

5 tips on writing better university assignments
Lecturer in Student Learning and Communication Development, University of Sydney
Disclosure statement
Alexandra Garcia does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
University of Sydney provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
University life comes with its share of challenges. One of these is writing longer assignments that require higher information, communication and critical thinking skills than what you might have been used to in high school. Here are five tips to help you get ahead.
1. Use all available sources of information
Beyond instructions and deadlines, lecturers make available an increasing number of resources. But students often overlook these.
For example, to understand how your assignment will be graded, you can examine the rubric . This is a chart indicating what you need to do to obtain a high distinction, a credit or a pass, as well as the course objectives – also known as “learning outcomes”.
Other resources include lecture recordings, reading lists, sample assignments and discussion boards. All this information is usually put together in an online platform called a learning management system (LMS). Examples include Blackboard , Moodle , Canvas and iLearn . Research shows students who use their LMS more frequently tend to obtain higher final grades.
If after scrolling through your LMS you still have questions about your assignment, you can check your lecturer’s consultation hours.
2. Take referencing seriously
Plagiarism – using somebody else’s words or ideas without attribution – is a serious offence at university. It is a form of cheating.

In many cases, though, students are unaware they have cheated. They are simply not familiar with referencing styles – such as APA , Harvard , Vancouver , Chicago , etc – or lack the skills to put the information from their sources into their own words.
To avoid making this mistake, you may approach your university’s library, which is likely to offer face-to-face workshops or online resources on referencing. Academic support units may also help with paraphrasing.
You can also use referencing management software, such as EndNote or Mendeley . You can then store your sources, retrieve citations and create reference lists with only a few clicks. For undergraduate students, Zotero has been recommended as it seems to be more user-friendly.
Using this kind of software will certainly save you time searching for and formatting references. However, you still need to become familiar with the citation style in your discipline and revise the formatting accordingly.
3. Plan before you write
If you were to build a house, you wouldn’t start by laying bricks at random. You’d start with a blueprint. Likewise, writing an academic paper requires careful planning: you need to decide the number of sections, their organisation, and the information and sources you will include in each.
Research shows students who prepare detailed outlines produce higher-quality texts. Planning will not only help you get better grades, but will also reduce the time you spend staring blankly at the screen thinking about what to write next.

During the planning stage, using programs like OneNote from Microsoft Office or Outline for Mac can make the task easier as they allow you to organise information in tabs. These bits of information can be easily rearranged for later drafting. Navigating through the tabs is also easier than scrolling through a long Word file.
4. Choose the right words
Which of these sentences is more appropriate for an assignment?
a. “This paper talks about why the planet is getting hotter”, or b. “This paper examines the causes of climate change”.
The written language used at university is more formal and technical than the language you normally use in social media or while chatting with your friends. Academic words tend to be longer and their meaning is also more precise. “Climate change” implies more than just the planet “getting hotter”.
To find the right words, you can use SkELL , which shows you the words that appear more frequently, with your search entry categorised grammatically. For example, if you enter “paper”, it will tell you it is often the subject of verbs such as “present”, “describe”, “examine” and “discuss”.
Another option is the Writefull app, which does a similar job without having to use an online browser.
5. Edit and proofread
If you’re typing the last paragraph of the assignment ten minutes before the deadline, you will be missing a very important step in the writing process: editing and proofreading your text. A 2018 study found a group of university students did significantly better in a test after incorporating the process of planning, drafting and editing in their writing.

You probably already know to check the spelling of a word if it appears underlined in red. You may even use a grammar checker such as Grammarly . However, no software to date can detect every error and it is not uncommon to be given inaccurate suggestions.
So, in addition to your choice of proofreader, you need to improve and expand your grammar knowledge. Check with the academic support services at your university if they offer any relevant courses.
Written communication is a skill that requires effort and dedication. That’s why universities are investing in support services – face-to-face workshops, individual consultations, and online courses – to help students in this process. You can also take advantage of a wide range of web-based resources such as spell checkers, vocabulary tools and referencing software – many of them free.
Improving your written communication will help you succeed at university and beyond.
- College assignments
- University study
- Writing tips
- Essay writing
- Student assessment

Quantitative Analyst

Director of STEM

Community member - Training Delivery and Development Committee (Volunteer part-time)

Chief Executive Officer

Head of Evidence to Action

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that they will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply —use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove their point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, they still have to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and they already know everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality they expect.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
The Beginner's Guide to Writing an Essay | Steps & Examples
An academic essay is a focused piece of writing that develops an idea or argument using evidence, analysis, and interpretation.
There are many types of essays you might write as a student. The content and length of an essay depends on your level, subject of study, and course requirements. However, most essays at university level are argumentative — they aim to persuade the reader of a particular position or perspective on a topic.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages:
- Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline.
- Writing : Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion.
- Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling, and formatting of your essay.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Essay writing process, preparation for writing an essay, writing the introduction, writing the main body, writing the conclusion, essay checklist, lecture slides, frequently asked questions about writing an essay.
The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay .
For example, if you’ve been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you’ll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay , on the other hand, you’ll need to spend more time researching your topic and developing an original argument before you start writing.
| 1. Preparation | 2. Writing | 3. Revision |
|---|---|---|
| , organized into Write the | or use a for language errors |
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Before you start writing, you should make sure you have a clear idea of what you want to say and how you’re going to say it. There are a few key steps you can follow to make sure you’re prepared:
- Understand your assignment: What is the goal of this essay? What is the length and deadline of the assignment? Is there anything you need to clarify with your teacher or professor?
- Define a topic: If you’re allowed to choose your own topic , try to pick something that you already know a bit about and that will hold your interest.
- Do your research: Read primary and secondary sources and take notes to help you work out your position and angle on the topic. You’ll use these as evidence for your points.
- Come up with a thesis: The thesis is the central point or argument that you want to make. A clear thesis is essential for a focused essay—you should keep referring back to it as you write.
- Create an outline: Map out the rough structure of your essay in an outline . This makes it easier to start writing and keeps you on track as you go.
Once you’ve got a clear idea of what you want to discuss, in what order, and what evidence you’ll use, you’re ready to start writing.
The introduction sets the tone for your essay. It should grab the reader’s interest and inform them of what to expect. The introduction generally comprises 10–20% of the text.
1. Hook your reader
The first sentence of the introduction should pique your reader’s interest and curiosity. This sentence is sometimes called the hook. It might be an intriguing question, a surprising fact, or a bold statement emphasizing the relevance of the topic.
Let’s say we’re writing an essay about the development of Braille (the raised-dot reading and writing system used by visually impaired people). Our hook can make a strong statement about the topic:
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
2. Provide background on your topic
Next, it’s important to give context that will help your reader understand your argument. This might involve providing background information, giving an overview of important academic work or debates on the topic, and explaining difficult terms. Don’t provide too much detail in the introduction—you can elaborate in the body of your essay.
3. Present the thesis statement
Next, you should formulate your thesis statement— the central argument you’re going to make. The thesis statement provides focus and signals your position on the topic. It is usually one or two sentences long. The thesis statement for our essay on Braille could look like this:
As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness.
4. Map the structure
In longer essays, you can end the introduction by briefly describing what will be covered in each part of the essay. This guides the reader through your structure and gives a preview of how your argument will develop.
The invention of Braille marked a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by blind and visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Write your essay introduction
The body of your essay is where you make arguments supporting your thesis, provide evidence, and develop your ideas. Its purpose is to present, interpret, and analyze the information and sources you have gathered to support your argument.
Length of the body text
The length of the body depends on the type of essay. On average, the body comprises 60–80% of your essay. For a high school essay, this could be just three paragraphs, but for a graduate school essay of 6,000 words, the body could take up 8–10 pages.
Paragraph structure
To give your essay a clear structure , it is important to organize it into paragraphs . Each paragraph should be centered around one main point or idea.
That idea is introduced in a topic sentence . The topic sentence should generally lead on from the previous paragraph and introduce the point to be made in this paragraph. Transition words can be used to create clear connections between sentences.
After the topic sentence, present evidence such as data, examples, or quotes from relevant sources. Be sure to interpret and explain the evidence, and show how it helps develop your overall argument.
Lack of access to reading and writing put blind people at a serious disadvantage in nineteenth-century society. Text was one of the primary methods through which people engaged with culture, communicated with others, and accessed information; without a well-developed reading system that did not rely on sight, blind people were excluded from social participation (Weygand, 2009). While disabled people in general suffered from discrimination, blindness was widely viewed as the worst disability, and it was commonly believed that blind people were incapable of pursuing a profession or improving themselves through culture (Weygand, 2009). This demonstrates the importance of reading and writing to social status at the time: without access to text, it was considered impossible to fully participate in society. Blind people were excluded from the sighted world, but also entirely dependent on sighted people for information and education.
See the full essay example
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The conclusion is the final paragraph of an essay. It should generally take up no more than 10–15% of the text . A strong essay conclusion :
- Returns to your thesis
- Ties together your main points
- Shows why your argument matters
A great conclusion should finish with a memorable or impactful sentence that leaves the reader with a strong final impression.
What not to include in a conclusion
To make your essay’s conclusion as strong as possible, there are a few things you should avoid. The most common mistakes are:
- Including new arguments or evidence
- Undermining your arguments (e.g. “This is just one approach of many”)
- Using concluding phrases like “To sum up…” or “In conclusion…”
Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind people were treated and the opportunities available to them. Louis Braille’s innovation was to reimagine existing reading systems from a blind perspective, and the success of this invention required sighted teachers to adapt to their students’ reality instead of the other way around. In this sense, Braille helped drive broader social changes in the status of blindness. New accessibility tools provide practical advantages to those who need them, but they can also change the perspectives and attitudes of those who do not.
Write your essay conclusion
Checklist: Essay
My essay follows the requirements of the assignment (topic and length ).
My introduction sparks the reader’s interest and provides any necessary background information on the topic.
My introduction contains a thesis statement that states the focus and position of the essay.
I use paragraphs to structure the essay.
I use topic sentences to introduce each paragraph.
Each paragraph has a single focus and a clear connection to the thesis statement.
I make clear transitions between paragraphs and ideas.
My conclusion doesn’t just repeat my points, but draws connections between arguments.
I don’t introduce new arguments or evidence in the conclusion.
I have given an in-text citation for every quote or piece of information I got from another source.
I have included a reference page at the end of my essay, listing full details of all my sources.
My citations and references are correctly formatted according to the required citation style .
My essay has an interesting and informative title.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (e.g. font, page numbers, line spacing).
Your essay meets all the most important requirements. Our editors can give it a final check to help you submit with confidence.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates.
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills.
Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How long is an essay? Guidelines for different types of essay
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
- How to conclude an essay | Interactive example
More interesting articles
- Checklist for academic essays | Is your essay ready to submit?
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
- Example of a great essay | Explanations, tips & tricks
- Generate topic ideas for an essay or paper | Tips & techniques
- How to revise an essay in 3 simple steps
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
- How to write a descriptive essay | Example & tips
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
- How to write a narrative essay | Example & tips
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
- How to write an essay outline | Guidelines & examples
- How to write an expository essay
- How to write the body of an essay | Drafting & redrafting
- Kinds of argumentative academic essays and their purposes
- Organizational tips for academic essays
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
- Transition sentences | Tips & examples for clear writing
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

