
- Case Studies
- Free Coaching Session

Production Plan in Business Plan: A Comprehensive Guide to Success
Last Updated:
October 29, 2024

In any business venture, a solid production plan is crucial for success. A production plan serves as a roadmap that outlines the steps, resources, and strategies required to manufacture products or deliver services efficiently. By carefully crafting a production plan within a business plan, entrepreneurs can ensure optimal utilisation of resources, timely delivery, cost efficiency, and customer satisfaction. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of creating an effective production plan in a business plan , exploring its key components, strategies, and the importance of aligning it with overall business objectives .
Key Takeaways on Production Plans in Business Planning
- A production plan : a detailed outline that guides efficient product manufacturing or service delivery.
- Importance of a production plan : provides a roadmap for operations, optimises resource utilisation, and aligns with customer demand.
- Key components : demand forecasting, capacity planning, inventory management, resource allocation, and quality assurance.
- Strategies : lean manufacturing, JIT inventory, automation and technology integration, supplier relationship management, and continuous improvement.
- Benefits of a well-executed production plan : improved efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced product quality, and increased profitability.

What is a Production Plan?
A production Seamless Searches plan is a detailed outline that specifies the processes, resources, timelines, and strategies required to convert raw materials into finished goods or deliver services. It serves as a blueprint for the entire production cycle, guiding decision-making and resource allocation. The production plan considers factors such as demand forecasting, capacity planning, inventory management, and quality assurance to ensure efficient operations and optimal customer satisfaction.
Why is a Production Plan Important in a Business Plan?
The inclusion of a production plan in a business plan is vital for several reasons. First and foremost, it provides a clear roadmap for business operations, helping entrepreneurs and managers make informed decisions related to production processes. A well-developed production plan ensures that resources are utilised efficiently, minimising wastage and optimising productivity. This is particularly important for any startup platform aiming to streamline its production processes and achieve sustainable growth.
Additionally, a production plan allows businesses to align their production capabilities with customer demand. By forecasting market trends and analysing customer needs, businesses can develop a production plan that caters to current and future demands, thus avoiding overstocking or understocking situations. For those interested in property development, understanding the dynamics of the real estate market can provide valuable insights into aligning production capabilities with demand, ensuring successful projects and investments.
Furthermore, a production plan helps businesses enhance their competitive advantage. By implementing strategies such as lean manufacturing and invoice automation , companies can streamline their production processes, reduce costs, improve product quality, and ultimately outperform competitors.
Key Components of a Production Plan
To create an effective production plan, it is crucial to consider several key components. These components work together to ensure efficient operations and successful fulfilment of customer demands. Let's explore each component in detail.
Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting is a critical aspect of production planning. By analysing historical data, market trends, and customer behaviour, businesses can predict future demand for their products or services. Accurate demand forecasting allows companies to optimise inventory levels, plan production capacity, and ensure timely delivery to customers.
One approach to demand forecasting is quantitative analysis, which involves analysing historical sales data to identify patterns and make predictions. Another approach is qualitative analysis, which incorporates market research, customer surveys, and expert opinions to gauge demand fluctuations. By combining both methods, businesses can develop a robust demand forecast, minimising the risk of underproduction or overproduction. Utilising a free notion template for demand forecasting can further streamline this process, allowing businesses to organise and analyse both quantitative and qualitative data efficiently in one centralised location.
Capacity Planning
Capacity planning involves determining the optimal production capacity required to meet projected demand. This includes assessing the production capabilities of existing resources, such as machinery, equipment, and labour, and identifying any gaps that need to be addressed. By conducting a thorough capacity analysis, businesses can ensure that their production capacity aligns with customer demand, avoiding bottlenecks or excess capacity.
An effective capacity plan takes into account factors such as production cycle times, labour availability, equipment maintenance, and production lead times.
Inventory Management
Efficient inventory management is crucial for a successful production plan. It involves balancing the cost of holding inventory with the risk of stockouts. By maintaining optimal inventory levels, businesses can reduce carrying costs while ensuring that sufficient stock is available to fulfil customer orders.
Inventory management techniques, such as the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model and Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory system, help businesses strike the right balance between inventory investment and customer demand. These methods consider factors such as order frequency, lead time, and carrying costs to optimise inventory levels and minimise the risk of excess or insufficient stock.
Resource Allocation
Resource allocation plays a pivotal role in a production plan. It involves assigning available resources, such as labour, materials, and equipment, to specific production tasks or projects. Effective resource allocation ensures that resources are utilised optimally, avoiding underutilisation or over-utilisation.
