What is a Marketing Plan & How to Write One [+ Examples]
Published: August 07, 2024
One of my favorite ways to break through writer’s block, whether the assignment is a marketing plan or a short story, is simply reading more examples. (I also recommend taking a long walk; you’d be surprised.)

I can’t take you on a walk, but I can give you some examples, some inspiration, and some guidelines to get your creativity humming.
If you don’t know where to start, we’ve curated lists of marketing plans and marketing strategies to help you write a concrete plan that will produce results.
Let’s start by understanding the differences between the two.
Table of Contents

Marketing Strategy Examples
What is a marketing plan, marketing plan vs. business plan, how to write a marketing plan, types of marketing plans, marketing plan examples, marketing plan faqs, sample marketing plan.

Free Marketing Plan Template
Outline your company's marketing strategy in one simple, coherent plan.
- Pre-Sectioned Template
- Completely Customizable
- Example Prompts
- Professionally Designed
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
A marketing plan is a strategic road map that businesses use to organize, execute, and track their marketing strategy over a given period. Marketing plans can include different marketing strategies for various marketing teams across the company, all working toward the same business goals.
The purpose of a marketing plan is to write down strategies in an organized manner. This will help keep you on track and measure the success of your campaigns.
Your marketing plan lays out each campaign‘s mission, buyer personas, budget, tactics, and deliverables. With all this information in one place, you’ll have an easier time staying on track with a campaign, and you can figure out what works and what doesn’t.
To learn more about creating your marketing plan, keep reading or jump to the relevant section:

A marketing plan is a strategic document that outlines marketing objectives, strategies, and tactics.
A business plan is also a strategic document. But this plan covers all aspects of a company's operations, including finance, operations, and more. It can also help your business decide how to distribute resources and make decisions as your business grows.
A marketing plan is a subset of a business plan; it shows how marketing strategies and objectives can support overall business goals. And if you need an assist executing a marketing plan, might I recommend HubSpot’s marketing hub ?
Marketing Strategy vs. Marketing Plan
A marketing strategy is the part of your marketing plan that describes how a business will accomplish a particular goal or mission.
This includes which campaigns, content, channels, and marketing software you’ll use to execute that mission and track its success.
A marketing plan contains one or more marketing strategies. It's the framework from which all your marketing strategies are created, and it helps you connect each strategy to a larger marketing operation and business goal.
For example, suppose your company is launching a new software product, and it wants customers to sign up. The marketing department needs to develop a marketing plan that'll help introduce this product to the industry and drive the desired sign-ups.
The department decides to launch a topical blog, debut a YouTube series to establish expertise, and create new X and Instagram accounts to join the conversation around this subject. All this serves to attract an audience and convert this audience into software users.
To summarize, a business' marketing plan is dedicated to introducing a new software product to the marketplace and driving sign-ups for that product. The business will execute that plan with three marketing strategies : a new industry blog, a YouTube video series, and an X account.
Of course, the business might consider these three things as one giant marketing strategy, each with its own specific content strategies. How granular you want your marketing plan to get is up to you. Nonetheless, every marketing plan goes through a particular set of steps in its creation.
- State your business' mission.
- Determine the KPIs for this mission.
- Identify your buyer personas.
- Describe your content initiatives and strategies.
- Clearly define your plan's omissions.
- Define your marketing budget.
- Identify your competition.
- Outline your plan's contributors and their responsibilities.
1. State your business' mission.
Your first step in writing a marketing plan is to state your mission. Although this mission is specific to your marketing department, it should serve as your business' main mission statement.
In my experience, you want to be specific, but not too specific. You have plenty of space left in this marketing plan to elaborate on how you'll acquire new customers and accomplish this mission.
For those of you running startups or small businesses, HubSpot’s starter bundle is a great all-in-one solution — it can help you find and win customers, execute content marketing plans, and more.
If your business' mission is “to make booking travel a delightful experience,” your marketing mission might be “to attract an audience of travelers, educate them on the tourism industry, and convert them into users of our bookings platform.”
Need help building your mission statement? Download this guide for examples and templates and write the ideal mission statement.
2. Determine the KPIs for this mission.
Every good marketing plan describes how the department will track its mission‘s progress. To do so, you need to decide on your key performance indicators (KPIs) .
KPIs are individual metrics that measure the various elements of a marketing campaign. These units help you establish short-term goals within your mission and communicate your progress to business leaders.
Let's take our example of a marketing mission from the above step. If part of our mission is “to attract an audience of travelers,” we might track website visits using organic page views. In this case, “organic page views” is one KPI, and we can see our number of page views grow over time.
Also, make sure to check whether your current reporting software facilitates the KPIs you need. Some reporting tools can only measure a set of pre-defined metrics, which can cause massive headaches in particular marketing campaigns.
However, other tools, like HubSpot’s analytics software , can offer full flexibility over the KPIs you wish to track.
You can generate custom reports that reveal average website engagement rates, page visits, email, social media traffic, and more.
These KPIs will come into the conversation again in step 4.
3. Identify your buyer personas.
A buyer persona is a description of who you want to attract. This can include age, sex, location, family size, and job title.
Each buyer persona should directly reflect your business' current and potential customers. All business leaders must agree on your buyer personas.
4. Describe your content initiatives and strategies.
Here‘s where you’ll include the main points of your marketing and content strategy.
Because there‘s a laundry list of content types and channels available today, you must choose wisely and explain how you’ll use your content and channels in this section of your marketing plan.
When I write this section, I like to stipulate:
- What types of content I'll create. These might include blog posts, YouTube videos, infographics, and ebooks.
- How much I'll create. I typically describe content volume in daily, weekly, monthly, or even quarterly intervals. It all depends on my workflow and the short-term goals for my content.
- The goals (and KPIs) I'll use to track each type. KPIs can include organic traffic, social media traffic, email traffic, and referral traffic. Your goals should also include which pages you want to drive that traffic to, such as product pages, blog pages, or landing pages.
- The channels on which I'll distribute my content. Popular channels include Facebook, X, LinkedIn, YouTube, Pinterest, and Instagram.
- Any paid advertising that will take place on these channels.
5. Clearly define your plan's omissions.
A marketing plan explains the marketing team's focus. It also explains what the marketing team will not focus on.
If there are other aspects of your business that you aren‘t serving in this particular plan, include them in this section. These omissions help to justify your mission, buyer personas, KPIs, and content.
You can’t please everyone in a single marketing campaign, and if your team isn’t on the hook for something, you need to make it known.
In my experience, this section is particularly important for stakeholders to help them understand why certain decisions were made.
6. Define your marketing budget.
Whether it's freelance fees, sponsorships, or a new full-time marketing hire, use these costs to develop a marketing budget and outline each expense in this section of your marketing plan.
You can establish your marketing budget with these 8 free marketing budget templates .
7. Identify your competition.
Part of marketing is knowing your competition. Research the key players in your industry and consider profiling each one.
Keep in mind that not every competitor will pose the same challenges to your business. For example, while one competitor might rank highly on search engines for keywords that you’re also chasing, another competitor might have a heavy footprint on a social network where you plan to launch an account.
Easily track and analyze your competitors with this collection of 10 free competitive analysis templates .
8. Outline your plan's contributors and their responsibilities.
With your marketing plan fully fleshed out, it‘s time to explain who’s doing what.
I don’t like to delve too deeply into my employees’ day-to-day projects, but I know which teams and team leaders are in charge of specific content types, channels, KPIs, and more.
Now that you know why you need to build an effective marketing plan, it’s time to get to work.
Starting a plan from scratch can be overwhelming if you haven't done it before.
That’s why there are many helpful resources that can support your first steps. We’ll share some of the best guides and templates to help you build effective results-driven plans for your marketing strategies.
Ready to make your own marketing plan? Get started with this free template.
The kind of marketing plan you create will depend on your company, your industry, and your business goals. We compiled different samples to suit your needs:
1. Quarterly or Annual Marketing Plans

This marketing plan by Visit Oxnard, a convention and visitors bureau, is packed with information: target markets, key performance indicators, selling points, personas, marketing tactics by channel, and much more.
It also articulates the organization’s strategic plans for the upcoming fiscal year, especially as it grapples with the aftereffects of the pandemic.
Lastly, it has impeccable visual appeal, with color-coded sections and strong branding elements.
- It states clear and actionable goals for the coming year.
- It includes data and other research that shows how the team made its decisions.
- It outlines how the team will measure the plan’s success.
4. Safe Haven Family Shelter

This marketing plan by a nonprofit organization is an excellent example to follow if your plan will be presented to internal stakeholders at all levels of your organization.
It includes SMART marketing goals , deadlines, action steps, long-term objectives, target audiences, core marketing messages , and metrics.
The plan is detailed yet scannable. By the end of it, one can walk away with a strong understanding of the organization’s strategic direction for its upcoming marketing efforts.
- It confirms ongoing marketing strategies and objectives while introducing new initiatives.
- It uses colors, fonts, and formatting to emphasize key parts.
- It closes with long-term goals, key themes, and other overarching topics to set the stage for the future.
5. Wright County Economic Development

- “Going viral” isn’t a goal; it’s an outcome.
- Be surprising. Subvert expectations.
- Be weird and niche if you want to be weird and niche, but establishing a shared cultural understanding might result in a bigger audience.
Pridemore Properties’ Instagram smash hit is unexpected, to say the least. You think you’re getting a home tour that takes your figurative breath away; you get a home tour that takes the agent’s literal breath away.

Verizon’s toe-tapping, hip-shaking Totalmente (aka Total by Verizon, a contractless phone plan) ad debuted during Univision’s Spanish-language broadcast of Super Bowl LVIII. The ad reinvents the 1998 Elvis Crespo song “Suavemente,” an earworm if I’ve ever heard one, replacing the lyrics with Total by Verizon features.
Verizon Value’s CMO and VP of Marketing, Cheryl Gresham, has admitted that she didn’t know much about marketing to a majority-Latinx audience.
In an interview with Campaign Live , she said she didn’t think the idea would have gotten off the ground “if it had just been me and a lot of other people that had a background like myself in that room.”
CampaignLive wrote, “Gresham says the team opted for a creative concept that spoke to all the Latinos in the room — despite Gresham herself not understanding the connection.”
Gresham’s marketing strategy hinged on knowing her audience and, just as importantly, trusting her fellow marketers who knew how to reach that audience.
Strategic Takeaways for Demographic Marketing
- Know what you don’t know.
- Foster diversity in marketing leadership and staff.
- Know your audience.
The catchy tune and the great storytelling certainly don’t hurt.
But more than that, Ogilvy and Verizon dug deep into Latinx culture — more than 25 years deep — to craft an ad that doesn’t feel like it’s just responding to the latest trend. They also tapped Venezuelan American comedian, musician, and producer Fred Armisen to direct the spot.
6. Chappell Roan

The Ultimate Guide to Marketing Strategies & How to Improve Your Digital Presence
![marketing aspects of a business plan 5 Steps to Create an Outstanding Marketing Plan [Free Templates]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketingplan_20.webp)
5 Steps to Create an Outstanding Marketing Plan [Free Templates]
![marketing aspects of a business plan 4 Clever Olympics Marketing Campaigns [+Top Takeaways]](https://knowledge.hubspot.com/hubfs/best-olympic-marketing-campaigns-1-20240809-9542066.webp)
4 Clever Olympics Marketing Campaigns [+Top Takeaways]
![marketing aspects of a business plan 6 Steps to Create an Outstanding Marketing Plan [Free Templates]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketingplan_20.webp)
6 Steps to Create an Outstanding Marketing Plan [Free Templates]

50 Small Business Marketing Ideas for 2024

The 2024 State of Marketing & Trends Report: Data from 1400+ Global Marketers

Mastering Social Media for Nonprofit Promotion: Insights and New Data from Experts

The AIDA Model: A Proven Framework for Converting Strangers Into Customers

Demystifying Marketing's 6 Biggest Mixed Messages of 2024 with Jasper's Head of Enterprise Marketing

9 Pivotal Marketing Trends to Watch in 2024, According to Experts
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Marketing What is a Marketing Plan & How to Create One [with Examples]
What is a Marketing Plan & How to Create One [with Examples]
Written by: Sara McGuire Oct 26, 2023

A marketing plan is a blueprint that outlines your strategies to attract and convert your ideal customers as a part of your customer acquisition strategy . It’s a comprehensive document that details your:
- Target audience: Who you’re trying to reach
- Marketing goals: What you want to achieve
- Strategies and tactics: How you’ll reach your goals
- Budget: Resources you’ll allocate
- Metrics: How you’ll measure success
In this article, I’ll explain everything you need to know about creating a marketing plan . If you need a little extra help, there are professionally designed marketing plan templates that’ll make the process much easier. So, let’s ditch the confusion and get started!
Click to jump ahead:
What is a marketing plan?
How to write a marketing plan .
- Marketing plan v.s. business plan
- Types of marketing plans
9 marketing plan examples to inspire your growth strategy
Marketing plan faqs.
A marketing plan is a report that outlines your marketing strategy for your products or services, which could be applicable for the coming year, quarter or month.
Watch this quick, 13-minute video for more details on what a marketing plan is and how to make one yourself:
Typically, a marketing plan includes:
- An overview of your business’s marketing and advertising goals
- A description of your business’s current marketing position
- A timeline of when tasks within your strategy will be completed
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) you will be tracking
- A description of your business’s target market and customer needs
- A description of how you will measure the performance of the strategy
For example, this marketing plan template provides a high-level overview of the business and competitors before diving deep into specific goals, KPIs and tactics:

Learning how to write a marketing plan forces you to think through the important steps that lead to an effective marketing strategy . And a well-defined plan will help you stay focused on your high-level marketing goals.
With Venngage’s extensive catalog of marketing plan templates , creating your marketing plan isn’t going to be hard or tedious. In fact, Venngage has plenty of helpful communications and design resources for marketers. If you’re ready to get started, sign up for Venngage for Marketers now. It’s free to register and start designing.

Whether you’re a team trying to set smarter marketing goals, a consultant trying to set your client in the right direction, or a one-person team hustling it out, Venngage for Marketers helps you get things done.
As mentioned above, the scope of your marketing plan varies depending on its purpose or the type of organization it’s for.
For example, you could look for performance marketing agency to create a marketing plan that provides an overview of a company’s entire marketing strategy or simply focus on a specific channel like SEO, social media marketing, content marketing and more, like in this example:

A typical outline of a marketing plan includes:
- Executive summary
- Goals and objectives
- User personas
- Competitor analysis/SWOT analysis
- Baseline metrics
- Marketing strategy
- Tracking guidelines
Below you will see in details how to write each section as well as some examples of how you can design each section in a marketing plan.
Let’s look at how to create a successful marketing plan (click to jump ahead):
- Write a simple executive summary
- Set metric-driven marketing goals
- Outline your user personas
- Research all of your competitors
- Set accurate key baselines & metrics
- Create an actionable marketing strategy
- Set tracking or reporting guidelines
1. Write a simple executive summary
Starting your marketing plan off on the right foot is important. You want to pull people into your amazing plan for marketing domination. Not bore them to tears.

One of the best ways to get people excited to read your marketing plan is with a well-written executive summary. An executive summary introduces readers to your company goals, marketing triumphs, future plans, and other important contextual facts.

Basically, you can use the Executive Summary as a primer for the rest of your marketing plan.
Include things like:
- Simple marketing goals
- High-level metrics
- Important company milestones
- Facts about your brand
- Employee anecdotes
- Future goals & plans
Try to keep your executive summary rather brief and to the point. You aren’t writing a novel, so try to keep it under three to four paragraphs.
Take a look at the executive summary in the marketing plan example below:

The executive summary is only two paragraphs long — short but effective.
The executive summary tells readers about the company’s growth, and how they are about to overtake one of their competitors. But there’s no mention of specific metrics or figures. That will be highlighted in the next section of the marketing plan.
An effective executive summary should have enough information to pique the reader’s interest, but not bog them down with specifics yet. That’s what the rest of your marketing plan is for!
The executive summary also sets the tone for your marketing plan. Think about what tone will fit your brand ? Friendly and humorous? Professional and reliable? Inspiring and visionary?
2. Set metric-driven marketing goals
After you perfect your executive summary, it’s time to outline your marketing goals.
(If you’ve never set data-driven goals like this before, it would be worth reading this growth strategy guide ).
This is one of the most important parts of the entire marketing plan, so be sure to take your time and be as clear as possible. Moreover, optimizing your marketing funnel is key. Employing effective funnel software can simplify operations and provide valuable customer insights. It facilitates lead tracking, conversion rate analysis, and efficient marketing optimization .
As a rule of thumb, be as specific as possible. The folks over at VoyMedia advise that you should set goals that impact website traffic, conversions, and customer success — and to use real numbers. Complement your goals with website optimization tools (e.g., A/B testing speed with Nostra – check Nostra AI review to learn more) to further improve conversions.
Avoid outlining vague goals like:
- Get more Twitter followers
- Write more articles
- Create more YouTube videos (like educational or Explainer videos )
- Increase retention rate
- Decrease bounce rate
Instead, identify key performance metrics (KPI) you want to impact and the percentage you want to increase them by.
Take a look at the goals page in the marketing plan example below:

They not only identify a specific metric in each of their goals, but they also set a timeline for when they will be increased.
The same vague goals listed earlier become much clearer when specific numbers and timelines are applied to them:
- Get 100 new Twitter followers per month
- Write 5 more articles per week
- Create 10 YouTube videos each year
- Increase retention rate by 15% by 2020
- Decrease bounce rate by 5% by Q1
- Create an online course and get 1,000 new leads
- Focus more on local SEO strategies
- Conduct a monthly social media report to track progress
You can dive even deeper into your marketing goals if you want (generally, the more specific, the better). Here’s a marketing plan example that shows how to outline your growth goals:

3. Outline your user personas
Now, this may not seem like the most important part of your marketing plan, but I think it holds a ton of value.
Outlining your user personas is an important part of a marketing plan that should not be overlooked.
You should be asking not just how you can get the most visitors to your business, but how you can get the right visitors.
Who are your ideal customers? What are their goals? What are their biggest problems? How does your business solve customer problems?
Answering these questions will take lots of research, but it’s essential information to get.
Some ways to conduct user research are:
- Interviewing your users (either in person or on the phone)
- Conducting focus groups
- Researching other businesses in the same industry
- Surveying your audience
Then, you will need to compile your user data into a user persona guide.
Take a look at how detailed this user persona template is below:

Taking the time to identify specific demographic traits, habits and goals will make it easier for you to cater your marketing plan to them.
Here’s how you can create a user persona guide:
The first thing you should add is a profile picture or icon for each user persona. It can help to put a face to your personas, so they seem more real.
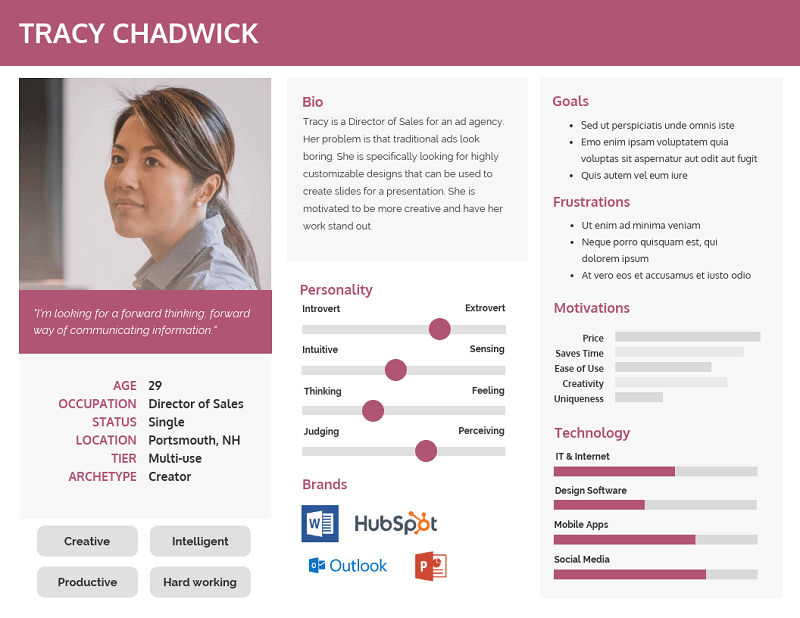
Next, list demographic information like:
- Identifiers
- Activities/Hobbies
The user persona example above uses sliding scales to identify personality traits like introversion vs. extroversion and thinking vs. feeling. Identifying what type of personality your target users tend to have an influence on the messaging you use in your marketing content.
Meanwhile, this user persona guide identifies specific challenges the user faces each day:

But if you don’t want to go into such precise detail, you can stick to basic information, like in this marketing plan example:

Most businesses will have a few different types of target users. That’s why it’s pertinent to identify and create several different user personas . That way, you can better segment your marketing campaigns and set separate goals, if necessary.
Here’s a marketing plan example with a segmented user persona guide:

The important thing is for your team or client to have a clear picture of who their target user is and how they can appeal to their specific problems.
Start creating robust user personas using Venngage’s user persona guide .
4. Conduct an extensive competitor analysis
Next, on the marketing plan checklist, we have the competitor research section. This section will help you identify who your competitors are, what they’re doing, and how you could carve yourself a place alongside them in your niche — and ideally, surpass them. It’s something you can learn to do with rank tracking software .
Competitor research is also incredibly important if you are starting a blog .
Typically, your competitor research should include:
- Who their marketing team is
- Who their leadership team is
- What their marketing strategy and strategic marketing plan are (this will probably revolve some reverse-engineering)
- What their sales strategy is (same deal)
- Social Media strategy (are they using discounting strategies such as coupon marketing to get conversions)
- Their market cap/financials
- Their yearly growth (you will probably need to use a marketing tool like Ahrefs to do this)
- The number of customers they have & their user personas
Also, take as deep a dive as you can into the strategies they use across their:
- Blog/Content marketing
- Social media marketing
- SEO Marketing
- Video marketing
- And any other marketing tactics they use
Research their strengths and weaknesses in all parts of their company, and you will find some great opportunities. Bookmark has a great guide to different marketing strategies for small businesses if you need some more information there.
You can use this simple SWOT analysis worksheet to quickly work through all parts of their strategy as well:

Click the template above to create a SWOT chart . Customize the template to your liking — no design know-how needed.
Since you have already done all the research beforehand, adding this information to your marketing plan shouldn’t be that hard.
In this marketing plan example, some high-level research is outlined for 3 competing brands:

But you could take a deeper dive into different facets of your competitors’ strategies. This marketing plan example analyses a competitor’s inbound marketing strategy :

It can also be helpful to divide your competitors into Primary and Secondary groups. For example, Apple’s primary competitor may be Dell for computers, but its secondary competitor could be a company that makes tablets.
Your most dangerous competitors may not even be in the same industry as you. Like the CEO of Netflix said, “Sleep is our competition.”
5. Set accurate key baselines & metrics
It’s pretty hard to plan for the future if you don’t know where your business stands right now.
Before we do anything at Venngage, we find the baselines so we can compare future results to something. We do it so much it’s almost like second nature now!
Setting baselines will allow you to more accurately track your progress. You will also be able to better analyze what worked and what didn’t work, so you can build a stronger strategy. It will definitely help them clearly understand your goals and strategy as well.
Here’s a marketing plan example where the baselines are visualized:

Another way to include baselines in your plan is with a simple chart, like in the marketing plan example below:

Because data can be intimidating to a lot of people, visualizing your data using charts and infographics will help demystify the information.
6. Create an actionable marketing strategy
After pulling all the contextual information and relevant metrics into your marketing plan, it’s time to break down your marketing strategy.
Once again, it’s easier to communicate your information to your team or clients using visuals .
Mind maps are an effective way to show how a strategy with many moving parts ties together. For example, this mind map shows how the four main components of a marketing strategy interact together:

You can also use a flow chart to map out your strategy by objectives:

However you choose to visualize your strategy, your team should know exactly what they need to do. This is not the time to keep your cards close to your chest.
Your strategy section may need to take up a few pages to explain, like in the marketing plan example below:

With all of this information, even someone from the development team will understand what the marketing team is working on.
This minimalistic marketing plan example uses color blocks to make the different parts of the strategy easy to scan:

Breaking your strategy down into tasks will make it easier to tackle.
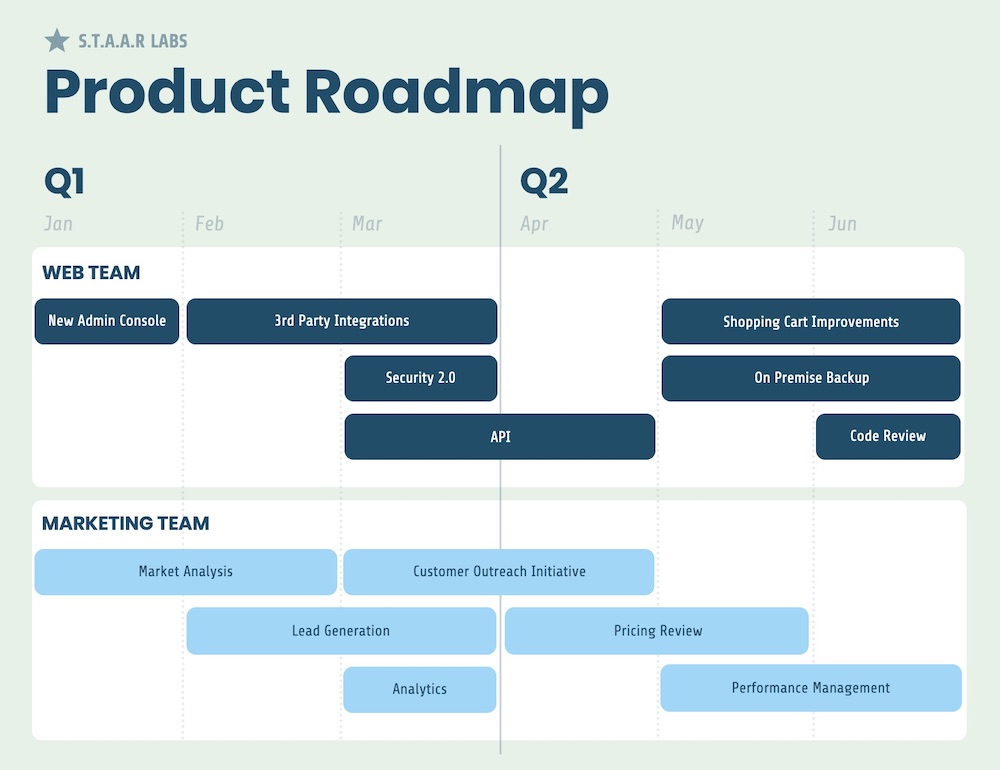
Another important way to visualize your marketing strategy is to create a project roadmap. A project roadmap visualizes the timeline of your product with individual tasks. Our roadmap maker can help you with this.
For example, this project roadmap shows how tasks on both the marketing and web design side run parallel to each other:
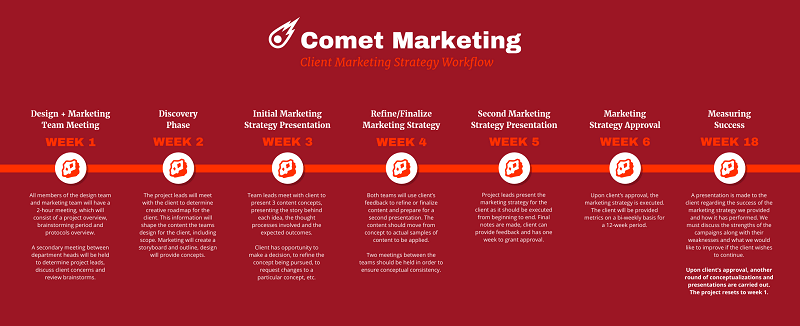
A simple timeline can also be used in your marketing plan:
Or a mind map, if you want to include a ton of information in a more organized way:

Even a simple “Next, Now, Later” chart can help visualize your strategy:

7. Set tracking or reporting guidelines
Close your marketing plan with a brief explanation of how you plan to track or measure your results. This will save you a lot of frustration down the line by standardizing how you track results across your team.
Like the other sections of your marketing plan, you can choose how in-depth you want to go. But there need to be some clear guidelines on how to measure the progress and results of your marketing plan.
At the bare minimum, your results tracking guidelines should specify:
- What you plan to track
- How you plan to track results
- How often you plan to measure
But you can more add tracking guidelines to your marketing plan if you see the need to. You may also want to include a template that your team or client can follow, for client reporting , ensure that the right metrics are being tracked.

