online Google Docs and Word alternative, Bit.ai is used in over 100 countries by professionals everywhere, from IT teams creating internal documentation and knowledge bases, to sales and marketing teams sharing client materials and client portals.
👉👉Click Here to Check out Bit.ai.
Recent Posts
Crafting engaging newsletters with the help of bit.ai, idea generation: how bit.ai sparks creativity, hospitality document template collection for efficient management process, healthcare document template collection: simplify your medical administration tasks, top 20 event management document templates for 2024, top 20 it management document templates for 2024.
- Free Project Management Software
- Agile Project Management Software
- Project Management Software for Nonprofits
- Organization Apps to Boost Productivity
- Resource Management Software
- Monday Review
- ClickUp Review
- Monday Pricing
- ClickUp Pricing
- Wrike Pricing
- Asana Pricing
- Smartsheet Pricing
- Teamwork Pricing
- Airtable Pricing
- Scoro Pricing
- Asana vs Monday
- ClickUp vs Monday
- Wrike vs Asana
- Trello vs Asana
- ClickUp vs Asana
- What is Agile Project Management?
- Key Benefits of Agile Methodology
- Most Important Agile Metrics
- Agile Manifesto: Values and Principles
- Agile Project Management Certifications
Progress Report: What is it & How to Write it? (+Examples)
Picture this: You're a project manager juggling multiple tasks, deadlines, and team members. Keeping the balance between different tasks is hard but very important.
Enter the progress report, your secret weapon in conquering chaos and ensuring smooth sailing.
But what exactly is a progress report, and how do you craft one effectively? In this blog post, I'll demystify progress reports and guide you through the process of writing one.
From daily progress reports to weekly progress reports, using practical progress report templates and a tried-and-true format.
What is a Progress Report?
A progress report is a vital tool in project management , designed to keep different types of stakeholders informed about the ongoing status of a project.
It's a concise document highlighting current achievements, challenges, and goals, allowing the project manager to track progress and make necessary adjustments.
Project progress reports are one of the most important types of project management reports . They help maintain transparency, communication, and accountability within a team, ensuring everyone is on the same page. They also provide valuable insights for decision-makers, helping them gauge the project's overall health and success.
Here's what you can expect to find in a typical progress report:
- Project Overview: A brief summary of the project's objectives and scope.
- Current Status: A snapshot of where the project stands regarding completed tasks, milestones reached, and overall progress.
- Challenges and Issues: Any technical difficulties, resource constraints, or personnel issues.
- Next Steps: The immediate tasks and goals on the horizon and how the team plans to tackle them.
- Progress Report Format: The layout of the report can vary depending on the organization's preferences or industry standards.
Writing a progress report can seem daunting, but it doesn't have to be. You'll create a valuable document that keeps everyone informed and aligned by breaking it down into manageable sections and using clear, concise language.
Embrace the progress report writing skill and watch your team's productivity and communication soar.
Why are Progress Reports Important?

