- Bibliography
- More Referencing guides Blog Automated transliteration Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Automated transliteration
- Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Referencing guides

Human resource accounting: a framework for valuation and application.
- Masters Thesis
- Helga Ruth Funk
- Michael Chatfield
- Craig School of Business
- Graduate Business Programs
- California State University, Fresno
- Master of Science in the School of Business and Administrative Sciences
- http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12680/k930c4937

Items in ScholarWorks are protected by copyright, with all rights reserved, unless otherwise indicated.
Accounting for Human Resources: Implications for Theory and Practice.
PDF Version Also Available for Download.
Description
Knowledge workers are an important resource for the typical modern business firm, yet financial reporting ignores such resources. Some researchers contend that the accounting profession has stressed reliability in order to make the accounting appear objective. Others concur, noting that accounting is an insecure profession and adopts strict rules when faced with uncertainty. Accountants have promulgated a strict rule to expense human resource costs, although many know that such resources have future benefits. Some researchers suggest that any discipline must modify its language in order to initiate change toward providing useful social ameliorations. If accounting theorists extend this idea to … continued below
Creation Information
Stovall, Olin Scott December 2001.
This dissertation is part of the collection entitled: UNT Theses and Dissertations and was provided by the UNT Libraries to the UNT Digital Library , a digital repository hosted by the UNT Libraries . It has been viewed 8175 times, with 8 in the last month. More information about this dissertation can be viewed below.
People and organizations associated with either the creation of this dissertation or its content.
- Stovall, Olin Scott
- Merino, Barbara D. Major Professor
Committee Members
- Luker, William Minor Professor
- Mayper, Alan G., 1952-
- Wu, Frederick H.
- Prybutok, Victor R.
- University of North Texas Place of Publication: Denton, Texas
Rights Holder
For guidance see Citations, Rights, Re-Use .
Provided By
Unt libraries.
The UNT Libraries serve the university and community by providing access to physical and online collections, fostering information literacy, supporting academic research, and much, much more.
Descriptive information to help identify this dissertation. Follow the links below to find similar items on the Digital Library.
Degree Information
- Name: Doctor of Philosophy
- Level: Doctoral
- Discipline: Accounting
- Department: Department of Accounting
- Grantor: University of North Texas
Knowledge workers are an important resource for the typical modern business firm, yet financial reporting ignores such resources. Some researchers contend that the accounting profession has stressed reliability in order to make the accounting appear objective. Others concur, noting that accounting is an insecure profession and adopts strict rules when faced with uncertainty. Accountants have promulgated a strict rule to expense human resource costs, although many know that such resources have future benefits. Some researchers suggest that any discipline must modify its language in order to initiate change toward providing useful social ameliorations. If accounting theorists extend this idea to the accounting lexicon.s description of investments in human resources, investors and other accounting user groups might gain greater insight into how a firm fosters and nourishes human capital. I tested three hypotheses related to this issue by administering an experiment designed to assess financial analysts. perceptions about alternative financial statement treatments of human resources in an investment recommendation task. I predicted that (1) analysts' perceptions of the reliability (relevance) of the information they received would decrease (increase) as the treatment of human resources increasingly violated GAAP (became more current-oriented), (2) analysts exposed to alternative accounting treatments would report a lower likelihood of recommending that their clients invest in the company in the task, and (3) financial analysts who ranked reliability (relevance) as a more important information quality would be less (more) likely to recommend that their clients buy the stock represented in the case because the treatment of human resources on the financial statements violated GAAP (was more current-oriented) as compared to analysts who ranked reliability (relevance) as being lower (higher) in importance. Analysts receiving financial statements with accounting treatments of human resource costs that violated GAAP judged such information as less reliable and were also less likely to recommend that their clients buy the stock in the task than analysts receiving financial statements that conformed to GAAP. Also, analysts who perceived reliability as a more important information quality reacted more negatively to a replacement cost approach to accounting for human resources than participants who perceived reliability as being less important. A potential confounding explanation of the results is the varied language used in the audit opinions included with the treatment financial statements. Whether explained by the audit opinion language or the actual differences contained in the financial statements, the results suggest that an important user group, financial analysts, may be subject to the aura of objectivity suggested by Porter in 1995.
- Human resource accounting
- financial analysts
- objectivity
- relevant experiment
- reliability
Library of Congress Subject Headings
- Human capital -- Accounting.
- Thesis or Dissertation
Unique identifying numbers for this dissertation in the Digital Library or other systems.
- OCLC : 51969862
- Archival Resource Key : ark:/67531/metadc3026
Collections
This dissertation is part of the following collection of related materials.
UNT Theses and Dissertations
Theses and dissertations represent a wealth of scholarly and artistic content created by masters and doctoral students in the degree-seeking process. Some ETDs in this collection are restricted to use by the UNT community .
What responsibilities do I have when using this dissertation?
Digital Files
- 183 image files available in multiple sizes
- 1 file (.pdf)
- Metadata API: descriptive and downloadable metadata available in other formats
Dates and time periods associated with this dissertation.
Creation Date
- December 2001
Added to The UNT Digital Library
- Sept. 25, 2007, 10:58 p.m.
Description Last Updated
- April 14, 2020, 3:19 p.m.
Usage Statistics
When was this dissertation last used?
Interact With This Dissertation
Here are some suggestions for what to do next.
Search Inside
- or search this site for other thesis or dissertations
Start Reading
- All Formats
Citations, Rights, Re-Use
- Citing this Dissertation
- Responsibilities of Use
- Licensing and Permissions
- Linking and Embedding
- Copies and Reproductions
International Image Interoperability Framework

We support the IIIF Presentation API
Print / Share
Links for robots.
Helpful links in machine-readable formats.
Archival Resource Key (ARK)
- ERC Record: /ark:/67531/metadc3026/?
- Persistence Statement: /ark:/67531/metadc3026/??
International Image Interoperability Framework (IIIF)
- IIIF Manifest: /ark:/67531/metadc3026/manifest/
Metadata Formats
- UNTL Format: /ark:/67531/metadc3026/metadata.untl.xml
- DC RDF: /ark:/67531/metadc3026/metadata.dc.rdf
- DC XML: /ark:/67531/metadc3026/metadata.dc.xml
- OAI_DC : /oai/?verb=GetRecord&metadataPrefix=oai_dc&identifier=info:ark/67531/metadc3026
- METS : /ark:/67531/metadc3026/metadata.mets.xml
- OpenSearch Document: /ark:/67531/metadc3026/opensearch.xml
- Thumbnail: /ark:/67531/metadc3026/thumbnail/
- Small Image: /ark:/67531/metadc3026/small/
- In-text: /ark:/67531/metadc3026/urls.txt
- Usage Stats: /stats/stats.json?ark=ark:/67531/metadc3026
Stovall, Olin Scott. Accounting for Human Resources: Implications for Theory and Practice. , dissertation , December 2001; Denton, Texas . ( https://digital.library.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metadc3026/ : accessed August 1, 2024 ), University of North Texas Libraries, UNT Digital Library, https://digital.library.unt.edu ; .
- My Shodhganga
- Receive email updates
- Edit Profile
Shodhganga : a reservoir of Indian theses @ INFLIBNET
- Shodhganga@INFLIBNET
- Dayalbagh Educational Institute
- Department of Accountancy and Law
| Title: | HUMAN RESOURCE ACCOUNTING IN INDIA WITH SPECIFIC REFERENCE TO BHEL AND SAIL |
| Researcher: | Ahuja Reshma |
| Guide(s): | |
| Keywords: | HUMAN RESOURCE ACCOUNTING |
| University: | Dayalbagh Educational Institute |
| Completed Date: | 2007 |
| Abstract: | newline |
| Pagination: | |
| URI: | |
| Appears in Departments: | |
| File | Description | Size | Format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attached File | 317.45 kB | Adobe PDF | ||
| 240.54 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 183.25 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 1.42 MB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 613.3 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 207.04 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 784.87 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 732.86 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 141.82 kB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 7.61 MB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 7.23 MB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 10.46 MB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 6.89 MB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 1.29 MB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 10.49 MB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 2.92 MB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 2.19 MB | Adobe PDF | |||
| 3 MB | Adobe PDF |
Items in Shodhganga are licensed under Creative Commons Licence Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0).

Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Human resource accounting: a historical perspective and future implications

2002, Management Decision
Related Papers
shreelatha H R
Industrial Relations
Gary Sundem
AFRICAN JOURNAL OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT
Ijaz Bokhari
International Journal of Advanced Research (IJAR)
IJAR Indexing
Human capital creates value by coordinating and managing other capitals to achieve corporate goals. Although intangible, the human factor gives life to entities, creates harmonious environment for improved efficiency, effectiveness and economy in the use of corporate resources. Its usefulness to internal productivity and external goodwill are acknowledged in the literature. Its quality, expertise, experience, character and integrity are attributes sought after by providers of financial and other capitals. Economic benefits flow to the entity from human capital. However, in corporate financial reports, human capital is not an element of the Statement of Financial Position or Balance Statement. Since financial values are not assigned to human resource like other assets, investment in and reward to human capital, which enhance its output, are expensed at the Income Statement level. This practice diminishes its status as the most critical resource of the organization as board chairmen often declare at annual general meetings. Using secondary data, this study supports the findings of previous research works that the assignment of financial values and reflection of human resource in balance sheet, will raise shareholders? wealth and eliminate hidden values in financial reports. Since human capital satisfies the criteria of identifiability and control by an entity set by IAS 38 for Intangible Assets, this study recommends that standard setters and policy makers should commence the process that will lead to the recognition of human capital in balance sheet.
Journal of Human Resource Costing & Accounting
Journal of Environmental, Cultural, Economic and Social Sustainability
Geoff Turner
Even though accounting for an organisation’s human resources was first discussed more than thirty years ago, it is yet to be recognised in mainstream accounting. This paper reviews the history of accounting for human resources and provides support for the continuing development and adoption of the paradigm. Along the way the excuses of an earlier era are refuted and propositions made to legitimise human resource accounting in the next epoch. The accounting profession is challenged to examine its current myopic approach to the provision of decision-making information. It is suggested the profession develop a more inclusive, socially acceptable information system, which includes accounting for human resources, that has its foundation in the measurement of the value created by an organisation for the economic sustainability of itself and its stakeholders.
Alomgir Hossain
Human Resource Accounting (HRA) involves accounting for costs related to human resources as assets as opposed to traditional accounting. Since the beginning of globalization of business and services, human elements are becoming more important input for the success of every organization. The strong growth of international financial reporting standards (IFRS) encourages the consideration of alternative measurement and reporting standards and lends support to the possibility that future financial reports will include non-traditional measurements such as the value of human resources using HRA methods. It helps the management to frame policies for human resources of their organizations. HRA is a process of identifying and measuring data about human resources. It will help to charge human resource investment over a period of time. It is not a new concept in the arena of business world. Economists consider human capital as a production factor, and they explore different ways of measuring its investment. Now accountants are recognizing human resource investment as an asset. This study is build upon Recognition, Measurement and Accounting Treatment of Human Resource Accounting in different organizations.
IOSR Journal of Business and Management
jaynob sarker
francis emeni
It has been increasingly argued in accounting and managerial literature the organization s failure to account for its human resource can have several a' consequences on the overall organizational effectiveness. In this wise the research discussed efforts done in this field by researchers and proposed a model known as I{ identifying and reporting investments made in human resources of an organization are not presently accounted for under conventional accounting practice. This IQR 1 is a three step model which classifies employees into separate Para-homogenous g and determines economic value of the various groups identified and gives the variable determined accounting treatment in the organizations books of account. On applyi1 IQR Model in this study, it was found that, total present value of employees (Junior, Senior) increases from year to year because they acquire skill and knowledge ove1 while on or off-the-job unlike physical assets. Some recommendations were made l on the co...
Jacob Birnberg , James Craft
5 Jacob G. Birnberg and Nicholas Dopuch, A Conceptual Approach to the Framework for Disclosure, Journal of Accountancy, CXV (February, 1963), 59. Also, see Roger H. Hermanson, Accounting for Human Assets, Occasional Paper No. 14, Bureau of Business ...
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Vijaya Murthy
ijifr journal
Journal of Management Studies
Fariborz Avazzadehfath
Global Journal of Management and Business Research: D Accounting and Auditing
Md. Tanjim Hossain
Dumitru Ionel
Publisher ijmra.us UGC Approved
Legesse Agegnehu
Kavitha C Achar
Olin Stovall
Huaiying Wang
Gürhan Uysal
Journal ijmr.net.in(UGC Approved)
Management Science Letters
Research Journal of Finance and Accounting
Ibukun Falayi
Academy of Management Review
Philip Mirvis
IOSR Journals publish within 3 days
Trang Linh Lê
nader naghshbandi
Simon Kamau
Asian Journal of Finance & Accounting
Australasian Accounting Business and Finance Journal
Vol. 12 No. 8 (2021)
farshad ganji , Hüseyin Arı
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Advertisement
Rejuvenating human resource accounting research: a review using bibliometric analysis
- Published: 05 July 2023
Cite this article

- Lakshmi Bhooshetty ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7152-1055 1
467 Accesses
Explore all metrics
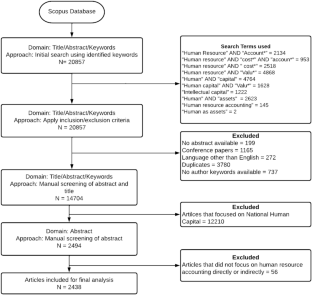
The current study attempts to map the intellectual structure of Human Resource Accounting to understand the research gaps and future trajectories. The study employs systematic literature review technique to extract relevant literature, bibliometric analysis to map the intellectual structure of research in human resource accounting, to identify underlying research themes and content analysis to identify avenues for future research. Based on 2438 publications, author keyword co-occurrences extracted four themes namely, Human Resource Management, Intellectual Capital, Human Capital, and Voluntary Disclosure. The study also summarizes significant findings of papers under each cluster through content analysis identifying areas for future research. The study provides a bird’s eye view of the intellectual structure of academic research efforts in the field of human resource accounting. The study is one of the first attempt to comprehensively review the academic literature from Scopus database employing systematic literature review, bibliometric methods, and content analysis in the field of human resource accounting.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
Research on environmental accounting: past studies and future trends

Research Trends in Green Human Resource Management: A Comprehensive Review of Bibliometric Data