To allocate resources efficiently, businesses must consider factors such as skill requirements, resource availability, project timelines, and cost constraints. By conducting a thorough resource analysis and implementing resource allocation strategies, businesses can streamline production processes, minimise bottlenecks, and maximise productivity .
Quality Assurance
Maintaining high-quality standards is essential for any production plan. Quality assurance involves implementing measures to monitor and control the quality of products or services throughout the production process. By adhering to quality standards and conducting regular inspections, businesses can minimise defects, ensure customer satisfaction, and build a positive brand reputation.
Quality assurance techniques, such as Total Quality Management (TQM) and Six Sigma , help businesses identify and rectify any quality-related issues. These methodologies involve continuous monitoring, process improvement, and employee training to enhance product quality and overall operational efficiency.
In addition to the core components of a production plan, it's also important for businesses to consider the broader aspects of their business strategy, including marketing and advertising. Understanding the costs and returns of different marketing approaches is crucial for comprehensive business planning . For instance, direct response advertising costs can vary significantly, but they offer the advantage of measurable responses from potential customers. This type of advertising can be a valuable strategy for businesses looking to directly engage with their target audience and track the effectiveness of their marketing efforts.
Strategies for Developing an Effective Production Plan
Developing an effective production plan requires implementing various strategies and best practices. By incorporating these strategies into the production planning process, businesses can optimise operations and drive success. Let's explore some key strategies in detail.
Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing is a systematic Seamless Searches approach aimed at eliminating waste and improving efficiency in production processes. It emphasises the concept of continuous improvement and focuses on creating value for the customer while minimising non-value-added activities.
By adopting lean manufacturing principles, such as just-in-time production, standardised work processes, and visual management, businesses can streamline operations, reduce lead times, and eliminate unnecessary costs. Lean manufacturing not only improves productivity but also enhances product quality and customer satisfaction.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory
Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory is a strategy that aims to minimise inventory levels by receiving goods or materials just when they are needed for production. This strategy eliminates the need for excess inventory storage, reducing carrying costs and the risk of obsolete inventory.
By implementing a JIT inventory system, businesses can optimise cash flow, reduce storage space requirements, and improve overall supply chain efficiency. However, it requires robust coordination with suppliers, accurate demand forecasting, and efficient logistics management to ensure timely delivery of materials.
Automation and Technology Integration
Automation and technology integration play a crucial role in modern production planning, as well as mobile app development . By leveraging technology, businesses can streamline processes, enhance productivity, and reduce human error. Automation can be implemented in various aspects of production, including material handling, assembly, testing, and quality control.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a fundamental principle of effective production planning. It involves regularly evaluating production processes, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing changes to enhance efficiency and quality.
By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, businesses can drive innovation, optimise resource utilisation, and stay ahead of competitors. Techniques such as Kaizen, Six Sigma, and value stream mapping can help businesses identify inefficiencies, eliminate waste, and streamline production workflows.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the role of a production plan in business planning.
A1: A production plan plays a crucial role in business planning by providing a roadmap for efficient production processes. It helps align production capabilities with customer demand, optimise resource utilisation, and ensure timely delivery of products or services.
How does a production plan affect overall business profitability?
A2: A well-developed production plan can significantly impact business profitability. By optimising production processes, reducing costs, and enhancing product quality, businesses can improve their profit margins and gain a competitive edge in the market.
What are the common challenges faced in production planning?
A3: Production planning can present various challenges, such as inaccurate demand forecasting, capacity constraints, supply chain disruptions, and quality control issues. Overcoming these challenges requires robust planning, effective communication, and the implementation of appropriate strategies and technologies.
What is the difference between short-term and long-term production planning?
A4: Short-term production planning focuses on immediate production requirements, such as daily or weekly schedules. Long-term production planning, on the other hand, involves strategic decisions related to capacity expansion, technology investments, and market expansion, spanning months or even years.
How can a production plan be adjusted to accommodate changes in demand?
A5: To accommodate changes in demand, businesses can adopt flexible production strategies such as agile manufacturing or dynamic scheduling. These approaches allow for quick adjustments to production levels, resource allocation, and inventory management based on fluctuating customer demand.
In conclusion, a well-crafted production plan is essential for business success. By incorporating a production plan into a comprehensive business plan, entrepreneurs can optimise resource utilisation, meet customer demands, enhance product quality, and drive profitability. Through effective demand forecasting, capacity planning, inventory management, resource allocation, and quality assurance, businesses can streamline production processes and gain a competitive edge in the market.
People Also Like to Read...

