EXPECTED VALUE WORD PROBLEMS WITH SOLUTIONS
Suppose the probability of an event occurring is p. If the trial is repeated n times, the expectation of the event, or the number of times we expect it to occur, is
Problem 1 :
In a particular region in Africa, the probability that it will rain on any one day is 0.177. On how many days of the year would you expect it to rain?
P(that it will rain) = 0.177
P(number of days of year would we expect rain)
= 365(0.177)
= 64.61
So, approximately 65 days.
Problem 2 :
(a) If 2 coins are tossed, what is the chance that they both fall heads?
(b) If the 2 coins are tossed 300 times, on how many occasions would you expect them to both fall heads
Possible outcomes = {HH, TT, HT, TH}
P(getting all heads) = 1/4
Expected value when coins are tossed 300 times
= 300(1/4)
= 75 times.
When 2 coins are tossed 300 times, we can expect 75 times all heads.
Problem 3 :
A certain type of drawing pin, when tossed 400 times, landed on its back 144 times.
a) Estimate the probability that it will land on its back if it is tossed once.
(b) If the drawing pin is tossed 72 times, how many “backs” would you expect?
(a) P(that it will land on its back) = 144/400
= 0.36
Estimated probability is is 0.36.
Expected value when it is tossed 72 times = 72(0.36)
= 25.92
So, we can expect back 26 times.
Problem 4 :
A bag contains 5 red and 3 blue discs. A disc is chosen at random and then replaced. This is repeated 200 times. How many times would you expect a red disc to be chosen?
Total number of discs = 5 red + 3 blue
P(Choosing red disc) = 5/8
Expected value of choosing red disc, when it is repeated 200 times.
= 200(5/8)
= 125 times
Problem 5 :
A die has the numbers
0, 1, 2, 2, 3 and 4 on its faces.
The die is rolled 600 times. How many times might we expect a result of :
c) 1, 2 or 3
d) not a 4?
Total possible outcomes = 6
(a) P(getting 0) = 1/6
Expected result of 0 when the die is tossed 600 times :
= 600(1/6)
= 100
(b) P(getting 2) = 2/6
Expected result of 2 when the die is tossed 600 times :
= 600(2/6)
= 200
c) P(Getting 1, 2 or 3) = 4/6
Expected result of 1, 2 or 3 when the die is tossed 600 times :
= 600(4/6)
= 400
c) P(not getting 4) = 5/6
Expected result of not getting 4 when the die is tossed 600 times :
= 600(5/6)
= 500
Problem 6 :
A charity fundraiser gets a licence to run the following gambling game:
A die is rolled and the returns to the player are given in the ‘pay table’ alongside. To play the game $4 is needed. A result of ‘6’ wins $10, so in fact you are ahead by $6 if you get a ‘6’ on the first roll.
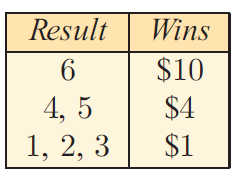
(a) What are your chances of playing one game and winning:
i) $10 ii) $4 iii) $1 ?
(b) Your expected return from throwing a 6 is 1/6 x $10. What is your expected return from throwing :
(i) a 4 or 5 (ii) a 1, 2 or 3 (iii) a 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6?
(c) What is your expected result at the end of one game? Remember to include the cost of playing the game.
(d) What is your expected result at the end of 100 games?
(a) (i) $10
To get $10, he has to get the result 6 on the die.
P(getting $10) = 1/6
(ii) P(getting $4) = 2/6 ==> 1/3
(iii) P(getting $1) = 3/6 ==> 1/2
(b) (i) a 4 or 5 = (2/6) x 4 ==> $1.33
(ii) a 1, 2 or 3 = (1/2) x 1 ==> $0.5
(iii) a 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 = (1/6)(10) + (2/6) (4) + (3/6) (1)
= (10/6) + (8/6) + (3/6)
= (10+8+3)/6
= 21/6
= $3.5

Apart from the stuff given above, i f you need any other stuff in math, please use our google custom search here.