A bibliometric review of bibliometric reviews of corporate governance: current topics and recommendations for future research
Albrecht SL, Bakker AB, Gruman JA, Macey WH, Saks AM (2015) Employee engagement, human resource management practices and competitive advantage. J Organ Eff People Perform 2(1):7–35. https://doi.org/10.1108/JOEPP-08-2014-0042
Article Google Scholar
Aliyev F, Urkmez T, Wagner R (2019) A comprehensive look at luxury brand marketing research from 2000 to 2016: a bibliometric study and content analysis. Manage Rev Quart 69(3):233–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-018-00152-3
Alvino F, Di Vaio A, Hassan R, Palladino R (2020) Intellectual capital and sustainable development: a systematic literature review. J Intellect Cap 22(1):76–94. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIC-11-2019-0259
Amalou-Döpke L, Süß S (2014) HR Measurement as an instrument of the HR department in its exchange relationship with top management: a qualitative study based on resource dependence theory. Manage Meas 30(4):444–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scaman.2014.09.003
American Accounting Association Report (1974) Report of the committee on accounting for human resources. Acc Rev 49:115–124
Google Scholar
Ananthram S, Nankervis A, Chan C (2013) Strategic human asset management: evidence from North America. Pers Rev 42(3):281–299. https://doi.org/10.1108/00483481311320417
Archer NP, Ghasemzadeh F, Lynn BE (1998) Performance evaluation in the new economy: Bringing the measurement and evaluation of intellectual capital into the management planning and control system. Int J Technol Manage 16(1–3):162–76. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJTM.1998.002654
Aria M, Cuccurullo C (2017) Bibliometrix: an R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Informet 11(4):959–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
Assefa SG, Rorissa A (2013) A bibliometric mapping of the structure of STEM education using co-word analysis. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol 64(12):2513–2536. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.22917
Bapna R, Langer N, Mehra A, Gopal R, Gupta A (2013) Human capital investments and employee performance: an analysis of IT services industry. Manage Sci 59(3):641–658. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.1120.1586
Bar-Ilan J (2008) Which H-index?—a comparison of WoS, scopus and google scholar. Scientometrics 74(2):257–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-008-0216-y
Bartolini M, Bottani E, Grosse EH (2019) Green warehousing: systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis. J Clean Prod 226 (July):242–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.055
Bassett GA (1972) Employee turnover measurement and human resources accounting. Hum Resour Manage (pre-1986_ 11(3):21
Becker B, Gerhart B (1996) The impact of human resource management on organizational performance: progress and prospects. Acad Manag J 39(4):779–801. https://doi.org/10.5465/256712
Bellucci M, Marzi G, Orlando B, Ciampi F (2021) Journal of intellectual capital: a review of emerging themes and future trends. J Intellect Cap 22(4):744–767. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIC-10-2019-0239
Bessieux-Ollier C, Nègre E, Verdier M-A (2022) Moving from accounting for people to accounting with people: a critical analysis of the literature and avenues for research. Eur Acc Rev. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638180.2022.2052922
Bharathi Kamath G (2008) Intellectual capital and corporate performance in Indian pharmaceutical industry. J Intellect Cap 9(4):684–704. https://doi.org/10.1108/14691930810913221
Block J, Fisch C, Rehan F (2020) Religion and entrepreneurship: a map of the field and a bibliometric analysis. Manage Rev Quart 70(4):591–627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-019-00177-2
Bontis N (1999) Managing organizational knowledge by diagnosing intellectual capital: framing and advancing the state of the field. Int J Technol Manag 18:433–462
Bontis N, Fitz-enz J (2002) Intellectual capital ROI: a causal map of human capital antecedents and consequents. J Intellect Cap 3(3):223–247. https://doi.org/10.1108/14691930210435589
Bontis N, Serenko A (2009) A causal model of human capital antecedents and consequents in the financial services industry. Edited by Nick Bontis and Christopher Bart. J Intell Cap 10(1):53–69. https://doi.org/10.1108/14691930910922897
Bontis N, Janošević S, Dženopoljac V (2015) Intellectual capital in Serbia’s hotel industry. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 27(6):1365–1384. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-12-2013-0541
Boxall P, Macky K (2007) High-performance work systems and organisational performance: bridging theory and practice. Asia Pac J Hum Resour 45(3):261–270. https://doi.org/10.1177/1038411107082273
Bradford SC (1934) Sources of information on specific subjects. Engineering 137:85–86
Brummet RL, Flamholtz EG, Pyle WC (1968) Human resource measurement – a challenge for accountants. Acc Rev 43(2):217–224
Bullay A, Abuhommous AA, Kukreja G (2021) The relationship between intellectual capital and employees’ productivity: evidence from the gulf cooperation council. J Manage Dev 40(6):526–541. https://doi.org/10.1108/JMD-05-2019-0210
Caddy I (2002) Issues concerning intellectual capital metrics and measurement of intellectual capital. Singap Manag Rev 24(3):77–88
Camuffo A, Comacchio A (2005) Linking intellectual capital and competitive advantage: a cross-firm competence model for North-East Italian SMEs in the manufacturing industry. Hum Resour Dev Int 8(3):361–377. https://doi.org/10.1080/13678860500149951
Cannon JA (1974) A further comment on human resource accounting. Pers Rev 3(4):38–42. https://doi.org/10.1108/eb055267
Caves RE (1980) Industrial organization, corporate strategy and structure. In: Emmanuel C, Otley D, Merchant K (eds) Readings in accounting for management control. Springer, Boston, pp 335–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-7138-8_16
Chapter Google Scholar
Chandler GN, Hanks SH (1998) An examination of the substitutability of founders human and financial capital in emerging business ventures. J Bus Vent 13(5):353–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-9026(97)00034-7
Chen X, Wang S, Tang Y, Hao T (2018) A bibliometric analysis of event detection in social media. Online Inf Rev 43(1):29–52. https://doi.org/10.1108/OIR-03-2018-0068
Cheng B, Wang M, Mørch AI, Chen N-S, Spector JM (2014) Research on E-learning in the workplace 2000–2012: a bibliometric analysis of the literature. Educ Res Rev 11:56–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2014.01.001
Chung Y, Colakoglu S (2018) A closer examination of how human resource management systems impact social and human capital in organisations. Int J Learn Intellect Cap 15(2):119–136. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJLIC.2018.091977
Coff RW (1999) How buyers cope with uncertainty when acquiring firms in knowledge-intensive industries: caveat emptor. Organ Sci 10(2):144–161
Collis DJ, Montgomery CA (1995) How do you create and sustain a profitable strategic? Competing on resources. Harv Bus Rev 73(4):118–128
Comerio N, Strozzi F (2019) Tourism and Its economic impact: a literature review using bibliometric tools. Tour Econ 25(1):109–131. https://doi.org/10.1177/1354816618793762
Couckuyt D, Van Looy A (2019) Green BPM as a business-oriented discipline: a systematic mapping study and research agenda. Sustainability 11(15):4200. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11154200
Criaco G, Minola T, Migliorini P, Serarols-Tarrés C (2014) ‘To have and have not’: founders’ human capital and university start-up survival. J Technol Transf 39(4):567–593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10961-013-9312-0
Dammak S (2015) Human capital disclosure and market capitalization. Corp Ownersh Control 13(1):502–513. https://doi.org/10.22495/cocv13i1c4p8
Daum JH (2003) Intangible assets and value creation. John Wiley & Sons
Davenport TH, Harris J, Shapiro J (2010) Competing on talent analytics. Harv Bus Rev 88(10):52–58
De Saá-Pérez P, GarcÍa-FalcÓn JM (2002) A resource-based view of human resource management and organizational capabilities development. Int J Hum Resour Manage 13(1):123–140. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585190110092848
De Winne S, Sels L (2010) Interrelationships between human capital, HRM and innovation in belgian start-ups aiming at an innovation strategy. Int J Hum Resour Manage 21(11):1863–1883. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585192.2010.505088
Delery JE, Roumpi D (2017) Strategic human resource management, human capital and competitive advantage: is the field going in circles? Hum Resour Manag J 27(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/1748-8583.12137
Ding Y, Chowdhury GG, Foo S (2001) Bibliometric cartography of information retrieval research by using co-word analysis. Inf Process Manage 37(6):817–842. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-4573(00)00051-0
dos Santos NMBF, Nunes D, Freitas FCR, Munhoz IP, Caldana A (2019) Human capital measurement: a bibliometric survey. In: Iano Y, Arthur R, Saotome O, Estrela VV, Loschi HJ (eds) Proceedings of the 4th Brazilian technology symposium (BTSym’18), pp 451–459. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies. Springer International Publishing, Cham https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16053-1_43
Dzenopoljac V, Yaacoub C, Elkanj N, Bontis N (2017) Impact of intellectual capital on corporate performance: evidence from the Arab region. J Intellect Cap 18(4):884–903. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIC-01-2017-0014
Dzinkowski R (2000) The measurement and management of intellectual capital: an introduction. Manage Acc 78(2):32–36
Edvinsson L (1997) Developing intellectual capital at Skandia. Long Range Plan 30:10
Elbannan MA, Farooq O (2016) Value relevance of voluntary human capital disclosure: european evidence. J Appl Bus Res (JABR) 32(6):1555–1560. https://doi.org/10.19030/jabr.v32i6.9807
Estrin S, Mickiewicz T, Stephan U (2016) Human capital in social and commercial entrepreneurship. J Bus Ventur 31(4):449–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2016.05.003
Fahimnia B, Sarkis J, Davarzani H (2015) Green supply chain management: a review and bibliometric analysis. Int J Prod Econ 162(April):101–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2015.01.003
Ferguson DH, Berger F (1985) Employees as assets: a fresh approach to human-resources accounting. Cornell Hotel Restaur Adm Quart 25(4):24–29. https://doi.org/10.1177/001088048502500407
Fernandez V, Maureen L, Nicolas C, Merigó JM, Arroyo-Cañada F-J (2019) Industrial marketing research: a bibliometric analysis (1990–2015). J Bus Ind Mark 34(3):550–560. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-07-2017-0167