Are You Ready For Your Expansion Plans?

How To Build Your Digital Marketing Plan
© 2016 - 2024 Robin Waite. All rights reserved.
- Entrepreneurship

How to Write a Production Plan for a Business?
A production plan is a critical component of any business that involves manufacturing, construction, or other forms of production. It outlines how a company will produce its goods or services, and it provides a roadmap for success. In this article, we’ll take a look at how to write a production plan for your business.
1. Understand Your Product
The first step in creating a production plan is to understand your product. What are you producing? What are its components? How is it made? Answering these questions will help you determine what resources you need, how long it will take to produce, and how you will produce it.
Before creating a production plan, make sure you have a clear understanding of what you are producing. This will help you make informed decisions about the production process and ensure that you are using the right resources.
2. Determine Your Production Capacity
Once you understand your product, you need to determine your production capacity. How much of your product can you produce in a given period? This will depend on the resources you have available, such as equipment, personnel, and materials.
To determine your production capacity, you should consider the following factors:
– The capacity of your equipment – The availability of raw materials – The number of personnel available – The amount of time required to produce each unit
By understanding your production capacity, you can create a production plan that is realistic and achievable.
3. Create a Production Schedule
With a clear understanding of your product and production capacity, you can create a production schedule. This schedule should outline when you will produce each unit of your product, as well as the resources required to produce it.
When creating a production schedule, you should consider the following factors:
– The production capacity of your equipment – The availability of raw materials – The number of personnel available – The amount of time required to produce each unit – The demand for your product
By creating a production schedule, you can ensure that you are using your resources effectively and efficiently.
4. Determine Your Material Requirements
To produce your product, you will need to determine your material requirements. This includes the raw materials needed to produce each unit, as well as any additional materials required for packaging or shipping.
When determining your material requirements, you should consider the following factors:
– The number of units you plan to produce – The amount of raw materials required for each unit – The cost of the raw materials – The availability of the raw materials
By understanding your material requirements, you can ensure that you have the resources you need to produce your product.
5. Develop a Quality Control Plan
Quality control is an essential component of any production plan. It ensures that your product meets the standards set by your company and your customers.
When developing a quality control plan, you should consider the following factors:
– The standards set by your company and your customers – The methods you will use to ensure quality – The personnel responsible for quality control – The equipment required for quality control
By developing a quality control plan, you can ensure that your product meets the highest standards of quality.
6. Determine Your Personnel Needs
To produce your product, you will need personnel with the right skills and experience. When determining your personnel needs, you should consider the following factors:
– The number of personnel required – The skills and experience required – The cost of personnel – The availability of personnel
By understanding your personnel needs, you can ensure that you have the right people in place to produce your product.
7. Develop a Maintenance Plan
Equipment maintenance is an essential component of any production plan. It ensures that your equipment is in good working order and reduces the risk of breakdowns.
When developing a maintenance plan, you should consider the following factors:
– The frequency of maintenance – The personnel responsible for maintenance – The cost of maintenance – The equipment required for maintenance
By developing a maintenance plan, you can ensure that your equipment is always in good working order.
8. Determine Your Cost of Production
To determine the profitability of your product, you need to determine your cost of production. This includes the cost of raw materials, personnel, equipment, and any other expenses associated with production.
When determining your cost of production, you should consider the following factors:
– The cost of raw materials – The cost of personnel – The cost of equipment – The cost of maintenance – The cost of overhead
By understanding your cost of production, you can ensure that your product is profitable.
9. Monitor and Adjust Your Production Plan
Once you have created your production plan, you need to monitor its effectiveness. This involves tracking your production output, monitoring your costs, and making adjustments as needed.
When monitoring and adjusting your production plan, you should consider the following factors:
– Production output – Cost of production – Quality control results – Equipment maintenance issues
By monitoring and adjusting your production plan, you can ensure that your product is produced efficiently and effectively.
10. Benefits of a Production Plan
A production plan offers several benefits to your business, including:
– Increased efficiency – Improved quality control – Reduced costs – Increased profitability – Better resource management