Kindly mail your feedback to [email protected]
We always appreciate your feedback.
© All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
- Sat Math Practice
- SAT Math Worksheets
- PEMDAS Rule
- BODMAS rule
- GEMDAS Order of Operations
- Math Calculators
- Transformations of Functions
- Order of rotational symmetry
- Lines of symmetry
- Compound Angles
- Quantitative Aptitude Tricks
- Trigonometric ratio table
- Word Problems
- Times Table Shortcuts
- 10th CBSE solution
- PSAT Math Preparation
- Privacy Policy
- Laws of Exponents

Recent Articles
Digital sat math problems and solutions (part - 15).
Sep 12, 24 08:16 AM
AP Calculus BC : Indeterminate Forms and L'Hopital's Rule
Sep 11, 24 07:32 PM
Derivative Problems and Solutions (Part - 3)
Sep 11, 24 06:33 PM

Section PC.3 – Expected Value Practice Problems
1. Determine whether each statement is true or false.
a. If the Expected Value of a game is zero, we say that it is a ‘fair game’. b. The probability of an event that is certain is 0. c. Expected Value is the actual gain or loss each time an event takes place. d. If P(A) is the probability that event A will occur, the probability event A will not occur is P(Ā) = 1 – P(A). e. Expected Value is the average gain or loss of an event if the procedure is repeated many times. f. The probability of an impossible event is −1. g. If the odds for an event are 3 to 5, then the odds against that event are 5 to 3.
2. Determine whether each statement is true or false.
a. If P(A) is the probability that event A will occur, the probability event A will not occur is P(Ā) = -P(A). b. Expected Value is the average gain or loss of an event if the procedure is repeated many times. c. The probability of an event that is certain is 1. d. If the Expected Value of a game is 1, we say that it is a ‘fair game’. e. Expected Value is the actual gain or loss each time an event takes place. f. If the odds for an event are 3 to 5, then the odds against that event are 5 to 3. g. The probability of an impossible event is 0.
3. A bag contains 3 gold marbles, 6 silver marbles, and 28 black marbles. Someone offers to play this game: You randomly select on marble from the bag. If it is gold, you win $3. If it is silver, you win $2. If it is black, you lose $1. What is your expected value if you play this game?
4. A bag contains 2 gold marbles, 10 silver marbles, and 25 black marbles. Someone offers to play this game: You randomly select one marble from the bag. If it is gold, you win $3. If it is silver, you win $2. If it is black, you lose $1. What is your expected value if you play this game?
5. A friend devises a game that is played by rolling a single six-sided die once. If you roll a 6, he pays you $3; if you roll a 5, he pays you nothing; if you roll a number less than 5, you pay him $1. Compute the expected value for this game. Should you play this game?
6. A company estimates that 0.7% of their products will fail after the original warranty period but within 2 years of the purchase, with a replacement cost of $350. If they offer a 2 year extended warranty for $48, what is the company’s expected value of each warranty sold?
7. A company estimates that 0.9% of their products will fail after the original warranty period but within 2 years of the purchase, with a replacement cost of $500. If they offer a 2 year extended warranty for $45, what is the company’s expected value of each warranty sold?
8. An insurance company estimates the probability of an earthquake in the next year to be 0.0013. The average damage done by an earthquake it estimates to be $60,000. If the company offers earthquake insurance for $100, what is their expected value of the policy?
9. A game is played using one die. If the die is rolled and shows 1, the player wins $1; if 2, the player wins $2; if 3, the player wins $3. If the die shows 4, 5, or 6, the player wins nothing. If there is a charge of $1.25 to play the game, what is the game’s expected value?
10. The PTO is selling raffle tickets to raise money for classroom supplies. A raffle ticket costs $2. There is 1 winning ticket out of the 290 tickets sold. The winner gets a prize worth $98. Round your answers to the nearest cent.
a. What is the expected value (to you) of one raffle ticket? b. Calculate the expected value (to you) if you purchase 6 raffle tickets. c. What is the expected value (to the PTO) of one raffle ticket? d. If the PTO sells all 290 raffle tickets, how much money can they expect to raise for the classroom supplies?