Filios VP (1991) Human resource accounting is social accounting: a managerial reappraisal. Hum Syst Manag 10(4):267–280. https://doi.org/10.3233/HSM-1991-10405
Fisch C, Block J (2018) Six tips for your (systematic) literature review in business and management research. Manage Rev Quart 68(2):103–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-018-0142-x
Fitz-enz J (2010) The new HR analytics: predicting the economic value of your company’s human capital investments. American Management Association, New York
Flamholtz E (1972) Human resource accounting: a review of theory and research. Acad Manag Proc 1:174–177. https://doi.org/10.5465/ambpp.1972.4981436
Flamholtz E (1976) The impact of human resource valuation on management decisions: a laboratory experiment. Acc Organ Soc 1(2–3):153–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/0361-3682(76)90019-2
Flamholtz EG (1980) The process of measurement in managerial accounting: a psycho-technical systems perspective. Acc Organ Soc 5(1):31–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/0361-3682(80)90019-7
Flamholtz EG, Main ED (1999) Current issues, recent advancements, and future directions in human resource accounting. J Hum Resour Cost Acc 4(1):11–20. https://doi.org/10.1108/eb029050
Flamholtz EG, Bullen ML, Hua W (2002) Human resource accounting: a historical perspective and future implications. Manag Decis 40(10):947–954. https://doi.org/10.1108/00251740210452818
Flamholtz EG, Kannan-Narasimhan R, Bullen ML (2004) Human resource accounting today: contributions, controversies and conclusions. J Hum Resour Cost Acc 8(2):23–37. https://doi.org/10.1108/eb029084
Fulmer IS, Ployhart RE (2014) ‘Our most important asset’: a multidisciplinary/multilevel review of human capital valuation for research and practice. J Manag 40(1):161–192. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206313511271
Galunic DC, Anderson E (2000) From security to mobility: generalized investments in human capital and agent commitment. Organ Sci 11(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.11.1.1.12565
Gamerschlag R, Moeller K (2011) The positive effects of human capital reporting. Corp Reput Rev 14(2):145–155. https://doi.org/10.1057/crr.2011.11
Gross-Gołacka E, Kusterka-Jefmańska M, Jefmański B (2020) Can elements of intellectual capital improve business sustainability?—The perspective of managers of SMEs in Poland. Sustainability 12(4):1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041545
Gupta BM, Dhawan SM (2009) Status of India in science and technology as reflected in its publication output in the scopus international database, 1996–2006. Scientometrics 80(2):473–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-008-2083-y
Guthrie J, Petty R (2000) Intellectual capital: australian annual reporting practices. J Intellect Cap 1(3):241–251
Hayton JC (2005) Competing in the new economy: the effect of intellectual capital on corporate entrepreneurship in high-technology new ventures. R&D Manage 35(2):137–155. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9310.2005.00379.x
Hekimian JS, Jones CH (1967) Put people on your balance sheet. Harvard Bus Rev 45:105–113
Hirsch JE (2005) An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102(46):16569–16572. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507655102
Hormiga E, Batista-Canino RM, Sánchez-Medina A (2011) The role of intellectual capital in the success of new ventures. Int Entrep Manage J 7(1):71–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-010-0139-y
Huang C-F, Hsueh S-L (2007) A study on the relationship between intellectual capital and business performance in the engineering consulting industry: a path analysis. J Civ Eng Manag 13(4):265–271. https://doi.org/10.3846/13923730.2007.9636446
Jain J, Walia N, Singh S, Jain E (2021) Mapping the field of behavioural biases: a literature review using bibliometric analysis. Manage Rev Quart. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-021-00215-y
Jia H, Zhou S, Allaway AW (2018) Understanding the evolution of consumer psychology research: a bibliometric and network analysis. J Consum Behav 17(5):491–502. https://doi.org/10.1002/cb.1734
Johnson WHA (2002) Leveraging intellectual capital through product and process management of human capital. J Intellect Cap 3(4):415–429. https://doi.org/10.1108/14691930210448323
Jones DMC (1973) Accounting for human assets. Manag Decis 11(3):183–194. https://doi.org/10.1108/eb001021
Joshi M, Cahill D, Sidhu J, Kansal M (2013) Intellectual capital and financial performance: an evaluation of the australian financial sector. J Intellect Cap 14(2):264–285. https://doi.org/10.1108/14691931311323887
Juma N, McGEE J (2006) The relationship between intellectual capital and new venture performance: an empirical investigation of the moderating role of the environment. Int J Innov Technol Manag 03(04):379–405. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219877006000892
Kamath GB (2021) Corporate governance and intellectual capital disclosure. Int J Learn Intellect Cap 18(4):365–398. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJLIC.2021.118412
Kaplan RS, Norton DP (2006) Alignment: using the balanced scorecard to create corporate synergies – Kaplan RS, Norton DP (eds). Harvard Business School Press, Boston
Kent Baker H, Pandey N, Kumar S, Haldar A (2020) A bibliometric analysis of board diversity: current status, development, and future research directions. J Bus Res 108(January):232–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.11.025
Komnenic B, Pokrajčić D (2012) Intellectual capital and corporate performance of MNCs in Serbia. J Intellect Cap 13(1):106–119. https://doi.org/10.1108/14691931211196231
Kouhy R, Vedd R (2000) Performance measurement in strategic human resource management. Int J Bus Perform Manage 2(1/2/3):137. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJBPM.2000.000073
Kryscynski D, Coff R, Campbell B (2021) Charting a path between firm-specific incentives and human capital-based competitive advantage. Strateg Manag J 42(2):386–412. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.3226
Kumar S, Sureka R, Colombage S (2020) Capital structure of SMEs: a systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis. Manage Rev Quart 70(4):535–565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-019-00175-4
Lajili K, Zéghal D (2006) Market performance impacts of human capital disclosures. J Acc Public Policy 25(2):171–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaccpubpol.2006.01.006
Lardo A, Dumay J, Trequattrini R, Russo G (2017) Social media networks as drivers for intellectual capital disclosure. J Intellect Cap 18(1):63–80. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIC-09-2016-0093
Leifheit N, Follert F (2021) Financial player valuation from the perspective of the club: the case of football. Manag Sport Leisure. https://doi.org/10.1080/23750472.2021.1944821
Leitner K-H (2011) The effect of intellectual capital on product innovativeness in SMEs. Int J Technol Manage 53(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJTM.2011.037235
Lev B (2001) Intangibles: management, measurement, and reporting. Brookings Institution Press
Lev B, Schwartz A (1971) On the use of the economic concept of human capital in financial statements. Account Rev 46(1):103–112
Li C, Kening Wu, Jingyao Wu (2017) A Bibliometric Analysis of Research on Haze during 2000–2016. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(32):24733–24742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0440-1
Likert R, Pyle WC (1971) A human organizational measurement approach. Financ Anal J 27(1):75–84
Lin CYY, Wei YC, Chen MH (2006) The role of board chair in the relationship between board human capital and firm performance. Int J Bus Gov Ethics 2(3/4):329. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJBGE.2006.011161
Macpherson A, Holt R (2007) Knowledge, learning and small firm growth: a systematic review of the evidence. Res Policy 36(2):172–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2006.10.001
Maditinos D, Chatzoudes D, Tsairidis C, Theriou G (2011) The impact of intellectual capital on firms’ market value and financial performance. J Intellect Cap 12(1):132–151. https://doi.org/10.1108/14691931111097944
Mao G, Huang N, Chen L, Wang H (2018) Research on biomass energy and environment from the past to the future: a bibliometric analysis. Sci Total Environ 635:1081–1090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.173
Mardini GH, Lahyani FE (2022) Impact of firm performance and corporate governance mechanisms on intellectual capital disclosures in CEO statements. J Intellect Cap 23(2):290–312. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIC-02-2020-0053
Martin BC, McNally JJ, Kay MJ (2013) Examining the formation of human capital in entrepreneurship: a meta-analysis of entrepreneurship education outcomes. J Bus Ventur 28(2):211–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2012.03.002
Martín-de-Castro G, Delgado-Verde M, López-Sáez P, Navas-López JE (2011) Towards ‘an intellectual capital-based view of the firm’: origins and nature. J Bus Ethics 98(4):649–662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-010-0644-5
Mavridis DG, Kyrmizoglou P (2005) Intellectual capital performance drivers in the greek banking sector. Manag Res News 28(5):43–62. https://doi.org/10.1108/01409170510629032
McGuirk H, Lenihan H, Hart M (2015) Measuring the impact of innovative human capital on small firms’ propensity to innovate. Res Policy 44(4):965–976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2014.11.008
Mehralian G, Rajabzadeh A, Sadeh MR, Rasekh HR (2012) Intellectual capital and corporate performance in iranian pharmaceutical industry. J Intellect Cap 13(1):138–158. https://doi.org/10.1108/14691931211196259
Michael Hall C (2011) Publish and perish? Bibliometric analysis, journal ranking and the assessment of research quality in Tourism. Tour Manage 32(1):16–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2010.07.001
Mihardjo LWW, Jermsittiparsert K, Ahmed U, Chankoson T, Hussain HI (2021) Impact of key HR practices (human capital, training and rewards) on service recovery performance with mediating role of employee commitment of the takaful industry of the Southeast Asian Region. Educ Train 63(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1108/ET-08-2019-0188
Mishra D, Gunasekaran A, Papadopoulos T, Childe SJ (2016) Big data and supply chain management: a review and bibliometric analysis. Ann Oper Res 270(1–2):313–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-016-2236-y
Mondal A, Ghosh SK (2012) Intellectual capital and financial performance of Indian Banks. J Intellect Cap 13(4):515–530. https://doi.org/10.1108/14691931211276115
Mouritsen J (2004) Measuring and intervening: how do we theorise intellectual capital management? J Intellect Cap 5(2):257–267. https://doi.org/10.1108/14691930410533687
Nguyen AH, Doan DT (2020) The impact of intellectual capital on firm value: empirical evidence from Vietnam. Int J Financ Res 11(4):74. https://doi.org/10.5430/ijfr.v11n4p74