By creating a production plan, you can ensure that your business is producing its products or services in the most efficient and effective way possible.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions and answers about writing a production plan for a business:
What is a production plan?
A production plan is a document that outlines the steps a business will take to manufacture or produce a product. It includes details about the materials needed, the timeline for production, and the resources required to complete the project. A production plan is essential for ensuring that a business can efficiently and effectively produce goods.
When writing a production plan, it’s important to consider factors like the demand for your product, the availability of resources, and the complexity of the manufacturing process. By taking these factors into account, you can create a plan that will help your business succeed.
What should be included in a production plan?
A production plan should include a detailed timeline for production, a list of the materials needed for manufacturing, and information about the resources required to complete the project. It should also outline the steps involved in the manufacturing process and any quality control measures that will be used to ensure that the final product meets the necessary standards.
Additionally, a production plan should include information about the expected demand for the product, as well as any potential challenges that may arise during production. By including these details in your plan, you can ensure that your business is prepared to meet the needs of your customers and overcome any obstacles that may arise.
What are the benefits of a production plan?
Having a production plan in place can provide several benefits for a business. For one, it can help ensure that the manufacturing process is efficient and cost-effective, as it allows you to identify any potential issues and address them before they become major problems. Additionally, a production plan can help you manage your resources more effectively, as it provides a clear timeline for production and ensures that you have the necessary materials and personnel in place to complete the project.
Finally, a production plan can help you stay on track and meet your deadlines, which is essential for maintaining a positive reputation with your customers and stakeholders. By creating a detailed plan and sticking to it, you can ensure that your business is able to deliver high-quality products on time and within budget.
How can I create a production plan?
To create a production plan, start by identifying the materials and resources you will need to manufacture your product. Then, create a detailed timeline for production that includes key milestones and deadlines. Be sure to consider factors like the complexity of the manufacturing process, the availability of resources, and the expected demand for your product.
Once you have a basic plan in place, review it carefully to identify any potential issues or challenges. Make adjustments as needed to ensure that your plan is realistic and achievable. Finally, communicate your plan clearly to your team and stakeholders to ensure that everyone is on the same page and working towards the same goals.
How often should I update my production plan?
It’s important to review and update your production plan regularly to ensure that it remains relevant and effective. Depending on the nature of your business and the products you produce, you may need to update your plan on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis.
When updating your plan, be sure to consider any changes in demand, resources, or production processes that may have occurred since the last update. This will help you ensure that your plan remains accurate and effective, and that your business is able to meet the needs of your customers and stakeholders.
Production Plan
To create a successful production plan, start by identifying your goals and objectives. Consider factors such as customer demand, production capacity, and available resources. From there, break down your plan into manageable steps, and set realistic timelines for each stage of production.
Lastly, remember that your production plan is not set in stone. As your business grows and evolves, your production plan will need to evolve with it. Be prepared to make changes and adjustments to your plan as needed, and don’t be afraid to seek out help and advice from experts in the field. With the right approach and a solid plan in place, you can take your business to the next level and achieve lasting success.
RELATED ARTICLES
What is sampling in marketing research, how much does it cost to do market research, how important is marketing for small business, how can managers use reinforcement theory to motivate employees, how de manager differ from non managerial employees, how to elect out of partnership audit rules, what is funding request in a business plan, 10 benefits of investing in money market instruments for businesses, 10 common business goals and how to set them, 10 common financial risks faced by businesses and how to manage them, 10 common types of bonds for business financing and investments, 10 customer retention techniques to foster long-term loyalty, how can trust be gained between the business and development, software startup ideas, the dummies guide to starting your own business, how to find new businesses before they open, what must an entrepreneur assume when starting a business, editor’s choice, how does budgeting help management coordinate and plan business activities, how long does it take to get twitch partnership, is business management or marketing better, are managers allowed to talk religion with employees, how long should a business plan be, stay in touch.
To be updated with all the latest news, offers and special announcements.
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use