11. One of the games at a carnival is Spin the Pointer, which uses a spinner like the one picture below. A carnival ticket that cost $2.00 is required to play the game. For each $2.00 ticket, a player spins the pointer once and receives the amount of money indicated in the sector where the pointer lands on the wheel. The spinner has an equal probability of landing in each of the 8 sectors.
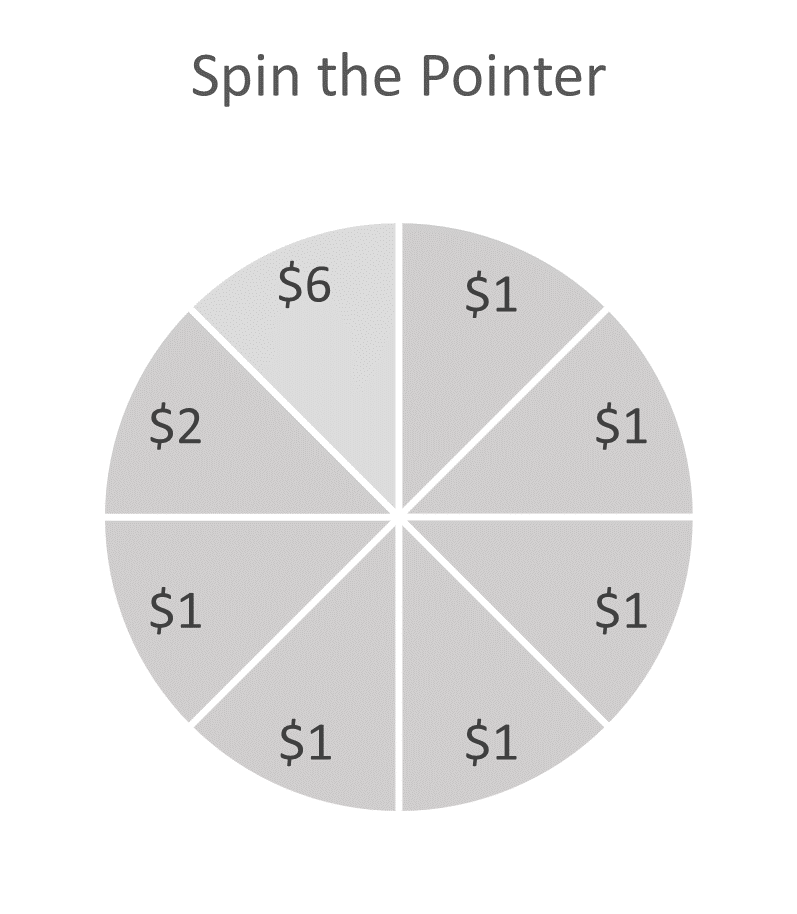
12. You are raising money for a local charity and plan on spending $1500 in upfront costs to host a tennis tournament. You expect to sell tickets worth $7000 the day of the tournament. However, if it rains on the day of the forecast tournament, you won’t sell any tickets and will lose all the money spent in upfront costs. If the weather for the tournament day is 35% chance of rain, what is your expected return? Is it a good idea to spend the money on upfront costs?
13. The table below give recent prizes and probabilities of winning (on a single $1 ticket) for a certain lottery. Find the expected value of the winnings for a single lottery ticket, given the following values. Is it a good idea to play this lottery?
| Prize | Probability |
| Win free ticket (worth $1) | [latex]\frac{1}{5}[/latex] |
| Win $5 | [latex]\frac{1}{100}[/latex] |
| Win $1000 | [latex]\frac{1}{100,000}[/latex] |
| Win $1,000,000 | [latex]\frac{1}{10,000,000}[/latex] |
14. A game is played using a standard 52-card deck. The player pays $3 to play and gets to pick one card at random from the deck. If the player picks an ace, they win $16. If they pick a face card, they win $8. If the player picks a numbered card, they win $3. What is the expected value of the game?