The marketing plan example below dedicates a whole page to tracking criteria:

Use a task tracker to track tasks and marketing results, and a checklist maker to note down tasks, important life events, or tracking your daily life.
Similarly, the marketing plan example below talks about tracking content marketing instead:

Marketing plan vs. marketing strategy
Although often used interchangeably, the terms “marketing plan” and “marketing strategy” do have some differences.
Simply speaking, a marketing strategy presents what the business will do in order to reach a certain goal. A marketing plan outlines the specific daily, weekly, monthly or yearly activities that the marketing strategy calls for. As a business, you can create a marketing proposal for the marketing strategies defined in your company’s marketing plan. There are various marketing proposal examples that you can look at to help with this.
A company’s extended marketing strategy can be like this:
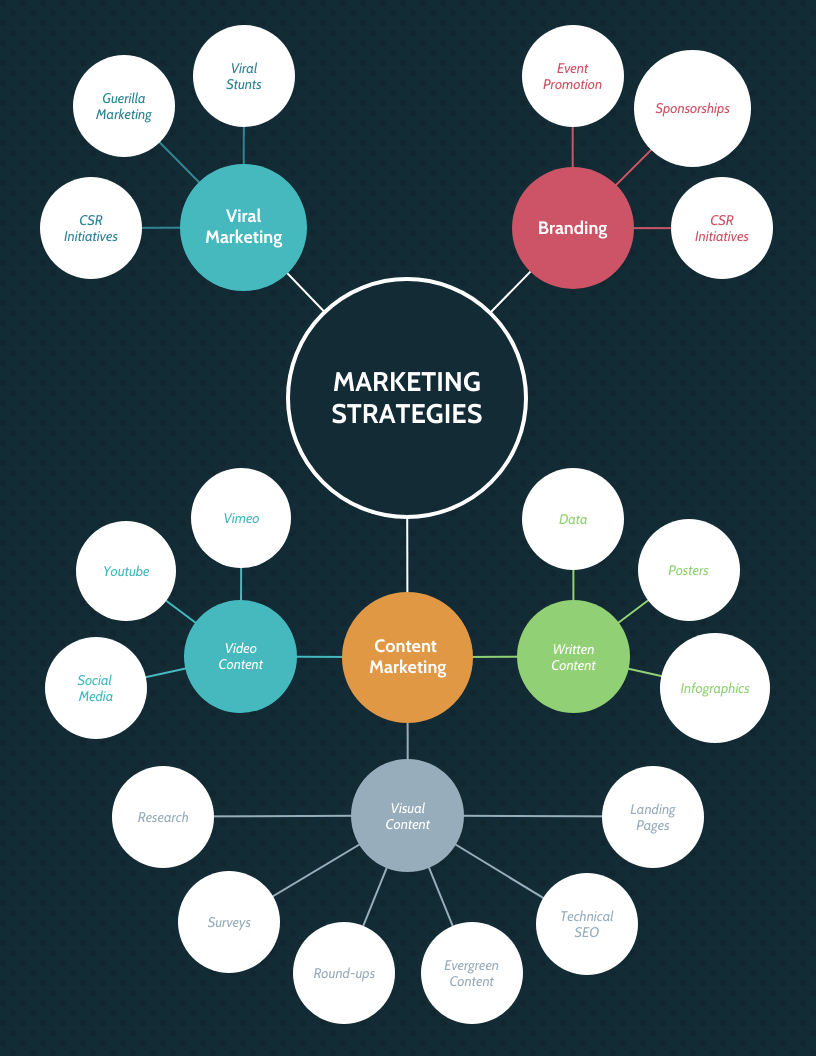
Notice how it’s more general and doesn’t include the actual activities required to complete each strategy or the timeframe those marketing activities will take place. That kind of information is included in a marketing plan, like this marketing plan template which talks about the content strategy in detail:

Marketing plan v.s business plan
While both marketing plans and business plans are crucial documents for businesses, they serve distinct purposes and have different scopes. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences:
Business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines all aspects of your business, including:
- Mission and vision
- Products or services
- Target market
- Competition
- Management team
- Financial projections
- Marketing strategy (including a marketing plan)
- Operations plan
Marketing plan on the other hand, dives deep into the specific strategies and tactics related to your marketing efforts. It expands on the marketing section of a business plan by detailing:
- Specific marketing goals (e.g., brand awareness, lead generation, sales)
- Target audience analysis (detailed understanding of their needs and behaviors)
- Product: Features, benefits, positioning
- Price: Pricing strategy, discounts
- Place: Distribution channels (online, offline)
- Promotion: Advertising, social media, content marketing, public relations
- Budget allocation for different marketing activities
- Metrics and measurement to track progress and success
In short, business plans paint the entire business picture, while marketing plans zoom in on the specific strategies used to reach your target audience and achieve marketing goals.
Types of marketing plans that can transform your business strategy
Let’s take a look at several types of marketing plans you can create, along with specific examples for each.
1. General marketing strategic plan / Annual marketing plan
This is a good example of a marketing plan that covers the overarching annual marketing strategy for a company:

Another good example would be this Starbucks marketing plan:

This one-page marketing plan example from coffee chain Starbucks has everything at a glance. The bold headers and subheadings make it easier to segment the sections so readers can focus on the area most relevant to them.
What we like about this example is how much it covers. From the ideal buyer persona to actional activities, as well as positioning and metrics, this marketing plan has it all.
Another marketing plan example that caught our eye is this one from Cengage. Although a bit text-heavy and traditional, it explains the various sections well. The clean layout makes this plan easy to read and absorb.

The last marketing plan example we would like to feature in this section is this one from Lush cosmetics.
It is a long one but it’s also very detailed. The plan outlines numerous areas, including the company mission, SWOT analysis , brand positioning, packaging, geographical criteria, and much more.

2. Content marketing plan
A content marketing plan highlights different strategies , campaigns or tactics you can use for your content to help your business reach its goals.
This one-page marketing plan example from Contently outlines a content strategy and workflow using simple colors and blocks. The bullet points detail more information but this plan can easily be understood at a glance, which makes it so effective.

For a more detailed content marketing plan example, take a look at this template which features an editorial calendar you can share with the whole team:

3. SEO marketing plan
Your SEO marketing plan highlights what you plan to do for your SEO marketing strategy . This could include tactics for website on-page optimization , off-page optimization using AI SEO , and link building using an SEO PowerSuite backlink API for quick backlink profile checks.
This SEO marketing plan example discusses in detail the target audience of the business and the SEO plan laid out in different stages:

4. Social media marketing plan
Your social media marketing plan presents what you’ll do to reach your marketing goal through social media. This could include tactics specific to each social media channel that you own, recommendations on developing a new channel, specific campaigns you want to run, and so on, like how B2B channels use Linkedin to generate leads with automation tools and expand their customer base; or like making use of Twitter walls that could display live Twitter feeds from Twitter in real-time on digital screens.
For B2C brands, you can target Facebook and Instagram. Gain Instagram likes to build trust for your brand’s profile and post engaging content on both platforms. Leverage AI social media tools to automate and scale your content plan..
Edit this social media marketing plan example easily with Venngage’s drag-and-drop editor:

5. Demand generation marketing plan
This could cover your paid marketing strategy (which can include search ads, paid social media ads, traditional advertisements, etc.), email marketing strategy and more. Here’s an example:

1. Free marketing plan template
Here’s a free nonprofit marketing plan example that is ideal for organizations with a comprehensive vision to share. It’s a simple plan that is incredibly effective. Not only does the plan outline the core values of the company, it also shares the ideal buyer persona.

Note how the branding is consistent throughout this example so there is no doubt which company is presenting this plan. The content plan is an added incentive for anyone viewing the document to go ahead and give the team the green light.
2. Pastel social media marketing campaign template
Two-page marketing plan samples aren’t very common, but this free template proves how effective they are. There’s a dedicated section for business goals as well as for project planning .
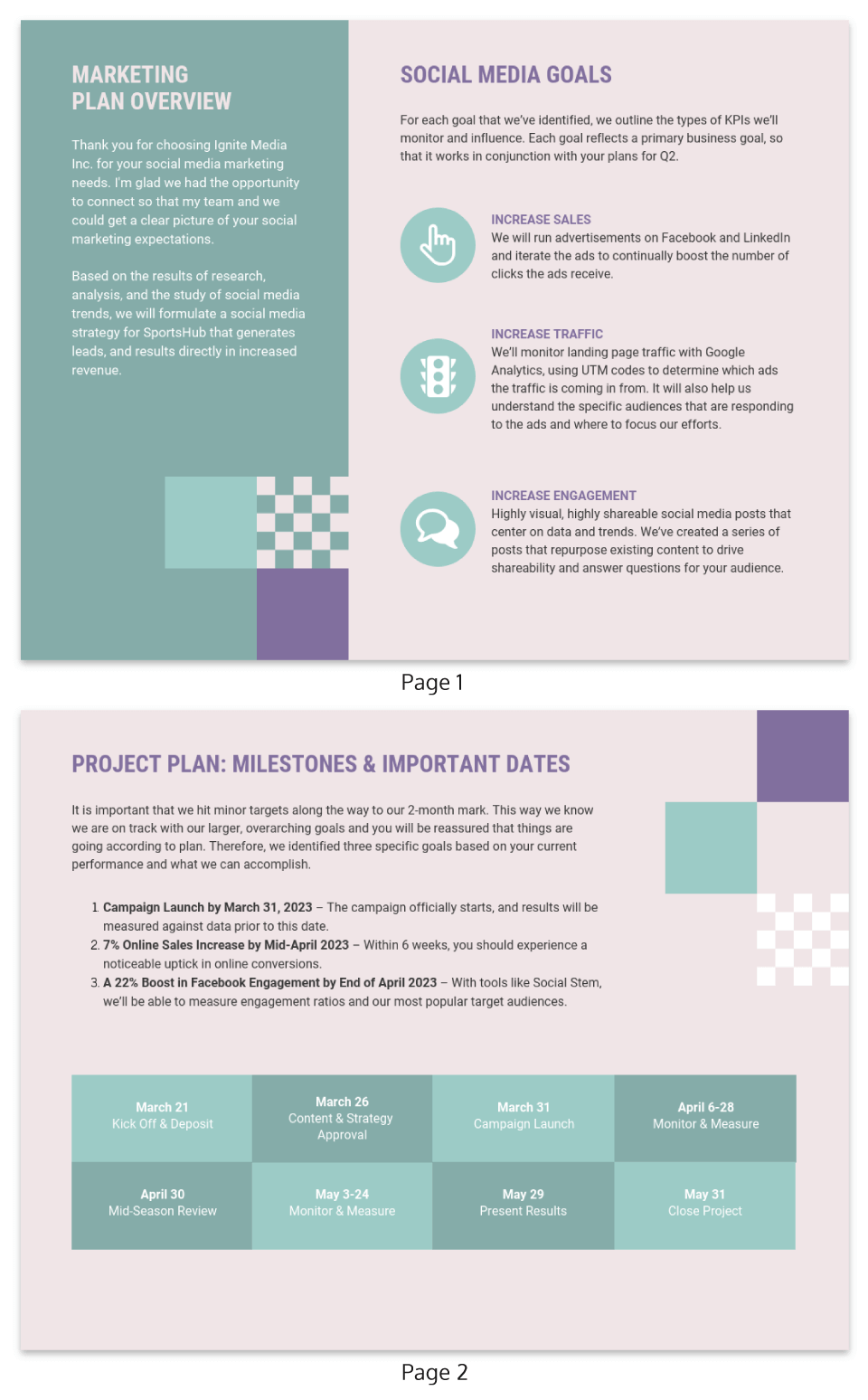
The milestones for the marketing campaign are clearly laid out, which is a great way to show how organized this business strategy is.
3. Small business marketing strategy template
This marketing plan template is perfect for small businesses who set out to develop an overarching marketing strategy for the whole year:
Notice how this aligns pretty well with the marketing plan outline we discussed in previous sections.
In terms of specific tactics for the company’s marketing strategy, the template only discusses SEO strategy, but you can certainly expand on that section to discuss any other strategies — such as link building , that you would like to build out a complete marketing plan for.
4. Orange simple marketing proposal template
Marketing plans, like the sample below, are a great way to highlight what your business strategy and the proposal you wan to put forward to win potential customers.

5. One-page marketing fact sheet template
This one-page marketing plan example is great for showcasing marketing efforts in a persuasive presentation or to print out for an in-person meeting.

Note how the fact sheet breaks down the marketing budget as well as the key metrics for the organization. You can win over clients and partners with a plan like this.
6. Light company business fact sheet template
This one-page sample marketing plan clearly outlines the marketing objectives for the organization. It’s a simple but effective way to share a large amount of information in a short amount of time.

What really works with this example is that includes a mission statement, key contact information alongside all the key metrics.
7. Marketing media press kit template
This press kit marketing plan template is bright and unmistakable as belonging to the Cloud Nine marketing agency . The way the brand colors are used also helps diversify the layouts for each page, making the plan easier to read.

We like the way the marketing department has outlined the important facts about the organization. The bold and large numbers draw the eye and look impressive.
8. Professional marketing proposal template
Start your marketing campaign on a promising note with this marketing plan template. It’s short, sharp and to the point. The table of contents sets out the agenda, and there’s a page for the company overview and mission statement.

9. Social media marketing proposal template
A complete marketing plan example, like the one below, not only breaks down the business goals to be achieved but a whole lot more. Note how the terms and conditions and payment schedule are included, which makes this one of the most comprehensive marketing plans on our list.

What should marketing plans include?
Marketing plans should include:
- A detailed analysis of the target market and customer segments.
- Clear and achievable marketing objectives and goals.
- Strategies and tactics for product promotion and distribution.
- Budget allocation for various marketing activities.
- Timelines and milestones for the implementation of marketing strategies.
- Evaluation metrics and methods for tracking the success of the marketing plan.
What is an executive summary in a marketing plan and what is its main goal?
An executive summary in a marketing plan is a brief overview of the entire document, summarizing the key points, goals, and strategies. Its main goal is to provide readers with a quick understanding of the plan’s purpose and to entice them to read further.
What are the results when a marketing plan is effective?
When a marketing plan is effective, businesses can experience increased brand visibility, higher customer engagement , improved sales and revenue, and strengthened customer loyalty.
What is the first section of a marketing plan?
The first section of a marketing plan is typically the “Executive Summary,” which provides a concise overview of the entire plan, including the business’s goals and the strategies to achieve them.
Now that you have the basics for designing your own marketing plan, it’s time to get started:
More marketing design guides and templates:
- Marketing Infographics: The Definitive Guide [Includes Infographic Templates]
- 20+ Business Pitch Deck Templates to Win New Clients and Investors
- 20+ White Paper Examples [Design Guide + White Paper Templates]
- The Evolution of Marketing [Timeline Infographic]
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
How to Write a Marketing Plan
By Joe Weller | March 28, 2024
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A marketing plan is a guide for achieving marketing initiatives on a set timeline. It includes analysis of a company's target audience, competitors, and market sector. Teams can build an organized strategy with that information to reach their goals.
Inside this article you’ll find a detailed, step-by-step guide to writing a marketing plan, with a free, downloadable marketing starter kit for beginners .
A marketing plan includes analysis of the target audience, the competitors, and the market so that teams can determine the best strategy for achieving their goals. The plan’s length and detail depend on the company's size and the scope of the marketing project. A marketing plan is useful for all types of marketing, including digital, social media, new product, small business, B2C, and B2B. Follow the steps below to write a comprehensive marketing plan.
1. Prepare for Success
Before you begin writing your marketing plan, set yourself up for success by conducting thorough market research and assembling a team with diverse skills in marketing strategy, content creation, digital marketing, and data analysis. Be sure to consult all your team members as you progress through these steps. It might also be helpful to assign leaders to complete different sections of the plan, depending on their areas of expertise. For example, you might assign the market analysis section to a team member with strong analytical skills and experience in data analysis.
2. Use a Marketing Plan Template
Download a free marketing plan template to ensure consistency and thoroughness in your final marketing plan.
For more template options, see this collection of free marketing plan templates and examples.
3. Identify Your Target Customers
To identify target customers for your marketing plan, collect information about their location, demographics (such as age, gender, and income), interests, values, and purchasing behaviors. This knowledge enables you to focus your marketing goals and tactics to meet their specific needs and preferences.
A customer persona is a fictional representation of your ideal customer that provides valuable insights for strategic decision-making. Use one of these customer persona templates to craft a detailed profile of your ideal customer.
4. Conduct a SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis is an important part of any marketing plan, because it helps identify a company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in relation to the market environment. To start, divide a page into four quadrants and label each as strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, brainstorm with your team to fill in each section. Be as honest and specific as possible, considering factors such as market trends, competition, and your own resources and capabilities. This information will allow the team to capitalize on strengths, prepare for challenges, and make sound strategic decisions throughout the marketing plan.
See this collection of marketing plan SWOT analysis templates for additional guidance.
5. Conduct a Market Analysis
A market analysis is an assessment of a market's size, growth, trends, customer segments, and competitor dynamics. Include it in your marketing plan to provide critical insights for strategic decision-making, helping to tailor products to customer needs, differentiate from competitors, and identify new opportunities.
To conduct a market analysis for your marketing plan, determine each of the following factors:
- Market Size: This is the total potential sales that a particular product or service can achieve within a defined market. Determine the market size by estimating the number of potential buyers for a particular service and multiplying that by the estimated number of purchases over a specific timeframe. (Number of Target Customers) x (Number of Purchases in a Given Time) = Market Size Imagine your company sells wireless headphones, and you estimate that the average consumer purchases a new pair every two years. If your market includes 1 million target customers, and assuming each customer buys one pair of headphones every two years, the calculation for annual market size would be as follows: (1 million target customers) x (0.5 purchases per year) = 500,000 pairs of wireless headphones per year
- Market Growth Rate: This measures the change in a market’s size over a specific time period and is typically expressed as a percentage. To determine the market growth rate, use the following formula: [(Current Market Size − Previous Market Size) ÷ Previous Market Size] × 100% = Growth Rate For example, if the market for wireless headphones was worth $1 billion last year and is worth $1.1 billion this year, the market growth rate would be as follows: [($1.1 Billion – $1 Billion) ÷ $1 Billion] x 100% = 10%
Market Share: This is the percentage of total sales in an industry generated by a particular company over a period of time. It provides a benchmark for assessing performance relative to competitors. Use this formula for calculating market share: (Company’s Revenue ÷ Total Industry Revenue) x 100% = Market Share
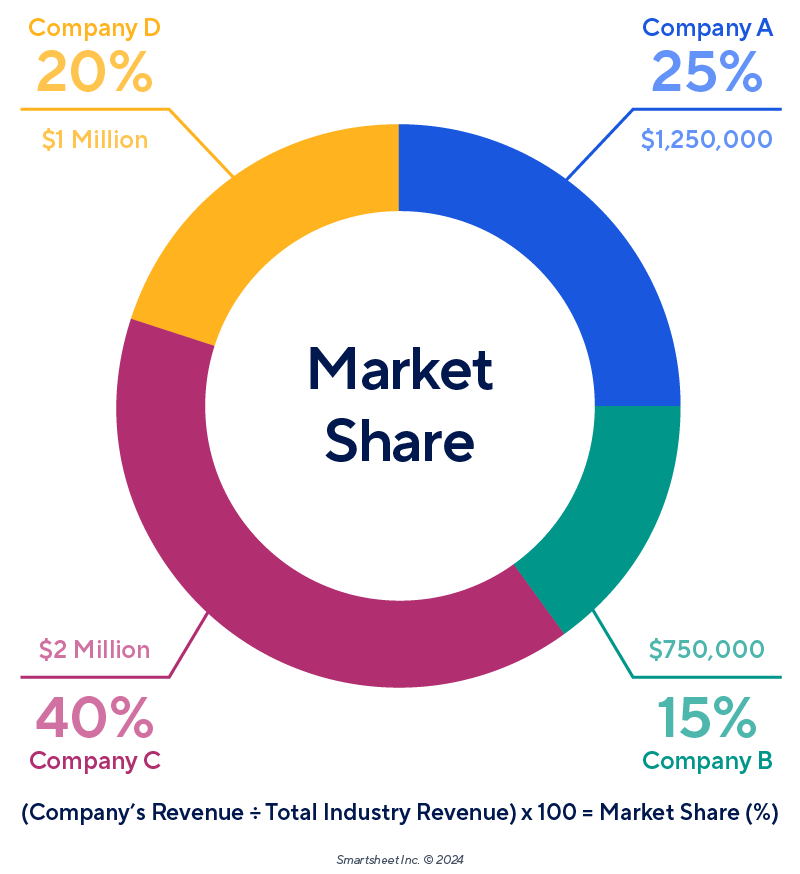
Tip: Keep in mind that the market size, share, and growth rate are all estimates. It’s impossible to be exact. To obtain the most accurate numbers, review the latest industry reports and seek insight from experts.
- Market Demand: This is the amount of a product or service a consumer is willing to purchase and how much they are willing to pay for it. To determine market demand in a market analysis, begin by conducting comprehensive research on consumer behavior, preferences, and purchasing patterns related to your product or service. Use tools such as surveys, SEO analytics, and interviews to gather data on potential customer interest and willingness to pay, and analyze competitor pricing and offerings.
- Market Trends: This is the growth or decline direction of a product or service’s price over a specific timeframe. To identify a market trend, monitor industry developments, consumer behavior, and technological advancements over time. Review industry reports and expert analyses to understand broader market movements and future projections. Summarize these observations and include them in your plan to highlight the direction in which the market is heading.
Market Segments: The broader market includes specific groups, categorized by shared characteristics. Generally, there are four types of market segments: geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavioral. In your marketing plan, detail how you'll target each segment by adapting your strategies to their unique characteristics. This targeted approach ensures more effective engagement with each segment.
- Competitor Analysis: A competitor analysis involves examining your competitors’ strengths, weaknesses, market positioning, product offerings, and marketing strategies. Describe how you'll conduct a comprehensive evaluation of key competitors by analyzing their market share, pricing, distribution channels, and promotional tactics. For more guidance, try downloading this competitor analysis template. Use it to identify areas where your rivals succeed and why. Their strengths indicate areas for improvement, while their weaknesses indicate opportunities.
6. List Your SMART Goals
Include SMART goals in your marketing plan to ensure that objectives are specific, measurable, actionable, relevant, and time-bound, providing a clear direction for strategic actions and performance evaluation. Start by identifying key performance areas that align with your overall business strategy. Then, for each goal, apply the SMART framework.
Here are two examples of SMART marketing goals:
- By Q4 end, increase search results page (SERP) position from 14th to the top three for keywords pertaining to our brand and lead to more organic traffic.
- Increase social media following, reach, and engagement by 25 percent in six months and 50 percent in one year.
Learn more about SMART goals and find a customizable SMART goals worksheet in this comprehensive guide to writing SMART goals .
7. Create a Marketing Strategy
A marketing strategy is the plan for achieving your SMART goals.