Essay and dissertation writing skills
Planning your essay
Writing your introduction
Structuring your essay
- Writing essays in science subjects
- Brief video guides to support essay planning and writing
- Writing extended essays and dissertations
- Planning your dissertation writing time
Structuring your dissertation
- Top tips for writing longer pieces of work
Advice on planning and writing essays and dissertations
University essays differ from school essays in that they are less concerned with what you know and more concerned with how you construct an argument to answer the question. This means that the starting point for writing a strong essay is to first unpick the question and to then use this to plan your essay before you start putting pen to paper (or finger to keyboard).
A really good starting point for you are these short, downloadable Tips for Successful Essay Writing and Answering the Question resources. Both resources will help you to plan your essay, as well as giving you guidance on how to distinguish between different sorts of essay questions.
You may find it helpful to watch this seven-minute video on six tips for essay writing which outlines how to interpret essay questions, as well as giving advice on planning and structuring your writing:
Different disciplines will have different expectations for essay structure and you should always refer to your Faculty or Department student handbook or course Canvas site for more specific guidance.
However, broadly speaking, all essays share the following features:
Essays need an introduction to establish and focus the parameters of the discussion that will follow. You may find it helpful to divide the introduction into areas to demonstrate your breadth and engagement with the essay question. You might define specific terms in the introduction to show your engagement with the essay question; for example, ‘This is a large topic which has been variously discussed by many scientists and commentators. The principal tension is between the views of X and Y who define the main issues as…’ Breadth might be demonstrated by showing the range of viewpoints from which the essay question could be considered; for example, ‘A variety of factors including economic, social and political, influence A and B. This essay will focus on the social and economic aspects, with particular emphasis on…..’
Watch this two-minute video to learn more about how to plan and structure an introduction:
The main body of the essay should elaborate on the issues raised in the introduction and develop an argument(s) that answers the question. It should consist of a number of self-contained paragraphs each of which makes a specific point and provides some form of evidence to support the argument being made. Remember that a clear argument requires that each paragraph explicitly relates back to the essay question or the developing argument.
- Conclusion: An essay should end with a conclusion that reiterates the argument in light of the evidence you have provided; you shouldn’t use the conclusion to introduce new information.
- References: You need to include references to the materials you’ve used to write your essay. These might be in the form of footnotes, in-text citations, or a bibliography at the end. Different systems exist for citing references and different disciplines will use various approaches to citation. Ask your tutor which method(s) you should be using for your essay and also consult your Department or Faculty webpages for specific guidance in your discipline.
Essay writing in science subjects
If you are writing an essay for a science subject you may need to consider additional areas, such as how to present data or diagrams. This five-minute video gives you some advice on how to approach your reading list, planning which information to include in your answer and how to write for your scientific audience – the video is available here:
A PDF providing further guidance on writing science essays for tutorials is available to download.
Short videos to support your essay writing skills
There are many other resources at Oxford that can help support your essay writing skills and if you are short on time, the Oxford Study Skills Centre has produced a number of short (2-minute) videos covering different aspects of essay writing, including:
- Approaching different types of essay questions
- Structuring your essay
- Writing an introduction
- Making use of evidence in your essay writing
- Writing your conclusion
Extended essays and dissertations
Longer pieces of writing like extended essays and dissertations may seem like quite a challenge from your regular essay writing. The important point is to start with a plan and to focus on what the question is asking. A PDF providing further guidance on planning Humanities and Social Science dissertations is available to download.
Planning your time effectively
Try not to leave the writing until close to your deadline, instead start as soon as you have some ideas to put down onto paper. Your early drafts may never end up in the final work, but the work of committing your ideas to paper helps to formulate not only your ideas, but the method of structuring your writing to read well and conclude firmly.
Although many students and tutors will say that the introduction is often written last, it is a good idea to begin to think about what will go into it early on. For example, the first draft of your introduction should set out your argument, the information you have, and your methods, and it should give a structure to the chapters and sections you will write. Your introduction will probably change as time goes on but it will stand as a guide to your entire extended essay or dissertation and it will help you to keep focused.
The structure of extended essays or dissertations will vary depending on the question and discipline, but may include some or all of the following:
- The background information to - and context for - your research. This often takes the form of a literature review.
- Explanation of the focus of your work.
- Explanation of the value of this work to scholarship on the topic.
- List of the aims and objectives of the work and also the issues which will not be covered because they are outside its scope.
The main body of your extended essay or dissertation will probably include your methodology, the results of research, and your argument(s) based on your findings.
The conclusion is to summarise the value your research has added to the topic, and any further lines of research you would undertake given more time or resources.
Tips on writing longer pieces of work
Approaching each chapter of a dissertation as a shorter essay can make the task of writing a dissertation seem less overwhelming. Each chapter will have an introduction, a main body where the argument is developed and substantiated with evidence, and a conclusion to tie things together. Unlike in a regular essay, chapter conclusions may also introduce the chapter that will follow, indicating how the chapters are connected to one another and how the argument will develop through your dissertation.
For further guidance, watch this two-minute video on writing longer pieces of work .
Systems & Services
Access Student Self Service
- Student Self Service
- Self Service guide
- Registration guide
- Libraries search
- OXCORT - see TMS
- GSS - see Student Self Service
- The Careers Service
- Oxford University Sport
- Online store
- Gardens, Libraries and Museums
- Researchers Skills Toolkit
- LinkedIn Learning (formerly Lynda.com)
- Access Guide
- Lecture Lists
- Exam Papers (OXAM)
- Oxford Talks
Latest student news
CAN'T FIND WHAT YOU'RE LOOKING FOR?
Try our extensive database of FAQs or submit your own question...
Ask a question