Production Plan

People face failure. Not all entrepreneurs are capable of thriving to survive in this industry. Indeed, businesses fail. And that is the truth about it. But do you remember how all the plans that didn’t push through? If you do, then now is the time to correct mistakes from the past. Don’t take planning as anything. Whether in food, film, or media production, organizing your activities helps in achieving your goals. Take your time to prepare a production plan . Be guided in executing the right activity to achieve your goals. Create a structure and release the doubt. Increase your potential and start planning for the production today.
21+ Production Plan Examples
1. daily production plan template.

2. Pre Production Plan Template

3. Film Production Plan Template

4. Production Control Plan Template

5. Production Support Plan Template


6. Web Production Plan Template

7. Production Company Business Plan Template

- Google Docs
8. Video Production Business Plan Template

9. Production Plan Template

- Apple Pages
Size: 14 KB
10. Production Deployment Plan Template

Size: 23 KB
11. Video production Project Plan Template

Size: 44 KB
12. Production Plan

13. Production Capacity and Material Planning
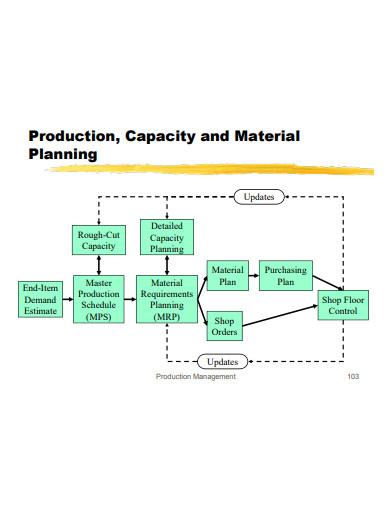
Size: 414 KB
14. Production Planning and Control