“A marketing plan should include strategic and tactical elements,” says Gayle Kalvert, Founder and CEO at Creo Collective , a full-service marketing agency. “From a strategic standpoint, it is critical that the marketing plan aligns to the overall goals of the organization. Tactically, what initiatives will the marketing team execute, and why? Tactics with no strategy lead to spotty results and poor-quality leads.”
Use one of these marketing strategy templates to get started. A successful marketing strategy will include the following elements:
7a. Customer Buying Cycle
The customer buying cycle is the path a potential customer follows from first having exposure to a product or service to becoming an advocate for it. Understanding this process allows marketers to effectively target communications and strategies at each stage in their marketing plan.
Pro Tip: “Consider your persona’s buyer's journey and ensure marketing has a role at each stage of the journey, especially after the close,” says Kalvert. “That is when customers can become advocates, sources of referral, and great subjects for marketing content for future buyers.”
7b. Unique Selling Proposition
A unique selling proposition (USP) is a specific benefit or advantage that sets your product or service apart from the competitors. By including a USP in a marketing plan, you help ensure that the team communicates why customers should choose your offering over others.
For example, Google’s USP is its powerful and accurate search algorithm that delivers relevant search results faster and more efficiently than its competitors.
7c. Branding
Branding is the development of a unique identity, image, and experience for a company. Marketers convey a brand through messaging, tone, logo, colors, and web design. The marketing strategy needs to align with the company’s brand in order to maintain consistency in messaging and experience, which ultimately builds customer trust.
7d. Marketing Mix A marketing mix refers to the set of actions that a company takes to promote its brand or product in the market, typically encapsulated by the four Ps: product, price, place, and promotion. Go through each of these steps when including the marketing mix in your strategy:
- Product: Describe the product and the problem it solves for your target customers. What makes your product or service different from the competition? Why is it special?
- Price: Explain how much your target customer is willing to pay for the product or service based on its real and perceived value. What do your competitors charge for a similar product? Will you run any seasonal promotions or discounts?
- Place: Describe where your product or service will be available for purchase by your target customers. Will you sell it online, through retail partners, or both? How will you manage logistics and supply chain to ensure your product is accessible to your target market?
- Promotion: Detail the strategies you will use to communicate your product’s value to consumers. This includes advertising, public relations, social media marketing, email campaigns, sales promotions, and direct marketing tactics.
7e. Channels
Identify the specific mediums and platforms — or channels — where you’ll share your message to your target audience. These should include distribution channels, communication channels, and engagement channels.
As you list them, explain how they will be used to effectively reach and engage with your target audience. For example, if you’re marketing a new fitness app, one distribution channel would be a direct download from the App Store to reach fitness enthusiasts directly on their smartphones. An engagement channel could be an in-app community feature for users where they can share progress.
Here is a brief list of popular marketing channels:
- Affiliate marketing
- Email marketing
- Social media
- Website marketing
7f. Tactics Tactics are the specific actions you will take to reach the goals outlined in your strategy. They cover everything from the creation and distribution of marketing materials to the scheduling of campaigns to the platforms used for advertising and engagement. Detail the specific actions and tools you will use to execute your marketing strategy, along with timelines, responsibilities, and budget allocations for each activity. This includes specifying the exact steps for product promotion, customer engagement, content creation, digital marketing efforts, and any other methods chosen to reach and convert your target audience. “Equally as important as using data is to build in time and resources to be flexible,” says Kalvert. “The marketing landscape is evolving at such a rapid pace. Tactics that worked last year may not work this year. Be open to experimenting with new tactics and adjusting your approach based on feedback and results.”
8. Determine the Budget
Start by estimating the costs associated with each tactic and channel outlined in your strategy, taking into account factors such as content creation, platform fees, and personnel costs. Next, prioritize spending based on the expected ROI for each tactic. Finally, document the budget in a clear, detailed format within your marketing plan, including an itemized list of costs for each tactic, total expenditure, and a contingency fund.
For more resources and help estimating marketing project costs, take a look at this collection of helpful free marketing plan budget templates .
9. Create a Calendar
Create a calendar to schedule and track deliverables. Include time for brainstorming, planning, executing, and analyzing results. List objectives, start dates, end dates, due dates, and responsible parties. Keep the calendar in a central location so that team members can easily access it.
10. List Marketing Tools and Technology
List any marketing tools or technologies your team will use to help achieve their goals. These can include email marketing software, blogging software, social media management software, or any other programs you plan to use.
11. Identify Metrics and KPIs
Identify the metrics for measuring and tracking your marketing goals. Metrics and KPIs eliminate ambiguity so that you can accurately measure progress. Select indicators that directly reflect the success of your marketing objectives, such as conversion rates, website traffic, lead generation, and customer acquisition costs.
12. Write an Executive Summary
Once you’ve completed all the sections in your marketing plan document, return to the first section to write the executive summary. Completing this section last ensures that you have a thorough understanding of all key elements before summarizing them.
Concisely highlight the main objectives, target market, and key strategies of the plan, providing a snapshot of the market analysis and expected outcomes. Outline the budget, resources required, and the metrics for measuring success. This section serves as a compelling overview, enticing stakeholders to delve into the plan.
For more detailed information on executive summaries, see this guide to writing an effective executive summary. You can also download a helpful template from this collection of free executive summary templates
Marketing Starter Kit for Beginners
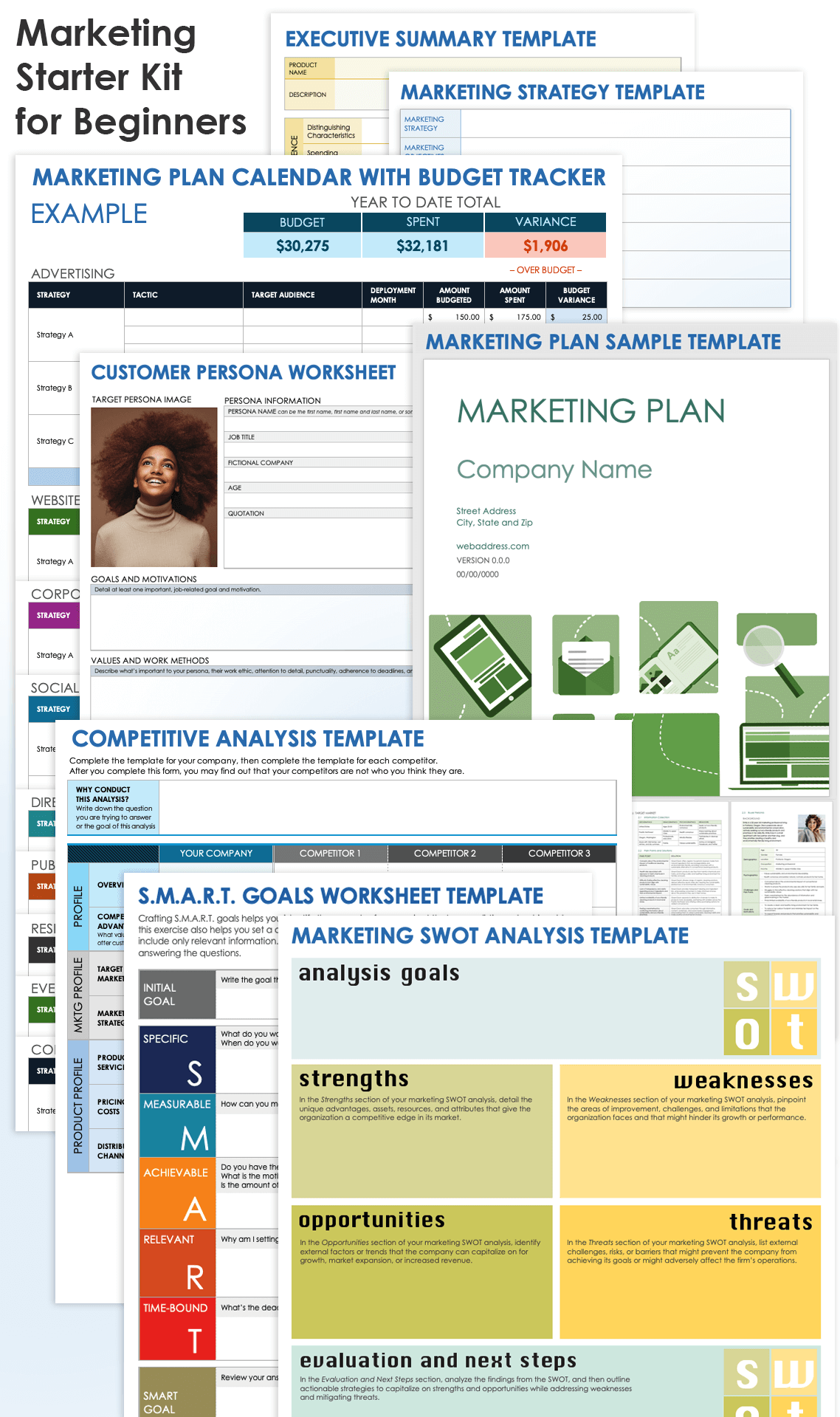
Download Marketing Starter Kit for Beginners
Get everything you need for creating a marketing plan with this free, downloadable marketing plan starter kit. The kit includes an executive summary template, a customer persona worksheet, a SWOT analysis template, a competitor analysis template, a SMART goals worksheet, a marketing strategy template, and a calendar template with a budget tracker, all in one easy-to-download file.
In this kit, you’ll find the following:
- An executive summary template for Microsoft Word to help you introduce the content of your marketing plan.
- A customer persona worksheet for Microsoft Word to collect information about your ideal customer.
- A SWOT analysis template for Microsoft Word to guide strategic decision-making based on the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- A competitor analysis template for Microsoft Word to help you compare and evaluate your competitors.
- A SMART goals worksheet for Microsoft Word to ensure each marketing objective follows SMART guidelines.
- A marketing strategy template for Microsoft Word to outline the plan for achieving your goals.
- A calendar template with budget tracker for Excel where you can organize, track, and manage marketing deliverables and their costs.
- A marketing plan template for Microsoft Word to ensure consistency and thoroughness in your final marketing plan.
Master Your Marketing Plan with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
The best marketing teams know the importance of effective campaign management, consistent creative operations, and powerful event logistics -- and Smartsheet helps you deliver on all three so you can be more effective and achieve more.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Improve your marketing efforts and deliver best-in-class campaigns.
- Start free trial
EXPAND YOUR REACH WITH SHOPIFY
Reach customers with email, SEO, targeted ads, and social media.

What Is a Marketing Plan and How To Write One (+ Template)
Learn the key elements of a marketing plan, access templates to get started, and get tips on how to write an effective plan.

No matter how much you stick to a plan, things go wrong. As the famous quote by US President Dwight D. Eisenhower goes: “Plans are useless, but planning is indispensable.”
When it comes to ecommerce, consumer trends shift, circumstances change, and initial experiments don’t always go as planned. All of these things impact your marketing plan.
Research shows that marketers who proactively write a marketing plan are 356% more likely to report success. So, what does a realistic ecommerce marketing plan look like? And how do you handle unexpected obstacles and overestimations that threaten your company’s marketing strategy? This guide shares the answers.
What is a marketing plan?
A marketing plan is the strategy a business uses to get its products or services in front of its target customer. It includes who the target market is, the channels used to reach them, and the messaging that will help the business sell its products.
The purpose of a marketing plan isn’t to create a step-by-step, never-fail manual. Rather, it’s a roadmap to help you accomplish the best-case scenario, while also maintaining realistic expectations for your marketing initiatives and establishing backup plans if something doesn’t work.
Marketing plan vs. business plan
A business plan paints a bigger picture of how you plan to run your business. It includes a mission statement, products you’ll launch, and market research. A marketing plan, on the other hand, is a specific document that details how you plan to achieve these wider goals through marketing .
Marketing plan vs marketing strategy
An overarching marketing strategy details how marketing will drive business results. A marketing plan is the route you’ll use to get there. It’s more specific than a strategy and includes a practical roadmap on how you’ll put your marketing activities into play.
Free marketing plan template to help you get started
Creating your own marketing plan is no small job. You put hours into customer and competitor research to find the channels likely to have the biggest impact on your marketing goals. You can check out marketing plan examples , but when it comes to creating your own, you can save time with a template.
Ditch the intimidating blank screen by building a marketing plan using Shopify’s free marketing plan template. Use it to guide your marketing strategy, tweaking the template to meet your business needs.
Download the template now
Types of marketing plans
Digital marketing plan.
A digital marketing plan is a specific type of marketing plan that revolves solely around online channels like social media, email, and search engines. It doesn’t include offline channels like billboards or radio ads.
Social media marketing plan
A social media marketing plan focuses specifically on how a business will use social media to reach its target market. It gives you a framework of which channels you’ll use, the types of content you’ll create, whether you’ll invest in social media ads, and how you’ll drive product sales. This can take place either through your online store or a social media storefront such as Facebook and Instagram Shops .
Content marketing plan
A content marketing plan details how you’ll produce content that turns people into paying customers. This can span multiple formats, including an email newsletter, infographics, product documentation, and user-generated content (such as social media posts).
Alongside the more traditional elements of a marketing plan, a content-marketing-specific strategy would include:
- Keywords you plan to target
- Who you’ll use to create the content (e.g., freelancers or in-house marketers)
- How you’ll promote and repurpose your content
Offline marketing plan
An offline marketing plan details how a business will reach its target market without using digital channels. This might include billboards, radio ads, direct mail, event sponsorships, and outdoor advertising.
How to write a marketing plan
Detail your unique value proposition, outline your buyer personas, run a swot analysis, detail product features and benefits, set key performance indicators, outline your marketing funnel.
- Define your marketing channels
Decide on your content formats
- Plan your marketing resources
Create a measurement and optimization plan
A unique value proposition underlines your entire marketing plan. Regardless of the channels and formats you plan to use, consistency is key. Mixed messages on what you sell and what your brand stands for will only confuse potential customers.
A simple way to refine your messaging is to focus on your unique selling point. Costco, for example, is cheaper than its competitors. Harper Wilde’s products are comfier than any other bra retailer. Find the marketing channels each retailer uses and you’ll see messaging centered around its adjective.
Consult your customers if you’re unsure what your value proposition adjective should be. Research is the biggest part of any copywriting process . Survey people who’ve already bought from you, run an Instagram poll to discover why people follow your brand, and see where your competitors’ weaknesses lie. Look for adjectives that crop up frequently during the process.
What overarching goal are you trying to accomplish with the business? Why does it exist? Summarize it in one sentence, and you’ll have a mission statement to inform everything you do, which includes your marketing strategies .
Going overboard with assumptions is a common mistake among marketers. The end result is a marketing plan that doesn’t actually result in revenue.
While data won’t give you a foolproof plan, every assumption is one more bit of uncertainty you’re folding into your marketing goals . If an amazing plan has a 40% chance of holding up to real-world scenarios, one without much rigor—and lots of assumptions—might hold up 10% of the time.
Consult your customer segments and buyer personas to get as much information as you can about the person buying your products, such as:
- Demographic data (location, age, and income level)
- Interests, goals, and challenges
- Channels they use to discover new products
Be careful not to confuse this with your target audience . Children would be the target audience of a toy brand; parents are the buyer persona. The latter is who you’ll be reaching out to with your marketing plan.
A SWOT analysis helps uncover your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats relative to your competitors. It’s useful to include one as part of your marketing plan because it can help anticipate problems you might encounter, make more data-driven decisions, and spot areas where you can get ahead of your competitors.
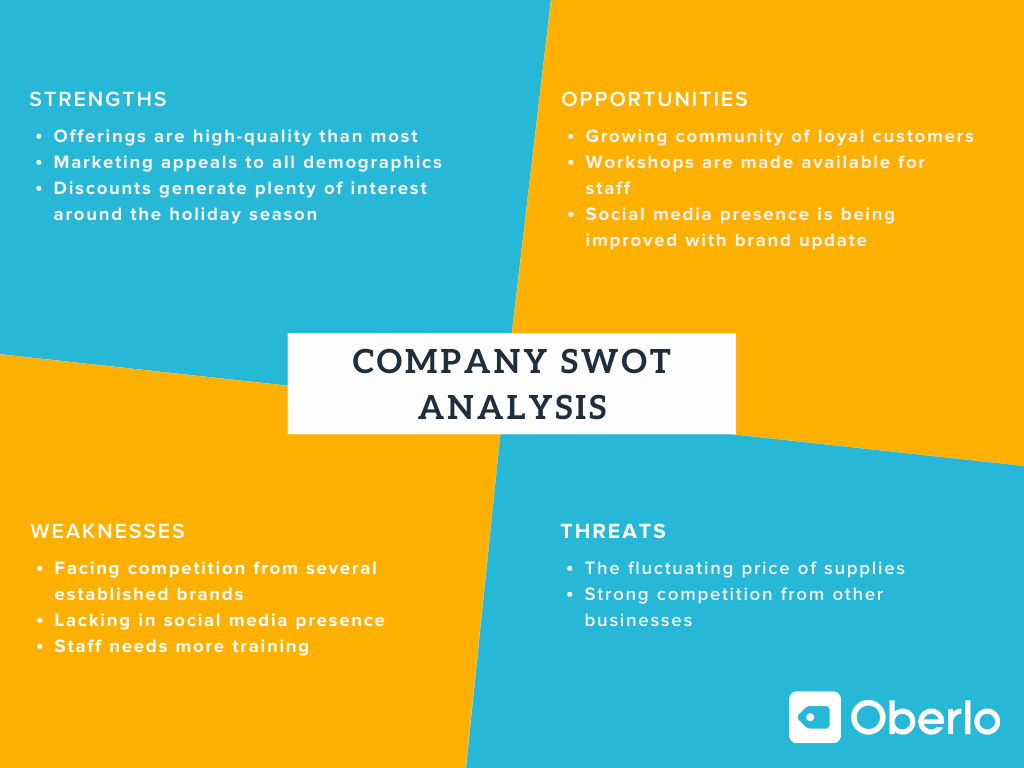
Dive deep into the data you already have about your customer base by investigating marketing analytics , social media audiences, and customer surveys . It reiterates who you’re trying to reach—and more importantly, the triggers that would make them buy your product over a competitor’s.
Remind yourself of your unique selling proposition (USP) throughout this process. Tailor your marketing plan around key takeaways from these.
Include any special features, competitive advantages, or customer favorites your marketing plan will lean on.
You could have the best mattress in the world—one made with 100 springs and cotton stitching, vigorously tested by sleep experts. But you’d struggle to market it if you lean too heavily on product features. A customer cares more about getting a peaceful night’s sleep than detailed product specifications.
“Every great marketing plan needs one thing first: a product that is 10 times better than the next,” says Nick Saltarelli, co-founder of Mid-Day Squares . “Once you have that, marketing is about deep human connections.”
Nick says, “It felt obvious that there was a sweet spot somewhere in between: people who wanted to follow along, and a true behind-the-scenes look into building a massive chocolate business from the ground up.”
As a result, the Mid-Day Squares marketing plan doesn’t prioritize product promotion. The brand instead “focuses on getting people to fall in love with us, the founders, to scale the human connection,” Nick says.
What are you trying to achieve with your marketing plan? Create both short- and long-term business goals that relate to financial metrics like revenue growth, retention , or new customers .
Most marketers measure success using return on investment (ROI) —the revenue you expect to generate after spending your marketing budget. It’s every marketer’s dream to get $100,000 in sales from $1,000 in marketing spend. While that isn’t the most realistic expectation, knowing your target ROI will prevent overspending. If your ROI is hurtling beyond your predictions, you can better allocate that budget to be spent elsewhere.
But there’s more to marketing measurement than dollar returns. Revenue isn’t always the end goal. Brand awareness, website traffic, and social media followers are short-term marketing objectives that aim to get new people into your marketing funnel. Nail them early on and you set your business up for success later down the road.
Not everyone will see your products and convert into a customer instantly. Most people progress through a sales funnel. Content that will make someone progress to the next stage depends on the one they’re currently in.
If you were to use Facebook ads to sell your products to a generic audience modeled on your buyer persona, for example, you might not get the highest conversion rate. These people don’t know who you are, what you stand for, or why they should choose you over a competitor.
But if you used Facebook ads to specifically target people at the bottom of your marketing funnel, you could use retargeting ads to show items someone had in their shopping cart. You’re bound to get a better return on your investment with this strategy because you’re only investing money into reaching people who just need a final nudge to convert.
Let’s break down how you might outline your marketing funnel in a marketing plan.
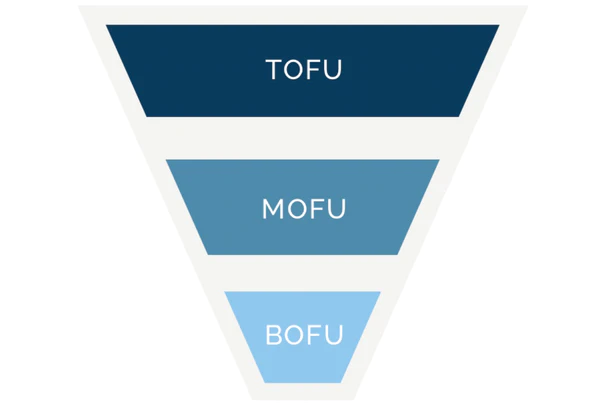
Top of the funnel (TOFU)
People at the top of your marketing funnel don’t understand who you are or what you sell. Social media, podcasts, and video content play huge roles here. Each channel is used by potential customers looking to learn or be inspired.
For this stage, prioritize metrics that give insight into how people are engaging with your top-funnel content, such as:
- Video views
- Website clicks
- Click-through rate (CTR)
- Cost per click (CPC)
Middle of the funnel (MOFU)
People reach the middle of the funnel when they know they have a problem that needs to be solved. Look at the marketing channels and formats you’re using to target these people. Most often, it’s search engines and retargeted ads.
Google Analytics is your best bet here. While the dashboard can feel overwhelming for a lot of people, you don’t need to look at every report. Use the following metrics to see how people engage with your middle-funnel content:
- Bounce rate
- Pages per session
- Users by traffic source
- Email subscriber conversion rate
To track the data above, especially for advertising campaigns, add the Meta pixel to all pages of your store.
Bottom of the funnel (BOFU)
Going for the hard sell? For marketing messages where the only goal is to convert your audience into paying customers, consult the back end of your ecommerce store. It’s home to sales and product-related data that helps you understand whether your marketing plan is successful, such as:
- Added to cart conversion rate
- Average order value (AOV)
- Number of orders
- Reached checkout conversion rate
- Sales conversion rate
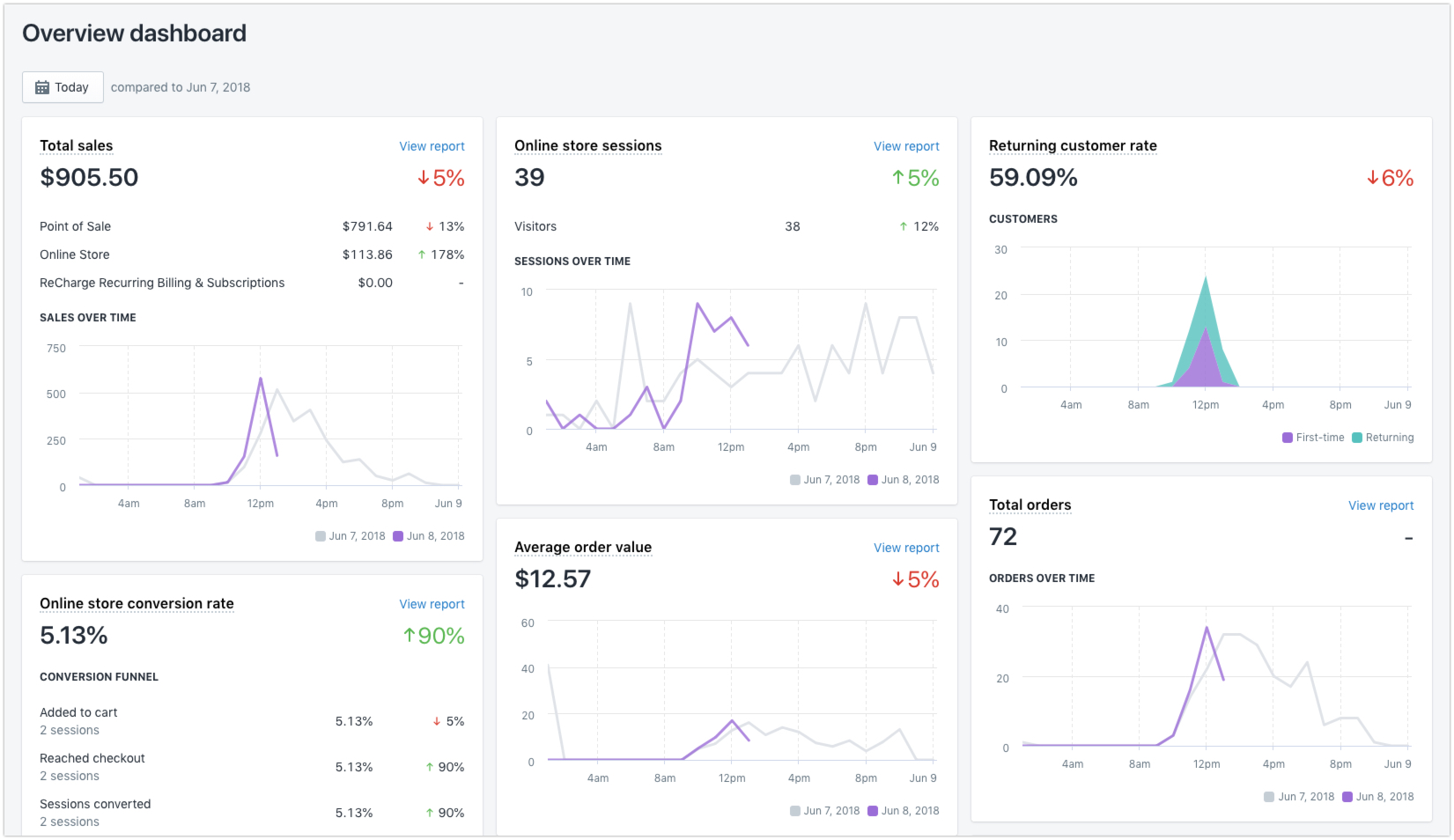
Post-funnel and retention
Planning to build a steady stream of paying customers off the back of your ecommerce marketing plan? It's easy to assume revenue growth comes from audience growth. But oftentimes, the easiest way to grow your revenue is by focusing on the people we forget about: existing customers.
Resist the temptation to focus on flashy metrics like social media followers and YouTube subscribers. Instead, involve existing customers in your marketing plan. Use them as a source of testimonials and word-of-mouth referrals.
“Happy customers have been powerful word-of-mouth catalysts for our brand, and it has made sense to keep them engaged,” says Chris Campbell, partner at The Charming Bench Company . “We’ve been getting a steady stream of five-star ratings on websites and social media, which we then share on our Facebook, X [formerly known as Twitter], Pinterest, and Instagram profiles. It’s a great alternative to pushing loud sales messages that don’t always work.”
Define your marketing channels
Channels are the platforms you’ll use as part of your marketing plan. Go back to your market research and uncover the online and offline channels your target audience is using to shop and get entertained or inspired.
Some of the most popular channels for ecommerce businesses include:
- Social media . Social media is used by more than six out of 10 people . Platforms like Instagram, Facebook, X, LinkedIn, and Pinterest are free to use (on the whole) and help brands reach their target audience.
- Search engines . Some 44% of online shoppers start their product research on search engines. By making search engine optimization (SEO) part of your marketing plan, you can generate new business by reaching people when they’re actively looking for your products or services.
- Email marketing and SMS marketing . Email and text message inboxes are two of the most sacred places for a marketer to reach. A phone number or email address gives you a direct line of communication with your target customers, if they opt in to hear from you.
- Podcasts . Record conversations you have with your team, customers, or experts in the industry and share them with your audience. By establishing yourself or your brand as a thought leader in your industry, you’ll inspire confidence that in turn builds trust in your products.
- Offline channels. While digital marketing is vital in today’s world, offline and in-person marketing efforts can be equally powerful. Get in front of people when they’re not online, using channels like word-of-mouth recommendations , radio, billboards and outdoor advertising , or TV marketing campaigns.
There’s a sweet spot to how many channels your marketing plan should include. Go too wide and you burn resources on channels with poor returns. But become too reliant on one channel and you’re at risk.
Algorithms power most digital marketing channels. They’re praised as the type of technology that delivers personalized experiences for their users, but any changes to an algorithm can make marketing plans utterly useless overnight.
“If you rely on SEO, then any algorithm updates could potentially cut your revenue for months before you recover,” explains Marquis Matson, VP of Growth at Sozy . “If you rely on paid ads, then any changes to privacy policies can cut your revenue. If you rely on email marketing, then any ESP [email service provider] policy changes can cut your revenue. Diversifying your acquisition is crucial in a fast-paced digital marketing world.”
Footwear brand Hippy Feet is one ecommerce brand that failed to diversify channels. “The original marketing plan was to drive traffic to our Shopify store through ads—relying heavily on paid Facebook and Instagram traffic,” says Sam Harper, Hippy Feet’s co-founder and CEO. “While this is still a major component of our marketing strategy, the decreasing effectiveness of these ads has forced us to expand our marketing efforts.
“A diverse media strategy is crucial to helping an ecommerce business survive in this highly-dynamic market. By driving traffic through SEO, email, and media coverage, we’re more resilient and less impacted by a single tech platform changing their algorithm.”
For each channel, define which content formats you’ll use to capture attention and drive website traffic. That could include:
- Audio. Reach podcast and radio listeners with audio content.
- Images. Capture visual learners and shoppers on visually dominant social media sites with infographics, GIFs, and memes.
- Video. Get listed on YouTube , the world's second largest search engine, with explainer videos and product demonstrations. Many social media platforms— Instagram and TikTok included—are also evolving to prioritize video content.
- Written content. Most search engine results retrieve links to optimized written content, such as blogs , transcripts, or landing pages .
Content marketing is a beast that constantly needs to be fed. Customers want newer, fresher, more exciting content on a regular basis. That’s demanding for a small business to keep up with.
If this sounds unsustainable, consider a content marketing strategy that collects user-generated content (UGC) from existing customers. The more they share their experiences with others, the more content you have to repurpose on each channel. It’s an effective route to scale your content marketing plan and stretch your editorial calendar if your marketing department has limited resources. Don’t have time to invest in promoting the content you create? Partner with popular influencers in your niche—those whose loyal audience overlaps with your target market .
Your marketing budget is the dollar amount you expect to spend executing your marketing plan. If you’re bootstrapped, you can run a marketing plan on a tight budget .
As part of your own marketing plan, state whether you intend to use each channel organically or boost it with advertising. Most channels allow businesses to run sponsored content, which is guaranteed to reach your target market across online and offline channels, like door-to-door sales , social media, TV, billboards, and radio.
“I apply for any competitions, press opportunities, and awards to get my small business out there at any given opportunity,” says Terri-Anne Turton, founder of The Tur-Shirt Company .
The strategy has worked: The Tur-Shirt Company has won a Junior Design Award for best fashion newcomer and a shoutout from media entrepreneur Steven Bartlett after entering his #DeserveToBeFound competition with Facebook.
“I focus on those my target market knows of to build credibility,” says Terri-Anne. “Plus, most of the awards I enter are free or low-cost; they just need some time investment and creativity to take part. It proves my USP to my target market—that my kids’ clothing products are unique—without investing thousands into advertising.”