Ni Y, Cheng Y-R, Huang P (2021) Do intellectual capitals matter to firm value enhancement? Evidences from Taiwan. J Intellect Cap 22(4):725–743. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIC-10-2019-0235
Nieves J, Quintana A, Osorio J (2014) Knowledge-based resources and innovation in the hotel industry. Int J Hosp Manag 38(April):65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2014.01.001
Nimtrakoon S (2015) The relationship between intellectual capital, firms’ market value and financial performance. J Intellect Cap 16(3):587–618. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIC-09-2014-0104
O’Donnell L, Kramar R, Dyball MC (2009) Human capital reporting: should it be industry specific? Asia Pac J Hum Resour 47(3):358–373. https://doi.org/10.1177/1038411108099293
Offstein EH, Gnyawali DR, Cobb AT (2005) A strategic human resource perspective of firm competitive behavior. Hum Resour Manag Rev 15(4):305–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2005.11.007
Oprean V-B, Oprisor T (2014) Accounting for soccer players: capitalization paradigm versus expenditure. Proc Econ Finance 15:1647–1654. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2212-5671(14)00636-4
Ozkan N, Cakan S, Kayacan M (2017) Intellectual capital and financial performance: a study of the Turkish banking sector. Borsa Istanbul Rev 17(3):190–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bir.2016.03.001
Peña I (2002) Intellectual capital and business start-up success. J Intellect Cap 3(2):180–198. https://doi.org/10.1108/14691930210424761
Persson O (2009) Celebrating scholarly communication studies. Int Soc Scientometr Informetr 5:9–24
Phusavat K, Comepa N, Sitko-Lutek A, Ooi K-B (2011) Interrelationships between intellectual capital and performance. Ind Manag Data Syst 111(6):810–829. https://doi.org/10.1108/02635571111144928
Pisano S, Lepore L, Lamboglia R (2017) Corporate disclosure of human capital via linkedin and ownership structure. J Intellect Cap 18(1):102–127. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIC-01-2016-0016
Qamar Y, Samad TA (2022) Human resource analytics: a review and bibliometric analysis. Pers Rev 51(1):251–283. https://doi.org/10.1108/PR-04-2020-0247
Quintero-Quintero W, Blanco-Ariza AB, Garzón-Castrillón MA (2021) Intellectual capital: a review and bibliometric analysis. Publications. https://doi.org/10.3390/publications9040046
Radhakrishna RB, Jackson GB (1995) Prolific authors in the journal of agricultural education: a review of the eighties. J Agric Educ 36(1):9
Ramli A, Rasdi RM (2021) Leveraging Intellectual Capital Dimensions for Promoting Learning Organization in a Rural Development Agency. Pertanika J Soc Sci Humanit. https://doi.org/10.47836/pjssh.29.1.37
Ramos-Rodríguez A-R, Ruíz-Navarro J (2004) Changes in the intellectual structure of strategic management research: a bibliometric study of the strategic management journal, 1980–2000. Strateg Manag J 25(10):981–1004. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.397
Rana S, Pragati (2022) A bibliometric and visualization analysis of human capital and sustainability. Vision. https://doi.org/10.1177/09722629221105773
Rodrigues H, Almeida F, Figueiredo V, Lopes SL (2019) Tracking E-learning through published papers: a systematic review. Comput Educ 136(July):87–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.03.007
Sadabadi AA, Ramezani S, Fartash K, Nikijoo I (2022) Intangible assets: scientometrics and bibliometric using social network analysis. Int J Inf Sci Manage (IJISM) 20(4):49–73
Samson K, Bhanugopan R (2022) Strategic human capital analytics and organisation performance: the mediating effects of managerial decision-making. J Bus Res 144(May):637–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.01.044
Secinaro S, Brescia V, Calandra D, Biancone P (2020) Employing bibliometric analysis to identify suitable business models for electric cars. J Clean Prod 264:121503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121503
Secundo G, Margherita A, Elia G, Passiante G (2010) Intangible assets in higher education and research: mission, performance or both?. Edited by Eric Kong. J Intellect Cap 11(2):140–157. https://doi.org/10.1108/14691931011039651
Seetharaman A, Sooria HHBZ, Saravanan AS (2002) Intellectual capital accounting and reporting in the knowledge economy. J Intellect Cap 3(2):128–148. https://doi.org/10.1108/14691930210424734
Sihotang P, Winata A (2008) The intellectual capital disclosures of technology-driven companies: evidence from indonesia. Int J Learn Intellect Cap 5(1):63–82. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJLIC.2008.018883
Singla HK (2020) Does VAIC affect the profitability and value of real estate and infrastructure firms in India? A panel data investigation. J Intellect Cap 21(3):309–331. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIC-03-2019-0053
Smith ME (2003) Another road to evaluating knowledge assets. Hum Resour Dev Rev 2(1):6–25. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534484302250598
Soewarno N, Tjahjadi B (2020) Measures that matter: an empirical investigation of intellectual capital and financial performance of banking firms in Indonesia. J Intellect Cap 21(6):1085–1106. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIC-09-2019-0225
Sollosy M, McInerney M, Braun CK (2016) Human capital: a strategic asset whose time has come to be recognized on organizations’ financial statements. J Corp Acc Finance 27(6):19–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcaf.22201
Sonnier BM (2008) Intellectual capital disclosure: high-tech versus traditional sector companies. J Intellect Cap 9(4):705–722. https://doi.org/10.1108/14691930810913230
Stewart T (1991) BRAINPOWER intellectual capital is becoming corporate America’s most valuable asset and can be its sharpest competitive weapon. The Challenge Is to Find What You Have -- and Use It. - June 3, 1991.” 1991. https://archive.fortune.com/magazines/fortune/fortune_archive/1991/06/03/75096/index.htm
Stewart T (1994) Your company’s most valuable asset: intellectual capital business pioneers are finding surprising ways to put real dollars on the bottom line as they discover how to measure and manage the ultimate intangible: knowledge. - October 3, 1994.” 1994. https://money.cnn.com/magazines/fortune/fortune_archive/1994/10/03/79803/
Stewart TA (1997) Intellectual capital: the new wealth of organizations, 1st edn. Doubleday/Currency, New York
Stovel M, Bontis N (2002) Voluntary turnover: knowledge management – friend or foe? J Intellect Cap. https://doi.org/10.1108/14691930210435633
Sydler R, Haefliger S, Pruksa R (2014) Measuring intellectual capital with financial figures: can we predict firm profitability? Eur Manag J 32(2):244–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2013.01.008
Teece DJ, Pisano G, Shuen A (1997) Dynamic capabilities and strategic management. Strat Manage J 18(7):509–533
Tobin J (1969) A general equilibrium approach to monetary theory. J Money Credit Bank 1(1):15–29. https://doi.org/10.2307/1991374
Tunc Bozbura F (2004) Measurement and application of intellectual capital in Turkey. Learn Organ 11(4/5):357–367. https://doi.org/10.1108/09696470410538251
Van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2014) Visualizing bibliometric networks. In: Ding Y, Rousseau R, Wolfram D (eds) Measuring scholarly impact. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 285–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10377-8_13
Vergauwen P, Bollen L, Oirbans E (2007) Intellectual capital disclosure and intangible value drivers: an empirical study. Manag Decis 45(7):1163–1180. https://doi.org/10.1108/00251740710773961
Vishnu S, Gupta VK (2014) Intellectual capital and performance of pharmaceutical firms in India. J Intellect Cap 15(1):83–99. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIC-04-2013-0049
Walsh K, Enz CA, Canina L (2008) The impact of strategic orientation on intellectual capital investments in customer service firms. J Serv Res 10(4):300–317. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670508314285
Wang X, Hou Y, Cullinane N (2015) How does the human resource department’s client relationship management impact on organizational performance in China? Mediate effect of human capital. S Afr J Econ Manage Sci 18(3):291–307. https://doi.org/10.17159/2222-3436/2015/V18N3A1
Welpe I, Rachbauer S (2006) What is different in human capital management? The necessity and advantages of a new philosophy for human resource departments. Int J Learn Intellect Cap 3(4):421. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJLIC.2006.011750
Wernerfelt B (1984) A resource-based view of the firm. Strateg Manag J 5(2):171–180. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.4250050207
Wiig KM (1997) Integrating intellectual capital and knowledge management. Long Range Plan 30:7
Winter SG, Nelson RR (1982) An Evolutionary Theory of Economic Change. SSRN Scholarly Paper ID 1496211. Rochester, NY: Social Science Research Network. https://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=1496211
Wright PM, McMahan GC, McWilliams A (1994) Human resources and sustained competitive advantage: a resource-based perspective. Int J Hum Resour Manage 5(2):301–326. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585199400000020
Xu XL, Chen HH, Zhang RR (2020) The impact of intellectual capital efficiency on corporate sustainable growth-evidence from smart agriculture in China. Agriculture 10(6):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10060199
Yang C-C, Lin C-Y (2009) Does intellectual capital mediate the relationship between HRM and organizational performance? Perspective of a healthcare industry in Taiwan. Int J Hum Resour Manage 20(9):1965–1984. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585190903142415
Yong JY, Yusliza M-Y, Ramayah T, Fawehinmi O (2019) Nexus between green intellectual capital and green human resource management. J Clean Prod 215(April):364–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.306
Zehir C, Gurol Y, Karaboga T, Kole M (2016) Strategic human resource management and firm performance: the mediating role of entrepreneurial orientation. Proc Soc Behav Sci 235(November):372–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2016.11.045
Zhao Y, Ruan W, Jiang Y, Rao J (2018) Salesperson human capital investment and heterogeneous export enterprises performance. J Bus Econ Manag 19(4):609–629. https://doi.org/10.3846/jbem.2018.6267
Zucker LG, Darby MR (1996) Star Scientists and Institutional Transformation: Patterns of Invention and Innovation in the Formation of the Biotechnology Industry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(23):12709–12716
Download references
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Commerce, Christ University, Bangalore, India
Lakshmi Bhooshetty
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The paper was authored by a single author.