- Schools & departments

Academic writing
Advice and resources to support you with effective academic writing.
Approaches to writing
Assignment writing is a process which involves planning, drafting and reviewing what you are going to say. You will find you need to review your initial plan and edit it as you go along. You should expect to have to redraft some sections of writing.
You should also check any guidance given to you as part of your course, as conventions vary between subject areas.
One of the hardest things can be to get started writing an assignment. Sometimes this is a question of taking the time to reflect on what you are being asked to do in the assignment brief.
Getting started with an assignment
The handout Getting started suggests a way in which you can break down your task, think about aspects of it and commit some of your initial ideas to paper. It also suggests ways you can start to adapt this method to suit you. Alternatively you may prefer to use a prompt list to start to analyse your title.
Getting started (pdf) Getting started (Word rtf)
Essay title prompts (pdf) Essay title prompts (Word rtf)
You will want to respond to the assignments you have been set as well as you can. This means paying attention to key words in the question or assignment brief. These are sometimes known as command or directive words because they tell you what to do. The document Directive words provides definitions of some of the commonly used words.
Directive words (pdf) Directive words (Word rtf) Directive words – British Sign Language translation (Media Hopper video)
Getting your ideas in order
In any written assignment you will be expected to organise and structure information which is synthesised from a range of sources. You will need to make notes from your readings to help you consolidate and connect your research to your question. The Reading at university page has strategies to help you develop effective skills for making notes from reading.
Reading at university
Making notes means you end up with lots of bits of writing which you need to link together for your reader. Sometimes it can be hard to know what to select and how to identify relationships between ideas and concepts.
There are suggestions in the Getting your ideas in order handout of practical ways in which you might reorganise your material in response to the task set. Playing around with the order can help you arrive at a line of reasoning that will convince the reader. Aim to experiment and find out what works for you.
Getting your ideas in order (pdf) Getting your ideas in order (Word rtf)
Essay parts and paragraphs
If you have been asked to write an academic essay, and you haven't done this before, you may be unsure of what is expected. The Parts of an essay handout gives a brief introductory overview of the component parts of an essay.
Parts of an essay (pdf) Parts of an essay (Word rtf)
Paragraphs are the building blocks of an essay and are a way of organising your thinking and making your meaning clear in your writing for your reader. The handout Developing writing in paragraphs encourages you to think about the way you shape your paragraphs and when to move on to a new one.
Developing writing in paragraphs (pdf) Developing writing in paragraphs (Word rtf)
Build an argument as you go
Identifying and writing about good evidence is not enough. You need to build an argument. An argument is:
Using reasons to support a point of view, so that known or unknown audiences may be persuaded to agree. Cottrell, S. (2011)Critical thinking skills: developing effective analysis and argument. 2nd edn. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan, p52.
You can develop your argument as you read and write by creating a working hypothesis or basic answer in response to the assignment brief.
Building an argument as you go (pdf) Building an argument as you go (Word rtf)
As you move through your studies lecturers will expect more from your written work. They will expect the accurate attribution of ideas from others (including academic and other authors, and the ideas of those who teach you). There is general advice and resources for referencing and citations (and avoiding plagiarism) on the Referencing and citations page.
Referencing and citations
Your marker(s) will expect written pieces to be logically structured with fluid expression of thought, and with deeper and more critical engagement with the subjects and ideas you are reading and learning about.
Aim to become familiar with the level of writing required by reading good quality examples. At an advanced level you are aiming to write to the style you read in academic journals.
As your written tasks become longer and more complex it can be helpful to reflect on your own writing process.
Reflect on your writing process (pdf) Reflect on your writing process (Word rtf)
Different types of academic writing
Academic writing is much more than just an essay. You might be asked to write a lab or business report, a policy brief, a blog post, a journal article or a reflection piece for example. These tend to be subject and task specific so you need to check the assignment brief and any criteria for details of their purpose, formatting, structure, things to include etc.
Reflective academic writing
In some subjects, assessment may be based on critical reflection. This can be a challenge as it is a very particular style and form of writing which you may not have come across before. As well as check your assignment brief for specifics, the University’s Employability Consultancy have created a Reflection Toolkit of resources, models and questions to help you develop your reflective writing skills.
The Reflection Toolkit
School-level support
Take advantage of any writing development sessions organised through or learning materials offered by your School, Deanery or course. These will help you develop the specific writing skills you need for your discipline or subject area.
Writing your own title
If you have to write your own title in response to the brief you have been set, you need to think about how to frame this. The Formulating your own title handout suggests some aspects to consider.
Formulating your own title (pdf) Formulating your own title (Word rtf)
Differences from non-academic writing
If you are studying during a career break, or part-time while still working, you need to be aware that academic writing is a very different skill from other forms of writing you may have done in the workplace. Academic writing tends to be more formal, requiring succinct prose rather than bullet points, and it is more about the argument than simply conveying, or describing, information. Writing for assessment requires you to think carefully about your assignment and criteria, your argument and content, use of your subject specific conventions (e.g. language, style etc.), and your audience.
Your written work needs to be grounded in and backed up by appropriate and informed opinion and sources, rather than solely by personal opinion and experience. Academic written work will also make fewer absolute statements. Language is often more tentative or cautious.
Academic Phrasebank is a collection of general phrases taken from academic sources created by John Morley at the University of Manchester. The phrases are sorted into writing and assignment themes such as being critical and writing conclusions.
This article was published on 2024-02-26
- Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt
- Asking Analytical Questions
- Introductions
- What Do Introductions Across the Disciplines Have in Common?
- Anatomy of a Body Paragraph
- Transitions
- Tips for Organizing Your Essay
- Counterargument
- Conclusions
- Strategies for Essay Writing: Downloadable PDFs
- Brief Guides to Writing in the Disciplines

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Writing Assignments
Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine

Introduction
Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research. Developing critical thinking and writing skills are also necessary to demonstrate your ability to understand and apply information about your topic. It is not uncommon to be unsure about the processes of writing assignments at university.
- You may be returning to study after a break
- You may have come from an exam based assessment system and never written an assignment before
- Maybe you have written assignments but would like to improve your processes and strategies
This chapter has a collection of resources that will provide you with the skills and strategies to understand assignment requirements and effectively plan, research, write and edit your assignments. It begins with an explanation of how to analyse an assignment task and start putting your ideas together. It continues by breaking down the components of academic writing and exploring the elements you will need to master in your written assignments. This is followed by a discussion of paraphrasing and synthesis, and how you can use these strategies to create a strong, written argument. The chapter concludes with useful checklists for editing and proofreading to help you get the best possible mark for your work.
Task Analysis and Deconstructing an Assignment
It is important that before you begin researching and writing your assignments you spend sufficient time understanding all the requirements. This will help make your research process more efficient and effective. Check your subject information such as task sheets, criteria sheets and any additional information that may be in your subject portal online. Seek clarification from your lecturer or tutor if you are still unsure about how to begin your assignments.
The task sheet typically provides key information about an assessment including the assignment question. It can be helpful to scan this document for topic, task and limiting words to ensure that you fully understand the concepts you are required to research, how to approach the assignment, and the scope of the task you have been set. These words can typically be found in your assignment question and are outlined in more detail in the two tables below (see Table 19.1 and Table 19.2 ).
Table 19.1 Parts of an Assignment Question
| Topic words | These are words and concepts you have to research and write about. |
| Task words | These will tell you how to approach the assignment and structure the information you find in your research (e.g., discuss, analyse). |
| Limiting words | These words define the scope of the assignment, e.g., Australian perspectives, relevant codes or standards or a specific timeframe. |
Make sure you have a clear understanding of what the task word requires you to address.
Table 19.2 Task words
| Give reasons for or explain something has occurred. This task directs you to consider contributing factors to a certain situation or event. You are expected to make a decision about why these occurred, not just describe the events. | the factors that led to the global financial crisis. | |
| Consider the different elements of a concept, statement or situation. Show the different components and show how they connect or relate. Your structure and argument should be logical and methodical. | the political, social and economic impacts of climate change. | |
| Make a judgement on a topic or idea. Consider its reliability, truth and usefulness. In your judgement, consider both the strengths and weaknesses of the opposing arguments to determine your topic’s worth (similar to evaluate). | the efficacy of cogitative behavioural therapy (CBT) for the treatment of depression. | |
| Divide your topic into categories or sub-topics logically (could possibly be part of a more complex task). | the artists studied this semester according to the artistic periods they best represent. Then choose one artist and evaluate their impact on future artists. | |
| State your opinion on an issue or idea. You may explain the issue or idea in more detail. Be objective and support your opinion with reliable evidence. | the government’s proposal to legalise safe injecting rooms. | |
| Show the similarities and differences between two or more ideas, theories, systems, arguments or events. You are expected to provide a balanced response, highlighting similarities and differences. | the efficiency of wind and solar power generation for a construction site. | |
| Point out only the differences between two or more ideas, theories, systems, arguments or events. | virtue ethics and utilitarianism as models for ethical decision making. | |
| (this is often used with another task word, e.g. critically evaluate, critically analyse, critically discuss) | It does not mean to criticise, instead you are required to give a balanced account, highlighting strengths and weaknesses about the topic. Your overall judgment must be supported by reliable evidence and your interpretation of that evidence. | analyse the impacts of mental health on recidivism within youth justice. |
| Provide a precise meaning of a concept. You may need to include the limits or scope of the concept within a given context. | digital disruption as it relates to productivity. | |
| Provide a thorough description, emphasising the most important points. Use words to show appearance, function, process, events or systems. You are not required to make judgements. | the pathophysiology of Asthma. | |
| Highlight the differences between two (possibly confusing) items. | between exothermic and endothermic reactions. | |
| Provide an analysis of a topic. Use evidence to support your argument. Be logical and include different perspectives on the topic (This requires more than a description). | how Brofenbrenner’s ecological system’s theory applies to adolescence. | |
| Review both positive and negative aspects of a topic. You may need to provide an overall judgement regarding the value or usefulness of the topic. Evidence (referencing) must be included to support your writing. | the impact of inclusive early childhood education programs on subsequent high school completion rates for First Nations students. | |
| Describe and clarify the situation or topic. Depending on your discipline area and topic, this may include processes, pathways, cause and effect, impact, or outcomes. | the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the film industry in Australia. | |
| Clarify a point or argument with examples and evidence. | how society’s attitudes to disability have changed from a medical model to a wholistic model of disability. | |
| Give evidence which supports an argument or idea; show why a decision or conclusions were made. Justify may be used with other topic words, such as outline, argue. | Write a report outlining the key issues and implications of a welfare cashless debit card trial and make three recommendations for future improvements. your decision-making process for the recommendations. | |
| A comprehensive description of the situation or topic which provides a critical analysis of the key issues. | Provide a of Australia's asylum policies since the Pacific Solution in 2001. | |
| An overview or brief description of a topic. (This is likely to be part of a larger assessment task.) | the process for calculating the correct load for a plane. |
The criteria sheet , also known as the marking sheet or rubric, is another important document to look at before you begin your assignment. The criteria sheet outlines how your assignment will be marked and should be used as a checklist to make sure you have included all the information required.
The task or criteria sheet will also include the:
- Word limit (or word count)
- Referencing style and research expectations
- Formatting requirements
Task analysis and criteria sheets are also discussed in the chapter Managing Assessments for a more detailed discussion on task analysis, criteria sheets, and marking rubrics.
Preparing your ideas
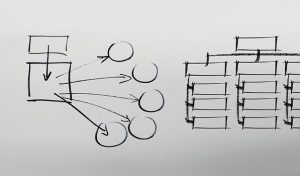
Brainstorm or concept map: List possible ideas to address each part of the assignment task based on what you already know about the topic from lectures and weekly readings.
Finding appropriate information: Learn how to find scholarly information for your assignments which is
See the chapter Working With Information for a more detailed explanation .
What is academic writing?
Academic writing tone and style.
Many of the assessment pieces you prepare will require an academic writing style. This is sometimes called ‘academic tone’ or ‘academic voice’. This section will help you to identify what is required when you are writing academically (see Table 19.3 ). The best way to understand what academic writing looks like, is to read broadly in your discipline area. Look at how your course readings, or scholarly sources, are written. This will help you identify the language of your discipline field, as well as how other writers structure their work.
Table 19.3 Comparison of academic and non-academic writing
| Is clear, concise and well-structured | Is verbose and may use more words than are needed |
| Is formal. It writes numbers under twenty in full. | Writes numbers under twenty as numerals and uses symbols such as “&” instead of writing it in full |
| Is reasoned and supported (logically developed) | Uses humour (puns, sarcasm) |
| Is authoritative (writes in third person- This essay argues…) | Writes in first person (I think, I found) |
| Utilises the language of the field/industry/subject | Uses colloquial language e.g., mate |
Thesis statements
Essays are a common form of assessment that you will likely encounter during your university studies. You should apply an academic tone and style when writing an essay, just as you would in in your other assessment pieces. One of the most important steps in writing an essay is constructing your thesis statement. A thesis statement tells the reader the purpose, argument or direction you will take to answer your assignment question. A thesis statement may not be relevant for some questions, if you are unsure check with your lecturer. The thesis statement:
- Directly relates to the task . Your thesis statement may even contain some of the key words or synonyms from the task description.
- Does more than restate the question.
- Is specific and uses precise language.
- Let’s your reader know your position or the main argument that you will support with evidence throughout your assignment.
- The subject is the key content area you will be covering.
- The contention is the position you are taking in relation to the chosen content.
Your thesis statement helps you to structure your essay. It plays a part in each key section: introduction, body and conclusion.
Planning your assignment structure