While you can run a strategy with little to no budget, this section of your marketing plan needs to account for more than any planned advertising spend. Time is a resource that needs to be managed and accounted for. Be sure to detail how much time you plan to spend executing your marketing strategy.
If you have a designated marketing team, it’s also worth noting who will be responsible for each element of your marketing plan. Who’s responsible for this marketing plan? Which team members are executing it? What experience do they have with marketing?
More importantly, detail what you expect from the resources you’re putting into your marketing plan. If you plan to spend $40,000 throughout the coming year, how much revenue will you get in return? If you’re producing a marketing plan for a large or public company, this is what stakeholders really want to see.
Go back to the KPIs (key performance indicators) you set in the earlier section of your marketing plan. How will you determine whether you’ve met these KPIs? What happens if you’re exceeding or falling short of your target? It’s good to have a plan of action for either case.
Let’s put that into practice and say you expected to increase sales by 20% through your social media marketing plan. Detail exactly how you’d measure this, for example, you could say, “we’ll look at our Shopify sales report once per month and analyze which channel is meeting this KPI. If a channel falls behind, we’ll evaluate why and either adjust our marketing plan or deprioritize it in favor of more effective channels.”
The best marketers approach their plans with an open mind. The hypothesis you started with might be proven wrong. Don’t take that as a negative. You just got closer to finding what will work.
Tips for creating your marketing plan
Set conservative expectations.
While it’s good to approach your marketing goals with confidence, high expectations often lead to disappointment when we fail to meet them. That disappointment is magnified in a marketing plan, as stakeholders or founders will have already bought into unrealistic predictions and business objectives.
Start small
Don’t overwhelm yourself and your team by trying to generate results with all marketing tactics at once: running Facebook ads, tweeting like crazy, writing daily blog posts for SEO, and making constant changes to site and content strategy to improve your conversion rate.
If you’re very lucky, one of these tactics will bring you consistent traffic and sales. But more often than not, trying everything at once will make you extremely busy without anything to show for it.
Take it from Jameela Ghann, owner of Alora : “When we first started Alora, 10 years ago, our marketing plan was unrealistic. We were just a couple of people making plans that were good on paper but almost impossible to execute with a small team.”
Originally, Jameela’s team planned to invest in several marketing channels—online and offline advertising, PR, trade shows, influencer marketing, and blogging included. However, the team changed its marketing plan. They went deep on one channel instead of spreading resources too thin by trying to be everywhere at once.
“We stuck to one course of action that was where our customers were, and ready to buy, and easiest for us to see a good ROI,” Jameela says. “What really worked for us was focusing on a handful of channels that we knew we could do well.”
Go back to your audience research and identify three channels your target audience uses most often. Put most of your energy into perfecting those before overcomplicating things with a more comprehensive marketing plan.
Use historical data as a guide
Past performance can help you temper your expectations for your marketing plan. If you know your click-through rate (CTR) for Facebook ads is 0.1%, don’t stray too far from that baseline with your social media marketing .
The same goes for website content optimized for search : If you’re currently getting 10,000 visitors per month from Google, scaling your traffic up to a million is a tough battle. Instead, 50,000 visitors is a more achievable goal.
Allow for flexibility
The purpose of a marketing plan isn’t to create a never-fail manual. Whether your marketing team has fallen victim to completion bias or focused too heavily on one channel, sticking rigidly to your original plan can be a big mistake.
Imine Martinez, assistant manager at Rainbowly , says: “Our regular campaigns targeting mainly birthday celebrations and anniversaries offered poor return on ad spend and inconsistent results over the months.
“That said, during festive seasons, such as Christmas or New Year’s, our targeted campaigns were particularly profitable, achieving five times return on ad spend with much cheaper cost per click and impression.”
Continuing with the same marketing strategies despite this data would only have resulted in heartbreak. Rainbowly would be pouring money down the drain on ads that wouldn’t perform, just because its marketing plan said to do so.
Creating a marketing plan is the first step
A lot of hard work goes into a successful marketing plan. To create an attainable one, you’ll need to spend hours diving into competitive research, audience data, and channels your target market consults when researching new products.
Most importantly, know that marketing is unpredictable. There are thousands of scenarios that fundamentally change the marketing strategy that’s best for your business. Global pandemics, PR crises, and the emergence of new social media platforms are unpredictable.
Treat your marketing plan like the best-case scenario. Plan SMART goals and strategies but remember to be flexible to give your marketing the best chance of success.
- The Ultimate Guide to International Ecommerce
- The 12 Best Ecommerce Platforms for 2024
- 130+ Dropshipping Products To Sell for Profit
- The Ultimate Guide To Dropshipping (2024)
- The 5-Step Marketing Strategy to Grow Your Business
- Amazon Dropshipping Guide- How To Dropship on Amazon (2024)
- How To Write a Return Policy (+ Free Template) (2024)
- A 14-Point Ecommerce Checklist to Launch Your Shopify Store
- Faster Checkout on Instagram and Facebook with Shop Pay
- What Is Marketing Automation? Definition and Guide
Marketing plan FAQ
How much does a marketing plan cost, how often should a marketing plan be reviewed, what are the 4 steps of a marketing plan.
- Conduct market research
- Outline your marketing channels and formats
- Create goals and measure performance
Why is marketing plan important?
What are some marketing plan mistakes.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Aug 22, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
How to Write an Effective Marketing Plan

Alan Gleeson
3 min. read
Updated October 27, 2023

A marketing plan is a core component of a business plan. It relates specifically to the marketing of a particular product or service and it describes:
- An overall marketing objective
- A broad marketing strategy
- The tactical detail related to specific marketing activities
- The various costs associated with these activities
- Those tasked with delivering these activities by name
The starting point for any marketing plan is an analysis of the strategic context, as a typical objective for most plans is promoting a good or service as effectively as possible. An assessment of the company, its environment and its customers helps to ensure that the author of the plan obtains a holistic view of the wider context. In turn this helps them to focus their energies and resources accordingly. This is particularly important given that most marketing managers will be subject to that all-too-familiar constraint—limited resources (invariably financial). In effect, a marketing plan is produced to ensure that limited resources are allocated to activities that are likely to bring the maximum return.
An assessment of the context will include analysis of both internal and external factors. There are a number of frameworks and tools designed to assist you with this:
- A SWOT analysis forces you to consider internal Strengths and Weaknesses alongside external Opportunities and Threats.
- Porter’s Five Forces is a framework designed to assist you in considering the broader competitive and environmental context.
It is also vital that you have a thorough understanding of your customers; look to whether segments exist within your broad customer group that can be profitably served utilizing specific and targeted marketing activities.
Following an analysis of broader conditions, a marketing strategy can then be put in place. This strategy needs to include financials so that all activities can be assessed in the context of their cost as a portion of the overall marketing budget. Regardless of the product or service, the objectives tend to be similar for most managers; create awareness, stimulate interest in the offering, and ultimately (profitably) convert this awareness into sales. All these factors are intertwined and, hence, the importance of effective market planning.
Using a local restaurant as an example, their marketing activities are going to be predominantly concentrated within a two to three mile radius of their restaurant, as this area is where the vast majority of their customers are likely to come from. Tactically, there is no point in such a restaurant advertising on TV (even locally) as the cost would be prohibitive in the context of their business model. They are limited in terms of capacity (number of seats) and their average cost per head so that, even if they created huge awareness and interest via TV advertising, the resultant revenues would still be unlikely to cover the cost of the specific marketing activity. On the other hand, stuffing leaflets through local letterboxes is extremely targeted and comes at low relative cost, which explains the sheer volume of fast-food fliers most of us get on a daily basis.
The reader of the plan should clearly be able to relate to the marketing initiatives in terms of the message, the target audience and the means to accessing this audience. A good marketing plan will detail specifics, i.e., a number of marketing activities, their respective costs, and the expected return on investment. Measuring return on marketing has historically been one of the greatest challenges the industry has faced. The advent of PPC (pay-per-click) advertising via the Internet has finally resulted in managers being able to track sales resulting from specific campaigns and adverts. However, this is just one means of advertising, and calculating effective ROI (return on investment) figures for other forms, such as billboards and TV, remains as elusive as ever.
In summary, a marketing plan should enable marketing managers to document their assessment of the opportunity in terms of effective allocation of limited resources. While most managers would love the luxury of a seven-figure marketing budget to spend on every conceivable advertising medium, the reality is that most need to market effectively on a pittance. A marketing plan assesses the most efficient means to attract potential customers and ultimately convert them to sales. Without a plan, a business is essentially rudderless and marketing activities are more likely to be reactive and, hence, considerably less effective.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Alan Gleeson is a CMO, consultant and entrepreneur with a background in marketing and SaaS. He currently works for Contento, a company building a Headless CMS for Tech Companies. Gleeson has experience in a variety of industries including financial services, technology, and SaaS.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

9 Min. Read
How to Create a Sales Plan for Your Business

6 Min. Read
How to Do a SWOT Analysis for Better Strategic Planning

8 Min. Read
How to Create A Digital Marketing Plan and Strategy

4 Min. Read
How to Develop a Positioning Statement for Your Business
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Product overview
- All features
- Latest feature release
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Capacity planning
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Marketing |
- How to create a winning marketing plan, ...
How to create a winning marketing plan, with 3 examples from world-class teams

A marketing plan helps leaders clearly visualize marketing strategies across channels, so they can ensure every campaign drives pipeline and revenue. In this article you’ll learn eight steps to create a winning marketing plan that brings business-critical goals to life, with examples from word-class teams.
To be successful as a marketer, you have to deliver the pipeline and the revenue.”
In other words—they need a well-crafted marketing plan.
Level up your marketing plan to drive revenue in 2024
Learn how to create the right marketing plan to hit your revenue targets in 2024. Hear best practices from marketing experts, including how to confidently set and hit business goals, socialize marketing plans, and move faster with clearer resourcing.

7 steps to build a comprehensive marketing plan
How do you build the right marketing plan to hit your revenue goals? Follow these eight steps for success:
1. Define your plan
First you need to define each specific component of your plan to ensure stakeholders are aligned on goals, deliverables, resources, and more. Ironing out these details early on ensures your plan supports the right business objectives, and that you have sufficient resources and time to get the job done.
Get started by asking yourself the following questions:
What resources do I need?
What is the vision?
What is the value?
What is the goal?
Who is my audience?
What are my channels?
What is the timeline?
For example, imagine you’re creating an annual marketing plan to improve customer adoption and retention in the next fiscal year. Here’s how you could go through the questions above to ensure you’re ready to move forward with your plan:
I will need support from the content team, web team, and email team to create targeted content for existing customers. One person on each team will need to be dedicated full-time to this initiative. To achieve this, the marketing team will need an additional $100K in budget and one new headcount.
What is the vision?
To create a positive experience for existing customers, address new customer needs, and encourage them to upgrade. We’ll do this by serving them how-to content, new feature updates, information about deals and pricing, and troubleshooting guides.
According to the Sales Benchmark Index (SBI) , CEOs and go-to-market leaders report that more than 60% of their net-new revenue will come from existing customers in 2023. By retaining and building on the customers we have, we can maintain revenue growth over time.
To decrease the customer churn rate from 30% to 10%, and increase upgrades from 20% to 30% in the next fiscal year.
All existing customers.
The main channel will be email. Supporting marketing channels include the website, blog, YouTube, and social media.
The first half of the next fiscal year.
One of the most important things to do as you create your marketing strategy is to identify your target audience . As with all marketing, you need to know who you’re marketing to. If you’re having a hard time determining who exactly your target audience is, try the bullseye targeting framework . The bullseye makes it easy for you to determine who your target audience is by industry, geography, company size, psychographics, demographics, and more.
2. Identify key metrics for success
Now it’s time to define what key marketing metrics you’ll use to measure success. Your key metrics will help you measure and track the performance of your marketing activities. They’ll also help you understand how your efforts tie back to larger business goals.
Once you establish key metrics, use a goal-setting framework—like objectives and key results (OKRs) or SMART goals —to fully flush out your marketing objectives. This ensures your targets are as specific as possible, with no ambiguity about what should be accomplished by when.
Example: If a goal of your marketing plan is to increase email subscriptions and you follow the SMART goal framework (ensuring your objective is specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound) your goal might look like this: Increase email subscription rate from 10% to 20% in H1 .
3. Research your competition
It’s easy to get caught up in your company’s world, but there’s a lot of value in understanding your competitors . Knowing how they market themselves will help you find opportunities to make your company stand out and capture more market share.
Make sure you’re not duplicating your competitors’ efforts. If you discover a competitor has already executed your idea, then it might be time to go back to the drawing board and brainstorm new ways to differentiate yourself. By looking at your competitors, you might be surprised at the type of inspiration and opportunities you’ll find.
To stay ahead of market trends, conduct a SWOT analysis for your marketing plan. A SWOT analysis helps you improve your plan by identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Example: If your competitor launches a social media campaign identical to what you had planned, go back to the drawing board and see how you can build off their campaign. Ask yourself: How can we differentiate our campaign while still getting our message across? What are the weaknesses of their campaign that we can capitalize on? What angles did they not approach?
4. Integrate your marketing efforts
Here’s where the fun comes in. Let’s dive into the different components that go into building a successful marketing plan. You’ll want to make sure your marketing plan includes multiple supporting activities that all add up into a powerful marketing machine. Some marketing plan components include:
Lead generation
Social media
Product marketing
Public relations
Analyst relations
Customer marketing
Search engine optimization (SEO)
Conversational marketing
Knowing where your consumer base spends the most time is significant for nailing this step. You need to have a solid understanding of your target audience before integrating your marketing efforts.
Example: If your target audience is executives that spend a lot of time on LinkedIn, focus your social media strategy around placing branded content on LinkedIn.
5. Differentiate with creative content
Forty-nine percent of marketers say visual images are hugely important to their content strategy. In other words, a clear brand and creative strategy is an essential component to every marketing plan. As you craft your own creative strategy, here are some tips to keep in mind:
Speak to your audience: When defining your creative strategy, think about your audience—what you want them to feel, think, and do when they see your marketing. Will your audience find your creative work relevant? If your audience can’t relate to your creative work, they won’t feel connected to the story you’re trying to tell.
Think outside the box: Find innovative ways to engage your audience, whether through video, animations, or interactive graphics. Know what screens your creative work will live on, whether desktop, mobile, or tablet, and make sure they display beautifully and load quickly across every type of device.
Tie everything back to CTAs: It’s easy to get caught up in the creative process, so it’s important to never lose sight of your ultimate goal: Get your audience to take action. Always find the best way to display strong Calls to Action (CTAs) in your creative work. We live in a visual world—make sure your creative content counts.
Streamline creative production: Once you’ve established a strong creative strategy, the next step is to bring your strategy to life in the production stage. It’s vital to set up a strong framework for your creative production process to eliminate any unnecessary back and forth and potential bottlenecks. Consider establishing creative request forms , streamlining feedback and approval processes, and taking advantage of integrations that might make your designers’ lives easier.
Example: If your brand is fun and approachable, make sure that shows in your creative efforts. Create designs and CTAs that spark joy, offer entertainment, and alleviate the pressure in choosing a partner.
6. Operationalize your marketing plan
Turn your plan into action by making goals, deliverables, and timelines clear for every stakeholder—so teams stay accountable for getting work done. The best way to do this is by centralizing all the details of your marketing plan in one platform , so teams can access the information they need and connect campaign work back to company goals.
With the right work management tool , you can:
Set goals for every marketing activity, and connect campaign work to overarching marketing and business objectives so teams focus on revenue-driving projects.
Centralize deliverables for your entire marketing plan in one project or portfolio .
Mark major milestones and visualize your plan as a timeline, Gantt chart, calendar, list, or Kanban board—without doing any extra work.
Quickly loop in stakeholders with status updates so they’re always up to date on progress. This is extremely important if you have a global team to ensure efforts aren’t being duplicated.
Use automations to seamlessly hand off work between teams, streamlining processes like content creation and reviews.
Create dashboards to report on work and make sure projects are properly staffed , so campaigns stay on track.
With everything housed in one spot, you can easily visualize the status of your entire marketing plan and keep work on track. Building an effective marketing plan is one thing, but how you operationalize it can be your secret to standout marketing.
Example: If your strategy focuses on increasing page views, connect all campaign work to an overarching OKR—like “we will double page views as measured by the amount of organic traffic on our blog.” By making that goal visible to all stakeholders, you help teams prioritize the right work.
See marketing planning in action
With Asana, marketing teams can connect work, standardize processes, and automate workflows—all in one place.

7. Measure performance
Nearly three in four CMOs use revenue growth to measure success, so it’s no surprise that measuring performance is necessary. You established your key metrics in step two, and now it’s time to track and report on them in step eight.
Periodically measure your marketing efforts to find areas of improvement so you can optimize in real-time. There are always lessons to be learned when looking at data. You can discover trends, detect which marketing initiatives performed well, and course-correct what isn’t performing well. And when your plan is complete, you can apply these learnings to your next initiative for improved results.
Example: Say you discover that long-form content is consistently bringing in 400% more page views than short-form content. As a result, you’ll want to focus on producing more long-form content in your next marketing plan.
Marketing plan examples from world-class teams
The best brands in the world bring their marketing plans to life every day. If you’re looking for inspiration, check out these examples from successful marketing teams.
Autodesk grows site traffic 30% three years in a row
When the Autodesk team launched Redshift, it was initially a small business blog. The editorial team executed a successful marketing plan to expand it into a premier owned-media site, making it a destination for stories and videos about the future of making.
The team scaled content production to support seven additional languages. By standardizing their content production workflow and centralizing all content conversations in one place, the editorial team now publishes 2X more content monthly. Read the case study to learn more about how Autodesk runs a well-oiled content machine. Trinny London perfects new customer acquisition
In consumer industries, social media is crucial for building a community of people who feel an affinity with the brand—and Trinny London is no exception. As such, it was imperative that Trinny London’s ad spend was targeted to the correct audience. Using a work management tool, Trinny London was able to nail the process of creating, testing, and implementing ads on multiple social channels.
With the help of a centralized tool, Trinny London improved its ad spend and drove more likes and subscriptions on its YouTube page. Read the case study to learn more about how Trinny London capitalized on paid advertising and social media.
Turn your marketing plan into marketing success
A great marketing plan promotes clarity and accountability across teams—so every stakeholder knows what they’re responsible for, by when. Reading this article is the first step to achieving better team alignment, so you can ensure every marketing campaign contributes to your company’s bottom line.
Use a free marketing plan template to get started
Once you’ve created your marketing strategy and are ready to operationalize your marketing plan, get started with one of our marketing templates .
Our marketing templates can help you manage and track every aspect of your marketing plan, from creative requests to approval workflows. Centralize your entire marketing plan in one place, customize the roadmap, assign tasks, and build a timeline or calendar.
Once you’ve operationalized your entire marketing plan with one of our templates, share it with your stakeholders so everyone can work together in the same tool. Your entire team will feel connected to the marketing plan, know what to prioritize, and see how their work contributes to your project objectives . Choose the best marketing template for your team:
Marketing project plan template
Marketing campaign plan template
Product marketing launch template
Editorial calendar template
Agency collaboration template
Creative requests template
Event planning template
GTM strategy template
Still have questions? We have answers.
What is a marketing plan.
A marketing plan is a detailed roadmap that outlines the different strategies your team will use to achieve organizational objectives. Rather than focusing solely on the end goal, a marketing plan maps every step you need to reach your destination—whether that’s driving pipeline for sales, nurturing your existing customer base, or something in-between.
As a marketing leader, you know there’s never a shortage of great campaign and project ideas. A marketing plan gives you a framework to effectively prioritize work that aligns to overarching business goals—and then get that work done. Some elements of marketing plans include:
Current business plan
Mission statement
Business goals
Target customers
Competitive analysis
Current marketing mix
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Marketing budget
What is the purpose of a marketing plan?
The purpose of a marketing plan is to grow your company’s consumer base and strengthen your brand, while aligning with your organization’s mission and vision . The plan should analyze the competitive landscape and industry trends, offer actionable insights to help you gain a competitive advantage, and document each step of your strategy—so you can see how your campaigns work together to drive overarching business goals.
What is the difference between a marketing plan and a marketing strategy?
A marketing plan contains many marketing strategies across different channels. In that way, marketing strategies contribute to your overall marketing plan, working together to reach your company’s overarching business goals.
For example, imagine you’re about to launch a new software product and the goal of your marketing plan is to drive downloads. Your marketing plan could include marketing strategies like creating top-of-funnel blog content and launching a social media campaign.
What are different types of marketing plans?
Depending on what you’re trying to accomplish, what your timeline is, or which facet of marketing you’re driving, you’ll need to create a different type of marketing plan. Some different types of marketing plans include, but aren’t limited to:
General marketing plan: A general marketing plan is typically an annual or quarterly marketing plan that details the overarching marketing strategies for the period. This type of marketing plan outlines marketing goals, the company’s mission, buyer personas, unique selling propositions, and more. A general marketing plan lays the foundation for other, more specific marketing plans that an organization may employ.
Product launch marketing plan: A product launch marketing plan is a step-by-step plan for marketing a new product or expanding into a new market. It helps you build awareness and interest by targeting the right audience, with the right messaging, in the right timeframe—so potential customers are ready to buy your new offering right away. Nailing your product launch marketing plan can reinforce your overall brand and fast-track sales. For a step-by-step framework to organize all the moving pieces of a launch, check out our product marketing launch template .
Paid marketing plan: This plan includes all the paid strategies in your marketing plan, like pay-per-click, paid social media advertising, native advertising, and display advertising. It’s especially important to do audience research prior to launching your paid marketing plan to ensure you’re maximizing ROI. Consult with content strategists to ensure your ads align with your buyer personas so you know you’re showing ads to the right people.
Content marketing plan: A content marketing plan outlines the different content strategies and campaigns you’ll use to promote your product or service. When putting together a content marketing plan, start by identifying your audience. Then use market research tools to get the best insights into what topics your target audience is most interested in.
SEO marketing plan: Your SEO marketing plan should work directly alongside your content marketing plan as you chart content that’s designed to rank in search results. While your content marketing plan should include all types of content, your SEO marketing plan will cover the top-of-funnel content that drives new users to your site. Planning search engine-friendly content is only one step in your SEO marketing plan. You’ll also need to include link-building and technical aspects in order to ensure your site and content are as optimized as possible.
Social media marketing plan: This plan will highlight the marketing strategies you plan to accomplish on social media. Like in any general or digital marketing plan , your social media strategy should identify your ideal customer base and determine how they engage on different social media platforms. From there, you can cater your social media content to your target audience.
Related resources

How Asana streamlines strategic planning with work management

Write better AI prompts: A 4-sentence framework

What is content marketing? A complete guide
Smooth product launches are simpler than you think

- Digital Marketing Strategy and Planning
- Content Marketing
- Digital Experience Management (Desktop/mobile website)
- Email Marketing
- Google Analytics
- Marketing Campaign Planning
- Search Engine Optimisation (SEO)
- Social Media Marketing
- Agency growth
- Business-to-Business
- Charity and Not-for-profit
- E-commerce / Retail
- Managing Digital Teams
- Managing Digital Branding
- Managing Digital Transformation
- Managing Lifecycle Marketing
- Managing International Marketing
- Startup and Small Businesses
How to structure an effective marketing plan in 15 sections
Using the RACE OSA process to structure a marketing plan
A marketing plan is an essential tool to compete and grow your business since it gives focus to your marketing activities by setting realistic, achievable priorities within your budget.
It simply defines what you want to gain from your investment in marketing and how you will achieve these goals through selecting the best marketing strategies and channels to acquire and retain customers.
A typical definition of a marketing plan used by traditional marketers is:
" A marketing plan is a strategic document that specifies your organization’s target markets, marketing objectives, programs, and activities to achieve them, expected timescales, resources to be utilized, according to defined budgets, and how success will be measured ".
This is logical and simple and that's what we need to achieve through the structure of an effective marketing plan. However, for today's marketing where digital marketing channels are so important we need a marketing plan and template structure that are fit for purpose. That's why we developed the RACE Growth System since it details the communications activities that need to be used for success.
In this post, I will explain RACE OSA, a practical three-part marketing plan structure particularly suitable for small and medium businesses to rapidly develop comprehensive marketing plans. OSA stands for:
Opportunity > Structure > Action.
For each of these 3 parts, I will summarize what you need to include and why. There are 5 steps in each part giving 15 sections in all. This is simple enough to make it quick and easy, but detailed enough to work in the real world.
You can download our Free marketing plan template based on this 15-step OSA structure!