Size: 409 KB
15. Production Planning and Execution
16. Sample Production Plan

Size: 486 KB
17. Simple Production Plan

Size: 181 KB
18. Production Line Production Plan

19. Demand Forecasting and Production Planning

Size: 76 KB
20. Elements of Production Planning and Control

21. Housing Production Plan

22. Production Plan Example

What is a Production Plan?
Small businesses are always tangled with several challenges while starting a business. You can expect that there will be projects, events, and daily activities. A production plan is a detailed document that outlines the structure of the company’s operations. In the plan, there is a structure, schedule, goal, activities, and the definition of resources in between. It is one step closer to success at a time. So, whenever your path is uncertain, a production plan will help in opening the right direction. This is why entrepreneurs must consider rewriting their planning techniques. If you are having issues with the layout, the proper organization saves the day.
Business Production Situation
According to an article published by Forbes, 80% out of 100 small business owners guarantee success in the first year of business operation. It manifests an above-average rate of success. However, behind this curtain are failing attempts for smaller businesses to stand out. Generally, the business industry is at a 50% stake in reaching accomplishment and failure. Surprisingly, many companies today face a battle without enough capital. Sometimes, competition is thick and no weapon to defend. These are just among the factors that affect the whole organization. But, don’t thrive for the worst. You need a little encouragement to compete. Here, you must adjust your business activities, schedule, and operations.
Generally, you need to plan. So, before you start getting back to your daily grind, let us learn more about writing down your production plan. Follow below.
How To Create a Production Plan
If you are a manufacturing firm, it is not always easy to look into the company’s needs. There will always be lapses. And that is one thing that you should avoid. But you can do this through planning. You need your plans outlined to track the inputs of the production. That is why we help you go through it. You should understand every step by following the list below.
1. Forecast Market Demand
First things first, you need to stretch it out. To effectively plan for the future of the business, you need an estimate of the sales through market demand. How many products should you produce to meet the target demand? When should these products be released? Another way to secure this process is through current and historical information. On top of the line, there will be orders in the coming weeks. So, you need to think ahead. In general, take advantage of internal and external resources.
2. Know the Production Options Available
Here, you need to verify the tools and resources necessary to produce your products and services. Take for example, when you have a bakery business, you need to know the machines that are required to produce bread and cakes. You can start this by listing the food on the menu. Then, create a flowchart. Once these are all secured, you can already identify the resources that should be available for the business to operate. You can improve the process by having the right materials.
3. Determine the Human Resources
Aside from the equipment, you need to count how many employees you will need to operate. Of course, it is not enough to operate without the labor workers that control and monitor the production. To do this accurately, separate each team into a department. But base them according to the availability of position and equipment. Your staff should be enough to deliver and produce without delays. But aside from that, you need to weigh in your production budget. Or else, it can lead to a big commotion.
4. Monitor Plan Control
An action plan without constant monitoring is just a waste of time. Neglecting this will eventually lead to pitfalls. So, you need to measure the risk factors. This is where you compare and contrast the production process. Record a report as this helps you determine a recurring problem. Don’t let issues happen in a blink of an eye. Monitor and control while you can.
5. Make the Necessary Adjustments
For the last step, make the adjustments you intend to make with your plan. What are the challenges? Does the plan need tweaking? Production planning can be a little tricky when done wrong. Now that you have monitored and measured the risk percentage, pen down all the actions necessary. Change them according to your evaluation. Here, you should achieve a comprehensive management plan . Weigh the budget, schedule, and activities too.
How do you define a production planning procedure?
Production planning is a process that is taken during manufacturing. It details all the necessary procedures for the company to operate. It includes hiring staff, checking the resources, evaluating the results. Through this process, the production will run smoothly.
What are the essential components of production?
Production consists of various components. These are essentials to execute the manufacturing process. This includes planning, producing, scheduling, evaluating, and following ups—all of these work hand in hand for the company to deliver quality products with no delay.
What are the primary goals of the production plan?
The general objective of production planning is to secure the workflow process of a manufacturing company. As the demand goes up, it is important to ensure that all the products released are of quality.
Are you struggling to meet your daily quota? Remember, one-day unproductive results in several risks in the business. This profoundly affects your reputation, and of course, the sales. But you can change honest mistakes. While you look at the list of tips in creating a production plan, you can resume your manufacturing business and align all the plans with your objectives. Understandably, running a business is daunting and frustrating. But you will never know your potential unless you try. So, start today. Highlight your potential by outlining all the plans necessary.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a study plan for final exams in high school
Develop a project timeline for a middle school science fair.
Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » strategy, how to build a manufacturing business plan.
A manufacturing business plan can help get your new venture off the ground and running smoothly.