When planning and drafting assignments, it is important to consider the structure of your writing. Academic writing should have clear and logical structure and incorporate academic research to support your ideas. It can be hard to get started and at first you may feel nervous about the size of the task, this is normal. If you break your assignment into smaller pieces, it will seem more manageable as you can approach the task in sections. Refer to your brainstorm or plan. These ideas should guide your research and will also inform what you write in your draft. It is sometimes easier to draft your assignment using the 2-3-1 approach, that is, write the body paragraphs first followed by the conclusion and finally the introduction.
Writing introductions and conclusions
Clear and purposeful introductions and conclusions in assignments are fundamental to effective academic writing. Your introduction should tell the reader what is going to be covered and how you intend to approach this. Your conclusion should summarise your argument or discussion and signal to the reader that you have come to a conclusion with a final statement. These tips below are based on the requirements usually needed for an essay assignment, however, they can be applied to other assignment types.
Writing introductions

Most writing at university will require a strong and logically structured introduction. An effective introduction should provide some background or context for your assignment, clearly state your thesis and include the key points you will cover in the body of the essay in order to prove your thesis.
Usually, your introduction is approximately 10% of your total assignment word count. It is much easier to write your introduction once you have drafted your body paragraphs and conclusion, as you know what your assignment is going to be about. An effective introduction needs to inform your reader by establishing what the paper is about and provide four basic things:
- A brief background or overview of your assignment topic
- A thesis statement (see section above)
- An outline of your essay structure
- An indication of any parameters or scope that will/ will not be covered, e.g. From an Australian perspective.
The below example demonstrates the four different elements of an introductory paragraph.
1) Information technology is having significant effects on the communication of individuals and organisations in different professions. 2) This essay will discuss the impact of information technology on the communication of health professionals. 3) First, the provision of information technology for the educational needs of nurses will be discussed. 4) This will be followed by an explanation of the significant effects that information technology can have on the role of general practitioner in the area of public health. 5) Considerations will then be made regarding the lack of knowledge about the potential of computers among hospital administrators and nursing executives. 6) The final section will explore how information technology assists health professionals in the delivery of services in rural areas . 7) It will be argued that information technology has significant potential to improve health care and medical education, but health professionals are reluctant to use it.
1 Brief background/ overview | 2 Indicates the scope of what will be covered | 3-6 Outline of the main ideas (structure) | 7 The thesis statement
Note : The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.