15. In a game of one-spot Keno, a card is purchased for $2. It allows a player to choose one number from 1 to 80. The dealer then chooses twenty numbers at random from 1 to 80. If the player’s number is among the numbers chosen by the dealer then the player is paid $3.90, but does not get to keep the $2 paid to play the game. Find the expected value of buying one card.
16. (Multiple Choice)
You are betting on a game in which each bet has an expected value of -$0.34. This means that:
a. You will win 34 cents every time you play. b. You will lose 34 cents every time you play. c. If you play the game many times, on average you will have won about 34 cents per game. d. If you play the game many times, on average you will have lost about 34 cents per game.
College Mathematics - MAT14X - 3rd Edition Copyright © by Adam Avilez; Shelley Ceinaturaga; and Terri D. Levine is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Probability Distribution
Videos and lessons to help High School students learn how to develop a probability distribution for a random variable defined for a sample space in which theoretical probabilities can be calculated; find the expected value. For example, find the theoretical probability distribution for the number of correct answers obtained by guessing on all five questions of a multiple-choice test where each question has four choices, and find the expected grade under various grading schemes.
Common Core: HSS-MD.A.3, HSS-MD.A.4

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
Math Worksheets Land
Math Worksheets For All Ages
- Math Topics
- Grade Levels
Expected Value Worksheets
When we are exploring the possible outcomes to an event through an experiment or data that we have collected common sense tells us of an anticipated result. To make it as simplistic as possible, consider flipping a penny. There are two possible outcomes. Putting the Chaos Theory to the side, we would anticipate a fifty percent result of landing on a heads or tails result. In statistics we would refer to that anticipated result as the expected value. This is the mean or weighted average of all the possible variables. It is also referred to as the probability distribution. The basic formula that you see is compilation of the product of the probability (P(x)) of the event multiplied by the number of time the event occurs (n): (P(x) n). As the situation gets more complex, so does the formula that you use. This topic will start by exploring the most basic form of this calculation and advance to more complex applications of this skill. This series of lessons and worksheets has students discover the best guess value of the probability-weighted average of all variables that are present in the problems.
Aligned Standard: HSS-MD.A.2
- Jake and the Roulette Wheel Step-by-step Lesson - See if you can figure out Jake's chance of success.
- Guided Lesson - Flipping a coin, the cultural show lottery, and the cost of picking chocolates.
- Guided Lesson Explanation - The probability distributions that are shown here are very commonly used on tests.
- Practice Worksheet - Sorry for the repetitive nature of these problems.
- Matching Worksheet - Match the random variables to the questions that created them.
- Answer Keys - These are for all the unlocked materials above.

Homework Sheets
These are fun. Who doesn't want to calculate their winnings?
- Homework 1 - Mike bets $2 on one of the numbers and wins $80 when the wheel lands on his number. If the wheel stops at another number, he would have lost his money.
- Homework 2 - See if you can gauge the value of one ticket.
- Homework 3 - Five thousand tickets are sold at $25 each for a charity raffle. Tickets are to be drawn at random and cash prizes are to be awarded as follows: 1 prize of $200, 4 prizes of $160, and 6 prizes of $90. What is the expected value of this raffle if you buy 1 ticket?
Practice Worksheets
When you actually run the numbers for some of these lottery questions, you wonder why people even buy lottery tickets.
- Practice 1 - An alphabet wheel has 26 equally likely spaced slots numbered A to Z. Sherry bets $2 on one of the numbers and wins $50. You earn $50 if it lands on your letter; otherwise you lose your bet. The random variable X assigns $50 to the wheel landing on letter chosen and -$2 to having the wheel land on any other letter. What is expected value of your winnings?
- Practice 2 - The random variable X assigns $ 100 to the wheel landing on number chosen and -$95 to having the wheel land on any other number. What is the expected value of your winnings?