Corresponding author
Correspondence to Lakshmi Bhooshetty .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author has no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Data availability statements
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Bhooshetty, L. Rejuvenating human resource accounting research: a review using bibliometric analysis. Manag Rev Q (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-023-00357-1
Download citation
Received : 23 October 2021
Accepted : 12 June 2023
Published : 05 July 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-023-00357-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Human resource accounting
- Bibliometric analysis
- Author keyword co-occurrences
- Network visualization
JEL Classification
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
HUMAN RESOURCE ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE OF SELECTED QUOTED NIGERIAN FOOD AND BEVERAGES FIRMS
- October 2022
- Finance & Accounting Research Journal 4(3):51-57
- CC BY-NC 4.0
- This person is not on ResearchGate, or hasn't claimed this research yet.

- Delta State University, Abraka
Abstract and Figures

Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Tolulope Olaitan Sule

- I R Akintoye
- I J Manukaji
- B C Osisioma
- P V C Okoye
- P C Eze-Nwosu
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

Home > Colleges & Schools > Soules College of Business > Human Resource Development > HRD_GRAD
Human Resource Development Theses and Dissertations
Theses/dissertations from 2023 2023.
CAMPUS-LEVEL TEACHER TURNOVER IN TEXAS PUBLIC ELEMENTARY SCHOOLS: AN EXAMINATION OF THE IMPACT OF LEADERSHIP FACTORS AND SCHOOL DEMOGRAPHICS USING HEIRARCHICAL LINEAR MODELING , Amy Welch Baskin
HUMAN RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT PROFESSIONALS’ COMPETENCIES AND CAREER SUCCESS IN THE SERVICE INDUSTRY: A QUALITATIVE STUDY , Cheryl DePonte
EVALUATING HEALTHCARE STUDENT LEARNING PERFORMANCE DURING THE INITIAL YEAR OF THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC: A CASE STUDY , Maria D. Garcia-Villarreal
LEADERSHIP BEHAVIORS, PRACTICES, AND SYTLES IN MERGERS AND ACQUISITIONS IN THE U.S. TECHNOLOGY-BASED ORGANIZATIONS: A QUALITATIVE STUDY , SUSAN E. GLOVER
THE IMPACT OF THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC ON EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT AND PERFORMANCE IN THE TELEWORKING CONTEXT IN THE U.S. PUBLIC SECTOR: A PHENOMENOLOGICAL CASE STUDY , Elizabeth Nesuda
Theses/Dissertations from 2022 2022
Exploring the Roles of the Craft Trainer in the Construction Industry , Mary M. Chatham
PREPARE FOR THE WORST, HOPE FOR THE BEST: A QUALITATIVE STUDY ON WORKPLACE VIOLENCE IN THE HEALTH CARE INDUSTRY , John Haymore
WORKPLACE FUN FOR EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT: A FUNCTION OF ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE? , Lacey Logan
TESTING THE PREDICTIVE VALIDITY OF A MANAGERIAL COACHING SCALE USING A CROSS-LAGGED PANEL DESIGN , Katherine Stone
Theses/Dissertations from 2021 2021
EFFECT OF TRAINING OPPORTUNITY AND JOB SATISFACTION ON TURNOVER INTENTIONS AMONG GEN X AND GEN Y , Regin Justin
The Effects of Perceived Organizational Justice of Inclusive Talent Management Practices on Employee Work Effort , Thomas Kramer
MENTORING EARLY CAREER TEACHERS UNDER COVID-19 PANDEMIC IN THE STATE OF TEXAS: A PHENOMENOLOGICAL CASE STUDY , Sonya H. Niazy
Theses/Dissertations from 2020 2020
EXAMINING MANAGERIAL COACHING DYADS AND THE DEVELOPMENTAL LEARNING OUTCOMES FOR MANAGERS SERVING AS COACHES AND THE REVERSE COACHING BEHAVIORS OF THEIR SUBORDINATE COACHEES , Beth Adele
Team-Based Effects on Individual Human Capital: A Proxy for Organizational Performance , Rob Carpenter
Testing the Modality Effect in an Online Training of Virtual Workers: An Experiment Inspired by Social Distancing , Janice Lambert Chretien
Examining the Mediating Effect of Job Crafting on the Relationship Between Managerial Coaching and Job Engagement in the Skilled Trades , Jennifer H. DuPlessis
PSYCHOLOGICAL WELL-BEING DURING RETIREMENT TRANSITION AND ADJUSTMENT FOR SOUTHERN BAPTIST PASTORS: A PHENOMENOLOGICAL MULTI-CASE STUDY , Tresa Gamblin
The Impact of Work Alienation on the Relationship Between Person-Organization Fit and Organizational Citizenship Behavior in Higher Education , Andrew R. Krouse
Antecedents to Strategic Project Success: A Qualitative Phenomenological Analysis of Project Leaders' Perceptions , Dave Silberman
Theses/Dissertations from 2019 2019
EXAMINING THE UNITED KINGDOM’S SOFT LAW APPROACH FOR WOMEN ON BOARDS WITH REGARD TO GENDER DIVERSITY AND THE GENDER PAY GAP: A REGRESSION DISCONTINUITY DESIGN , Silvana Chambers
ORGANIZATIONAL COGNITION AS INTERVENED BY ORGANIZATIONAL SUPPORT AND ENGAGEMENT ON MEDICAL CODERS’ EXHIBITION OF ORGANIZATIONAL CITIZENSHIP BEHAVIORS , David W. Conley
EXPLORING GRIEF AND MOURNING IN WORK TEAMS: A PHENOMENOLOGICAL MULTI-CASE STUDY , Ashley L. Kutach
EFFECTS OF THE DIMENSIONS OF QUALITY OF WORK LIFE ON TURNOVER INTENTION OF MILLENNIAL EMPLOYEES IN THE U.S. , Julie Lewis
EXAMINING THE DIRECT EFFECT OF CEO PERCEPTIONS OF COLLECTIVE ORGANIZATIONAL ENGAGEMENT ON PATIENT EXPERIENCE IN ACUTE-CARE HOSPITALS , Mary Lynn Lunn
SUCCESS AND FAILURE RATES, FACTORS, AND ALIGNMENT WITH CHANGE MODELS: A META-ETHNOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF PLANNED ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE QUALITATIVE CASE STUDY LITERATURE , Diana McBurnett
- Collections
- Disciplines
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
Author Corner
- Submit Research
- UT Tyler Human Resource Development PhD Degree
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
You're reading a free article with opinions that may differ from The Motley Fool's Premium Investing Services. Become a Motley Fool member today to get instant access to our top analyst recommendations, in-depth research, investing resources, and more. Learn More
Cathie Wood Thinks This Artificial Intelligence (AI) Stock Can Soar by 1,082%. Here's Why I Think It Could Run Even Higher Than That.
- Cathie Wood sees Tesla's planned robotaxi fleet as its next major catalyst.
- Beyond self-driving car technology, Tesla is investing heavily in other areas of artificial intelligence (AI) such as humanoid robotics.
- The energy storage business is the fastest growing part of the company, yet it feels as if it's being ignored by the prognosticators.
- Motley Fool Issues Rare “All In” Buy Alert
NASDAQ: TSLA

Ark Invest's iconic boss just raised her five-year price target on Tesla stock to $2,600 per share.
2024 has been a tumultuous year for Tesla ( TSLA -6.55% ) investors.
For the first six months of the year, its shares drastically underperformed the S&P 500 and Nasdaq Composite as the stock cratered by roughly 20%. Nevertheless, longtime Tesla bull Cathie Wood of Ark Invest recently revised her price target for the EV stock. Wood is calling for Tesla shares to reach $2,600 by 2029 -- 1,082% higher than its recent level.
While some investors may argue such a forecast is outlandish, I personally think Wood may be underestimating Tesla's prospects.
Wood's thesis hinges on robotaxis, but...
Tesla is a pioneer among electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers. After making considerable headway over the last several years, the company is now laser-focused on what it expects will be its next chapter -- autonomous driving technology.
CEO Elon Musk is so compelled by the potential of autonomous driving that during the company's latest earnings call, he said: "I recommend anyone who doesn't believe that Tesla will solve vehicle autonomy should not hold Tesla stock. They should sell their Tesla stock. If you believe Tesla will solve autonomy, you should buy Tesla stock."
That's a polarizing statement, but those are pretty much par for the course with Musk. However, he isn't the only one with a strong conviction that autonomous driving is an enormous opportunity.
In Wood's latest model, she is projecting that subscriptions to Tesla's autonomous driving software -- dubbed full-self driving (FSD) -- will be the major catalyst for the company's future growth. In essence, FSD represents a source of high-margin recurring revenue for its EV operation.
Moreover, if the company ends up as the superior developer of self-driving technology , Tesla will have an enormous opportunity to disrupt areas such as rental car businesses, delivery services, and ride-hailing applications.
But while I understand the opportunities FSD presents, I think Wood is underestimating Tesla's long-run potential.

Image Source: Getty Images
...what about robotics and energy storage?
Autonomous driving is merely an extension of the EV business. But on a deeper level, FSD is an advanced application of artificial intelligence (AI). While Musk and his team remain steadfast in its FSD pursuits, Tesla has far more ambitions in the broader AI realm. In particular, it is developing a line of humanoid robots called Optimus. The idea is that it could enhance its efficiency and productivity by augmenting its human workforce with Optimus robots.
Should this effort prove successful, Tesla would have an incredibly lucrative opportunity to commercialize Optimus and sell robots to other companies. This could revolutionize the labor market -- and Wood does not seem to be accounting for that potential in her model.
The main reason why Wood isn't banking much on Optimus at the moment is that she believes commercialization of the robots is more than five years away. However, at the risk of being overly Pollyanna-ish, I think Wood may want to rethink that position. On Tesla's second-quarter earnings call , Musk said "we expect to have several thousand Optimus robots produced and doing useful things by the end of next year in the Tesla factories." He further predicted that in 2026 the company would be "ramping up production quite a bit" and selling them to external customers.
Beyond its AI initiatives, Tesla has already built a thriving energy storage business that I think is criminally underappreciated.
The table below breaks down the financial results for Tesla's energy generation and storage segment over the last several quarters.
| Category | Q2 2023 | Q3 2023 | Q4 2023 | Q1 2024 | Q2 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy generation and storage revenue | $1.5 billion | $1.6 billion | $1.4 billion | $1.6 billion | $3.0 billion |
| Energy generation and storage gross margin | 18% | 24% | 22% | 25% | 25% |
Data source: Tesla.
Tesla has doubled its revenues from the energy storage business over the last year. But even more impressive, it has achieved strong unit economics, underpinned by a consistently expanding gross margin profile.
These dynamics are important because the growth in the energy storage segment is helping offset the stagnation and decline of its core EV business. Moreover, because it's generating strong and growing profits from its energy generation unit, Tesla is still able to invest in important growth initiatives -- particularly in AI.
Looking at Tesla's valuation
One thing that Wall Street analysts can't seem to agree on is Tesla's valuation. And on the surface, I totally get it. Its market capitalization is currently around $700 billion -- nearly 16 times that of Ford and 14 times the size of General Motors . Fundamentally, that doesn't really check out.
However, like Wood and Musk, I see Tesla as much more than a car company. Investors need to look at the different components of its overall operation and analyze their valuations individually. This is commonly referred to as a sum-of-the-parts valuation.
Beyond its EV segment, the company is making inroads in two areas with strong secular tailwinds : AI and sustainable energy. Admittedly, it has yet to really monetize its AI products at scale. For that reason, I understand if bearish investors remain skeptical. But as a Tesla shareholder for many years, I have a strong belief that the company will continue making progress toward FSD. Moreover, I think success in FSD will lead to a surge of demand as the company attempts to differentiate its fleet from the competition.
In addition, I'm compelled by the case around Optimus and am aligned with Musk on the premise that these robots will be commercialized sooner rather than later. Lastly, the energy storage business is growing faster than any other part of the company, and I don't see demand in that area slowing down anytime soon.
Whether or not the stock reaches Wood's price target on her forecast schedule is moot. In the long run, Tesla has a lot of opportunities to disrupt several more markets other than EVs, and I am bullish about its prospects for executing on its vision. For these reasons, I think Tesla is a strong buy for investors with a long-term time horizon.
Adam Spatacco has positions in Tesla. The Motley Fool has positions in and recommends Tesla. The Motley Fool recommends General Motors and recommends the following options: long January 2025 $25 calls on General Motors. The Motley Fool has a disclosure policy .
Related Articles