Free marketing plan template
Our popular marketing planning template is structured across the Smart Insights RACE OSA Framework. Join Smart Insights as a Free Member to download our marketing plan template today
Access the Free marketing plan template
Many marketing plan templates were created long ago for larger businesses and aren’t so relevant to small and startup businesses competing in today’s marketplace where effective digital marketing is essential. Long plans with sections labelled ‘mission and vision statement’ and ‘corporate strategies’ are irrelevant for smaller businesses.
Our recommended format is far more practical since it relates to the real-world challenges and opportunities of a smaller business. The template shares the key features of our RACE Growth system since it is designed to be:
- Quick to create and implement an actionable plan with simple steps
- Data-driven, defining SMART objectives based on forecasts
- Practical to implement using a 90-day planning approach to give you focus
- Designed for smaller businesses, but relevant for larger businesses too
But first, we need to remind ourselves of the goals for our marketing plan and how it fits within the business as a whole. We will also introduce the Smart Insights RACE Growth System.
What is the purpose of a marketing plan?
The purpose of a marketing plan is to define strategies to engage audiences in order to achieve business objectives.
The goal of a marketing plan is to ensure marketing activities are structured, relevant, and timely to achieve an organization’s objectives.
It’s a plan defining your company's sustainable competitive position, structuring and setting marketing goals, and defining the resources necessary to achieve your business vision.
A marketing plan should include:
- The current performance , priorities , and direction of your organization
- Its marketplace position in relation to external environmental factors including competitors and PESTLE macro-factors
- A critical analysis of your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. We recommend using the powerful TOWs marketing plan analysis summary .
- Clearly defined SMART marketing objectives and a way to benchmark their success
- The means by which to achieve those objectives through strategies for STP: Segmentation, Targeting and Brand Positioning
- Relevant and timely actions and responsibilities by function, product or service, and market segment
- Investment in communications activities to reach your audience and convince them to convert including, all important always-on marketing activities .
- Investment in sales and customer service activities to encourage them to buy for the first time and repeat purchases.
- The finances and resources required and forecasted revenues
- Regular measurement of progress and outcomes against benchmarks
So, to summarize, a solid marketing plan outline has:
- Clear, realistic goals that you can be confident of hitting
- The best strategy to achieve these goals against your competition
- Sufficient details of the tactics and actions needed to translate the strategy into action
- A method to check you are on track with your plans
The business context of a marketing plan
Where does the marketing plan fit within the business? Here’s another way of understanding the context of a marketing plan, to put it into context with other types of plans, as shown in this table:
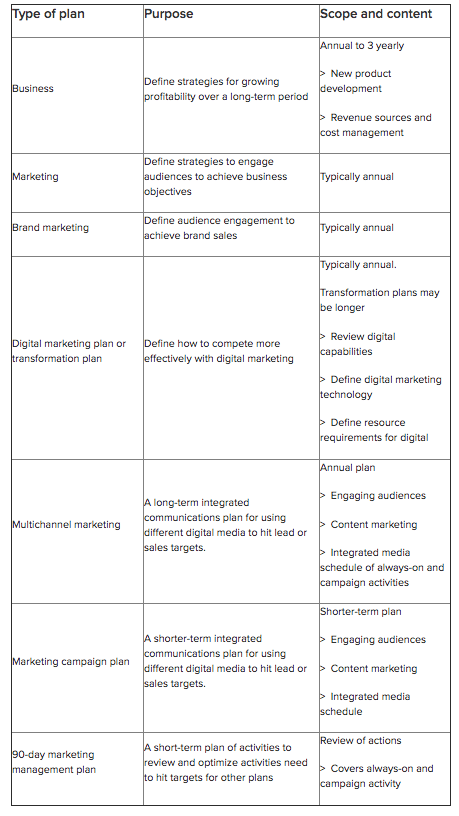
When to use a marketing plan?
The process of marketing planning within an organization will differ, depending on whether a strategic marketing plan or an operational marketing plan is utilized. Here are the differences between the two:
- A strategic marketing plan outlines the overall strategy within a market, connecting customers, competitors, and what the organization is capable of achieving. It is typically created at divisional or company level.
- An operational marketing plan outlines the marketing mix strategy that will be used to gain an advantage in the market. It typically focuses on products; market segments and how marketing communications and campaigns achieve targets defined in the strategic marketing plan. It usually has separate sections covering tactics for customer acquisition and retention which will sometimes be covered in separate plans in larger organizations.
In an organization’s planning process, marketing links:
- Customers’ needs and wants
- Competitor value proposition and actions
- Strategic direction
- Organizational objectives
What should your plan include? Our recommended marketing plan structure
Before we get into the details, let's look at the big picture which defines the process you will follow to develop and implement your marketing plan.
3-step marketing plan outline
Within the RACE system, we call this process OSA to keep it simple - marketing plans don't have to be complex. OSA stands for Opportunity, Strategy, Action. The visual outline shows some of the activities that are needed to plan for success under each stage of OSA.
Within OSA for a marketing plan format, these are the sections we recommend that are included in our template with more details on each.
Opportunity
- Audit performance
- Review marketplace
- Key issues summary
- Set objectives
- Review marketing and digital strategy options
- Assess budget / business case
- Prioritize and select strategic initiatives
- Plan 90-day activities
- Implement plans
- Review results
Use our free planning templates to get started with using RACE to grow your business. These will help you create a 90-day prioritized plan to improve your results from digital marketing. We recommend 25+ key marketing activities across RACE that are essential for businesses to compete by improving their digital marketing maturity.
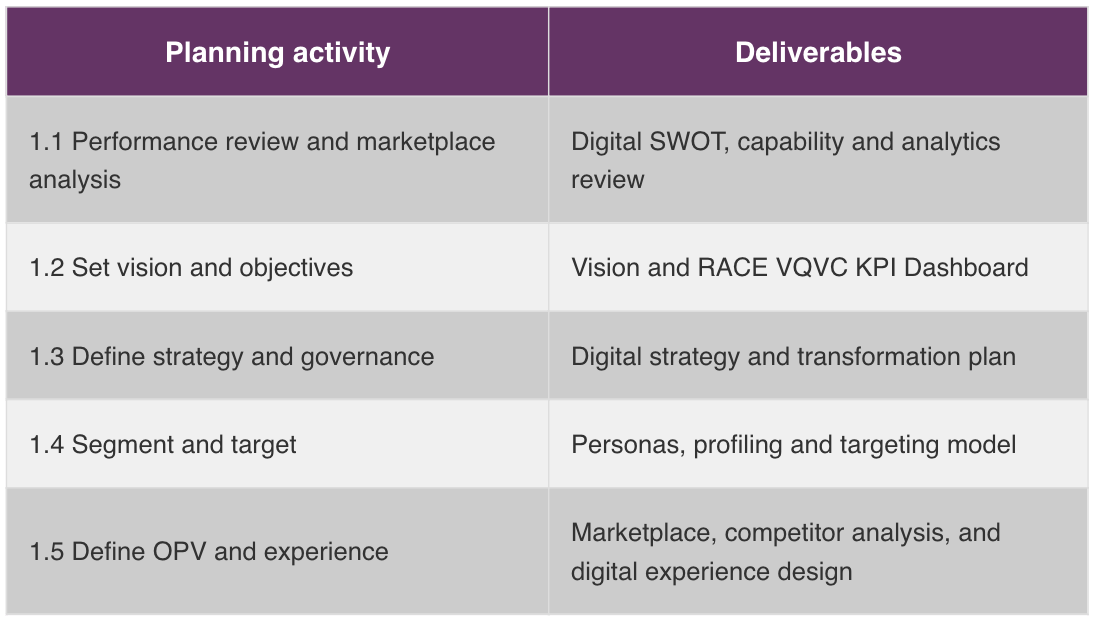
Which types of businesses use marketing plans?
Marketing planning will assist in the day-to-day running of any size, type or age of business. The targets and milestones set will help organizations, from small start-ups to large corporates, to effectively:
- Allocate resources and budget
- Motivate teams
- Manage the performance of staff members and marketing efforts
Marketing plans for small businesses
In smaller businesses, the scope of a plan is typically annual and for the whole business. Typically, SMEs are working with smaller budgets and tighter turnaround times.
A marketing plan for a small business typically looks to identify where to prioritize the investment of time and available budget to generate results.
Smaller organizations typically have:
- Small market shares
- Owners involved in all aspects of strategic and operational management
- Independence
- A high degree of uncertainty
- Difficulty innovating owing to limited resources
Such differences between large and smaller organizations tend to be reflected in the development of marketing plans.
When establishing a small start-up, marketing planning is an essential element. A small number of these businesses launch and grow, but for those that are successful, a strategic marketing approach will ensure continued development.
Marketing plans for large organizations
In large organizations, its focus will change, depending on the type of organization. A separate marketing plan might be:
- Geographically-based
- Product-based
- Business unit based
- Focused on segmentation
A marketing plan in a large organization may integrate a number of plans, specific to individual parts of the business. It is practical planning that takes place at a divisional, business unit, or individual company level.
Larger organizations with clearly defined management structures and a wealth of resources will make use of marketing principles very differently from smaller organizations.
Structure an effective marketing plan with RACE
Did you know - nearly half of companies don't have a clearly defined digital marketing strategy ? These companies are missing opportunities for better integration and risk losing customers due to out-of-date processes.
Savvy marketers and Smart Insights members already recognize that a practical, integrated marketing plan is essential for business growth in 2024 and beyond.
If you're looking for a quick marketing plan structure to hone your performance and strategize your approach to marketing, why not download our free marketing plan template ?
How to format your marketing funnel
Although the techniques for marketing planning may vary between different sizes and types of organizations, the outcome is always the same: to implement the objectives, strategies, and activities in order to gain an advantage.
That's why our RACE Framework is structured across a simple 5-step marketing and sales funnel which can be applied to every size of business from startups to multinational corporations:
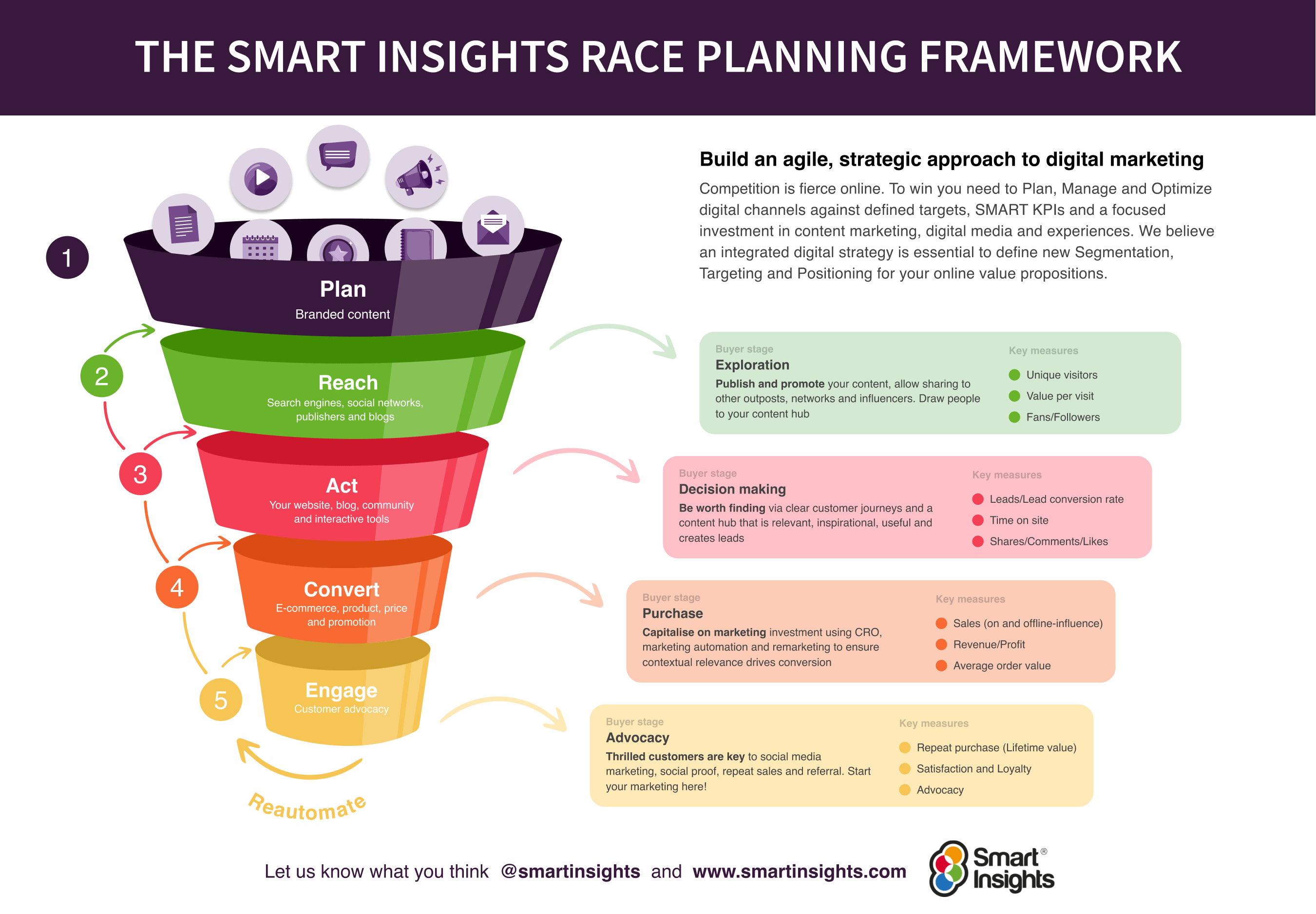
How does a marketing plan relate to other plans?
The plan should not be formulated or used in isolation; it should be informed by the corporate objectives identified in your organization’s business plan .
Integrated with a marketing plan may also be a digital plan, multi-channel plan and campaign plan, for example. The marketing plan informs these plans and vice-versa.
An effective marketing plan will ensure the integration of activities, the scheduling of requirements, distinguishing responsibilities and the provision of benchmarks for measuring success.
Different organizations will utilize differing plans, covering different areas and timeframes. What is crucial in a business is that the plans being utilized, the timeframes allocated, and how they integrate with each other are collectively established.
Structure your marketing plan around a funnel proven to boost performance. Join Smart Insights as a Free Member for instant access to our Free marketing plan template to hone your skills and drive the results you need.
By Dave Chaffey
Digital strategist Dr Dave Chaffey is co-founder and Content Director of online marketing training platform and publisher Smart Insights. 'Dr Dave' is known for his strategic, but practical, data-driven advice. He has trained and consulted with many business of all sizes in most sectors. These include large international B2B and B2C brands including 3M, BP, Barclaycard, Dell, Confused.com, HSBC, Mercedes-Benz, Microsoft, M&G Investment, Rentokil Initial, O2, Royal Canin (Mars Group) plus many smaller businesses. Dave is editor of the templates, guides and courses in our digital marketing resource library used by our Business members to plan, manage and optimize their marketing. Free members can access our free sample templates here . Dave is also keynote speaker, trainer and consultant who is author of 5 bestselling books on digital marketing including Digital Marketing Excellence and Digital Marketing: Strategy, Implementation and Practice . In 2004 he was recognised by the Chartered Institute of Marketing as one of 50 marketing ‘gurus’ worldwide who have helped shape the future of marketing. My personal site, DaveChaffey.com, lists my latest Digital marketing and E-commerce books and support materials including a digital marketing glossary . Please connect on LinkedIn to receive updates or ask me a question .
Turbocharge your results with this toolkit containing 7 resources
- Marketing campaign plan template
- Campaign timeline/project plan template and example
- Editorial calendar spreadsheet
- View the Toolkit
The Marketing Campaign Planning toolkit contains:

FREE marketing planning templates
Start your Digital Marketing Plan today with our Free membership.
- FREE practical guides to review your approach
- FREE digital marketing plan templates
- FREE alerts on the latest developments
Solutions to your marketing challenges
- Digital Transformation
- Email Marketing and Marketing Automation
- Managing Digital Marketing Teams
- Marketing Strategy and Planning
- Multichannel lifecycle marketing
Expert advice by sector
- Business-to-Business (B2B)
- Charity and Not-For-Profit
- E-commerce and Retail
- Sector Technology Innovation
- Startups and Small Businesses
Improve your digital marketing skills with our FREE guides and templates

Join the Conversation
Recommended Blog Posts
Free 3-page marketing plan template for a small business
Use our simple, 15 section download to quickly create a marketing plan for your business Many marketing plan templates you will find online were created long ago for larger businesses and aren’t so relevant to small and startup business competing …..
How to create a marketing plan in 2024
A Marketing Plan is a bit like a job description for your company. Everyone should have one, but they’re often not fit for purpose, out of date and reviewed infrequently… Research has shown that businesses with plans succeed…
How do you choose the best marketing plan for your business?
Discover our top 7 recommended different types of marketing plan options for developing and streamlining your marketing planning activities Planning is a must for any business that wants to succeed, but choosing the right type of plan to define your …..
- Starting a Business
Our Top Picks
- Best Small Business Loans
- Best Business Internet Service
- Best Online Payroll Service
- Best Business Phone Systems
Our In-Depth Reviews
- OnPay Payroll Review
- ADP Payroll Review
- Ooma Office Review
- RingCentral Review
Explore More
- Business Solutions
- Entrepreneurship
- Franchising
- Best Accounting Software
- Best Merchant Services Providers
- Best Credit Card Processors
- Best Mobile Credit Card Processors
- Clover Review
- Merchant One Review
- QuickBooks Online Review
- Xero Accounting Review
- Financial Solutions
Human Resources
- Best Human Resources Outsourcing Services
- Best Time and Attendance Software
- Best PEO Services
- Best Business Employee Retirement Plans
- Bambee Review
- Rippling HR Software Review
- TriNet Review
- Gusto Payroll Review
- HR Solutions
Marketing and Sales
- Best Text Message Marketing Services
- Best CRM Software
- Best Email Marketing Services
- Best Website Builders
- Textedly Review
- Salesforce Review
- EZ Texting Review
- Textline Review
- Business Intelligence
- Marketing Solutions
- Marketing Strategy
- Public Relations
- Social Media
- Best GPS Fleet Management Software
- Best POS Systems
- Best Employee Monitoring Software
- Best Document Management Software
- Verizon Connect Fleet GPS Review
- Zoom Review
- Samsara Review
- Zoho CRM Review
- Technology Solutions
Business Basics
- 4 Simple Steps to Valuing Your Small Business
- How to Write a Business Growth Plan
- 12 Business Skills You Need to Master
- How to Start a One-Person Business
- FreshBooks vs. QuickBooks Comparison
- Salesforce CRM vs. Zoho CRM
- RingCentral vs. Zoom Comparison
- 10 Ways to Generate More Sales Leads
Business.com aims to help business owners make informed decisions to support and grow their companies. We research and recommend products and services suitable for various business types, investing thousands of hours each year in this process.
As a business, we need to generate revenue to sustain our content. We have financial relationships with some companies we cover, earning commissions when readers purchase from our partners or share information about their needs. These relationships do not dictate our advice and recommendations. Our editorial team independently evaluates and recommends products and services based on their research and expertise. Learn more about our process and partners here .
Your Guide to Creating a Small Business Marketing Plan
Follow these templates and guidelines to get started on your business's marketing plan.


Table of Contents
To have a successful business, you need a well-thought-out marketing plan to promote your products or services. Although making a few social media posts or blasting a few promotional emails may seem simple enough, disjointed marketing efforts not only confuse your target audience, but can ultimately harm your business.
What is a marketing plan?
A marketing plan is a strategic road map for how you communicate (online and offline) with your target audience to successfully promote your products or services. Depending on your goal, marketing plans can be extremely basic or highly detailed.
According to Molly Maple Bryant, vice president of marketing at Vibrent Health, a marketing plan is not simply a list of things you want to accomplish. Instead, it should list the outcomes you seek — measurable and contextual, like the pipeline you’re developing, or leads you’re generating — and it should explain the high-level strategies you will use to achieve those outcomes. Developing strategies can be complicated, but they make a major difference in keeping you on track and avoiding diversions, also called scope creep .
“Once you have an agreed-upon plan, you are able to compare any incoming requests against your strategies to determine ‘Yes, this adheres to my strategy so we can add it,’ or ‘No, this sounds good in theory, but it doesn’t adhere to our agreed-upon strategy, so we won’t adjust resources,'” Bryant told us.
Types of marketing plans
There are several different types of marketing plans you can use based on certain strategies that make sense for your organization. Your business will likely need a combination of the following marketing plans to create an effective, comprehensive marketing strategy:
- Advertising plan
- Branding plan
- Content marketing plan
- Customer acquisition plan
- Direct marketing plan
- Email marketing plan
- Public relation plan
- Print marketing plan
- Reputation management plan
- Retention plan
- Search engine optimization plan
- Social media marketing plan
Why is it important to have a marketing plan for your business?
A marketing plan is a crucial resource for any small business because it helps you identify the market needs your product or service meets, how your product is different from competitors, and who your product or service is for. Marketing plans also serve as a road map for your sales strategy, branding direction and building your overall business. This is important for successfully conveying your brand messaging to your target audience .
Another significant benefit of a marketing plan for your company is that rather than simply guessing metrics, it forces you to sit down and do the math about your business goals and how to realistically fulfill them. When you look at your growth outcomes, you can delve further to determine what it will take to get to those numbers.
Bryant offered the following example: “Need $100,000 in revenue? How many sales is that? If 10, what’s your close rate? Let’s say 10 percent from lead to closed deal. Now you have a metric to start with — to get to 10 sales, we need 100 leads. Where will they come from, and what strategies will you use? The plan helps you put it all on paper so you can map out resources and tactics later with a lot of preparation and realism,” said Bryant.
When analyzing outcomes and resources, you can save time and avoid scope creep by focusing only on strategies that are relevant to your marketing plan. A marketing plan helps you think realistically about your strategies, gets your stakeholders on the same page, and holds your marketing team accountable for their decisions.
“When everyone’s tasks and goals are laid out for the stakeholders and company partners to see, it is much easier for the entire team to feel at ease about reaching sales goals and allowing the marketing team the space and freedom needed to execute work without constant supervision,” said Cassady Dill, digital marketing consultant and owner of Ethos Agency.
Additionally, Dill said a marketing plan should be easily understood by your entire team, executives and outside departments. Your plan should also serve as an easy guide for future marketing managers and team members to understand and implement.
What are the key elements of an effective business marketing plan?
A marketing plan should be customized to fit your business; however, Dill said, all marketing plans contain five essential functions:
- Your business goals
- Key metrics (how you quantify and measure success)
- Strategies (an overview of implementation and how that will achieve goals)
- A plan (the details of execution and the human resources, departments and software that will be involved)
- Reporting (what reports of progress will include and/or look like)
We broke down those five functions into 10 actionable categories to help you create a marketing plan that is unique and effective for your business.
1. Executive summary
The executive summary is a great place to give the reader of your plan an overview of your business’s mission or goals, as well as the marketing strategy you’re looking to employ. An executive summary is often written after you’ve completed the rest of the marketing plan, to ensure it covers all the important elements of your plan. If the executive summary is the only part of your marketing plan that someone reads (which is highly possible), you want to be sure they understand the most crucial details.
2. Mission statement
The mission statement , not to be confused with a vision statement, is a statement that encompasses your company’s values and how they relate to your overall goals as an organization. Here are some good questions to get you thinking:
- What does your company do today?
- What’s important to your company?
- What would your company like to do in the future?
- What is your brand identity?
- What’s your culture like ?
- How does your company benefit customers, employees and stakeholders?
3. Target markets
Identifying your target market is one of the most important parts of your marketing plan. Without a defined target audience, your marketing expenses will be wasted. Think of it like this: Some people need your service or product but don’t know it exists yet. Who are those people?
Here are some other questions to help you brainstorm your target market :
- What is the demographic of your customers (gender, age, income, education, etc.)?
- What are their needs and interests?
- What’s their psychographic profile (attitudes, philosophies, values, lifestyle, etc.)?
- How do they behave?
- What are some existing products they use?
4. Products and services
In this section, don’t just list what your product or service is. Think critically about what you have to offer your customers and what that value proposition means to them.
- What do you make or provide for customers?
- What are your customers’ needs?
- How does your product or service fulfill customers’ needs?
- What value do you add to your customers’ lives?
- What type of product or service are you offering?
5. Distribution channels
At this point in your report, you should transition your thinking into actual marketing theory and practices. Distribution channels are the avenues you’ll use to reach a prospective customer or business . Think of all current and potential sales channels on which your specific target audience is active. One distribution channel that works great for one organization may be useless to another. For example, one company may host their website for free on a site like HubSpot and solely rely on that as their sales channel, while another company may have a whole team of people using Pinterest to drive sales. [Learn how CRM systems can help track your marketing leads based on various distribution channels.]
Examples of sales channels include the following:
- Mobile text message marketing
- Social media
- Print (newspapers, magazines, brochures, catalogs, direct mail)
- Broadcast (TV, radio)
- Press releases
- Trade shows, product demonstrations, event marketing
6. Competitive profile
One of the major aspects of your marketing plan is developing your unique selling proposition (USP). A USP is a feature or stance that separates your product or service from competitors. Finding your USP is all about differentiation and distinguishing your company as a sole proprietor of one type of good or service. Conduct a competitive analysis to identify your competitive profile and how you stack up against the competition. It is important to remain unbiased when conducting this analysis.
Here are some ideas to consider:
- What’s your USP?
- Who are your competitors? What do they offer?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of your competition?
- What needs of the market (or customer) are not being served? What can you do to meet those needs?
7. A pricing strategy
Consider pricing when drafting your marketing plan. Developing the right pricing strategy helps you better market your product. Think about your current and projected finances when developing a long-term marketing strategy that is realistic and beneficial for your business. Here are some key questions to ask yourself about your pricing:
- What are reasonable margins to make a profit and cover production costs?
- Is there a market for products or services at your projected price point?
- Are you willing to sacrifice profit margins in return for a greater market share?
- What are your marketing and distribution costs?
8. Objectives
Consider your objectives when developing a marketing plan. This aspect of your plan should involve specific goals related to market penetration and revenue targets. Be sure to keep your marketing objectives on-brand with your business. Here are some things to consider:
- Sales quotas
- Number of new customers gained
- Customer retention percentages
- Revenue targets
- Market penetration
- Brand awareness
- Website traffic
9. Action plans
With all of the above items outlined, determine what steps need to be taken to enact your marketing plan. This includes determining the proper steps, setting goals, breaking down responsibilities, and establishing an overall timeline.
It’s also important to brainstorm potential roadblocks your business could face and some solutions to overcome them. Your research is useless if you don’t have an actionable plan that can be realistically implemented to carry out your ideas.
10. Financial projections
This last step allows you to establish a realistic marketing budget and better understand your marketing plan from a cost perspective. In addition to setting a budget, consider the overall return on investment as well. Here are some other financial projections to consider:
- Cost of implementation
- Cost to produce product or service
- Existing and projected cash flow
- Projected sales
- Desired profit margin on projected sales
What is a template for creating a successful marketing plan?
The internet is full of useful tools, including paid and free marketing plan templates, to help you build a successful marketing plan .
Whether you are looking for a free template generator to build a new marketing plan or a benchmarking tool to evaluate your current strategies, several great resources are available. Keep in mind that the best marketing plan for your business will be a customized one.
“Ultimately, you should design a marketing plan that best serves the needs of your team as you see fit,” said Dill. “Don’t force yourself into a plan that doesn’t fit your team. Use templates to shorten the workload time, but then adjust it for a more custom plan.”
Here are some tools and templates to get you started:
- Free marketing plan template : business.com has developed a free template that is fully customizable based on the needs of your business. Each section provides in-depth explanations, examples and resources to help you create an impressive marketing plan.
- Smart Insights: In addition to offering marketing plan templates, some companies, like Smart Insights, offer marketing benchmarking templates to help you evaluate your strategy performance. These are accessible with a free Smart Insights membership.
- GERU: Similarly, GERU offers a funnel-planning, profit-prediction and simulation tool to help you assess mock business ideas and simulations. This can help you identify weak points in your marketing strategy that need improvement. Although GERU requires users to sign up for a paid account, you can access a free trial to test it out.
What mistakes should you avoid when creating your marketing plan?
When creating an effective marketing plan, you need to avoid falling for common missteps and mistakes. For starters, failing to identify any of the 10 actionable categories above is an obvious mistake.
Here are some other key mistakes to avoid:
- Setting unrealistic budgets: Underestimating the costs of marketing activities or setting an unrealistic budget can limit your ability to execute your plan effectively. Marketing can be expensive, so it’s important to fully understand the estimated cost and budget before building a marketing strategy that you can’t afford.
- Focusing on quantity over quality: “More” doesn’t always mean “better” if you are posting on irrelevant marketing channels or your efforts are bringing in unqualified leads. Prioritizing the quantity of marketing activities over their quality can lead to superficial engagement and a lack of meaningful results.
- Not testing campaigns: Launching large campaigns without testing can lead to wasted resources if the messaging or tactics don’t resonate as expected. Test out your new campaigns to ensure they achieve your intended goal.
- Ignoring customer feedback: You may be tempted to ignore negative feedback, but disregarding customer comments and failing to address their concerns can lead to negative perceptions of your brand. Instead, use customer feedback to your advantage to improve your product and marketing efforts.
- Overpromising and underdelivering: Setting unrealistic expectations in your marketing messages that your products or services can’t fulfill can damage your brand’s reputation.
- Ignoring seasonality and trends: Failing to account for seasonal trends and market changes can result in missed opportunities for timely marketing efforts.
- Not reviewing and updating your plan: A rigid marketing plan that doesn’t allow for adjustments in response to market feedback and changing conditions can hinder your success. A marketing plan should be a living document that is regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the market and your business’s goals.
Avoiding these mistakes and missteps can help you create a more effective and successful marketing plan that drives results for your business.
How can you take action with your new marketing plan?
Before you dive into marketing plan templates, it’s important to understand how to think about a marketing plan.
A good marketing plan targets who your buyers are, establishes the service or product you are offering, and determines your unique selling proposition. From here, you will tackle the marketing planning process and develop the best way to get your product in front of buyers who want your product or service.
Dill created a simple four-step process for how small businesses can take action with creating a marketing plan.
- The first step is to hold a marketing meeting with all the marketing team and executives or stakeholders. This gives them time to offer questions, concerns and criticisms you haven’t thought of so you can go back to the board room and revise your strategy or plan.
- Next, add a timeline to all your tasks and assign team members and all the help you’ll need to execute that plan.
- Once your plan is in action, hold weekly check-ins in person or by email to keep everyone on track.
- Share a weekly progress report with all parties involved and execs to ensure you are moving in the right direction.
In addition to drafting your own plan, you can work with a digital marketing agency or use internet marketing and pay-per-click management services to leverage your online presence.
Once you’ve established a general road map, update it annually. Developing an evolving marketing plan sets your business up for continued success because it allows you to prepare for the unexpected and establish a connection between your brand and your audience.
Matt D’Angelo contributed to this article. Source interviews were conducted for a previous version of this article.