Writing conclusions
You should aim to end your assignments with a strong conclusion. Your conclusion should restate your thesis and summarise the key points you have used to prove this thesis. Finish with a key point as a final impactful statement. Similar to your introduction, your conclusion should be approximately 10% of the total assignment word length. If your assessment task asks you to make recommendations, you may need to allocate more words to the conclusion or add a separate recommendations section before the conclusion. Use the checklist below to check your conclusion is doing the right job.
Conclusion checklist
- Have you referred to the assignment question and restated your argument (or thesis statement), as outlined in the introduction?
- Have you pulled together all the threads of your essay into a logical ending and given it a sense of unity?
- Have you presented implications or recommendations in your conclusion? (if required by your task).
- Have you added to the overall quality and impact of your essay? This is your final statement about this topic; thus, a key take-away point can make a great impact on the reader.
- Remember, do not add any new material or direct quotes in your conclusion.
This below example demonstrates the different elements of a concluding paragraph.
1) It is evident, therefore, that not only do employees need to be trained for working in the Australian multicultural workplace, but managers also need to be trained. 2) Managers must ensure that effective in-house training programs are provided for migrant workers, so that they become more familiar with the English language, Australian communication norms and the Australian work culture. 3) In addition, Australian native English speakers need to be made aware of the differing cultural values of their workmates; particularly the different forms of non-verbal communication used by other cultures. 4) Furthermore, all employees must be provided with clear and detailed guidelines about company expectations. 5) Above all, in order to minimise communication problems and to maintain an atmosphere of tolerance, understanding and cooperation in the multicultural workplace, managers need to have an effective knowledge about their employees. This will help employers understand how their employee’s social conditioning affects their beliefs about work. It will develop their communication skills to develop confidence and self-esteem among diverse work groups. 6) The culturally diverse Australian workplace may never be completely free of communication problems, however, further studies to identify potential problems and solutions, as well as better training in cross cultural communication for managers and employees, should result in a much more understanding and cooperative environment.
1 Reference to thesis statement – In this essay the writer has taken the position that training is required for both employees and employers . | 2-5 Structure overview – Here the writer pulls together the main ideas in the essay. | 6 Final summary statement that is based on the evidence.
Note: The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing paragraphs
Paragraph writing is a key skill that enables you to incorporate your academic research into your written work. Each paragraph should have its own clearly identified topic sentence or main idea which relates to the argument or point (thesis) you are developing. This idea should then be explained by additional sentences which you have paraphrased from good quality sources and referenced according to the recommended guidelines of your subject (see the chapter Working with Information ). Paragraphs are characterised by increasing specificity; that is, they move from the general to the specific, increasingly refining the reader’s understanding. A common structure for paragraphs in academic writing is as follows.
Topic Sentence
This is the main idea of the paragraph and should relate to the overall issue or purpose of your assignment is addressing. Often it will be expressed as an assertion or claim which supports the overall argument or purpose of your writing.
Explanation/ Elaboration
The main idea must have its meaning explained and elaborated upon. Think critically, do not just describe the idea.
These explanations must include evidence to support your main idea. This information should be paraphrased and referenced according to the appropriate referencing style of your course.
Concluding sentence (critical thinking)
This should explain why the topic of the paragraph is relevant to the assignment question and link to the following paragraph.
Use the checklist below to check your paragraphs are clear and well formed.
Paragraph checklist
- Does your paragraph have a clear main idea?
- Is everything in the paragraph related to this main idea?
- Is the main idea adequately developed and explained?
- Do your sentences run together smoothly?
- Have you included evidence to support your ideas?
- Have you concluded the paragraph by connecting it to your overall topic?
Writing sentences
Make sure all the sentences in your paragraphs make sense. Each sentence must contain a verb to be a complete sentence. Avoid sentence fragments . These are incomplete sentences or ideas that are unfinished and create confusion for your reader. Avoid also run on sentences . This happens when you join two ideas or clauses without using the appropriate punctuation. This also confuses your meaning (See the chapter English Language Foundations for examples and further explanation).
Use transitions (linking words and phrases) to connect your ideas between paragraphs and make your writing flow. The order that you structure the ideas in your assignment should reflect the structure you have outlined in your introduction. Refer to transition words table in the chapter English Language Foundations.
Paraphrasing and Synthesising
Paraphrasing and synthesising are powerful tools that you can use to support the main idea of a paragraph. It is likely that you will regularly use these skills at university to incorporate evidence into explanatory sentences and strengthen your essay. It is important to paraphrase and synthesise because:
- Paraphrasing is regarded more highly at university than direct quoting.
- Paraphrasing can also help you better understand the material.
- Paraphrasing and synthesising demonstrate you have understood what you have read through your ability to summarise and combine arguments from the literature using your own words.
What is paraphrasing?
Paraphrasing is changing the writing of another author into your words while retaining the original meaning. You must acknowledge the original author as the source of the information in your citation. Follow the steps in this table to help you build your skills in paraphrasing (see Table 19.4 ).
Table 19.4 Paraphrasing techniques
| 1 | Make sure you understand what you are reading. Look up keywords to understand their meanings. |
| 2 | Record the details of the source so you will be able to cite it correctly in text and in your reference list. |
| 3 | Identify words that you can change to synonyms (but do not change the key/topic words). |
| 4 | Change the type of word in a sentence (for example change a noun to a verb or vice versa). |
| 5 | Eliminate unnecessary words or phrases from the original that you don’t need in your paraphrase. |
| 6 | Change the sentence structure (for example change a long sentence to several shorter ones or combine shorter sentences to form a longer sentence). |
Example of paraphrasing
Please note that these examples and in text citations are for instructional purposes only.
Original text
Health care professionals assist people often when they are at their most vulnerable . To provide the best care and understand their needs, workers must demonstrate good communication skills . They must develop patient trust and provide empathy to effectively work with patients who are experiencing a variety of situations including those who may be suffering from trauma or violence, physical or mental illness or substance abuse (French & Saunders, 2018).
Poor quality paraphrase example
This is a poor example of paraphrasing. Some synonyms have been used and the order of a few words changed within the sentences however the colours of the sentences indicate that the paragraph follows the same structure as the original text.
Health care sector workers are often responsible for vulnerable patients. To understand patients and deliver good service , they need to be excellent communicators . They must establish patient rapport and show empathy if they are to successfully care for patients from a variety of backgrounds and with different medical, psychological and social needs (French & Saunders, 2018).
A good quality paraphrase example
This example demonstrates a better quality paraphrase. The author has demonstrated more understanding of the overall concept in the text by using the keywords as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up to see how much the structure has changed from the original text.
Empathetic communication is a vital skill for health care workers. Professionals in these fields are often responsible for patients with complex medical, psychological and social needs. Empathetic communication assists in building rapport and gaining the necessary trust to assist these vulnerable patients by providing appropriate supportive care (French & Saunders, 2018).
The good quality paraphrase example demonstrates understanding of the overall concept in the text by using key words as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up, which indicates how much the structure has changed from the original text.
What is synthesising?
Synthesising means to bring together more than one source of information to strengthen your argument. Once you have learnt how to paraphrase the ideas of one source at a time, you can consider adding additional sources to support your argument. Synthesis demonstrates your understanding and ability to show connections between multiple pieces of evidence to support your ideas and is a more advanced academic thinking and writing skill.
Follow the steps in this table to improve your synthesis techniques (see Table 19.5 ).
Table 19.5 Synthesising techniques
| 1 | Check your referencing guide to learn how to correctly reference more than one author at a time in your paper. |
| 2 | While taking notes for your research, try organising your notes into themes. This way you can keep similar ideas from different authors together. |
| 3 | Identify similar language and tone used by authors so that you can group similar ideas together. |
| 4 | Synthesis can not only be about grouping ideas together that are similar, but also those that are different. See how you can contrast authors in your writing to also strengthen your argument. |
Example of synthesis
There is a relationship between academic procrastination and mental health outcomes. Procrastination has been found to have a negative effect on students’ well-being (Balkis, & Duru, 2016). Yerdelen, McCaffrey, and Klassens’ (2016) research results suggested that there was a positive association between procrastination and anxiety. This was corroborated by Custer’s (2018) findings which indicated that students with higher levels of procrastination also reported greater levels of the anxiety. Therefore, it could be argued that procrastination is an ineffective learning strategy that leads to increased levels of distress.
Topic sentence | Statements using paraphrased evidence | Critical thinking (student voice) | Concluding statement – linking to topic sentence
This example demonstrates a simple synthesis. The author has developed a paragraph with one central theme and included explanatory sentences complete with in-text citations from multiple sources. Note how the blocks of colour have been used to illustrate the paragraph structure and synthesis (i.e., statements using paraphrased evidence from several sources). A more complex synthesis may include more than one citation per sentence.
Creating an argument
What does this mean.
Throughout your university studies, you may be asked to ‘argue’ a particular point or position in your writing. You may already be familiar with the idea of an argument, which in general terms means to have a disagreement with someone. Similarly, in academic writing, if you are asked to create an argument, this means you are asked to have a position on a particular topic, and then justify your position using evidence.
What skills do you need to create an argument?
In order to create a good and effective argument, you need to be able to:
- Read critically to find evidence
- Plan your argument
- Think and write critically throughout your paper to enhance your argument
For tips on how to read and write critically, refer to the chapter Thinking for more information. A formula for developing a strong argument is presented below.
A formula for a good argument
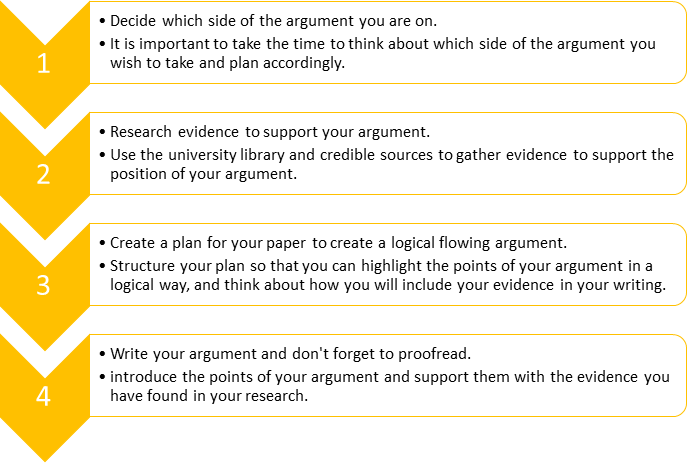
What does an argument look like?
As can be seen from the figure above, including evidence is a key element of a good argument. While this may seem like a straightforward task, it can be difficult to think of wording to express your argument. The table below provides examples of how you can illustrate your argument in academic writing (see Table 19.6 ).
Table 19.6 Argument
| Introducing your argument | • This paper will argue/claim that... • ...is an important factor/concept/idea/ to consider because... • … will be argued/outlined in this paper. |
| Introducing evidence for your argument | • Smith (2014) outlines that.... • This evidence demonstrates that... • According to Smith (2014)… • For example, evidence/research provided by Smith (2014) indicates that... |
| Giving the reason why your point/evidence is important | • Therefore this indicates... • This evidence clearly demonstrates.... • This is important/significant because... • This data highlights... |
| Concluding a point | • Overall, it is clear that... • Therefore, … are reasons which should be considered because... • Consequently, this leads to.... • The research presented therefore indicates... |
Editing and proofreading (reviewing)
Once you have finished writing your first draft it is recommended that you spend time revising your work. Proofreading and editing are two different stages of the revision process.
- Editing considers the overall focus or bigger picture of the assignment
- Proofreading considers the finer details
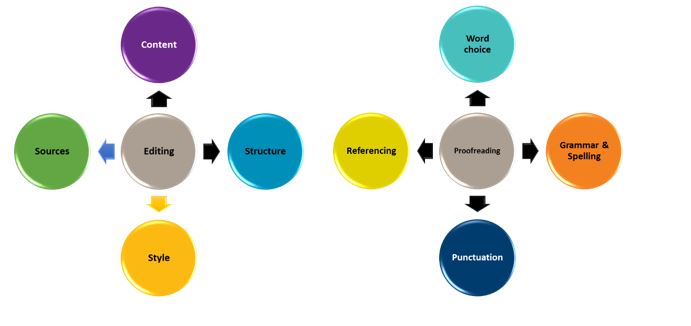
As can be seen in the figure above there are four main areas that you should review during the editing phase of the revision process. The main things to consider when editing include content, structure, style, and sources. It is important to check that all the content relates to the assignment task, the structure is appropriate for the purposes of the assignment, the writing is academic in style, and that sources have been adequately acknowledged. Use the checklist below when editing your work.
Editing checklist
- Have I answered the question accurately?
- Do I have enough credible, scholarly supporting evidence?
- Is my writing tone objective and formal enough or have I used emotive and informal language?
- Have I written in the third person not the first person?
- Do I have appropriate in-text citations for all my information?
- Have I included the full details for all my in-text citations in my reference list?
There are also several key things to look out for during the proofreading phase of the revision process. In this stage it is important to check your work for word choice, grammar and spelling, punctuation and referencing errors. It can be easy to mis-type words like ‘from’ and ‘form’ or mix up words like ‘trail’ and ‘trial’ when writing about research, apply American rather than Australian spelling, include unnecessary commas or incorrectly format your references list. The checklist below is a useful guide that you can use when proofreading your work.
Proofreading checklist
- Is my spelling and grammar accurate?
- Are they complete?
- Do they all make sense?
- Do they only contain only one idea?
- Do the different elements (subject, verb, nouns, pronouns) within my sentences agree?
- Are my sentences too long and complicated?
- Do they contain only one idea per sentence?
- Is my writing concise? Take out words that do not add meaning to your sentences.
- Have I used appropriate discipline specific language but avoided words I don’t know or understand that could possibly be out of context?
- Have I avoided discriminatory language and colloquial expressions (slang)?
- Is my referencing formatted correctly according to my assignment guidelines? (for more information on referencing refer to the Managing Assessment feedback section).
This chapter has examined the experience of writing assignments. It began by focusing on how to read and break down an assignment question, then highlighted the key components of essays. Next, it examined some techniques for paraphrasing and summarising, and how to build an argument. It concluded with a discussion on planning and structuring your assignment and giving it that essential polish with editing and proof-reading. Combining these skills and practising them, can greatly improve your success with this very common form of assessment.
- Academic writing requires clear and logical structure, critical thinking and the use of credible scholarly sources.
- A thesis statement is important as it tells the reader the position or argument you have adopted in your assignment. Not all assignments will require a thesis statement.
- Spending time analysing your task and planning your structure before you start to write your assignment is time well spent.
- Information you use in your assignment should come from credible scholarly sources such as textbooks and peer reviewed journals. This information needs to be paraphrased and referenced appropriately.
- Paraphrasing means putting something into your own words and synthesising means to bring together several ideas from sources.
- Creating an argument is a four step process and can be applied to all types of academic writing.
- Editing and proofreading are two separate processes.
Academic Skills Centre. (2013). Writing an introduction and conclusion . University of Canberra, accessed 13 August, 2013, http://www.canberra.edu.au/studyskills/writing/conclusions
Balkis, M., & Duru, E. (2016). Procrastination, self-regulation failure, academic life satisfaction, and affective well-being: underregulation or misregulation form. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 31 (3), 439-459.
Custer, N. (2018). Test anxiety and academic procrastination among prelicensure nursing students. Nursing education perspectives, 39 (3), 162-163.
Yerdelen, S., McCaffrey, A., & Klassen, R. M. (2016). Longitudinal examination of procrastination and anxiety, and their relation to self-efficacy for self-regulated learning: Latent growth curve modeling. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice, 16 (1).
Writing Assignments Copyright © 2021 by Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- The Open University
- Accessibility hub
- Guest user / Sign out
- Study with The Open University
My OpenLearn Profile
Personalise your OpenLearn profile, save your favourite content and get recognition for your learning
Essay and report writing skills