Progress reports play a vital role in project management, serving as a communication tool to keep stakeholders updated. Let's delve into why progress reports are crucial for the success of any project or business.
Transparency and Accountability
Progress reports eliminate ambiguity and promote transparency. By regularly sharing project updates with stakeholders, the project team is held accountable for their work. This accountability ensures everyone is on track to meet the project milestones and objectives.
Identify Potential Issues Early
Progress reports help identify potential problems before they escalate. Team members can spot bottlenecks, delays, and other issues by examining project data and analyzing the progress report.
Early detection enables the team to take prompt action and prevent these issues from derailing the project.
Effective Decision-Making
Armed with accurate and timely information from progress reports, project managers and stakeholders can make informed decisions.
When a project progresses smoothly, management can allocate resources more efficiently or plan for future phases. On the other hand, if a project encounters challenges, swift decisions can be made to reallocate resources or change course.
Maintaining Momentum
A progress report's important aspect is maintaining momentum. When team members see their progress documented and shared, it fosters a sense of accomplishment and motivation.
This positive reinforcement encourages teams to keep pushing forward and maintain their productivity.
Improved Communication and Collaboration
Progress reports facilitate better communication and collaboration among team members. By sharing updates and insights, the entire team stays informed, reducing the chances of miscommunication or misunderstandings.
Moreover, progress reports provide a platform for team members to ask questions, provide feedback, and offer support.
Performance Tracking
Business progress reports, such as quarterly, monthly, or annual progress reports, help track performance over time.
By comparing past reports, management can gauge the business's overall health and identify trends or patterns. This historical data can inform future strategies and drive continuous improvement.
How to Write a Progress Report
Step 1: define the purpose.
The first step in writing a progress report is understanding its purpose. Progress reports inform stakeholders about the project's status, including what has been accomplished, any challenges encountered, and future planning. This allows project managers to keep everyone in the loop and make informed decisions.
The purpose of this monthly progress report is to update the management team on the project's status. It presents an overview of completed tasks, in-progress tasks, upcoming tasks, and any challenges faced during the reporting period. This report will also provide insight into key performance metrics and future planning .
Step 2: Know Your Audience
Determine who will read the progress report. Is it for higher-ups, clients, or team members? Tailor the language, tone, and level of detail accordingly.
Step 3: Set the Timeframe
Decide the reporting period – weekly, monthly, or quarterly. Choose a timeframe that best suits your project's pace and stakeholder expectations.
Step 4: Collect Information
Gather data on tasks completed, team members involved, and any obstacles faced. Consult previous progress reports, project documentation , and team members for accurate information.
Step 5: Organize Content
Break down the report into logical sections. Here’s what we suggest:
- Summary: A brief overview of the report's contents.
- Completed Tasks: List tasks accomplished during the reporting period.
- In-Progress Tasks: Describe ongoing tasks and their current status.
- Upcoming Tasks: Outline tasks scheduled for the next reporting period.
- Challenges: Discuss any obstacles encountered and how they were addressed.
- Key Metrics: Highlight key project performance indicators and progress towards goals.
- Future Planning: Discuss plans for the next reporting period and any adjustments needed.
Step 6: Write the Summary
Craft a concise summary that provides a snapshot of the report. Mention key achievements, challenges, and plans for the future. Keep it brief but informative.
This progress report covers our team's accomplishments during Q1, with a particular focus on the completion of the website redesign and the initiation of our social media marketing campaign. We've encountered some challenges in coordinating with external vendors, but we've implemented solutions to overcome those obstacles .
Step 7: Detail Completed Tasks
List all tasks completed during the reporting period. Include the following information:
- Task description
- Team members involved
- Start and end dates
- Any relevant metrics (e.g., hours spent, budget used)
- Task 1 – Implement a user login system.
- Team members: Jeff and Sarah.
- Start date: January 1st.
- End date: January 15th.
- Metrics: 98% successful login rate.
Step 8: Discuss In-Progress Tasks
Outline ongoing tasks, their current status, and expected completion dates. Explain any delays and their impact on the project timeline .
- Task 2 – Develop a mobile app.
- Current status: 70% completed.
- Expected completion date: February 15th.
Step 9: Describe Upcoming Tasks
Identify tasks scheduled for the next reporting period. Provide details such as:
- Assigned team members
- Estimated start and end dates
- Dependencies on other tasks
- Task 3 – Launch marketing campaign.
- Assigned team members: Anas and Mark.
- Estimated start date: February 16th.
- Estimated end date: March 1st.
- Dependencies: Completion of mobile app development.
Step 10: Address Challenges
Discuss any challenges encountered during the reporting period. Describe how they were resolved or any plans to address them in the future.
- Challenge 1 – Unforeseen technical issues causing delays.
- Resolution: Increased resources and adjusted project timeline to accommodate the additional time required.
Step 11: Present Key Metrics
Highlight key project management performance indicators and progress toward project goals. Use visuals like charts or graphs to make the data more digestible.
- Metric 1 – User registration rate.
- Current status: 500 new users per week.
- Target goal: 1,000 new users per week.
Step 12: Plan for the Future
Discuss plans for the next reporting period, including any adjustments required. This may involve reallocating resources, revising timelines, or redefining objectives.
In the next reporting period, our focus will shift to improving user retention and engagement. We plan to implement new features based on user feedback and optimize the onboarding process.
Step 13: Proofread and Revise
Review the report for clarity, accuracy, and readability. Ensure all information is presented in a clear, concise manner.
Step 14: Submit the Report
Submit the progress report to the relevant stakeholders, ensuring they have ample time to review and provide feedback.
Example Progress Report Template
Use this template as a starting point for your progress report:
By following these steps and guidelines, you'll be well-equipped to write an effective progress report that keeps stakeholders informed and drives project success. Clear communication is key to maintaining momentum and ensuring everyone is on the same page.
Examples of Progress Reports
1. business progress report.