Premium Investing Services
Invest better with The Motley Fool. Get stock recommendations, portfolio guidance, and more from The Motley Fool's premium services.
Human Subjects Office
July 2024 irb connection newsletter, irb efficiency initiatives and results to date, irb efficiency initiative: current and upcoming, herky hint: help messages, aahrpp accreditation: preparing for site visit interviews, course-related student projects: is irb approval required, learning opportunity: irb overview lecture in icon, in the news, upcoming educational events, irb efficiency initiative s and results to date, by kelly o’berry and michele countryman.
Beginning in January 2024, the Human Subjects Office (HSO) rolled out six major initiatives to improve Institutional Review Board (IRB) and Human Research Protection Program (HRPP) review processes. This article provides an evaluation of previous programming changes that were presented at the May IRB Efficiency Initiative Information Session .
Here’s a brief overview of the initiatives and results to date:
60-Day Withdrawal Due to PI Inactivity (effective 1/29/24): 1,059 New Project and Modification Forms submitted since implementation. Of these, 106 forms were withdrawn (10%), 17 were recreated, and 9 were resubmitted.
DSP Approval Timing (effective mid-February 2024): The new process for faster signoffs from the Division of Sponsored Programs allowed the release of HRPP approvals an average of 48 days earlier ( 36 days median).
Required Actions After the IRB Meeting (effective 4/1/24): the average time to provide the PI with required actions from IRB meeting minutes has gone from 9 days to less than 24 hours since April 1.
Assign a Meeting Date Goal (effective 4/1/24): Limited data is available, but 71% of studies met the date goal. More in-depth information will be available after the June rollout that separated IRB review from HRPP Committee Approvals.
60-Day Withdrawal Due to PI Inactivity (effective 1/29/24)
HawkIRB forms are automatically withdrawn if there is no response to workflow in 60 days . This change will allow for more accurate metrics for IRB review time.
In addition to the two-week reminders, a new 55-day HawkIRB email notice states that the form will be withdrawn in five days. The form in the PI’s inbox shows the number of days in Workflow over the total days since submission. At 55 days , the form is highlighted in red in the PIs inbox.
Evaluation data for New Project forms and Modification forms:
The 106 withdrawn forms represent a considerable timesaving for HSO staff reviewers. Most withdrawn forms have not been recreated and very few recreated forms have been submitted to the IRB.
NOTE: For a withdrawn form, the PI can only use the “recreate” link once. It is best to hold off on recreating the form until all issues that were holding up the response to the workflow questions in the original form have been resolved.
DSP Approval Timing (effective mid-February 2024)
Division of Sponsored Programs (DSP) approval is required in HawkIRB for industry-initiated, industry-funded clinical trials where a research contract is required to document institution and sponsor expectations. The research application can be approved by the IRB, but not released to the study team until DSP approval is documented. In February, DSP updated their “contract approval” process for these industry-sponsored clinical trials. DSP approval used to be documented when the contract was fully executed; contract negotiations were complete, all signatures in place (institution, PI, and sponsor), and budget approved. Now DSP issues approval in HawkIRB when contract negotiations are complete, even if signatures and/or budget remain pending. This removed a significant delay in the HRPP approval process. Note: The PI must continue to work with the sponsor to obtain signatures and finalize the budget prior to initiating the research.
This change affected 38 studies from mid-February to early June. Faster DSP sign off allowed the release of HRPP approvals 48 days earlier than the previous average. For these studies, the median turnaround for IRB approval was 36 days , which is considerably below the goal of a 45-day median from submission to approval for full board review.
Assign a Meeting Date Goal (effective 4/1/24)
Application Analysts can now set an IRB meeting date goal, and a due date for meeting this goal, at the beginning of the IRB review process.
NOTE: There were several limiting factors for evaluation of this change. IRB meeting agendas were full through April 22 when this change took effect on April 1. The first New Project form included in this evaluation was submitted on April 2 and scheduled to a meeting on May 9. This evaluation is based on data from early May through mid-June.
Also, when this change took effect the hold for three Human Research Protection Program (HRPP) committees prevented scheduling forms to an IRB meeting. The IRB Efficiency Initiative rollout on June 14, 2024, lifted this hold by separating the IRB and HRPP Committee approvals. Future data will provide a more in-depth evaluation.
Required Actions After the IRB Meeting (effective 4/1/24)
HSO staff can now provide required actions to the PI shortly after the IRB meeting, which gives the PI/research team a head start to address required actions before receiving the full set of IRB meeting minutes.
Before April 1, 2024, the average time to provide required actions to the PI in the full meeting minutes was 9 days. The goal is to provide required actions within 24 hours and the full set of meeting minutes within four business days.
Of 167 sets of meeting minutes completed between April 1 and mid-June, HSO staff effectively decreased the average time to provide required actions to the PI to less than 24 hours. The research community has provided positive feedback about this change.
Seventeen sets of minutes (10%) did not meet the goal due to the complexity of the issues the board discussed. Approximately half of these minutes were from a monthly IRB-01 Executive Committee meeting. The Executive Committee reviews more complex study design and compliance-related issues.
IRB Efficiency Initiative Announcements and Updates
See IRB Efficiency Initiative Announcements and Updates for information about o ther initiatives that are in progress or have been implemented since June 2024, including: launching the new HSO website , adding a chair designee to assist with IRB-02 post-approval forms, onboarding a new IRB-02 chair, Primary Reviewer process enhancements and more.
By Kelly O’Berry and Michele Countryman
The IRB Efficiency Initiative rollout in June 2024 separated IRB review and approval from the other Human Research Protection Program (HRPP) committee approvals. This article provides an overview of that change and a summary of other initiatives in progress, updated documents, policies and procedures and information session/demonstration recordings.
Separate IRB and HRPP Committee Approvals - June 2024 Rollout
HawkIRB programming changes rolled out June 14, 2024, separated IRB review and approval from other HRPP Committee approvals. Prior to this change, the IRB could not begin the convened board review process until the issuance of approval from three committees/entities: Conflict of Interest in Research (CIRC) , Protocol Review and Monitoring Committee (PRMC, in Holden Comprehensive Cancer Center) , and Research Billing Compliance (RBC) . The HSO can now schedule a New Project or Modification form to a convened IRB meeting before the completion of these HRPP committee reviews/approvals.
The second programming change allows the IRB to grant full IRB approval before the issuance of all HRPP approvals. Prior to this efficiency initiative, the IRB would hold approval pending approval from these additional HRPP committees: Pharmacy & Therapeutics (P&T) , Medical Radiation and Protection Committee (MRPC) , Institutional Biosafety Committee and Nursing Research Committee (NRC) . Additionally, the IRB can now grant approval before the Division of Sponsored Programs (DSP) signs off on the grant or contract.
The Principal Investigator (PI) can now submit a Modification form in HawkIRB to address requests from HRPP Committees that complete their review after the IRB approves the New Project form. The New Project form is released when the Modification form is approved and released in HawkIRB.
Several documents, policies and procedures were updated or added in June. See a detailed list at the end of this article .
What’s Next for the IRB Efficiency Initiative?
The following initiatives are in progress or have already been implemented since the June IRB Efficiency Initiative Information Session:
New IRB review and approval structure for IRB-02 (social/behavioral research) – Effective at the start of Fiscal Year 2025, we added an IRB Chair Designee to assist with approval of post approval forms (e.g., Modification, Continuing Review, or Modification/Continuing Review) meeting an expedited or exempt criteria for approval. This enhancement is consistent with a long-standing IRB-01 review structure and is consistent with IRB practices across the nation. The new IRB-02 Chair Designee is an experienced IRB member who is already serving as an IRB-01 Chair Designee.
New IRB-02 Chair – The new IRB-02 Chair, an experienced IRB member, will begin onboarding and training in August as part of succession planning for IRB-02 Chairs.
Primary Reviewer process enhancements for full board review – HawkIRB programming is underway to update the Primary Reviewer Checklist used at convened board meetings and enhance the training process for Primary Reviewers.
HawkIRB Application Redesign – This initiative to streamline the HawkIRB application began with the rollout of Section III updates on January 29, 2024. The goal is to make forms easier for researchers to complete and more efficient for the IRB review. This is a continuation of the 2022-2023 initiative to update the HawkIRB form for projects that qualify for Exempt Status. The next HawkIRB application redesign rollout will focus on updates to the single IRB review process. This is in preparation for the anticipated FDA adoption of the revised Common Rule regulations regarding the use of a single IRB for multi-site projects.
New HSO website – The new HSO website is now live! HSO staff are still making final tweaks and corrections to URLs. It will take time for search engines to only identify pages of the new website. Use the gold buttons on the home page and the menu options to find what you need. We welcome your feedback. For assistance with finding anything on the new website or to provide feedback, please contact us at [email protected].