Course description
Course content, course reviews.
Writing reports and assignments can be a daunting prospect. Learn how to interpret questions and how to plan, structure and write your assignment or report. This free course, Essay and report writing skills, is designed to help you develop the skills you need to write effectively for academic purposes.
Course learning outcomes
After studying this course, you should be able to:
- understand what writing an assignment involves
- identify strengths and weaknesses
- understand the functions of essays and reports
- demonstrate writing skills.
First Published: 10/08/2012
Updated: 26/04/2019
Rate and Review
Rate this course, review this course.
Log into OpenLearn to leave reviews and join in the conversation.
Create an account to get more
Track your progress.
Review and track your learning through your OpenLearn Profile.
Statement of Participation
On completion of a course you will earn a Statement of Participation.
Access all course activities
Take course quizzes and access all learning.
Review the course
When you have finished a course leave a review and tell others what you think.
For further information, take a look at our frequently asked questions which may give you the support you need.
About this free course
Become an ou student, download this course, share this free course.
We use cookies to give you the best experience on our website. By continuing you agree with our cookie policy .
- Assignment Writer
Best Assignment Writers Are Here
Experts are online now
- Verified writers
- On-time delivery
- Safe & secure
Price per page : £0.00
Total price: £ 0 .00 £ 0 .00
Professional Assignment Writers Available for Every Student
Are you a student looking for an assignment writer to help you with your academic writing? Are you studying in the UK and looking for a British assignment writer who speaks English as a first language and understands how to UK educational system works?
If you answered yes to the above questions, then you are in the right place. UKWritings.com is the leading British assignment writing service, hiring only assignment writers UK (which means they are based in the UK and have academic qualifications from UK universities).
Liam reviewed UKWritings:
I’ve used online writing services before but I’ve never had one this good. The ordering process was really easy and as promised, the quote I was given was my full price. No added extras to release my assignment. It was written well by to assignment writers and all of the key points where covered and fully explained.
Rating: 5 /5
Tell the world about your experience with assignment writers, write your review to help others learn about UKWritings.com. Our service is rated 5 based on 464 votes.
Where to Find an Assignment Writer
You will find extensive information at UKWritings.com about each of our assignment writers, including their academic qualifications, their areas of expertise and their customer feedback score.
We don’t believe in hiding our writers away. They are the backbone of our services and we want you, the customer, to be able to see our writers and what they can do. We are proud of each online assignment writer we hire and we are happy for you to see them and ask them questions to ensure you choose the perfect writer for you and your assignment.
Why Is It So Difficult for Students to Write Assignments?
Academic style writing is hard. It is hard to get the assignment to flow well and be engaging to the reader whilst also ensuring you get all of the relevant information in there.
This is a skill which takes practice, and most students have enough things to do without having to sit writing practice assignments. Our writers write assignments all day long. They are expert academic writers who know the structure of a perfect assignment and can make even the most boring of topics come to life.
You Can Find Quality Help Here
UKWritings.com want all of our customers to be happy with their assignments. For this reason, we take great care to ensure we only hire the best custom assignment writer.
All of our assignments are high-quality papers that are written from scratch with no plagiarism and will never be resold. We only use reputable sources in our research and our customer feedback backs up our claims of being the best.
We have a high level of return customers, which we believe is the best way to show you the quality of our work – people wouldn’t return if the assignments we write weren’t good quality.
To see the quality of the writing for yourself, check out our sample essays (there are not customer essays – we would never display your essay as a sample essay).
Why Choose UKWritings.com?
If you’re looking for the best British assignment writer who can provide you with a high-quality assignment at a low price, you should choose UKWritings.com.
You might find cheaper services out there, but you won’t find a better balance of affordable prices and quality assignment writing.
Order Now with Our Simple Ordering System
To order an assignment from a top assignment writer, just fill out the simple order form. Make sure to fill out all of the required information boxes, and then you can choose to give us as much or as little extra information as you wish. Our writers are happy to incorporate your ideas and are equally happy to write you a winning paper without any guidance.
You can then browse through the UKWritings.com assignment writer page and choose the writer who you believe is the best match for your assignment. If you are unsure which of our writers is the best one for you, you can message them and ask them questions.
Or of course, you can skip this step and we will select the best assignment writer for your assignment based on their areas of expert knowledge and their academic qualifications.
You can, at any time, check your order’s progress by logging in to your dashboard and selecting the relevant assignment. You can also message your writer though this page to provide any additional information.
Finally, you need to approve your paper. Once it’s approved, all that’s left to do is download the paper and hand it in.
So basically, you can sit back and relax knowing you are on for the highest grade through UKWritings.com.

- Limitless Amendments
- Bibliography
- Plagiarism Report
Timely delivery is among our core guarantees. We offer:
- Urgent paper writing (3 hours+)
- Draft delivery upon your request
- Final paper delivery before your deadline
UKwritings guarantee the privacy of all the customers and never share their personal information with third parties. For more details read our Privacy Policy.
Dissertation, 5 days, Master's
UKWritings made my dissertation journey smooth. The assigned writer was an expert and their systematic approach ensured every aspect was handled meticulously. Communication was consistent and collaborative, resulting in a logically structured and ...
Case Study, 7 days, Undergraduate
My encounter with UKWritings has set a benchmark for excellence. Faced with a complex case study, I turned to them for assistance. The writer's expertise was evident, resulting in a well-analysed and insightful case study. The final piece not only...
Essay, 5 days, HNC/HND
Ukwritings.com nailed my assignment. They captured my thoughts and delivered before the deadline. The writer was attentive to every single detail. Highly recommend it!
Research paper, 6 days, Doctoral
UKWritings helped me complete a research paper on time and to a high standard. Their expert guidance and responsiveness to feedback made the process seamless. Thanks to their support, I achieved an excellent grade. Highly recommend!
Dissertation, 6 days, Master's
My experience has been nothing short of excellent. They exceeded all my expectations. The research was thorough and my advisor was pleased. UK Writings delivers great value for such a reasonable price.