Get Weekly 5-Minute Business Advice
B. newsletter is your digest of bite-sized news, thought & brand leadership, and entertainment. All in one email.
Our mission is to help you take your team, your business and your career to the next level. Whether you're here for product recommendations, research or career advice, we're happy you're here!

- Join the AMA
- Find learning by topic
- Free learning resources for members
- Credentialed Learning
- Training for teams
- Why learn with the AMA?
- Marketing News
- Academic Journals
- Guides & eBooks
- Marketing Job Board
- Academic Job Board
- AMA Foundation
- Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
- Collegiate Resources
- Awards and Scholarships
- Sponsorship Opportunities
- Strategic Partnerships
We noticed that you are using Internet Explorer 11 or older that is not support any longer. Please consider using an alternative such as Microsoft Edge, Chrome, or Firefox.
![What is a Marketing Plan & How To Write One? [Easy Guide] What is a Marketing Plan & How To Write One? [Easy Guide]](https://www.ama.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/marketing-plan-2.jpeg?resize=1360%2C550)
What is a Marketing Plan & How To Write One? [Easy Guide]

What is a Marketing Plan?
A marketing plan is a strategic guide that helps businesses map out their advertising and promotional strategies to attract prospective customers and connect with their intended audience. It offers clear and detailed direction on how to achieve business objectives through targeted marketing efforts.
Marketing Plan vs. Business Plan
Understanding the distinction between a marketing plan and a business plan is crucial for any organization aiming to navigate the complexities of strategic planning and resource allocation.
- Marketing Plan: This is a focused document dedicated to the marketing segment of an organization’s strategy. It meticulously outlines the marketing objectives, strategies, and tactics that will be employed to achieve the desired market presence and customer engagement.
- Business Plan: A business plan has a broader scope, encompassing every facet of the company’s operations. While it includes marketing, it also delves into finance, operations, human resources, and more, providing a comprehensive overview of the entire business.
Marketing Strategy vs. Marketing Plan
Differentiating between a marketing strategy and a marketing plan is essential for implementing effective marketing operations within a business. These two elements, while closely related, serve distinct functions in the marketing process.
- Marketing Strategy: This aspect defines the overarching approach and long-term vision for a company’s engagement in the market. Each element of the marketing strategy is designed to align with the company’s top-level goals and contribute to realizing its vision statement. In essence, the marketing strategy answers the “what” and “why” behind a company’s marketing efforts, outlining what the company aims to achieve and why those goals are important.
- Marketing Plan: In contrast, the marketing plan focuses on the “how” of reaching strategic objectives. It is a practical document that outlines specific actions, timelines, and resources required to execute the marketing strategy. It details the campaigns, channels, tools, and tactics that will be used to achieve the strategic goals outlined in the marketing strategy.

3 Hours | 25 Modules | Beginner
Modern Marketing: Strategy and Execution
Learn from Inc. Magazine’s prize-winning editorial content about the basic concepts of digital marketing, including targeting, value proposition, and more.
Types of Marketing Plans
Marketing plans vary depending on their focus, scope, and objectives. Understanding the different types of plans is crucial for businesses aiming to target their marketing efforts and resources effectively. Here are some of the key types:
- Go-to-market/Product Launch: This plan is specifically designed to introduce a new product. It outlines the target audience, market entry strategy, and advertising tactics to be employed.
- Social Media : A social media plan is tailored to the unique dynamics of social media platforms. It details the advertising strategies to be used on these platforms, focusing on engaging with users and leveraging specific features to maximize reach and impact.
- General Marketing Strategic Plan / Annual Marketing Plan: This comprehensive plan covers a company’s overall marketing activities for the entire year. It encompasses various marketing efforts and campaigns, outlining a cohesive strategy that supports the company’s annual goals.
- Content Marketing Plan : Focused on content creation and distribution, this plan outlines the strategies, campaigns, and tactics for using content to achieve business objectives. It details how different types of content (blog posts, videos, infographics) will be used to attract and engage the target audience.
- SEO Marketing Plan: Dedicated to search engine optimization, this plan outlines the strategies and actions to improve a website’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs). It focuses on keyword research, content optimization, link building, and other tactics to drive organic traffic to the website.
Benefits of a Marketing Plan
Having a structured plan is invaluable. It acts as a strategic roadmap, guiding businesses toward achieving their goals through well-organized and monitored marketing activities.
Here are five important benefits of creating a marketing plan:
- Goal Setting: It allows your business to define clear marketing objectives and set measurable targets. This facilitates focused efforts toward lead generation, sales increase, market share expansion, brand awareness, and customer acquisition.
- Strategic Direction: The plan provides a detailed outline of your promotional strategy, helping identify the target audience, their preferences, and the best methods to reach and engage them effectively.
- Competitive Advantage: A plan helps you articulate and leverage your unique selling proposition (USP), ensuring you stand out in the market and secure a competitive edge.
- Consistency and Integration: The plan fosters consistency and integration in marketing efforts, ensuring a unified brand message and customer experience across all marketing channels and touchpoints,
- Long-term Sustainability: A comprehensive plan not only focuses on immediate goals but also lays the groundwork for sustained growth and adaptability to market evolution, customer demands, and emerging trends.
How To Write a Marketing Plan
- Create a mission statement
The foundation of any effective marketing plan begins with a clear and concise mission statement. This crucial step sets the stage for all subsequent planning by articulating the core purpose and direction of your company’s marketing efforts. A mission statement serves as a compass, guiding your marketing strategies and ensuring they align with your organization’s broader goals.
Developing a mission statement is more than just a formality; it’s a strategic exercise that clarifies your marketing vision and sets a purposeful path for your team. With a compelling mission statement in place, you can craft a plan that resonates with your audience and drives your business toward its long-term objectives.
- Set your goals/KPIs
Establishing clear goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) is a pivotal step in crafting a marketing plan that aligns with your company’s value proposition and ensures measurable success. This stage involves setting financial and non-financial objectives to guide your marketing efforts and evaluate their effectiveness.
Marketers who set specific goals are significantly more likely to report success. By defining financial and non-financial objectives, you create a comprehensive framework for guiding your marketing strategies. This dual focus not only drives economic value but also fosters qualitative improvements in your marketing efforts, ensuring a balanced approach to achieving your company’s vision.
- Identify Your Target Market
Pinpointing your target market is a crucial step in any marketing plan. Understanding who your product or service is for and why forms the backbone of your marketing efforts and influences decisions on marketing channels, content creation, and overall outreach strategies.
A key outcome of market research is the development of buyer personas. These semi-fictional representations of your ideal customers are crafted based on real data and insights about your existing clientele. Buyer personas detail your target market’s characteristics, needs, and motivations, offering a detailed profile that guides your marketing strategies.
- Conduct Competitive Analysis
Conducting a competitive analysis is integral to crafting a robust marketing plan. This process involves identifying your main competitors, understanding their strategies, and evaluating how your business can establish a distinctive and superior position in your niche. Through this analysis, you’ll gain insights into the competitive landscape, helping you to leverage your own strengths and identify areas for improvement.
Understanding both the internal and external factors that influence your market positioning is crucial. They include:
- Internal factors: Examine what could impact your competitive advantage, such as your team’s expertise, proprietary technology, or customer service practices.
- External factors: Look beyond your immediate competitive environment to broader market conditions that could affect your position. This includes economic trends, regulatory changes, and technological advancements.
- Economic considerations: Assess how the current economic climate might influence consumer purchasing behavior and, consequently, your market strategy.
- Sociological trends: Understand shifting societal values, lifestyles, and consumer behaviors and how they offer new market opportunities.
- Industry trends: Keep an eye on overarching trends within your industry, including emerging technologies, shifts in consumer preferences, and new regulatory frameworks.
- Set Your Budget
Your marketing budget is the planned amount of money you’ll spend to achieve your marketing goal. Knowing the financial resources you have available for marketing activities allows you to craft a plan that maximizes impact while maintaining fiscal responsibility. This financial foresight prevents overspending and ensures that every dollar spent contributes to achieving your marketing objectives.
This overview should include all sources of funding and any constraints or stipulations attached to them. Having a comprehensive understanding of your financial resources sets the groundwork for all subsequent planning and decision-making.
- Execute your Plan
Execution involves the detailed scheduling of marketing activities, assigning responsibilities to team members, and setting deadlines that align with the marketing plan’s timelines. It’s about bringing the plan to life through a series of coordinated efforts, from launching advertising campaigns to engaging with customers on social media platforms. This phase is where the theoretical aspects of the plan, such as target audience engagement and brand messaging, are put into practice through concrete actions like content creation, digital marketing, and promotional events.
In conclusion, a well-crafted marketing plan is the linchpin of successful marketing efforts, offering a strategic blueprint that guides businesses through the intricate landscape of market engagement and customer interaction. From the initial stages of understanding the marketing plan’s scope and its relationship with the overarching business strategy to the detailed planning and execution of marketing activities, each step is vital in steering an organization toward its desired market position.
By continuing to use this site, you accept the use of cookies, pixels and other technology that allows us to understand our users better and offer you tailored content. You can learn more about our privacy policy here

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

How to Write the Marketing Plan in Business Plan?
A marketing plan in business plan is one of the very important sections of a business plan. Marketing is done to spread awareness about your business and its product/service.
An effective marketing strategy helps you achieve early success.
Use this article to write an effective marketing plan section in a business plan.
What is a marketing plan?
A marketing section of a business plan gives you a roadmap to organize, execute and track the progress of your marketing efforts.
Your marketing plan helps you align your marketing efforts with your business goals. It gives your marketing effort a direction and you can evaluate your efforts at any point.
Types of marketing plan
A perfect type of marketing plan in business plan will depend on your business, your goals, and how soon you want to achieve them.
We have outlined some marketing plans that most businesses need to use. Since this is the age of the internet, we have also included online marketing plans and digital marketing plans.
Want to write a business plan?
Hire our professional business plan writers to prepare your business plan!
Quarterly or Annual Marketing Plans
These are your business marketing plans with a timeline. Every business has its quarterly, bi-yearly, and yearly goals. You will use these goals to monitor the effectiveness of your marketing efforts over time.
Paid Marketing Plans
Paid marketing plans include online advertising, buying billboards, or marketing on vehicles. Pay Per Click marketing and social media marketing for your small business.
Social Media Marketing Plan
Social media marketing plan for business plan can be done in two ways. You can hire a team and raise awareness about your business by sharing regular updates.
You can also do paid marketing on social media. You will need to invest in buying ads on that social media platform and pay for a team of social media marketers.
You can also leverage these effective digital marketing channels for your business.
Content Marketing Plan
A content marketing plan is about attracting potential customers to your website with the help of SEO. You create value for your potential customer first and then by extension, market your business. It can be offline in the form of free workshops etc or online in the form of guides and resources.
Product Launch Marketing Plan
A product lunch sales and marketing plan in business plan will help you decide on the marketing tools, tactics, and tracking you will do when launching a new product or service.
You can also hire WiseBusinessPlans Digital Marketing Services to run successful marketing campaigns for your business.
Marketing Plan vs Marketing Strategy
The difference between a marketing plan and a marketing strategy is simple; a marketing plan is what methods, tools, and tactics you will use for marketing, and a market strategy in business plan is how you will implement your plan.
Learn how to develop an effective marketing strategy with this detailed guide.
Access our free business plan examples now!
How to write a marketing plan for a business plan.

Follow these simple steps to write a marketing plan in business plan.
Business Mission
Write your business mission statement and translate it into the efforts the marketing department will make.
For example, your business mission is to help people with home gardening. Your marketing department version will be to attract people who want to do home gardening.
These are performance indicators. These metrics will help you evaluate performance and progress. An example of KPIs for marketing is customer visits to your website, social media page, or brick-and-mortar store.
Create Buyer Personas
A buyer persona is a short description of your average customer. When you have no data, a buyer persona will describe the customer you want to attract.
Decide on Marketing Strategies and Content
Go through the marketing strategies you can use and select the one that will produce the best return on investment for your business.
Similarly, think about the content type that is attractive to your target audience . For example, video format may attract your audience or you may need to share more about your business on social media to grab their attention.
Define Marketing Plan Scope
Define the scope and limits of your marketing plan. Clearly mention what your marketing team will do and will not do.
This will help you save time, cost, and effort in wasted resources.
Set Marketing Budget
You can only spend a set amount on marketing. Set your marketing budget and be creative in that budget to produce the best return.
Your budget is directly related to your marketing goals. Set your marketing budget in a way that does not hamper marketing efforts.
Know your Competition
Knowing and profiling your customer helps you market better. See what are strong spots of competitors’ marketing plans, are and how they are attracting audiences to make a plan to compete effectively.
Appoint your Team & their Responsibilities
Decide on job roles for your team. Set their KPIs, marketing channels they will manage, what content they will create, etc.
Bonus Tip: Here is a step by step guide on how to write a marketing plan executive summary with example and template.
Example of Marketing Plan in Business Plan PDF
See this example of a marketing plan in a business plan to understand how it is done. You can create your marketing plan in the same way.
In the marketing plan section, include details about your target market, competition analysis, marketing strategies, pricing, promotion, and distribution channels. It should outline your approach to reaching and engaging your target audience.
Conduct market research by analyzing your target audience, understanding their needs and preferences, studying your competitors, and identifying market trends. Use surveys, interviews, and industry reports to gather relevant data for your marketing plan.
Consider including a mix of marketing strategies such as digital marketing, social media marketing, content marketing, email marketing, advertising, public relations, and networking. Choose strategies that align with your target audience and business goals.
Determine pricing by considering factors such as production costs, competitor pricing, market demand, and perceived value. Conduct a pricing analysis to ensure your prices are competitive and profitable for your business.
It is recommended to review and update your marketing plan regularly, at least annually or whenever there are significant changes in your business or market conditions. This allows you to adapt your strategies, stay relevant, and capitalize on new opportunities.
WiseBusinessPlans is the company that writes business plans
Quick links.

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Marketing Plan?
Understanding marketing plans, how to write a marketing plan, marketing plan vs. business plan.
- Marketing Plan FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Marketing Essentials
What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
James Chen, CMT is an expert trader, investment adviser, and global market strategist.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/photo__james_chen-5bfc26144cedfd0026c00af8.jpeg)
Pete Rathburn is a copy editor and fact-checker with expertise in economics and personal finance and over twenty years of experience in the classroom.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/E7F37E3D-4C78-4BDA-9393-6F3C581602EB-2c2c94499d514e079e915307db536454.jpeg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
Investopedia / Zoe Hansen
A marketing plan is an operational document that outlines an advertising strategy that an organization will implement to generate leads and reach its target market . It details the outreach and PR campaigns to be undertaken and for how long, as well as the ways in which the company will measure the effect of these initiatives. It reflects a company’s overall marketing strategy.
Key Takeaways
- The marketing plan details the strategy that a company will use to market its products to customers.
- The plan identifies the target market, value proposition of the brand or product, campaigns to be initiated, and metrics to be used to assess the effectiveness of marketing initiatives.
- The marketing plan should be adjusted on an ongoing basis based on which efforts are having an impact and which are not.
- Digital marketing shows results almost in real time, whereas TV ads require rotation to realize any level of market penetration.
- A marketing plan is part of a business plan, which describes all of the important aspects of a business, such as its goals, values, mission statement, budget, and strategies.
The terms “marketing plan” and “marketing strategy” are often used interchangeably because the former is developed based on an overarching strategic framework. In some cases the strategy and the plan may be incorporated into one document, particularly for smaller companies that may only run one or two major campaigns in a year. The plan outlines marketing activities on a monthly, a quarterly, or an annual basis, while the strategy delineates the overall value proposition .
The components of a marketing plan include:
- Market research – This provides information to support pricing decisions and new market entries.
- Tailored messaging – This involves targeting certain demographics and geographic areas and can include the use of affiliate marketing with third-party publishers who bring customers to the table.
- Platform selection – This looks at the best vehicles for disseminating product information for each advertising campaign: traditional venues such as radio, TV, newspapers, and commercial and trade magazines; digital methods such as websites, online ads, search engine results, informational videos, social media groups (Facebook, YouTube, etc.), email, and text messages; or any mix of these platforms.
- Performance metrics – Metrics accurately assess the results of marketing efforts and their reporting timelines and are crucial to the success of the plan.
The four most important social media networks in 2023 for global marketers were, in descending order, Facebook, Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok.
Types of Marketing Plans
There are a variety of marketing plans that suit different businesses and their needs. These include:
- Product Launch – A product-launch marketing plan outlines how a new product will enter the market, the audience it will target, and the advertising methods used.
- Social Media – A social media marketing plan focuses on the advertising strategies on different social media platforms and how to engage with their users.
- Time Based – Time-based marketing plans, such as those that are executed quarterly or annually, focus on the time of the year, the current condition of the business, and the best strategies in that period.
- Content Based – A content-based marketing plan looks in detail at what kinds of content (blogs, videos, graphics, etc.) will reach the target audience.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) – An SEO marketing plan is all about getting the most hits online. It involves keyword research, content optimization, link building, and more, all with the goal of drawing customers to your website.
Mission and Value Proposition
The mission and value proposition is a statement that articulates the value that a product or brand will deliver to a customer. It should appear front and center on the company website and any branding materials.
The value proposition should delineate how a product or brand solves the customer’s problem, the benefits of the product or brand, and why the customer should buy from this company and not another. The marketing plan is based on it.
Set Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Establishing your key performance indicators (KPIs) will allow you to measure the success of your marketing plan in relation to your company’s value proposition. In other words, they track the effectiveness of your marketing strategy. For example, if your goal is to engage with a certain demographic in a certain region, you can track social media impressions and website visits.
There are a number of KPIs that help you measure success including the search engine ranking, click-through rate, cost per click, return on investment (ROI), and conversion rates, which tracks the percentages of visitors to your website that make a specific action such as buying a product or becoming a newsletter subscriber.
In 2023, Facebook and Instagram were tied for having the highest ROI across social media platforms for global marketers, while YouTube fell next in line.
Identify Your Target Market
The marketing plan identifies the target market for a product or brand. Market research is often the basis for a target market and marketing channel decisions. For example, whether the company will advertise via social media, online ads, or regional TV.
Knowing to whom you want to sell and why is an extremely critical component of any business plan. It allows you to focus your business and measure its success. Different demographics have different tastes and needs; knowing your target market will help you market to them.
Strategy and Execution
The marketing plan includes the rationale for these decisions. The plan should focus on the creation, timing, scheduling, and placement of specific campaigns and include the metrics that will measure the outcomes of your marketing efforts. For example, will you advertise on social media or TV? What time will you schedule your marketing if they are through email newsletters? The strategy may include flighting scheduling , which includes the times when you can make the most of your advertising dollars.
Set Your Budget
A marketing plan costs money. Setting a budget will allow you to create a workable plan, prevent runaway costs, and properly allocate your funds.
Adjust Your Plan
A marketing plan can be adjusted at any point based on the results from its metrics. If digital ads are performing better than expected, for example, the budget for a campaign can be adjusted to fund a higher-performing platform, or the company can initiate a new budget. The challenge for marketing leaders is to ensure that every platform has sufficient time to show results.
Without the correct metrics to assess the impact of outreach and marketing efforts, an organization will not know which campaigns to repeat and which to drop. In short, maintaining ineffective initiatives wastes money.
Digital marketing shows results almost immediately, whereas TV ads require rotation to realize any level of market penetration. In the traditional marketing mix model, a marketing plan would fall under the category of “promotion,” which is one of the “ four Ps ,” a term coined by Neil Borden to describe the marketing mix of product, price, promotion, and place.
A business plan is a roadmap that details how a business will operate and function in its entirety. It should cover the goals, missions , values, financials, and strategies that the business will use in day-to-day operations and the achievement of its objectives. Among its many elements are an executive summary, the products and services sold, a marketing analysis, a marketing strategy, financial planning, and a budget .
As mentioned, a business plan should include a marketing plan, which focuses on creating a strategy for creating awareness of the company’s product or service, reaching the target market, and generating sales.
Example of a Marketing Plan
Consider the following marketing plan framework that is designed to help direct marketing objectives:
- Executive Summary: Describes company mission, key executives, and where it is headquartered.
- SWOT Analysis: Describes strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for the company. This helps you define how to build on your strengths and how to find ways to improve on your weaknesses. It also helps a company analyze their competitors and how they may achieve an advantage based on their unique value proposition.
- Business Initiatives: Outlines the goals of the marketing plan, such as the number of impressions, Google rankings, or email subscribers.
- Customer Analysis: Describes your target market and audience characteristics based on market research. These may include age, pain points, and location, among other variables.
- Competitor Analysis: Outlines the companies providing similar goods or services to your target audience. In addition, it describes their strengths, market share, pricing structure, and most importantly where your company can fill an important gap.
What Is a Marketing Plan Template?
A marketing plan template is a guide for writing a marketing plan. It contains all the important elements needed to create one, including its goals and KPIs, marketing channels, budget, content type, teams involved, and design.
What Is an Executive Summary in a Marketing Plan?
The executive summary is a nutshell description of the marketing plan. It should contain the key findings of the market research, the company’s objectives and marketing goals, an overview of the marketing trends, the description of the product or service being marketed, information on the target market, and the plan budget.
What Is a Top-Down Marketing Strategy?
A top-down marketing strategy is a traditional one, in which a business decides how best to sell its product or brand, and customers are then spurred to take action through advertisements, generally found on radio and/or television. It is usually determined by company executives, which is then communicated with management to delegate to employees. These employees then develop tactics to meet the strategy's objectives.
What Is a Bottom-Up Marketing Strategy?
In comparison to a traditional top-down marketing strategy, a bottom-up strategy begins with employees who formulate marketing tactics based on their analysis of customer preferences and needs. This then may lead to collaboration with other employees to develop a concrete marketing plan, which is sent to executives for review.
Today’s consumer wants to relate to a product or service in a meaningful way, and a bottom-up marketing strategy seeks to achieve this through customer-centric tactics.
How Much Does a Marketing Plan Cost?
The cost of a marketing plan will vary based on the company, the plan’s complexity, and the length of the overall strategy. In 2023, marketing costs made up 10.1% of corporate revenues on average. The consumer packaged goods sector spent the most, at 18.5% of revenues while the mining and construction sector spent the least, at 1% of revenues.
A separate analysis shows that the cost can range anywhere from $10,000 to over $40,000 for a marketing plan.
A marketing plan is the advertising strategy that a business implements to sell its product or service. It determines the target market, how best to reach it, at what price point the product or service should be sold, and how the company will measure its efforts.
Constantly monitoring and adjusting a market plan is an important part of running a business, as it shows the most effective ways to generate sales. As the consumer landscape evolves, it is important for businesses to adapt in order to meet customer needs and better achieve their marketing objectives.
Statista. " Marketing Worldwide – Statistics and Facts ."
American Marketing Association. " What Is a Marketing Plan and How to Write One? [Easy Guide] ."
HubSpot. " The 2024 State of Marketing & Trends Report: Data from 1400+ Global Marketers ."
Deloitte. " The CMO Survey: Managing Marketing Technology, Growth and Sustainability ." Page 16.
Laire. " How Much Does a Marketing Plan Cost? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Marketing-Strategy-20dd671d870c4f1db1c9166de9e44e27.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
Marketing Plan
A document that lays out the marketing efforts of a business in an upcoming period
What is a Marketing Plan?
A marketing plan is a document that lays out the marketing efforts of a business in an upcoming period, which is usually a year. It outlines the marketing strategy, promotional, and advertising activities planned for the period.