Math Skill Quizzes
I went heavy on the spinning wheel question because you will see a lot of that on most exams.
- Quiz 1 - A hundred tickets are sold for a circus at the cost of $20 each. Some tickets have cash prizes as a part of promotional campaign. One prize of $500, three prizes of $ 250, and five prizes of $100. What is the expected value if you buy 1 ticket?
- Quiz 2 - An experiment consists of choosing 1 of 6 cookies labeled 1 through 6 in a packet at random. Let the random variable X be the cookie that turns up. What is the expected value of X?
How to Find the Expected Value?
Expected value is a term that we come across very frequently in our daily lives and even in mathematics. Expected value refers to the result you can expect from a particular action. Students must understand the expected value even in probability and statistics where it refers the mean value of the theoretical values that we get after repeating an experiment several times.
It is the measure of central tendency. In the case of normal probability distribution, the outcome plurality will be close to the expected value. The primary purpose of this value is to summarize all the information a variable hold. In case of discrete random variable, we can calculate the expected value by multiplying each outcome with its probability. The scaling of random variable effects the expected value.
The basic expected value formula is; P(x) × n. Here P(x) is the probability of an outcome and n is number of times an event or experiment is taking place. The formula for calculating expected value of binomial random variable is; P(x) × X Here P(x) is the probability of success and X is the number of trials.
In practice we simply see expected value as the value of probability multiplied by the value of each potential outcome. These measures are used in any situation where statistics can be used to better understand the situation. It is often a measure used on financial markets and in financial products. Games of chance are often centered around this measure as well.
Get Access to Answers, Tests, and Worksheets
Become a paid member and get:
- Answer keys to everything
- Unlimited access - All Grades
- 64,000 printable Common Core worksheets, quizzes, and tests
- Used by 1000s of teachers!
Worksheets By Email:
Get Our Free Email Now!
We send out a monthly email of all our new free worksheets. Just tell us your email above. We hate spam! We will never sell or rent your email.
Thanks and Don't Forget To Tell Your Friends!
I would appreciate everyone letting me know if you find any errors. I'm getting a little older these days and my eyes are going. Please contact me, to let me know. I'll fix it ASAP.
- Privacy Policy
- Other Education Resource
© MathWorksheetsLand.com, All Rights Reserved

Probability Practice Questions
Click here for questions, click here for answers, gcse revision cards.

5-a-day Workbooks

Primary Study Cards

Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Corbettmaths © 2012 – 2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The expected value of the game is given by 12 2 12 20 8 30 12 3 10* 12 4 2* 12 5 ( ) 4* = − + − = E X = + − You should expect to lose $16.67 after one-hundred games. 4. In this problem we want to determine the detective's fee so that the expected value is zero. Let y be the amount of his fee. Let X be the random variable that takes on ...
View Answer. The Ohio lottery has a game called Pick 4 where a player pays $4 and picks a four-digit number. If the four numbers come up in the order you picked, then you win $1,500. What is your expected value... View Answer. At a raffle, 1,500 tickets are sold at $2 each for four prizes of $500, $250, $150, and $75.
a) Estimate the probability that it will land on its back if it is tossed once. (b) If the drawing pin is tossed 72 times, how many "backs" would you expect? Solution : (a) P (that it will land on its back) = 144/400. = 0.36. Estimated probability is is 0.36. Expected value when it is tossed 72 times = 72 (0.36) = 25.92.
If you roll a die and get a 6, you get $10. However, if you get a 5 or below, you lose $1. Is this a game you'd want to play? Let's look at the expected value: The probability of winning is 1 6 1 6 and the probability of losing is 5 6 5 6, so the expected value is $ 10 × 1 6 + (− $ 1) × 5 6 = 5 6 ≈ $ 0.83 $ 10 × 1 6 + (− $ 1) × 5 ...