- Peterborough

How to Write in University
Organized, clear, and analytical writing.
University-level writing should be organized, clear, and analytical. The following guides provide direction on different types of writing assignments and strategies for writing.
Planning your Assignment
- 10 Steps to Complete your Assignment
How to Approach Any Assignment
- How to Write Essays
- How to Write English Essays
- How to Write Lab Reports
- How to Write Annotated Bibliographies
- How to Write Research Proposals
- How to Write Academic Reviews
- How to Write Article Summaries
- How to Write a Policy Assignment
- How to Write Literature Reviews
- How to Write Business Reports
- How to Write Reflections
- How to Prepare and Deliver Oral Presentations
- How to Create Effective Powerpoint Slides
- How to Create a Poster Presentation
Developing an Argument
- Developing a Topic
- Developing a Thesis
- Outline Checklist
- Beyond the 5-Paragraph Essay: A Flexible Essay Model
Writing Introductions, Conclusions, and Body Paragraphs
- Successful Paragraphs
- Effectively Integrating Evidence
- Creating Coherence (or Flow)
- Writing an Introduction
- Writing a Conclusion
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Common Writing Assignments

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
These OWL resources will help you understand and complete specific types of writing assignments, such as annotated bibliographies, book reports, and research papers. This section also includes resources on writing academic proposals for conference presentations, journal articles, and books.
Understanding Writing Assignments
This resource describes some steps you can take to better understand the requirements of your writing assignments. This resource works for either in-class, teacher-led discussion or for personal use.
Argument Papers
This resource outlines the generally accepted structure for introductions, body paragraphs, and conclusions in an academic argument paper. Keep in mind that this resource contains guidelines and not strict rules about organization. Your structure needs to be flexible enough to meet the requirements of your purpose and audience.
Research Papers
This handout provides detailed information about how to write research papers including discussing research papers as a genre, choosing topics, and finding sources.
Exploratory Papers
This resource will help you with exploratory/inquiry essay assignments.
Annotated Bibliographies
This handout provides information about annotated bibliographies in MLA, APA, and CMS.
Book Report
This resource discusses book reports and how to write them.
Definitions
This handout provides suggestions and examples for writing definitions.
Essays for Exams
While most OWL resources recommend a longer writing process (start early, revise often, conduct thorough research, etc.), sometimes you just have to write quickly in test situations. However, these exam essays can be no less important pieces of writing than research papers because they can influence final grades for courses, and/or they can mean the difference between getting into an academic program (GED, SAT, GRE). To that end, this resource will help you prepare and write essays for exams.
Book Review
This resource discusses book reviews and how to write them.
Academic Proposals
This resource will help undergraduate, graduate, and professional scholars write proposals for academic conferences, articles, and books.
In this section
Subsections.
- MyU : For Students, Faculty, and Staff
Writing Across the Curriculum
Ask a question
- Research & Assessment
- Writing Plans
- WEC Liaisons
- Academic Units
- Engage with WEC
- Teaching Resources
- Teaching Consultations
- Faculty Writing Resources

- Designing Effective Writing Assignments
One of the best ways for students to determine what they know, think, and believe about a given subject is to write about it. To support students in their writing, it is important to provide them with a meaningful writing task, one that has an authentic purpose, clear guidelines, and engages students in their learning. In this section, you can read about key principles of assignment design, review examples of effective writing assignments, and use a checklist to guide your own designs. You can also consult with a Writing Across the Curriculum Program team member . We’re happy to think with you about your writing assignment, whether it is in the inkling stage or undergoing a few minor tweaks.
What makes an assignment effective?
A good deal of educational research points to the benefits of writing assignments that exhibit the following features:
Meaningful tasks. A task is given meaning by its relevance to and alignment with the learning aims in the course. What counts as meaningful in one course context might not be meaningful in another. As Eodice, Geller, and Lerner (2016) have shown, meaningful writing assignments do occur across all disciplines and they are typically ones that “offer students opportunities to engage with instructors, peers, and texts and are relevant to past experiences and passions as well as to future aspirations and identities.”
Maximized learning time. As Linda Suskie argues, effectiveness is determined by the “learning payoff,” not by size of the assignment. Will students learn four times as much on an assignment that takes 20 hours outside of class than one that takes 5? Longer research-based assignments and elaborate class activities (mock conferences, debates, poster sessions, etc.) can greatly maximize learning, but there must be an appropriate level of writing and learning time built into the task. Term papers are much more effective when students have time to draft and revise stages of the assignment, rather than turning in one final product at the end.

Logical sequencing. A writing task that includes discrete stages (research, drafting, review, revising, etc.) is more likely to be an effective learning experience than one that only specifies the final product. Furthermore, these stages are more effective when they are scaffolded so simpler tasks precede more complex tasks. For example, a well-sequenced 10-12 page essay assignment might involve discrete segments where students generate a central inquiry question, draft and workshop a thesis statement, produce a first draft of the essay, give and receive feedback on drafts, and submit a revision. Read more about sequencing assignments .
Clear criteria will help students connect an assignment’s relevance to larger scale course outcomes. The literature on assignment design strongly encourages instructors to make the grading criteria explicit to students before the assignment is collected and assessed. A grading scheme or rubric that is handed out along with the assignment can provide students with a clear understanding of the weighted expectations and, thus help them decide what to focus on in the assignment. It becomes a teaching tool, not just an assessment tool.
Forward-thinking activities more than backward-thinking activities. Forward-thinking activities and assignments ask students to apply their learning rather than simply repeat it. The orientation of many writing prompts is often backward, asking students to show they learned X, Y, and Z. As L. Dee Fink (2013) points out, forward-thinking assignments and activities look ahead to what students will be able to do in the future having learned about X, Y, and Z. Such assignments often utilize real-world and scenario-based problems, requiring students to apply their learning to a new situation. For Grant Wiggins (1998) , questions, problems, tests, and assignments that are forward-thinking often:
- Require judgment and innovation. Students have to use knowledge and skills to solve unstructured problems, not just plug in a routine.
- Ask students to do the subject. Beyond recitation and replication, these tasks require students to carry out explorations, inquiry, and work within specific disciplines.
- Replicate workplace and civic contexts. These tasks provide specific constraints, purposes, and audiences that students will face in work and societal contexts.
- Involve a repertoire of skills and abilities rather than the isolation of individual skills.
Feel free to use this assignment checklist , which draws on the principles and research described on this page.
- African American & African Studies
- Agronomy and Plant Genetics
- Animal Science
- Anthropology
- Applied Economics
- Art History
- Carlson School of Management
- Chemical Engineering and Materials Science
- Civil, Environmental, and Geo- Engineering
- College of Biological Sciences
- Communication Studies
- Computer Science & Engineering
- Construction Management
- Curriculum and Instruction
- Dental Hygiene
- Apparel Design
- Graphic Design
- Product Design
- Retail Merchandising
- Earth Sciences
- Electrical and Computer Engineering
- Environmental Sciences, Policy and Management
- Family Social Science
- Fisheries, Wildlife, and Conservation Biology
- Food Science and Nutrition
- Geography, Environment and Society
- German, Nordic, Slavic & Dutch
- Health Services Management
- Horticultural Science
- Hubbard School of Journalism and Mass Communication
- Industrial and Systems Engineering
- Information Technology Infrastructure
- Mathematics
- Mechanical Engineering
- Medical Laboratory Sciences
- Mortuary Science
- Organizational Leadership, Policy, and Development
- Political Science
- School of Architecture
- School of Kinesiology
- School of Public Health
- Spanish and Portuguese Studies
- Speech-Language-Hearing Sciences
- Theatre Arts & Dance
- Youth Studies
- New Enrollments for Departments and Programs
- Legacy Program for Continuing Units
- Writing in Your Course Context
- Syllabus Matters
- Mid-Semester Feedback Strategies
- Writing Assignment Checklist
- Scaffolding and Sequencing Writing Assignments
- Informal, Exploratory Writing Activities
- 5-Minute Revision Workshops
- Reflective Memos
- Conducting In-Class Writing Activities: Notes on Procedures
- Now what? Responding to Informal Writing
- Teaching Writing with Quantitative Data
- Commenting on Student Writing
- Supporting Multilingual Learners
- Teaching with Effective Models of Writing
- Peer Response Protocols and Procedures
- Using Reflective Writing to Deepen Student Learning
- Conferencing with Student Writers
- Designing Inclusive Writing Assigments
- Addressing a Range of Writing Abilities in Your Courses
- Effective Grading Strategies
- Designing and Using Rubrics
- Running a Grade-Norming Session
- Working with Teaching Assistants
- Managing the Paper Load
- Teaching Writing with Sources
- Preventing Plagiarism
- Grammar Matters
- What is ChatGPT and how does it work?
- Incorporating ChatGPT into Classes with Writing Assignments: Policies, Syllabus Statements, and Recommendations
- Restricting ChatGPT Use in Classes with Writing Assignments: Policies, Syllabus Statements, and Recommendations
- What do we mean by "writing"?
- How can I teach writing effectively in an online course?
- What are the attributes of a "writing-intensive" course at the University of Minnesota?
- How can I talk with students about the use of artificial intelligence tools in their writing?
- How can I support inclusive participation on team-based writing projects?
- How can I design and assess reflective writing assignments?
- How can I use prewritten comments to give timely and thorough feedback on student writing?
- How can I use online discussion forums to support and engage students?
- How can I use and integrate the university libraries and academic librarians to support writing in my courses?
- How can I support students during the writing process?
- How can I use writing to help students develop self-regulated learning habits?
- Submit your own question
- Short Course: Teaching with Writing Online
- Five-Day Faculty Seminar
- Past Summer Hunker Participants
- Resources for Scholarly Writers
- Consultation Request
- Faculty Writing Groups
- Further Writing Resources
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.
University Writing Program
Carly schnitzler and the new edition of textgened: continuing experiments.