A manufacturing business plan outlines the goals, strategies, and operations of a manufacturing company. Use this article as a road map for your business and to help recruit investors as your operation grows.
Manufacturing business plans vary slightly compared to business plans for other types of companies. Here's what goes into a manufacturing business plan and how to create one for your venture.
Why do companies need manufacturing business plans?
Manufacturing business plans are used for the same purpose as other companies' plans. These documents help set clear goals and objectives for internal stakeholders. They provide a framework for making decisions around financing, budgeting, hiring, and procurement. Additionally, investors and lenders often require a business plan to assess the venture's potential.
Business plans are meant to be flexible, living documents that are revisited periodically as the business grows. Writing a manufacturing business plan is a good exercise in understanding what equipment will be needed, evaluating the size of the market your business is based in, and assessing your competition. These things will change over time, so make sure you adjust your plan as your company matures.
[Read more: How to Use AI Tools to Write a Business Plan ]
What goes into a manufacturing business plan?
Manufacturing plans can be very detailed, but at a minimum should include the following sections:
- An executive summary.
- A company description.
- A production plan.
- An industry analysis.
- The target market.
- Compliance.
- A financial plan.
Some manufacturing plans also include sections for marketing, management, and operations. An operations plan can include the details of how you will source materials, your design process, how you will manage production, and ways to coordinate logistics with potential buyers. Marketing sections detail how you will position your product and reach potential buyers, while management identifies the key roles for which you will hire.
[Read more: 6 Product Design Software Programs for Beginners ]
While there's a lot of overlap with a normal business plan, manufacturing companies have unique processes and constraints they need to consider and address in their plan.
Why are manufacturing business plans unique?
The production plan section should provide a detailed outline of the manufacturing process, equipment, facilities, and supply chain. It should also include operational details that are crucial to the success of the manufacturing business: quality control, inventory management, and supply chain logistics, which should be covered extensively.
Manufacturing business plans also play an outsized role in recruiting funding. Manufacturers often require significant capital investments in equipment, machinery, and facilities. The financial projections included in the plan must accurately reflect these costs to ensure adequate funding for getting off the ground.
Finally, meeting global environmental, safety, and quality regulations is no easy feat. Identifying these requirements early positions the manufacturer to be compliant, as well as to assess which supply chain partners are also able to meet these rules. A manufacturing business plan should detail supply chain management, compliance demands, and steps to streamline both of these key elements.
How to write a manufacturing business plan
The easiest way to get started is to use a template. A few outlines are available online, like this one from Katana or this one from MoreBusiness.com . Start by defining your business and answering questions such as:
- What product will the business manufacture?
- Who is the target market of ideal customers?
- What makes this product unique?
- What business structure will be used?
From there, you can work through section by section to conduct market research, develop your operations plan, prototype your product, and identify supply chain partners. Include financial projections such as your startup costs, operational costs, revenue projections, and the break-even point.
"It's important to be optimistic when starting a new business, but you also need to be realistic. This is especially true when it comes to financial projections. Don't overestimate the amount of revenue you will generate or underestimate the costs of goods sold," wrote Katana .
Breaking your plan down into smaller sections can make it easier to identify areas where you need outside help too. Don't be shy about asking others in the industry for advice.
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
For more business strategies
What is an annual report, and how do you file it, how to write a company vehicle use policy, how long should your small business keep documents.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How to Write the Operations Plan Section of a Business Plan
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
How to Write the Operations Plan Section of the Business Plan
Stage of development section, production process section, the bottom line, frequently asked questions (faqs).
The operations plan is the section of your business plan that gives an overview of your workflow, supply chains, and similar aspects of your business. Any key details of how your business physically produces goods or services will be included in this section.
You need an operations plan to help others understand how you'll deliver on your promise to turn a profit. Keep reading to learn what to include in your operations plan.
Key Takeaways
- The operations plan section should include general operational details that help investors understand the physical details of your vision.
- Details in the operations plan include information about any physical plants, equipment, assets, and more.
- The operations plan can also serve as a checklist for startups; it includes a list of everything that must be done to start turning a profit.
In your business plan , the operations plan section describes the physical necessities of your business's operation, such as your physical location, facilities, and equipment. Depending on what kind of business you'll be operating, it may also include information about inventory requirements, suppliers, and a description of the manufacturing process.
Staying focused on the bottom line will help you organize this part of the business plan.
Think of the operating plan as an outline of the capital and expense requirements your business will need to operate from day to day.
You need to do two things for the reader of your business plan in the operations section: show what you've done so far to get your business off the ground and demonstrate that you understand the manufacturing or delivery process of producing your product or service.