Elements of a Marketing Plan
A marketing plan will typically include the following elements:
Marketing objectives of the business : The objectives should be attainable and measurable – two goals associated with SMART, which stands for Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
Current business marketing positioning : An analysis of the current state of the organization concerning its marketing positioning.
Market research : Detailed research about current market trends, customer needs, industry sales volumes, and expected direction.
Outline of the business target market : Business target market demographics.
Marketing activities : A list of any actions concerning marketing goals that are scheduled for the period and the indicated timelines.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) to be tracked
Marketing mix : A combination of factors that may influence customers to purchase products. It should be appropriate for the organization and will largely be centered on the 4Ps of marketing – i.e., product, price, promotion, and place.
Competition : Identify the organization’s competitors and their strategies, along with ways to counter competition and gain market share .
Marketing strategies : The development of marketing strategies to be employed in the coming period. These strategies will include promotional strategies, advertising, and other marketing tools at the disposal of the organization.
Marketing budget : A detailed outline of the organization’s allocation of financial resources to marketing activities. The activities will need to be carried out within the marketing budget .
Monitoring and performance mechanism : A plan should be in place to identify if the marketing tools in place are bearing fruit or need to be revised based on the past, current, and expected future state of the organization, industry, and the overall business environment.
A marketing plan should observe the 80:20 rule – i.e., for maximum impact, it should focus on the 20% of products and services that account for 80% of volumes and the 20% of customers that bring in 80% of revenue.
Purpose of a Marketing Plan
The purpose of a marketing plan includes the following:
- To clearly define the marketing objectives of the business that align with the corporate mission and vision of the organization. The marketing objectives indicate where the organization wishes to be at any specific period in the future.
- The marketing plan usually assists in the growth of the business by stating appropriate marketing strategies, such as plans for increasing the customer base.
- State and review the marketing mix in terms of the 8Ps of marketing – Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, Physical Evidence, and Performance.
- Strategies to increase market share, enter new niche markets, and increase brand awareness are also encompassed within the marketing plan.
- The marketing plan will contain a detailed budget for the funds and resources required to carry out activities indicated in the marketing plan.
- The assignment of tasks and responsibilities of marketing activities is well enunciated in the marketing plan.
- The identification of business opportunities and any strategies crafted to exploit them is important.
- A marketing plan fosters the review and analysis of the marketing environment, which entails market research, customer needs assessment, competitor analysis, PEST analysis , studying new business trends, and continuous environmental scanning.
- A marketing plan integrates business functions to operate with consistency – notably sales, production, finance, human resources, and marketing.
Structure of a Marketing Plan
The structure of a marketing plan can include the following sections:
Marketing Plan Objectives
This section outlines the expected outcome of the marketing plan with clear, concise, realistic, and attainable objectives. It contains specific targets and time frames.
Metrics, such as target market share, the target number of customers to be attained, penetration rate, usage rate, sales volumes targeted, etc. should be used.
Market Research – Market Analysis/Consumer Analysis
Market analysis includes topics such as market definition, market size, industry structure, market share and trends, and competitor analysis. Consumer analysis includes the target market demographics and what influences their buying decisions – e.g., loyalty, motivation, and expectations.
Target Market
This defines the target customers by their demographic profile, such as gender, race, age, and psychographic profile, such as their interests. This will assist in the correct marketing mix for the target market segments.
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis will look at the organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats. SWOT analysis includes the following:
- Strengths are the organization’s competitive advantages that are not easily duplicated. They represent the skills, expertise, and efficiencies that an organization possesses over its competitors.
- Weaknesses are impediments found in the operations of an organization, and they stifle growth. These can include outdated machinery, inadequate working capital, and inefficient production methods.
- Opportunities are prospects for growth in the business through the adoption of ways to take advantage of the chances. They could include entry into new markets, adopting digital marketing strategies, or following new trends.
- Threats are external factors that can affect the business negatively, such as a new powerful competitor, legislative changes, natural disasters, or political situations.
Marketing Strategy
The marketing strategy section covers actual strategies to be included according to the marketing mix. The strategy centers on the 8Ps of marketing. However, firms are also at liberty to use the traditional 4 P’s of marketing – product, price, place, and promotion. The 8 P’s are illustrated below.
The correct marketing mix is determined by the target market. The most expensive options are advertising, sales promotions, and PR campaigns. Networking and referrals are less costly.
Marketers also need to pay attention to digital marketing strategies that make use of technology to reach a wider market and have also proven to be cost-effective.
Digital marketing channels, which became popular in the early 21 st century, may eventually overtake traditional marketing methods. Digital marketing encompasses trending methods, such as the use of social media for business.
Other strategies within the marketing strategy include pricing and positioning strategy, distribution strategy, conversion strategy, and retention strategy.
Marketing Budget
The marketing budget or projection outlines the budgeted expenditure for the marketing activities documented in the marketing plan. The marketing budget consists of revenues and costs stated in the marketing plan in one document.
It balances expenditures on marketing activities and what the organization can afford. It’s a financial plan of marketing activities to be carried out – e.g., promotional activities, cost of marketing materials and advertising, and so on. Other considerations include expected product volume and price, production and delivery costs, and operating and financing costs.
The effectiveness of the marketing plan depends on the budget allocated for marketing expenditure. The cost of marketing should be able to make the company break even and make profits.
Performance Analysis
Performance analysis aims to look at the variances of metrics or components documented in the marketing plan. These include:
Revenue variance analysis : An analysis of positive or negative variance of revenue. A negative variance is worrisome, and reasons should be available to explain the cause of deviations.
Market share analysis : An analysis of whether the organization attained its target market share. Sales may be increasing whilst the organization’s share of the market is decreasing; hence, it is paramount to track this metric.
Expense analysis : An analysis of marketing expense to sales ratio . This ratio needs to be compared to industry standards to make informed comparisons.
The ratio enables the organization to track actual expenditures versus the budget. It is also compared to other metrics, such as revenue analysis and market share analysis. It can be dissected into individual expenditures to sales to get a clearer picture.
Administration of a Marketing Plan
The marketing plan should be revised and adapted to changes in the environment periodically. The use of metrics, budgets, and schedules to measure progress towards the goals set in the marketing plan is a continuous process by marketing personnel.
There should be a continuous assessment to verify that the goals of the marketing plan are being achieved. The marketing manager should be able to review if the strategies documented are being effective, given the operating environment.
It is irrational for the marketing manager to notice anomalies and wait to review at year-end when the situation might have already deteriorated.
Changes in the environment may necessitate a review of plans, projections, strategies, and targets. Therefore, a formal periodical review – such as monthly or quarterly – may need to be in place. This may mean preparing an annual marketing plan but reviewing the plan quarterly to keep targets and plans aligned closely to environmental changes. It goes without saying that plans are as good as their feasibility to succeed in the given environment.
More Resources
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Marketing Plan. To keep learning and advancing your career, the additional CFI resources below will be useful:
- 4 P’s of Marketing
- Market Research
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)
- Competitive Advantage
- See all management & strategy resources
- Share this article

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in
More From Forbes
Five essential elements of a marketing plan for a small business.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Getty Images
If you are planning to open your own small business, the first step is to develop a business plan. The next step is to develop a marketing plan, as all business plans should be paired with a strategy for marketing your products or services. Marketing strategies vary in format, but they all have the common goal of attracting and building relationships with customers. The style is up to you, but it should include the following elements.
1. Marketing Goals and Objectives
You will need to develop realistic and measurable marketing goals that cover a full calendar year and are aligned with your business plan. Common goals in a marketing strategy include a targeted increase in products sold and a growth in customers. Your strategy will help you achieve your goals. As you develop it, you should factor in the type of products or services you are selling, how and where you sell them, and the level of consumer awareness surrounding your business.
2. Define Your Target Audience
Fully describe the characteristics of your potential customers, as well as their media viewing habits. For example, some restaurants target gourmets with an average income of over $100,000, while others focus on providing affordable meals to individuals on a fixed income. Take the time to define your audience and customers for your products or services, along with their unique demographic characteristics, such as age range, marital status, gender, race, income level, or education. This will also help you lay out your plan for distinguishing yourself from your competition.
3. Research Marketing Tactics
There are more marketing tactics available today than ever before and trying to determine which one is best for your business can be overwhelming. Take the time to research all marketing vehicles, which range from traditional (billboard, television, radio, newspaper, and magazine) to digital (pay-per-click ads with Google, social media efforts with Facebook and Twitter, etc.). A full understanding of these tactics will make you more comfortable in selecting which ones are best for your business.
4. Plan Your Marketing Tactics
Once you have completed the research, select the tactics and channels you will use to accomplish your goals and reach your target audience. This could be determined by customer habits and should align with your sales strategy. Be sure to also monitor your competition and stay current with new tactics and channels that your target audience is using.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024.
5. Develop Your Timeline and Budget
Establish a timeline and budget for your marketing strategy that reaches your audience throughout the year. It should include all scheduled promotions for the entire year and a complete breakdown of their cost. Examples of items in a marketing timeline include increased advertising during the holiday season and a month-long promotion to boost sales.
It is also important to remember that a marketing strategy is not set in stone. As your business grows and evolves, so will your marketing strategy. Be on the lookout for courses, webinars, and articles to help stay up-to-date with current trends.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How To Write a Marketing Strategy for Your Business Plan
Potential investors want to see how you plan to sell
Alyssa Gregory is an entrepreneur, writer, and marketer with 20 years of experience in the business world. She is the founder of the Small Business Bonfire, a community for entrepreneurs, and has authored more than 2,500 articles for The Balance and other popular small business websites.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/alyssa-headshot-2018-5b73ee0046e0fb002531cb50.png)
How Marketing Strategy Fits Into Your Business Plan
The 4 ps: product, promotion, price, and place, 7 tips for writing a marketing strategy, the bottom line, frequently asked questions (faqs).
Bulent Ince / E+ Collection / Getty Images
A marketing strategy is important for all businesses because it clearly outlines how they'll find new customers and promote their products and services to ultimately achieve more sales. You can use the marketing strategy as a stand-alone tool, as part of a marketing plan, or as part of a business plan, all with slightly different components.
Let's focus on some marketing strategy examples for your business plan.
- A solid marketing strategy addresses the four Ps: product, promotion, price, and place.
- Your success can depend on understanding your clients’ needs and being flexible enough to find a way to meet them.
- Keep your budget in mind. You can only do what you can afford to do, and you should plan for accommodating periodic shortfalls.
The marketing strategy section of your business plan builds upon the market analysis section . The marketing strategy outlines where your business fits into the market and how you'll price, promote, and sell your product or service. It can also act as a source of important information for potential investors who are analyzing your business.
You can break down the key information in the marketing strategy section using the 4 Ps of marketing concept: product, promotion, price, and place.
Product can refer to either a physical product or a service that you plan on offering. Some of the product areas that fall into this section include:
- Related products or services
- Functionality
Promotion covers the various aspects of how you plan on marketing your product or service. The areas you should address include:
- Advertising
- Marketing budget
- Promotional strategy
- Publicity and public relations
- Sales force
- Sales promotion
This addresses the way you plan on pricing your product or service. The aspects of pricing you should address are:
- Bundling (if you have related products/services)
- Pricing flexibility
- Pricing strategy
- Retail price
- Seasonal price (if applicable)
- Wholesale (volume) price
Also known as distribution, this part is all about the delivery of your product or service to your customers. Some areas you should cover include:
- Distribution centers
- Distribution channels
- Inventory management
- Order processing
- Transportation
- Warehousing
Keep seven things in mind as you write the marketing strategy section of your business plan to make it as effective and relevant as possible.
Show How Unique You Are
The foundation of your marketing strategy should be your unique selling proposition (USP). This is the statement that outlines what differentiates you from everyone else in the market. Create your USP first, then build upon it by relating it to each of the 4 Ps.
The common thread through each part of your marketing strategy should be how your business solves a problem or meets a need better than anyone else.
Know Your Customers/Clients
The information you include in your marketing strategy should incorporate all the research you conducted in your market analysis . Make sure you have a clear idea of who your ideal customers or clients are, what they like, what they need, and what they expect. This will make your marketing strategy more accurate and applicable to your target audience.
Be Flexible
The 4 Ps of marketing work well for physical products, but you may have to tweak them a bit for services. For example, you might use your website instead of a physical location for the place section. Your website should also be a part of your promotion section, as should any social media platforms that you participate in.
Do Your Research
When you’re determining your pricing, you should have plenty of data to back up your decision when you're determining your pricing. Include industry reports, competitor ads, and comparisons that demonstrate the research you conducted and how you came to the conclusion that you're pricing your product or service correctly.
Use Visuals
As in other sections of your business plan, using charts, graphs, and images to illustrate your facts can make them easier for your audience to absorb and understand. Is your pricing right at the median of the industry? Are you planning to use a four-step distribution process?
Use visual aids to drive your point home.
Remember Your Budget
You'll outline the financial analysis of your company in another section of your business plan but keep those numbers in mind as you write your marketing strategy. Your marketing process may look good by itself, but you'll have a difficult time meeting your goals unless you tie it directly to your financial status.
Include Your Collateral
You should include samples as exhibits if you're going to talk about your marketing collateral in your marketing section. These might include brochures, fact sheets, videos, and photos.
Your marketing strategy is your overall plan for how you're going to make your business profitable. Larger enterprises might have different strategies for various arms of their operations. Sole proprietors carry the weight of a single plan on their own. But addressing all these components will increase your odds of success in any case.
What are the four types of marketing strategies?
Many consider the four Ps to be the basic types of marketing strategies, but others focus on four possible ways you can reach clients and consumers: search engine optimization, paid advertising, content marketing, and sales.
What are the seven Cs of marketing?
The seven Cs organize your marketing strategy. They can vary depending on who you talk to and the nature of your business, but you can tailor yours to best meet your goals and needs. Most include customer, consistency, creativity, and communication. Some include other factors, such as convenience, competition, credibility, culture, and change.
American Marketing Association. " The Four Ps of Marketing ."
Notes Learning. " 7 Cs of Marketing ."
OBC. " The 7 Cs of Marketing: How to Apply Them ."
📢 Join our webinar on leveraging AI for creating viral social posts!
- Social Calendar Streamline content planning with Social Calendar.
- Bulk Scheduling Maximize productivity with Bulk Scheduling.
- Shareable calendar Get client and team feedback and approval seamlessly
- Team Collaboration Boost productivity with seamless Team Collaboration.
- Evergreen Content Marketing Drive traffic and engagement with Evergreen Content.
- Cover image for Video Posts A striking cover photo serves as the gateway to captivating content.
- Tailored Posts Tweak each post by tailoring your message or media.
- Social Inbox Read and reply to incoming messages
- Import from Social Quickly import your existing content to RecurPost
- Tag Users Mention others in your posts to attract and collaborate
- Seasonal Libraries Repurpose seasonal content year after year
- Reports and analytics performance insights of your social media posts.
- Custom fields Personalize your posts based on data
- White Label Reports Personalize and impress with White Label Reports.
- First Comment Optimize post visibility and Interaction
- Royalty Free Images Access stunning visuals with no strings attached.
- AI Content Generator No more writers block, let AI take you viral.
- Social Platforms
- Facebook Stay consistent and save time with Facebook Scheduling.
- Instagram Optimize engagement with effortless Instagram Scheduling.
- X (Twitter) Tweet smarter, not harder with Twitter Scheduling.
- LinkedIn Boost your professional presence with LinkedIn Scheduling.
- Pinterest Maximize your Pinterest impact with effortless scheduling.
- Google Business Profile Maximize local engagement with Google business scheduling.
- YouTube Effortless YouTube scheduling for optimal engagement.
- TikTok Manage and grow your business on Tiktok.
- Integrations
- Canva Integration Create stunning visuals with Canva Integration.
- ChatGPT for Content Revolutionize social media with AI Content Generator.
- Zapier Automation Get posts from other apps like Google Drive.
- AI image generator Generate visuals for any type of content.
- Bit.ly Integration Shorten links, save space, share more.
- AI Caption Generators
- Instagram Caption Generator Generate scroll-stopping Instagram captions using our AI tool.
- Facebook Post Generator Use our AI-powered tool to create engaging Facebook posts quickly.
- TikTok Caption Generator Create engaging TikTok captions fast with our AI-powered tool.
- LinkedIn Post Generator Effortlessly create engaging LinkedIn content with our AI tool.
- X (Twitter) Post Generator Effortlessly create compelling tweets with our X (Twitter) generator.
- Agency Pricing Calculator Find Out What You Should Charge: Try Our Pricing Tool!
- Campaign Proposal Generator Generate Winning Social Media Campaigns Instantly with Our AI!
- Social media Strategy Template Drive client success: Click for your essential social media strategy template!
- Case Studies
- Honni Hayton RecurPost’s Cure: The Prescription for Social Media Success
- Jackson Calame How Jackson Calame Used RecurPost for Authentic Engagement
How to Create a Marketing Plan for Small Business? A Guide
- August 22, 2024
Table of Contents
Running a small business is no small feat. With countless tasks demanding your attention, it’s easy to overlook the importance of having a solid social media strategy . Yet, a well-crafted marketing plan for small businesses is essential—the strategic foundation ensures your efforts are effective and your resources are well spent.
Why is a Marketing Plan Essential for Small Businesses?
When you think about marketing, your mind might immediately jump to social media posts, flyers, or even local ads. However, these activities might not bring the results you need without a guiding plan. A marketing plan for small businesses serves as your roadmap, steering your efforts toward your goals and helping you navigate the complex landscape of customer acquisition and retention.
According to a McKinsey report in 2024, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that actively engage in strategic planning, including a well-defined marketing plan, significantly outperform those that do not. Specifically, businesses with a comprehensive marketing plan see up to a 40% increase in growth potential compared to those without such a plan. Without a clear plan, your marketing efforts can feel like trying to drive without a map—constantly turning but never knowing if you’re on the right track.
A marketing plan for small business clarifies your goals, identifies your target audience, and aligns your tactics with your business objectives. This alignment is critical for small businesses, where resources are often limited. Instead of spreading yourself thin across multiple channels, you focus on what truly matters, maximizing your impact.
If you’re interested in optimizing your social media presence as part of your marketing plan for small business, this blog will provide valuable insights that tie directly into your overall marketing plan.
Understanding Your Market: Research and Analysis
A deep understanding of your market is the cornerstone of any successful marketing plan for small businesses. The process starts with thorough market research and analysis, which helps you understand the environment in which you operate.
What is Market Research?
Market research involves gathering data about your industry, competitors, and customers. It comes in two forms: primary & secondary research . Primary research is data you collect through surveys, interviews, or observations. Secondary research involves analyzing existing data, like reports, studies, or statistics from credible sources. Consequently, you can get more clients for your digital marketing agency as a service provider.
Understanding your market helps you identify opportunities and threats. For example, if you discover a competitor struggling with customer satisfaction. Such mishaps might allow you to differentiate your business by emphasizing superior customer service within a marketing plan for small businesses.
Identifying Your Target Audience
Start by segmenting your audience into groups based on demographics, psychographics, and behavior. Creating customer personas—detailed profiles of your ideal customers—can make this process more tangible and direct in a marketing plan for small businesses.
Competitive Analysis
Another key component of your marketing plan for small businesses is understanding your competitors. A competitive analysis helps you identify your Unique Value Proposition (UVP)—the key factor that sets your business apart. Your UVP should be a focal point of your marketing plan for small business marketing messages. This approach can help you get cost-effective marketing tips .
Setting Clear and Achievable Marketing Goals
Now that you understand your market, it’s time to set goals. Without clear goals, you won’t know if your marketing plan for small businesses is paying off.
SMART Goals Framework
The SMART framework is a popular method for setting Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound goals. For example, instead of saying, “I want more customers,” a SMART goal within your marketing plan for small businesses would be: “Increase website traffic by 20% in the next three months through targeted email campaigns.”
Aligning Goals with Business Objectives
Your marketing goals should directly support your broader business objectives. For example, if your business goal is to increase sales by 15% this year, your marketing goal within the marketing plan for small businesses could focus on lead generation or customer retention strategies that contribute to that target.
Setting short-term and long-term goals helps you stay focused and measure progress over time. Remember, your goals should be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the market, ensuring that your marketing plan for small businesses remains effective.
Crafting Your Marketing Strategy
With your goals in place, the next step in your marketing plan for small business is crafting a strategy that will help you achieve them. Utilize a social media strategy template to fulfill your marketing purpose.
Defining Your Brand
Your brand is more than just a logo or a tagline. It’s the overall impression you leave on your customers. Key elements include the brand’s voice, messaging, and visual identity. Consistency across all these elements is crucial to building brand recognition and trust, and these should align with your marketing plan for small businesses.
For small businesses, a strong brand can make a significant difference. It sets the tone for all your marketing efforts and helps you stand out in a crowded market, a crucial factor in your marketing plan for small business.
Choosing the Right Marketing Channels
There are many marketing channels to choose from—social media, email marketing, content marketing, search engine optimization (SEO), and more. However, not all channels will be right for every business, so you must carefully design a marketing plan for small businesses and select the most appropriate channels. Understanding the dynamics of social media marketing for different industries is vital for this step.
Choosing the proper channels depends on where the target audience spends their time and the content they engage with. For example, if your target audience is younger, platforms like Instagram or TikTok might be more effective than traditional advertising methods, which should be reflected in your marketing plan for small businesses.
To dive deeper into this, consider reading our blog on the best social media management tools .
Developing Your Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
Your USP is what makes your business unique. It’s the reason customers should choose you over your competitors. Your USP should be clear, compelling, and prominently featured in all your marketing communications as part of a marketing plan for small businesses.
Budgeting for Your Marketing Plan
No marketing plan for small businesses is complete without a budget. Budgeting ensures your marketing efforts are sustainable and aligned with your financial resources. If you are a digital marketing service provider, utilize our social media pricing calculator to provide your clients with detailed and accurate budget information.
Determining Your Marketing Budget
A common rule of thumb is to allocate 5-10% of your revenue to marketing. However, this can vary depending on your business goals, industry, and growth stage. For startups or businesses looking to grow aggressively, a higher percentage may be necessary within their marketing plan for small businesses.
Allocating Funds Across Channels
Once you’ve determined your budget, the next step in your marketing plan for small business is to allocate it across different channels. Consider factors like the cost of each channel, the expected return on investment (ROI), and the goals you’ve set. For example, if your goal is to increase brand awareness, you might allocate more funds to social media advertising or influencer partnerships.
Cost-Effective Marketing Tactics
For small businesses with limited budgets, it’s important to maximize every dollar in your marketing plan for small businesses. This might involve focusing on organic growth strategies like SEO or content marketing, which require time but have lower upfront costs. Additionally, leveraging free or low-cost email marketing tools, content marketing tools , automation tools , digital marketing tools , social media marketing tools , and social media analytics tools can help stretch your budget further.
For more ideas on cost-effective marketing strategies, check out the blog on must-have marketing agency tools .
Creating a Content Plan and Calendar
Content is the fuel that powers many of your marketing channels. A well-thought-out content plan is essential for engaging your audience and driving traffic within a marketing plan for small businesses.
Content Marketing Basics
Content marketing involves creating and distributing valuable, relevant content to attract and engage your target audience . This process can include blog posts, videos, infographics, ebooks, and more. The key is to provide content that answers your audience’s questions or solves their problems as part of your marketing plan for small business.
Planning Your Content
Start by brainstorming social media content ideas that align with your audience’s interests and your marketing goals. For example, if you’re launching a new product. You might create a series of blog posts, videos, and social media updates highlighting its features and benefits, all coordinated within a marketing plan for small businesses.
Once you have a list of ideas, organize them into a content calendar. A content calendar helps you plan and schedule your content in advance, ensuring a consistent flow of material that keeps your audience engaged as part of your marketing plan for small business.
Content Distribution
Creating great content is just the first step. You also need a strategy for getting it in front of your audience. This might involve sharing it on social media, optimizing it for search engines, or promoting it through email marketing—all vital parts of a marketing plan for small businesses.
If you are new to the digital marketing business, you can easily target clients who find content creation overwhelming. By using the social media campaign proposal generator , you can become affluent in gaining such client accounts.
Implementing and Managing Your Marketing Plan
With everything in place, it’s time to put your marketing plan for small business into action.
Action Steps for Implementation
Start by breaking down your marketing plan for small business into actionable steps. Assign tasks to team members, set deadlines, and ensure everyone is clear on their responsibilities. Multiple tools can help you manage projects and track progress.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your Plan
As you execute your plan, you must monitor your performance closely. Track key metrics like website traffic, conversion rates, social media engagement , and social media positioning to see if your efforts are delivering the desired results.
If something isn’t working, don’t be afraid to pivot. Adapting to new information is one of the strengths of a well-managed marketing plan for small businesses. Regularly reviewing and updating your plan ensures it stays aligned with your business goals.
Tools and Software for Marketing Management
Managing a marketing plan for small businesses can be complex, but the right tools can make it easier. Consider using marketing automation software to streamline your efforts. For example, RecurPost offers social media scheduling and content management features that can save you time and keep your marketing on track.
Creating a marketing plan for small businesses might seem daunting at first, but it’s one of the most important steps you can take to ensure the success of your business. Social media optimization will become easy by following the steps outlined in this guide and you’ll be well on your way to achieving your business goals.
Don’t wait to get started. The sooner you have a marketing plan for small businesses in place, the sooner you can begin seeing the results. Take the first step today and start crafting your marketing plan.
Ideally, you should review your marketing plan for small business quarterly to ensure it remains relevant and effective. However, major business changes or shifts in the market may require more frequent updates.
If your efforts aren’t working, start by reviewing your goals and metrics. Identify any areas where performance is lagging and adjust your strategy accordingly. It might involve changing messaging, targeting a different audience segment, or reallocating your budget to more effective channels within your marketing plan for small business.
Focus on organic strategies like SEO, content marketing, and social media. These can be low-cost but highly effective if done correctly. Additionally, make the most of free tools and resources available online, which can be part of a cost-effective marketing plan for small businesses.
The best approach depends on your audience. Digital marketing offers precise targeting and tracking, often ideal for small businesses. However, traditional methods like print advertising or direct mail might still be effective if your audience is local or less tech-savvy. These should be considered within your marketing plan for small businesses.

Ruchi Dhimar is a skilled content writer with 4 years of experience. She is passionate about crafting compelling narratives, specializing in writing content for different industries.
Try RecurPost
Schedule and Publish your posts on multiple social accounts, read and reply to incoming messages with social inbox, and collaborate with your team and clients with ease.
Financial modeling spreadsheets and templates in Excel & Google Sheets
- Your cart is empty.