We are thrilled to share that Carly Schnitzler has published a new edition of TextGenEd: Continuing Experiments .
In it, there are 15 open-access assignments that reinforce the humanity of writing, while experimenting with, challenging, and questioning LLMs (Large Language Models) as part of the writing process. Annette Vee and Schnitzler have an assignment in this edition , one that Schnitzler has taught in her Reintroduction to Writing courses multiple times, inspired by Vauhini Vara’s “Ghosts” essay.
Schnitzler and her co-editors hope this resource proves valuable for writing teachers across different career stages, institution types, and levels of familiarity with AI/LLMs. They encourage others to adopt and share these assignments widely, as they believe they offer significant utility.
APOL 988 Dissertation Writing in Applied Apologetics II
- Course Description
In this course, the doctoral candidate will compose the middle chapters of a dissertation based on the candidate’s research and organization of content.
For information regarding prerequisites for this course, please refer to the Academic Course Catalog .
Course Guide
View this course’s outcomes, policies, schedule, and more.*
*The information contained in our Course Guides is provided as a sample. Specific course curriculum and requirements for each course are provided by individual instructors each semester. Students should not use Course Guides to find and complete assignments, class prerequisites, or order books.
This course is the first course dedicated primarily to the writing of the dissertation for the PhD in Applied Apologetics. All assignments in this course are devoted to completing compelling drafts of both the introductory sections (introduction/statement of thesis/literature review) and first major portions of the body of the argument of the dissertation. Completion of this course should allow students to complete a major percentage of their dissertation project and prepare them for matriculation into the next phase of their dissertation writing.
Course Assignment
No details available.
After reading the Syllabus and Student Expectations , the student will complete the related checklist found in the Course Overview.
These assignments require the student to submit progressive portions of his/her dissertation for review and evaluation.
These assignments ask the student to interface with mentor feedback and interpret any necessary improvements/changes that need to be applied to his/her dissertation. Each assignment will be 4-6 pages in length.
This quiz seeks to evaluate the student’s readiness as he/she embarks on the dissertation writing process. This quiz will be open-book/open-notes, contain 4 true/false, short-answer questions, and will have a 15-minute time limit.
These quizzes verify that the student is having regular meaningful discussions with his/her dissertation mentor. Each quiz will be open-book/open-notes, contain 4 true/false, short-answer questions, and will have a 15-minute time limit.
These quizzes will evaluate what elements of the dissertation are being submitted at different intervals of the dissertation-writing process. Each quiz will be open-book/open-notes, contain 2 essay questions, and will have a 30-minute time limit.
This quiz evaluates the student’s readiness for an additional reader to be assigned to the dissertation project. This quiz will be open-book/open-notes, contain 5 true/false questions, and will have a 15-minute time limit.

Have questions about this course or a program?
Speak to one of our admissions specialists.
Inner Navigation
- Assignments
Have questions?

Are you ready to change your future?
Apply FREE This Week*
Request Information
*Some restrictions may occur for this promotion to apply. This promotion also excludes active faculty and staff, military, non-degree-seeking, DGIA, Continuing Education, WSB, and certificate students.
Request Information About a Program
Request info about liberty university online, choose a program level.
Choose a program level
Bachelor’s
Master’s
Certificate
Select a Field of Study
Select a field of study
Select a Program
Select a program
Next: Contact Info
Legal first name.
Enter legal first name
Legal Last Name
Enter legal last name
Enter an email address
Enter a phone number
Full Address
Enter an address
Apt., P.O. Box, or can’t find your address? Enter it manually instead .
Select a Country
Street Address
Enter Street Address
Enter State
ZIP/Postal Code
Enter Zip Code
Back to automated address search
Start my application now for FREE

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
5 tips on writing better university assignments
What Is Academic Writing? | Dos and Don'ts for Students
Academic Writing | Jeffrey R. Wilson
Understanding Assignments - UNC Writing Center
The Beginner's Guide to Writing an Essay | Steps & Examples
Harvard College Writing Center 2 Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt When you receive a paper assignment, your first step should be to read the assignment prompt carefully to make sure you understand what you are being asked to do. Sometimes your assignment will be open-ended ("write a paper about anything in the course that interests you").
Essay and dissertation writing skills
What Is Academic Writing?
Academic writing
Courses and assignments should be planned with this in mind. Three principles are paramount: 1. Name what you want and imagine students doing it. However free students are to range and explore in a paper, the general kind of paper you're inviting has common components, operations, and criteria of success, and you should make these explicit ...
7. Structure your argument. As you write the body of your assignment, make sure that each point you make has some supporting evidence. Use statistics or quotes you gathered during your reading to support your argument, or even as something to argue against. Expert tip: If you're using a lot of different sources, it's easy to forget to add ...
Strategies for Essay Writing | Harvard College Writing Center
hardest thinking, and feel the greatest sense of mastery and. growth, in their writing. Cour. es. and assignments should be planned with this in mi. d. Three principles are paramount:1. Name what you want and imagine students doing itHowever free students are to range and explore in a paper, the general kind of paper you're inviting has com.
Writing Assignments - Academic Success
Course description. Writing reports and assignments can be a daunting prospect. Learn how to interpret questions and how to plan, structure and write your assignment or report. This free course, Essay and report writing skills, is designed to help you develop the skills you need to write effectively for academic purposes.
Order Now with Our Simple Ordering System. To order an assignment from a top assignment writer, just fill out the simple order form. Make sure to fill out all of the required information boxes, and then you can choose to give us as much or as little extra information as you wish. Our writers are happy to incorporate your ideas and are equally ...
Put It in Writing: While you'll want to present your assignment orally in class, be sure to give your students a written copy, too, so they can refer to it as they work. Putting it down on paper may also help you clarify your own expectations about the assignment. Anticipate the Inevitable: You're enthusiastically explaining the limitless ...
Introduction to 'Planning and preparing to write assignments'. This handbook on preparing to write assignments is designed to help you develop your strategies for planning. Hopefully, it will help you to get the most out of your experience of writing at University and provide encouragement for managing this type of assessment.
Understanding Writing Assignments - Purdue OWL
Successful Paragraphs. Effectively Integrating Evidence. Creating Coherence (or Flow) Writing an Introduction. Writing a Conclusion. Organized, Clear, and Analytical Writing University-level writing should be organized, clear, and analytical. The following guides provide direction on different types of writing assignments and strategies for ...
Common Writing Assignments Introduction - Purdue OWL
As Eodice, Geller, and Lerner (2016) have shown, meaningful writing assignments do occur across all disciplines and they are typically ones that "offer students opportunities to engage with instructors, peers, and texts and are relevant to past experiences and passions as well as to future aspirations and identities.". Maximized learning time.
1. The Academic Papers UK: Best Assignment Service Overall. The Academic Papers UK started their journey of academic excellence in 2003. With over two decades of experience, a 4.7 Trustpilot ...
Psychology document from California Coast University, 1 page, GED 215 - PSYCHOLOGY OF ADJUSTMENT Course Revision Date: 02/2021 Writing Assignment 1 *NOTE TO THE READER* The writer of this essay did not fully capture the meaning of ambient stress and stressors. This essay is posted as an example of how it can be conf
Carly Schnitzler has published a new edition of TextGenEd: Continuing Experiments. In it, there are 15 open-access assignments that reinforce the humanity of writing, while experimenting with, challenging, and questioning LLMs (Large Language Models) as part of the writing process. Annette Vee and Schnitzler have an assignment in this edition, one that Schnitzler has taught...
This course is the first course dedicated primarily to the writing of the dissertation for the PhD in Applied Apologetics. All assignments in this course are devoted to completing compelling ...