When you're writing this section of the operations plan, start by explaining what you've done to date to get the business operational, then follow up with an explanation of what still needs to be done. The following should be included:
Production Workflow
A high-level, step-by-step description of how your product or service will be made, identifying the problems that may occur in the production process. Follow this with a subsection titled "Risks," which outlines the potential problems that may interfere with the production process and what you're going to do to negate these risks. If any part of the production process can expose employees to hazards, describe how employees will be trained in dealing with safety issues. If hazardous materials will be used, describe how these will be safely stored, handled, and discarded.
Industry Association Memberships
Show your awareness of your industry's local, regional, or national standards and regulations by telling which industry organizations you are already a member of and which ones you plan to join. This is also an opportunity to outline what steps you've taken to comply with the laws and regulations that apply to your industry.
Supply Chains
An explanation of who your suppliers are and their prices, terms, and conditions. Describe what alternative arrangements you have made or will make if these suppliers let you down.
Quality Control
An explanation of the quality control measures that you've set up or are going to establish. For example, if you intend to pursue some form of quality control certification such as ISO 9000, describe how you will accomplish this.
While you can think of the stage of the development part of the operations plan as an overview, the production process section lays out the details of your business's day-to-day operations. Remember, your goal for writing this business plan section is to demonstrate your understanding of your product or service's manufacturing or delivery process.
When writing this section, you can use the headings below as subheadings and then provide the details in paragraph format. Leave out any topic that does not apply to your particular business.
Do an outline of your business's day-to-day operations, including your hours of operation and the days the business will be open. If the business is seasonal, be sure to say so.
The Physical Plant
Describe the type, size, and location of premises for your business. If applicable, include drawings of the building, copies of lease agreements, and recent real estate appraisals. You need to show how much the land or buildings required for your business operations are worth and tell why they're important to your proposed business.
The same goes for equipment. Besides describing the equipment necessary and how much of it you need, you also need to include its worth and cost and explain any financing arrangements.
Make a list of your assets , such as land, buildings, inventory, furniture, equipment, and vehicles. Include legal descriptions and the worth of each asset.
Special Requirements
If your business has any special requirements, such as water or power needs, ventilation, drainage, etc., provide the details in your operating plan, as well as what you've done to secure the necessary permissions.
State where you're going to get the materials you need to produce your product or service and explain what terms you've negotiated with suppliers.
Explain how long it takes to produce a unit and when you'll be able to start producing your product or service. Include factors that may affect the time frame of production and describe how you'll deal with potential challenges such as rush orders.
Explain how you'll keep track of inventory .
Feasibility
Describe any product testing, price testing, or prototype testing that you've done on your product or service.
Give details of product cost estimates.
Once you've worked through this business plan section, you'll not only have a detailed operations plan to show your readers, but you'll also have a convenient list of what needs to be done next to make your business a reality. Writing this document gives you a chance to crystallize your business ideas into a clear checklist that you can reference. As you check items off the list, use it to explain your vision to investors, partners, and others within your organization.
What is an operations plan?
An operations plan is one section of a company's business plan. This section conveys the physical requirements for your business's operations, including supply chains, workflow , and quality control processes.
What is the main difference between the operations plan and the financial plan?
The operations plan and financial plan tackle similar issues, in that they seek to explain how the business will turn a profit. The operations plan approaches this issue from a physical perspective, such as property, routes, and locations. The financial plan explains how revenue and expenses will ultimately lead to the business's success.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A production plan: a detailed outline that guides efficient product manufacturing or service delivery. Importance of a production plan: provides a roadmap for operations, optimises resource utilisation, and aligns with customer demand.
To write a production plan for a business, follow these steps: Define the business’s goals and objectives. Determine the production process, including materials, labor, and equipment needed. Set production targets and timelines. Allocate resources and determine a budget. Create contingency plans for potential issues.
A production plan is a detailed document that outlines the structure of the company’s operations. In the plan, there is a structure, schedule, goal, activities, and the definition of resources in between.
Manufacturing plans can be very detailed, but at a minimum should include the following sections: An executive summary. A company description. A production plan. An industry analysis. The target market. Compliance. A financial plan. Some manufacturing plans also include sections for marketing, management, and operations.
You need to do two things for the reader of your business plan in the operations section: show what you've done so far to get your business off the ground and demonstrate that you understand the manufacturing or delivery process of producing your product or service.
Bottom Line. Frequently Asked Questions. Show more. Every business starts with a vision, which is distilled and communicated through a business plan. In addition to your high-level hopes and...