What are the 12 Components of a Business Plan You Need to Know

Crafting a business plan is a crucial step for any entrepreneur aiming to start or grow a business. This foundational document not only sets the vision and direction for the venture but also provides a structured approach to achieving objectives. A well-thought-out business plan encompasses various elements that collectively form a comprehensive strategy. By understanding and implementing these key components, business owners can ensure they are well-prepared to navigate challenges and seize opportunities as they arise. Moreover, this plan acts as a bridge, communicating your business potential to investors and other stakeholders effectively.
The intricacies of what are the 12 components of a business plan stretch far beyond mere bullet points; each segment serves a distinct purpose in the framework of your business strategy. These components range from the Executive Summary, that encapsulates the essence of the plan, to financial projections that detail the anticipated economic performance. Attention to each part ensures clarity and thoroughness, thereby enhancing the credibility of the business plan. Emphasizing these components helps in identifying any gaps or weaknesses early, enabling proactive adjustments to strengthen the overall business strategy.
Understanding the 12 Components of a Business Plan
Creating a successful business requires a well-structured plan that serves as a roadmap for growth and accountability. The blueprint for this endeavor is composed of 12 essential components, each playing a critical role in guiding a venture towards its goals. By understanding these components, aspiring entrepreneurs can articulate their vision clearly and attract potential investors and partners.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is often considered the heart of the business plan. This section condenses the entire plan into a brief overview, providing a concise summary of the objectives and key elements of the venture. It should capture attention and compel the reader to explore further.
2. Company Description
A detailed company description follows the executive summary. This section outlines the business’s history, mission statement, vision, and objectives. When detailing your company, emphasize what sets it apart from competitors and its unique value proposition.
3. Market Analysis
Understanding your market is crucial. A comprehensive market analysis includes research on industry trends, target demographics, and competitive landscape. This data helps in identifying potential customer segments and validates the need for your service or product.
4. Organization and Management
In this component, you present the organizational structure of your business. Clarify who is responsible for what, outlining the management team, their qualifications, and roles within the organization. A clear organizational chart can enhance understanding.
5. Service or Product Line
This section delves into the products or services your business will offer. Describe their benefits, lifecycle, and potential for growth. It’s essential to show how your offerings address specific customer needs and what differentiates them from others in the market.
6. Marketing and Sales Strategy
The marketing and sales strategy outlines how you plan to attract and retain customers. Discuss your branding approach, marketing channels, and sales techniques. Highlight any anticipated challenges and how you intend to overcome them to create a sustainable customer base.
7. Funding Request
If you’re seeking funding, this element is vital. Clearly indicate how much money you need, the purpose of the funds, and the type of funding you are seeking—be it equity, loans , or grants. Make sure to present a well-reasoned case for your request based on solid financial projections.
8. Financial Projections
Financial projections provide an outlook on the expected revenue and expenses over a specific period, often spanning three to five years. Include income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets. These documents help reinforce the viability of your business plan to investors.
9. Appendix
The appendix serves as a supplementary section for additional information that enhances your business plan. Include resumes, legal agreements, product images, or any market research data here. This allows readers to delve deeper into specifics if they choose to.
10. Implementation Plan
Your implementation plan outlines actionable steps required to launch and operate your business effectively. It should present a timeline of critical milestones and measurable objectives to track progress, ensuring that the venture remains on course.
11. Exit Strategy
An exit strategy details your plan for the future, whether you intend to sell the business, pass it on to heirs, or close it down. Addressing this component shows potential investors that you have considered long-term sustainability and potential returns on their investment.
12. Risk Assessment
Every business faces risks, and a thoughtful risk assessment identifies potential challenges and their possible impact. Address market fluctuations, competition, and operational risks, and articulate your plans to mitigate these issues. This demonstrates proactive management techniques to investors.
When composing a business plan, integrating these 12 components ensures a comprehensive, detailed, and compelling document. Each section serves a purpose, contributing to the overall narrative of your business and reinforcing your vision. By carefully addressing these elements, entrepreneurs can pave the way for their business’s success and secure the necessary support to fulfill their aspirations.
The Importance of Market Analysis in Business Planning
Effective business planning hinges on numerous crucial factors, but few are as vital as understanding the market landscape. A detailed market analysis empowers entrepreneurs to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and seize opportunities that may not be immediately apparent. This detailed approach helps ensure that businesses are not only prepared to enter the market but are also strategically aligned with consumer needs and industry trends.
One of the core reasons for conducting a market analysis lies in identifying and understanding target demographics. By gathering demographic data, businesses can delineate their potential customer base, paying attention to factors such as age, gender, income level, and lifestyle. This information is pivotal in shaping marketing strategies and product development.
Analyzing Market Trends
Market analysis also includes scrutinizing current trends and forecasting future developments. Understanding these trends provides a roadmap for businesses, allowing them to adapt their offerings promptly. Consideration of elements such as:
- Consumer behavior
- Technological advancements
- Economic indicators
- Regulatory changes
These factors play a considerable role in shaping market dynamics and influencing business strategies.
Competitive Analysis
Another essential component of market analysis is competitive assessment. Gaining insight into competitors helps businesses ascertain their strengths and weaknesses relative to the market. This competitive analysis involves examining:
- Market share of competitors
- Their pricing strategies
- Their marketing approaches
- Their product or service offerings
By understanding where they stand in comparison to competitors, businesses can position themselves more effectively and discover gaps in the market that they can exploit.
Identifying Opportunities and Risks
Through thorough market analysis, businesses can identify both opportunities and risks. Opportunities might arise from underserved customer needs or niche markets that have not been fully capitalized. Conversely, understanding risks involves being aware of potential challenges that could hinder growth, such as economic downturns, increasing competition, or shifting regulations. Businesses can formulate strategies to mitigate these risks, ensuring their plans are resilient and adaptable.
Setting Realistic Goals
Furthermore, a well-rounded market analysis helps in setting realistic and measurable objectives. Knowledge of market conditions allows businesses to create goals that are attainable based on empirical evidence instead of mere speculation. This data-driven approach ensures that targets are both challenging yet achievable, fostering a culture of accountability and success.
Tailoring Marketing Strategies
With insights gleaned from market analysis, businesses can tailor their marketing strategies to engage effectively with their target audience. This can include selecting the most effective channels for advertising, such as social media, email campaigns, or traditional media. A clear understanding of customer preferences informs the creation of marketing messages that resonate with potential customers, ultimately boosting conversion rates.
Enhancing Product Development
Market analysis also informs product development. By understanding customer needs and preferences, businesses can design products or services that directly cater to market demands. This alignment between product offerings and consumer expectations increases the likelihood of successful market entry and customer satisfaction.
In addition to driving product innovation, a comprehensive market analysis allows businesses to assess pricing strategies accurately. Understanding the perceived value of offerings in the context of competition helps in setting competitive yet profitable pricing structures. This analysis ultimately supports sustainable revenue growth.
Incorporating market analysis into business planning promotes an agile approach. In a rapidly changing business environment, having a finger on the pulse of the market allows companies to pivot quickly when necessary, adapting their strategies to align with evolving trends and consumer preferences. This flexibility is crucial for long-term viability and success.
The importance of market analysis in business planning cannot be overstated. It is a multi-faceted tool that aids in understanding the market landscape, identifying opportunities, minimizing risks, setting realistic goals, and ultimately driving successful business outcomes. By prioritizing a thorough market analysis, businesses can create robust strategies that pave the way for sustained growth and success.
Crafting an Effective Executive Summary
Creating an effective executive summary is a crucial part of any business plan. This section serves as the first impression for your readers, often determining whether they will engage with the rest of your document. A concise and compelling executive summary not only encapsulates key elements of your business plan but also highlights the unique aspects that set your business apart from the competition.
To craft a narrative that is engaging and informative, consider the following components to include:
- Business Overview: Start with a brief description of your business. Clearly state what your company does, the products or services offered, and your target market. This sets the stage for the rest of the summary.
- Mission Statement: Include your mission statement to communicate your core purpose. This should convey the essence of your business and what you aim to achieve in the long term.
- Market Opportunity: Describe the market needs your business addresses. Present any data or insights that demonstrate a clear opportunity for growth, indicating why your business is well-positioned to succeed.
- Business Model: Explain how your business plans to make money. Clearly outline the revenue streams, pricing strategies, and any unique selling propositions that differentiate you from competitors.
- Target Audience: Detail your target audience. Understanding your ideal customer is vital for tailoring your services and marketing strategies effectively.
- Competitive Advantage: Discuss how your business stands out in the marketplace. Highlight any unique skills, technologies, or intellectual property that provides an edge over competitors.
- Financial Projections: Provide an overview of expected revenue and profitability. Use clear, concise figures instead of jargon to make the information easily digestible.
- Funding Requirements: If applicable, outline your funding needs. Specify how much money you are looking to raise, how it will be used, and the expected outcomes from these investments.
- Milestones and Objectives: List critical milestones across the timeline of your business. It could include product launches, partnership agreements, or sales targets that mark your path to success.
- Management Team: Introduce key members of your team. Highlight their experience, qualifications, and roles within the company, demonstrating that you have the right people in place to execute your plan.
- Call to Action: End with a compelling call to action. Encourage readers to take the next step, whether it’s to schedule a meeting or to delve deeper into the complete business plan.
As you compile these elements into your summary, remember to keep it focused and to the point. Ideally, the executive summary should be no longer than one to two pages. Strive for clarity and engage the reader immediately; your writing should possess a natural flow.
When drafting, use active voice to convey confidence and directness. Phrases like “We provide innovative solutions” rather than “Innovative solutions are provided by us” create a stronger sense of ownership and commitment. Furthermore, breaking up lengthy sentences will help maintain the reader’s attention. Short, impactful sentences mirror how people communicate in conversations.
Another essential factor is the tone. Although it’s crucial to maintain a professional demeanor, you should also express enthusiasm for your business. Show potential investors or stakeholders why they should be excited about your company.
Visual elements can also enhance engagement. bullet points, bolding essential terms, or including charts can help your executive summary stand out. Visuals break down complex information, making it more accessible for the reader.
Before finalizing your executive summary, solicit feedback. Share it with colleagues or mentors to get their perspective. A fresh set of eyes can identify areas that might be unclear or unconvincing. Consider their feedback seriously and make revisions accordingly.
Crafting an effective executive summary requires careful thought and consideration. By focusing on the key components outlined, maintaining a clear and engaging style, and utilizing feedback, you can create a summary that captivates and informs your audience. Remember, this is your chance to make a remarkable first impression—so invest the time needed to make it outstanding.
Financial Projections: Building a Sustainable Budget
Building a sustainable budget requires careful planning and financial projections serve as the backbone of that process. Without clear projections, businesses can find themselves floundering as they navigate financial challenges. Understanding how to create reliable financial projections can help businesses not only survive but thrive in competitive environments. Here’s an insightful breakdown of how to approach this important aspect of business planning.
Understanding Financial Projections
Financial projections are essentially estimates of future income and expenses. They help business owners regulate their budgets, make informed decisions, and allocate resources efficiently. These projections typically cover a specific period, often three to five years, and consist of several key components that provide a roadmap for businesses.
The 12 Key Components for Effective Financial Projections
To create a robust financial projection, consider including the following components:
- Sales Forecast: Estimate the expected revenue based on past performance, market trends, and sales strategies. Use data analytics to support your forecasts.
- Expense Forecast: Outline operational costs, including both fixed and variable expenses. Understanding where your money will go is crucial for financial health.
- Cash Flow Projections: Analyze incoming and outgoing cash to anticipate liquidity needs and maintain solvency. This will reveal how much cash is available at any given time.
- Profit and Loss Statement: This projected income statement details expected revenues, costs, and profits over time, providing insights into overall profitability.
- Balance Sheet Forecast: Include projections about the assets, liabilities, and equity of the business to understand its financial position at various points in the future.
- Break-even Analysis: Determine the level of sales needed to cover costs, indicating when the business will start generating profits.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Analyze how changes in key assumptions, like sales volume or cost increases, can impact financial outcomes.
- Funding Requirements: Identify how much capital the business needs, when it will be needed, and possible sources to secure that funding.
- Investment and Capital Expenditure Projections: Outline anticipated investments in long-term assets and how they align with expected revenue growth.
- Assumptions and Methodologies: Clearly state the assumptions behind each projection, including market conditions and business strategies.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establish metrics to measure financial health and performance against projections.
- Scenario Planning: Prepare for varying outcomes by developing best-case, worst-case, and expected-case scenarios to ensure flexibility.
Creating the Budget
Once you have gathered all necessary projections, you can start creating a sustainable budget. This involves allocating funds based on your forecasts while regularly revisiting your projections. You might find the following strategies helpful:
- Prioritize Expenses: Categorize essential and non-essential expenses to focus spending on what drives your business forward.
- Incorporate Flexibility: Allow a buffer in your budget for unpredicted costs or changes in market conditions.
- Regular Reviews: Schedule monthly or quarterly reviews of your budget against actual performance to adjust your plans as necessary.
- Use Software Tools: Implement budgeting software to help streamline the planning process and maintain organization.
The Importance of Accurate Data
In crafting financial projections, the quality of your data is key. Utilize reliable sources and incorporate historical data for accuracy. Always validate your numbers through alternative methods, like industry benchmarking. This not only improves the reliability of your projections but also instills trust among stakeholders.
Engaging Professionals
If you’re feeling overwhelmed, don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance. Financial consultants can provide expert insights, ensuring that your projections are realistic and aligned with industry standards. They can help identify potential pitfalls before they become issues, ultimately supporting a sustainable financial future.
By understanding and implementing these components, you create a comprehensive framework for financial projections and budgeting. Doing so helps position your business for sustainable growth and operational stability. Remember, the most effective budgets evolve over time, reflecting the changing dynamics of the market and your business’s unique circumstances.
Target Audience: Defining Your Market Segment
Identifying your target audience is a critical step when launching any business or service. Understanding who will buy your product or use your service allows you to shape your marketing strategies effectively. You can optimize your efforts and resources by tailoring your message to the right individuals or groups.
First, begin with demographic information. This is the basic data that encompasses age, gender, income level, marital status, and education. Gathering this info gives you a foundational understanding of who your audience is. For instance, a luxury spa might target affluent women aged 30-50, while a budget gym could focus on young adults in their 20s. The clearer you define your demographics, the more effectively you can tailor your approach.
Next, delve into psychographics, which offer insights into the values, interests, and lifestyles of your potential customers. These factors go beyond basic demographics and reveal what truly motivates your audience. For example, a company selling eco-friendly products may appeal to consumers who value sustainability and are environmentally conscious. Understanding psychographics allows you to create messages that speak directly to the needs and desires of your audience.
Another valuable aspect to consider is geographic segmentation. The location of your audience can significantly impact their purchasing behavior. A business operating in an urban area may adopt a different strategy than one in a rural setting. For instance, a coffee shop in a city might need to focus on convenience and quick service, while a shop in a quieter town can offer a more relaxed environment. Tailoring your approach based on where your audience lives can enhance engagement and drive sales.
Behavioral segmentation is also crucial. This considers how customers interact with your brand, including purchasing habits, brand loyalty, and usage frequency. By analyzing these behaviors, you can generate insights into how to market your product or service effectively. For example, if consumers frequently purchase a specific item, consider promoting it more prominently in your marketing campaigns to foster loyalty.
To help clarify these concepts, here’s a formatted list that encapsulates key steps for defining your target audience:
- Conduct Market Research: Use surveys, interviews, and focus groups to gather insights directly from potential customers.
- Analyze Existing Customers: Look at your current customer base to identify shared characteristics and preferences.
- Utilize Data Analytics: Make use of web analytics and social media insights to track user behavior and preferences.
- Develop Customer Personas: Create fictional profiles that represent segments of your audience to guide marketing strategies.
- Test and Adapt: Regularly revisit your audience definition as markets and consumer preferences can change.
Also, don’t underestimate the power of competition analysis. Examining who your competitors are targeting can reveal valuable insights. If a competitor targets a similar market segment but offers a slightly different product, you may find an opportunity to differentiate yourself further and capture a unique niche.
As you define your market segment, remember that reaching your target audience effectively involves utilizing the right channels. Whether through social media, email marketing, or traditional advertising, understanding where your audience spends their time helps guide your strategy. Using channels that align with your audience’s preferences boosts engagement and conversion rates.
In addition, it’s essential to stay flexible. As customer preferences and market dynamics change, so should your approach. Regularly collecting feedback allows you to refine your audience definition and marketing strategies continuously. Whether it’s adjusting messaging, changing visuals, or trying new platforms, adaptability can set you apart from rigid competitors.
Defining your target audience is not just about identifying who might buy your product. It’s about understanding them on a deeper level—demographics, psychographics, geographical location, behaviors, and preferences all intertwine to create a picture of your ideal customer. By investing the time and resources to accurately define and continuously adapt your market segment, you position your business for success.
Operational Plan: Structuring Your Business for Success
Building a successful business requires more than just a great idea; it demands a well-structured operational plan that lays out the pathway to achieving your goals. An effective operational plan details the processes, resources, and strategies you’ll employ to ensure your business runs smoothly. It’s a crucial element that aligns your operational activities with your overall strategy. Here’s how you can structure your operational plan to set your business up for success.
Define Your Business Objectives
The first step in creating an operational plan is to define your business objectives clearly. What do you want to achieve in the short and long term? Having concrete objectives will guide every aspect of your operational strategy. Consider using the SMART criteria—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound—to formulate your goals.
Identify Key Functional Areas
Your operational plan will span several key functional areas of your business. These typically include:
- Production or Service Delivery
- Marketing and Sales
- Customer Support
- Human Resources
- Finance and Accounting
Identifying these areas helps in allocating resources more effectively and facilitates streamlined operations.
Detail Your Processes
Creating a detailed outline of your business processes is essential. This includes how products will be created or how services will be delivered. Break down your processes into specific steps:
- Input: What materials, resources, or data do you need?
- Activity: What actions will be taken using these inputs?
- Output: What will the final product or service look like?
Having a clear picture of these processes helps to minimize errors and enhance efficiency.
Establish Performance Metrics
To gauge the success of your operational strategies, you need to establish key performance indicators (KPIs). These are measurable values that help you track progress toward your objectives. Consider metrics like:
- Customer satisfaction scores
- Operational costs
- Production times
- Employee turnover rates
Choosing relevant KPIs allows you to make data-driven decisions and adjust strategies as needed.
Resource Allocation
Effective resource allocation is crucial in an operational plan. Identify what resources you need to achieve your objectives, including:
- Financial Investments
- Materials and Supplies
Ensuring that resources are appropriately allocated will minimize waste and maximize outputs.
Create a Timeline
Alongside your budget and resources, create a timeline for implementation. Outline when specific tasks will be completed and who will be responsible for them. This timeline provides accountability, ensuring tasks are completed on schedule.
Risk Management Strategy
Every operational plan must include a risk management component. Identify potential risks that could disrupt operations and create contingency plans to address them. This could involve:
- Insurance covering potential losses
- Backup suppliers for key materials
- Strategies to handle personnel shortages
A strong risk management strategy can save your business from unexpected setbacks.
Regular Review and Updates
Your operational plan should be a living document. Make it a habit to review your operational outcomes regularly. Are your objectives being met? Are adjustments needed in processes, resource allocation, or timelines? Regular updates can ensure your operational plan remains aligned with your business goals.
By following these steps, you can construct an operational plan that not only guides your daily operations but also serves as a compass that points your business toward sustained success. Keep your focus on clear objectives, efficient processes, and strategic planning to turn your vision into reality.
Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators in Business Plans
In the world of business, the quest for success is often defined by measurable outcomes. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) serve as critical tools in a business plan, guiding both strategists and stakeholders toward objectives that lead to growth and profitability. By clearly determining what success looks like, companies can effectively track performance and make informed decisions.
KPIs are quantifiable metrics that help businesses assess their progress in achieving specific goals. These indicators can vary widely depending on the industry and the specific aspirations of a business. However, a few essential KPIs consistently stand out as vital components across various sectors.
Defining Financial KPIs
Financial performance is paramount for any business. Key financial KPIs often include:
- Revenue Growth Rate: Measures the increase in a company’s sales over a specified period, indicating market demand.
- Net Profit Margin: This figure shows what percentage of revenue remains after expenses, reflecting overall profitability.
- Operating Cash Flow: A gauge of cash generated from operational activities, providing insight into liquidity and financial health.
Understanding Customer-Centric KPIs
Monitoring customer engagement and satisfaction is crucial for sustainable growth. Consider these essential customer KPIs:
- Customer Retention Rate: Represents the percentage of customers retained over a given period, demonstrating loyalty and satisfaction.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Measures customer willingness to recommend a business, indicating overall satisfaction.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): This metric calculates the cost involved in gaining a new customer, critical for evaluating marketing efficiency.
Operational Efficiency Indicators
To determine how effectively resources are utilized, businesses can leverage operational KPIs. Key metrics include:
- Inventory Turnover: The frequency at which inventory is sold and replaced, indicating efficiency in inventory management.
- Employee Productivity: This can be measured through output per employee or revenue per employee, highlighting workforce effectiveness.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA) Compliance: For service-oriented businesses, tracking the adherence to predefined service standards is essential.
Setting Targets and Benchmarks
Establishing clear targets for each KPI is crucial. Each metric should align with the overall business objectives while considering industry standards. For instance, a startup might aim for a high customer acquisition rate in the early stages, while an established company may focus on enhancing profit margins through operational efficiencies.
Benchmarking your KPIs against competitors or industry standards can help contextualize performance. Understanding where a business stands in relation to its peers can provide valuable insights for improvement.
Regular Monitoring and Analysis
Success in business is not static; it requires continuous assessment and adjustment. Regularly reviewing KPIs allows businesses to adapt their strategies in real-time. For example, if customer acquisition costs are climbing, a company might need to revise its marketing strategy or explore different channels.
Furthermore, incorporating data analytics tools can facilitate deeper insights into KPI trends. Visual representations through dashboards can make complex data more intuitive, enabling quick adjustments and informed decision-making.
The Impact on Strategic Planning
Integrating KPIs into the business planning process solidifies their importance across all organizational levels. From executive to operational roles, every stakeholder can align their efforts toward common objectives. This fosters accountability and drives a performance-oriented culture within the organization.
Ultimately, the use of KPIs in business plans isn’t just about numbers; it’s about creating a narrative around performance and progress. It helps businesses identify strengths and weaknesses, make informed decisions, and ensure long-term success. By focusing on the right indicators, organizations can sustain growth, adapt to market changes, and enhance overall stakeholder satisfaction.
Understanding and measuring success through KPIs is fundamental to any business strategy. By continually evaluating performance against clear metrics, companies can navigate the complexities of the market and achieve their desired outcomes.
Creating a thorough business plan is undeniably a crucial step for any entrepreneur. Each of the 12 components serves as a building block that supports the overall structure of your business strategy. They collectively provide a roadmap, guiding you through the intricate process of establishing and growing your business. By understanding each component, you can ensure that your business plan is not only detailed but also functional and aligned with your goals.
Market analysis stands out as a fundamental aspect of successful business planning. It allows you to gain insights into your competitors and understand the dynamics within your industry. A well-researched market analysis equips you with data that aids in making informed decisions, helping you adapt to market trends and consumer demands. By identifying potential opportunities and risks, you can position your business strategically for success.
The executive summary, often the first section potential investors or partners will read, encapsulates the key highlights of your entire business plan. Crafting an effective summary requires not just a brief overview of your business, but also a compelling narrative that grabs attention. It should effectively communicate your mission, vision, and values while summarizing your financial projections and market analysis. A strong executive summary can set the tone for the rest of the plan, making it imperative to take time perfecting this element.
Financial projections are essential for building a sustainable business budget. They provide a realistic outlook on your anticipated income, expenses, and profit margins over a specified time. Investors and stakeholders often look for solid financial plans that indicate growth potential and profitability. By meticulously forecasting your finances, you create trust in your business acumen while also highlighting your understanding of cash flow management, break-even analysis, and how to handle financial contingencies.
Defining your target audience is another critical component that amplifies your business strategy. By identifying specific market segments, you can tailor your products or services to meet their unique needs and preferences. Understanding who your customers are allows for more effective marketing efforts and better product development. A targeted approach helps in maximizing customer satisfaction and loyalty, which in turn will reflect positively on your bottom line.
The operational plan is the skeleton of your business strategy, showcasing how all the pieces work together. This is where you detail the day-to-day operations, management structure, and the logistics that drive your business forward. An effective operational plan not just outlines what needs to be done but also who will be responsible for each task. This clarity is vital for fostering accountability and ensuring that everyone in your team is aligned towards common objectives.
Measuring success is an ongoing endeavor, and establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) reflects your organization’s commitment to continuous improvement. These metrics allow you to gauge performance across various aspects of your business, aligning them with your strategic goals. Whether it’s sales growth, customer retention rates, or market reach, having specific KPIs set in advance offers a benchmark against which you can measure success, adapt strategies, and make informed decisions.
Each component of your business plan intricately weaves into the others, creating a cohesive strategy that supports long-term objectives. They enable you to stay organized, focused, and adaptable in an ever-changing landscape. The journey of entrepreneurship is filled with challenges and uncertainties, but a detailed business plan rooted in the 12 components can instill confidence in your path forward.
By investing the time and resources into building a comprehensive business plan, you are laying the groundwork for sustainable growth and success. Ultimately, the clarity and direction provided by these carefully devised sections can serve as a catalyst for your business, attracting investment and fostering stakeholder interest. Moving forward, remember that writing a business plan isn’t merely a checkbox activity; it’s an ongoing process that should evolve as your business grows. Engage with your classmates, mentors, and peers, and continually refine your business plan to ensure it remains relevant and strategically sound in navigating your entrepreneurial journey.

Freight Brokerage Financial Model Excel Template
Discover Freight Brokerage Pro Forma Projection. Impress bankers and investors with a proven, strategic business plan that impresses every time.... read more
- Excel - Multi-User – $129.00
- Excel - Single-User – $99.00
- Free Demo – $0.00

Port Operator Financial Model
Port Operator Financial Model presents the business case of an already operating port terminal (with planned refurbishments) and an investment in a ne... read more
- Excel Model – $119.00
- Free PDF – $0.00

Public-Private Partnership (PPP) Financial Model
Financial Model presenting development and operating scenarios of various projects under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) agreement.
- Excel Financial Model – $119.00 Version 1
- PDF Free Demo – $0.00 Version 1

Airport Financial Model (Development, Operation & Valuation)
Financial Model presenting a development and operating scenario of an Airport under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) agreement.
- Excel Financial Model – $149.00 Version 1

Project Finance Excel Model – 10 Year Projection
The template creates a financial model for your individual project finance initiative The model is suitable for any type of business / industry Includ... read more
- Full Version – $79.00 Version 3
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
A marketing plan is a strategic document that outlines marketing objectives, strategies, and tactics. A business plan is also a strategic document. But this plan covers all aspects of a company's operations, including finance, operations, and more. It can also help your business decide how to distribute resources and make decisions as your ...
Marketing plan v.s business plan. While both marketing plans and business plans are crucial documents for businesses, they serve distinct purposes and have different scopes. Here's a breakdown of the key differences: Business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines all aspects of your business, including: Mission and vision; Products ...
A marketing plan is the first step in creating a successful marketing program for your new business. Fortunately, it doesn't have to be complicated in order to work. Here are the 10 basic components of a marketing plan. You started a company and now you're thinking about developing a marketing program. You need to begin with a marketing plan.
1. Describe your product/service and target market. The idea is to paint a picture of your product or service as valuable to the customers in your target market. This component details what you ...
A marketing plan includes analysis of the target audience, the competitors, and the market so that teams can determine the best strategy for achieving their goals. The plan's length and detail depend on the company's size and the scope of the marketing project. A marketing plan is useful for all types of marketing, including digital, social media, new product, small business, B2C, and B2B.
Marketing plan vs. business plan. A business plan paints a bigger picture of how you plan to run your business. It includes a mission statement, products you'll launch, and market research. A marketing plan, on the other hand, is a specific document that details how you plan to achieve these wider goals through marketing.
A marketing plan is a core component of a business plan. It relates specifically to the marketing of a particular product or service and it describes: An overall marketing objective. A broad marketing strategy. The tactical detail related to specific marketing activities. The various costs associated with these activities.
You need to have a solid understanding of your target audience before integrating your marketing efforts. Example: If your target audience is executives that spend a lot of time on LinkedIn, focus your social media strategy around placing branded content on LinkedIn. 5. Differentiate with creative content.
Marketing planning will assist in the day-to-day running of any size, type or age of business. The targets and milestones set will help organizations, from small start-ups to large corporates, to effectively: Allocate resources and budget. Motivate teams. Manage the performance of staff members and marketing efforts.
A plan (the details of execution and the human resources, departments and software that will be involved) Reporting (what reports of progress will include and/or look like) We broke down those five functions into 10 actionable categories to help you create a marketing plan that is unique and effective for your business. 1.
Creating a marketing plan is a step-by-step process. Make sure you take your time with each step before moving on to the next one. 1. Create an Executive Summary. An executive summary is a ...
Marketing Plan vs. Business Plan. ... Marketing Strategy: This aspect defines the overarching approach and long-term vision for a company's engagement in the market. Each element of the marketing strategy is designed to align with the company's top-level goals and contribute to realizing its vision statement. In essence, the marketing ...
A marketing plan in business plan is one of the very important sections of a business plan. Marketing is done to spread awareness about your business and its product/service. [lwptoc] An effective marketing strategy helps you achieve early success. Use this article to write an effective marketing plan section in a business plan.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
Sales and distribution plan. Advertising and promotions plan. The easiest way to develop your marketing plan is to work through each of these sections, referring to the market research you completed when you were writing the previous sections of the business plan. (Note that if you are developing a marketing plan on its own, rather than as part ...
Marketing Plan: A marketing plan is a business's operational document for advertising campaigns designed to reach its target market . A marketing plan pulls together all the campaigns that will be ...
A marketing plan is a document that a business uses to execute a marketing strategy. It is tactical in nature, and, as later sections of this article explore, it typically includes campaign objectives, buyer personas, competitive analysis, key performance indicators, an action plan, and a method for analyzing campaign results.
The purpose of a marketing plan includes the following: To clearly define the marketing objectives of the business that align with the corporate mission and vision of the organization. The marketing objectives indicate where the organization wishes to be at any specific period in the future. The marketing plan usually assists in the growth of ...
We need to be more thoughtful and more measurable with our actions, and a sound marketing plan should be that blueprint. So let's cover each of these elements in detail: Business goals. Marketing goals. Target audiences. Messaging. Strategy. Tactics. Budget.
5. Develop Your Timeline and Budget. Establish a timeline and budget for your marketing strategy that reaches your audience throughout the year. It should include all scheduled promotions for the ...
A marketing strategy is important for all businesses because it clearly outlines how they'll find new customers and promote their products and services to ultimately achieve more sales. You can use the marketing strategy as a stand-alone tool, as part of a marketing plan, or as part of a business plan, all with slightly different components.
A marketing plan for small business clarifies your goals, identifies your target audience, and aligns your tactics with your business objectives. This alignment is critical for small businesses, where resources are often limited. Instead of spreading yourself thin across multiple channels, you focus on what truly matters, maximizing your impact
Include income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets. These documents help reinforce the viability of your business plan to investors. 9. Appendix. The appendix serves as a supplementary section for additional information that enhances your business plan. Include resumes, legal agreements, product images, or any market research ...