Find the expected value for the number of heads. An automobile insurance company has determined the probabilities for various claim amounts for drivers ages 16 through 21, shown in Table 11.10. Calculate the expected value and describe what this means in practical terms. You are a realtor considering listing a $500,000 house for 4 months.
The probability of landing on $100 is 4/9. The probability of landing on $300 is 2/9. The probability of landing on $400 is 2/9. The probability of landing on $800 is 1/9. ... Answers: 1. Since the expected value of the game is approximately $.42, it is to the player's advantage to play the game. 2. Señor Rick is not crazy since the expected ...
The probability of an event that is certain is 0. c. Expected Value is the actual gain or loss each time an event takes place. d. If P(A) is the probability that event A will occur, the probability event A will not occur is P(Ā) = 1 - P(A). e. Expected Value is the average gain or loss of an event if the procedure is repeated many times. f.
Probability and Expected Values. Examples, solutions, videos and lessons to help High School students learn how to weigh the possible outcomes of a decision by assigning probabilities to payoff values and finding expected values. A. Find the expected payoff for a game of chance. For example, find the expected winnings from a state lottery ...
If oil is hit, the revenue for the company will be $500,000. If natural gas is found, the revenue will be $150,000. If the probability of hitting oil is 3% and of hitting gas is 6%, find the expected value of sinking a test well. A $1 lottery ticket offers a grand prize of $10,000; 10 runner-up prizes each pay $1000; 100 third-place prizes each ...
MAT230: Homework on Expected Value 1 Homework on Expected Value Problem 1. What is the expected number of heads that come up when a fair coin is ipped 10 times? Problem 2. What is the expected number of times a 6 appears when a fair die is rolled 10 times? Problem 3. A coin is biased so that the probability a head comes up when it is ipped is 0.6.
Question: Finding Expected Value In Exercises 35-40, use the probability distribution or histogram to find the (a) mean, (b) variance, (c) standard deviation, and (d) expected value of the probability distribution, and (e) interpret the results. 35. Quiz Students in a class take a quiz with eight questions. The random variable x represents the ...
For example, find the theoretical probability distribution for the number of correct answers obtained by guessing on all five questions of a multiple-choice test where each question has four choices, and find the expected grade under various grading schemes. Common Core: HSS-MD.A.3, HSS-MD.A.4. Constructing probability distribution for random ...
Homework 2 - See if you can gauge the value of one ticket. Homework 3 - Five thousand tickets are sold at $25 each for a charity raffle. Tickets are to be drawn at random and cash prizes are to be awarded as follows: 1 prize of $200, 4 prizes of $160, and 6 prizes of $90. ... Students must understand the expected value even in probability and ...
Click here for Answers. Practice Questions. Previous: Direct and Inverse Proportion Practice Questions. Next: Reverse Percentages Practice Questions. The Corbettmaths Practice Questions on Probability.
Statistics and Probability; Statistics and Probability questions and answers; MAT 143 10.6 Expected Value Worksheet Please answer each question below regarding expected value. You must show all work to receive credit. Papers submitted with no work attached will earn agrade of 0 . This is an independent assignment and should be completed on your ...
Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy-to-learn solution you can count on. Question: 12. When doing an expected value problem, are the below probabilities a probability distribution that you can use for an expected value problem? Probabilities: 1/3, 1/3, 1/3, 1/4, 1/5 True or False? O True O False.
Finance questions and answers; Ch 5 - Expected ValueBelow is a chart that describes the probability of an investment return, with x being the return on your investment and P(x), the probability of that return on the investment.\table[[x,P(x)
Question: When measuring a contingency, IFRS requires the use of the probability-weighted expected value of the loss. ASPE requiresthe midpoint of the range of possible outcomes.the same calculation.the best estimate within the range of possible outcomes, if one exists; if not, the minimum of the range of possible outcomes,with the range disclosed.the minimum of the
Statistics and Probability; Statistics and Probability questions and answers; 2.4. Now consider the probability that UNC wins the game as a variable. If Kush thinks his bethas an expected value of zero, what must he think is the probability that UNC wins thenext game?