A business progress report helps track company growth, accomplishments, and areas for improvement. It includes:
- Revenue and sales figures.
- Market trends and competition.
- Operational efficiency.
- Employee performance.
- Goals and milestones achieved.
2. Quarterly Progress Reports

These reports offer a snapshot of a project or business every three months. They cover:
- Major achievements.
- Challenges faced and solutions.
- Key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Updated project timeline.
- Budget status.
3. Monthly Progress Reports
Monthly progress reports provide more frequent updates on projects or departments. They highlight:
- Accomplishments and setbacks.
- Progress towards monthly goals.
- Resource utilization.
- Issues and risks.
- Action items for the upcoming month.
4. Project Status

Project status reports focus on a specific project's progress. They showcase:
- Project documentation updates.
- Completed tasks and upcoming deliverables.
- Risks and issues encountered.
- Team members' performance.
- Changes to project scope or timeline.
5. Personal Progress
Personal progress reports help individuals track their growth and development. They include:
- Personal goals and objectives.
- Achievements and lessons learned.
- Skill development and training.
- Performance feedback.
- Areas for improvement and action plans.
Best Practices for Writing Progress Reports

Know Your Target Audience
When you create a progress report, start by identifying your target audience . Project stakeholders, team members, and future decision-makers should all benefit from your report.
Write in such a way that it is easy for them to understand. Avoid technical jargon and explain industry-specific language so everyone stays on the same page.
Reporting Frequency and Dates
Establish a reporting frequency for your progress reports. Whether weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly, maintain consistency. Include report dates and the expected completion date of the current project to provide a clear timeline.
Stick to the Project's Scope
Focus on the project's scope and stay within the project's purpose. Don't digress or include unrelated details. A concise report ensures that readers remain engaged and informed.
Review Previous Reports
Refer to the previous report to identify any changes or developments. Highlight the work completed, project deliverables , and any updates to the project plan. Doing so will maintain continuity and keep stakeholders informed about the department's progress.
Prioritize and Organize
Arrange project priorities logically, focusing on the most critical aspects first. Organize the information in a clear, easy-to-follow format. Use headings, subheadings, and bullet points for better readability.
Be Transparent About Problems
Don't shy away from discussing problems or challenges. Addressing issues helps stakeholders understand the project's status and any hurdles that may affect successful completion. Offer potential solutions or workarounds to demonstrate proactive thinking.
Back Up Progress with Relevant Data
Use relevant data to support your progress. Figures, charts, and percentages can provide a quick overview of the project's status. Make sure your data is accurate, up-to-date, and presented in an easy-to-understand format.
Highlight Team Member Contributions
Acknowledge team members who have made significant contributions to the project. This recognition boosts morale and encourages continued excellence.
Include Future Projections
Discuss what's next for the project, such as upcoming tasks or milestones. This helps stakeholders understand the trajectory of the project and anticipate the work ahead.
Keep it Simple and Actionable
Present complex ideas in a simple, easy-to-understand language. Break down complicated concepts into manageable chunks. Offer actionable insights and practical takeaways, so stakeholders can quickly grasp the project details.
Establish a Database
Create a database to store all progress reports. This repository helps stakeholders access past reports and provides valuable insights for future projects. It also ensures that information is preserved and easily accessible when needed.
Proofread and Edit
Before sharing your progress report, proofread and edit for clarity, consistency, and accuracy. This step ensures that your report is polished, professional, and easy to understand.
Progress Reporting FAQs
A progress report is most valuable when you're working on a long-term project. It's a way to keep stakeholders updated on progress and share important insights.
The primary purpose of a progress report is to provide a clear and concise overview of a project's status. This includes: – Communicating progress toward goals – Identifying potential issues and solutions – Demonstrating accountability and commitment to the project – Providing a step-by-step guide of completed tasks and upcoming work – Offering visual aids, like charts and graphs, to illustrate data A well-crafted progress report keeps stakeholders informed and fosters collaboration. It's also valuable for maintaining momentum and motivation throughout the project.
Writing Progress Reports Does Not Need to Be Hard
So, you've reached the end of this blog post. You're now equipped with the knowledge and tools to make progress report writing a breeze. Remember, it doesn't have to be a daunting task.
Keep it simple, stick to the facts, and let your progress shine. Talk about what you achieved, any challenges you faced, and how you overcame them. Use a clear, concise, structured format to ensure your message is easily understood.
To simplify the process, check out our guide on project reporting tools .
Ask yourself:
- What are the key takeaways from this period?
- How can I best communicate the status of the project?
- Are there any challenges that need addressing?
Considering these questions will make your progress report informative, actionable, and engaging. And don't forget, practice makes perfect. The more progress reports you write, the easier and more efficient the process will become.
Explore Further
- Essential Components of Project Management
- Best Project Management Software 2023
- The Inspiring History of Project Management. How Did It Begin?
- 9 Essential Roles In Project Management
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.

IMAGES
VIDEO