AAHRPP Accreditation Site Visit – 2024-2025 is our HRPP reaccreditation period and will involve a significant amount of HSO time and resources. There are two steps in the reaccreditation process. The UI is currently at Step I; the initial application was submitted in March, and we are currently responding to AAHRPP review of submission materials. Step II is the site visit which will occur this fall. The site visit includes interviews with select PIs and research staff. See February through July IRB Connection Newsletter articles for additional information about accreditation and preparing for the site visit.
Announcements and Updated Resources
The following documents were updated or added during the June IRB Efficiency Initiative rollout:
New Resources:
Other HRPP Committee Tool – Includes an organizational chart, information about each committee and when their review is required, and regulatory references for these reviews. [Link at end of first paragraph]
HRPP Committee Review Process Flow Chart – Illustrates the timing of steps in the IRB review process and HRPP committee approvals. [Link in first sentence of the second full paragraph]
UI IRB Standard Operating Procedures and Researcher Guide
Updated Policies and Procedures:
External IRB Standard Operating Procedures
VA Researcher Guide
May 2024 IRB Efficiency Initiative Information Session (recording)
Trainings and Demos:
HawkIRB demo: Separating IRB and HRPP Committee Approvals (recording)
WCG Training (recording, June 19, 2024)
IRB ICON Course for Researchers – Slides, recordings, demo recordings and instruction documents
Herky Hint: Help Messages
By rachel kinker, mpa.
Are you working on your HawkIRB application and not sure how to answer a particular question? Within the application, there are little blue circles with “i” (for “information”) associated with most of the questions in the HawkIRB application.
For example, the Help Message on the index page provides a lot of information:
Overview of the HawkIRB system
Template Consent Forms and Other Attachments
Resources for assistance with preparing HawkIRB applications
About the Help Messages
Resources on the Human Subjects Office website
Principal Investigator (PI) Responsibilities
HawkIRB Delegates
Guidance for Community-Based Research
Throughout the application, other Help Messages provide guidance for what information to include in response to specific questions in the HawkIRB form. When you click on the Help Message, a new window will appear with additional text describing what to include in the response to each question.
For example, in section VII.E., each Help Message describes what to submit and how to respond to the question.
The Help Messages may also contain links to other departments that you may need to connect with or specific policies you should know. For example, the cash handling policy appears in the Help Message for question VII.E.9
Utilizing the Help Messages throughout the application can answer researcher questions along the way and may expedite the application process by reducing workflow. If you have suggestions for how to improve the existing Help Messages, please contact [email protected].
AAHRPP Accreditation: Preparing for Site Visit Interviews
By emily shultz, cip .
The Human Subjects Office (HSO) is preparing for the Association for the Accreditation of Human Research Protection Programs (AAHRPP) site visit that will take place in late summer/early fall 2024. The University of Iowa Human Research Protection Program (HRPP) has maintained accreditation since 2003. The practice of becoming accredited and maintaining accreditation is one of receiving input on how well the UI is following policies and procedures, and how well these policies and procedures meet the accreditation standards.
About six weeks prior to the site visit, AAHRPP staff will send an email that contains:
the names of the site visit team members,
a draft agenda for the site visit,
a list of personnel who will be interviewed.
During the virtual site visit, the site visitors will meet (via Zoom) with small groups of HSO staff, IRB Chairs, IRB members, UI researchers and UI research team members, as well as members of committees with research oversight responsibilities, such as:
Medical Radiation Protection Committee
Pharmacy & Therapeutics Committee
Institutional Biosafety Committee
Nursing Research Committee
Division of Sponsored Programs
Conflicts of Interest in Research Committee
The interviews are typically done with two site visitors and 2 or 3 interviewees. Most interview time is with the IRB chairs, IRB members, and staff.
Utilizing the documents submitted with the application for reaccreditation and the information gathered during the site visit, AAHRPP site visitors will look for evidence that, “the entire HRPP meets accreditation standards—and that protecting research participants is a shared organizational priority.” A month or two after the site visit, the HSO will receive feedback on how well the UI HRPP is meeting the requirements and will receive recommendations on areas where improvements can be made.
Site Visit Interviews
Andy Bertolatus , emeritus associate professor of internal medicine and one of the UI IRB-01 chairs, has been an AAHRPP site visitor for more than 20 years. The following information is based on insights he provided, in addition to information available from AAHRPP.
When site visitors meet with members of the research community, they do not expect anyone to be able to recite federal regulations on the required elements of consent or the criteria for approval. When interviewing researchers, the site visitors will likely ask questions about the researcher’s:
Areas of expertise and type(s) of research conducted
Approach to conducting the consent processes
Feelings about working with the IRB
How they find out about changes in IRB policies/procedures
Where they go for information or whom they contact for questions
Resources Available
For the UI research community, many resources are available online. These include, but are not limited to the following:
UI IRB Standard Operating Procedures and Researcher Guide
Human Subjects Office (HSO) website
Conflict of Interest in Research website
HHS Electronic Code of Federal Regulations 45 CFR 46
OHRP Guidance
FDA Regulations Part 50
FDA Regulations Part 56
FDA Guidance
This is the final article in the AAHRPP Accreditation series. Previous articles are available on the HSO website IRB Connection page . Information for this article was adapted from the AAHRPP website .
Course-Related Student Projects: Is IRB Approval Required?
Students may conduct some research projects with human participants as a course assignment without approval from the Institutional Review Board (IRB). According to the UI and IRB policies, all human subjects research conducted by University of Iowa faculty, staff, or students must have approval from the IRB prior to initiation. IRB review is required if the project is intended to “develop or contribute to generalizable knowledge,” including thesis or dissertation projects. However, research methods course projects are generally more limited in scope and are intended to help students learn how to conduct research. These projects satisfy curriculum requirements and are not intended to further scientific knowledge in a particular field or discipline.
IRB Approval Not Required
Course-related research activities would not require IRB approval if:
The purpose of the assignment is to teach research methodology.
The results of the assignment will not “contribute to generalizable knowledge” because they are only used to satisfy a course requirement or because of limits on who will have access to the results of the project.
The procedures will be limited to surveys, questionnaires, interview procedures, observation of public behavior, or standard educational exercises.
The projects will not include people who are incarcerated or minors as participants or utilize data about these two populations.
Data will be recorded without any identifying information (such as code numbers, birth dates, etc.) or identified data are not sensitive in nature (i.e., do not pose a risk of harm to the participants’ reputation, employment, financial standing, or do not put them at risk for criminal or civil liability).
The project is not receiving monetary compensation or direct financial support from an external company, organization, or agency.
The project will not be conducted at the Veteran’s Administration Health Care System (VAHCS) or use any VA resources.
The project is not conducted or supported by a federal department or agency that follows the federal regulations for the protection of human subjects (the ‘Common Rule’).
NOTE: Honors, master’s, and doctoral thesis and dissertation projects always require IRB approval if they involve research with human subjects. If any aspect of the class project is intended to be used for a thesis or dissertation, students must obtain IRB approval prior to any study activities (recruitment, data collection, etc.).
Policy and Checklist
The “Course-Related Student Project” policy specifies the parameters for class projects that can be conducted without IRB approval and contains a link to the Course-Related Student Projects Checklist .
The checklist is a fillable pdf that helps students and instructors determine whether a project qualifies as a course-related student project. If any aspect of the project design indicates that IRB approval might be required, a pop-up message directs the student to submit a Human Subjects Research Determination (HSRD) form in the HawkIRB system to ask if the project needs IRB approval. If that occurs, there will be a red STOP on the completed checklist.
Students should complete the Course-Related Student Project Checklist based on their project design and submit it to the instructor. Based on the completed Checklist, the instructor is authorized to determine that a project complies with the policy and can be conducted without IRB approval. If there is a red STOP in the Checklist, the instructor should advise the student to submit an HSRD form and receive a determination before conducting any research activities.
The policy and the checklist can be found in the UI Standard Operating Procedures and Researcher Guide ( Section I, Part 12.D). See also the Course Instructor Responsibilities for using the Course-Related Student Project policy and checklist.
Information for Participants
Even when a course-related student project can be conducted without IRB approval, it is a recommended best-practice that the student share the following information with potential subjects:
Student name and name of the course
Course instructor name and their contact information
Who will have access to individual and summarized results (e.g., instructor, group/team members, the whole class, an outside company/agency/organization)
That participation is voluntary, and they may stop participating at any time.
Resources
For more information, students and instructors may review the Course-Related Student Research Projects web page and the Course-Related Student Research Projects Policy and Procedures educational tool the Human Subjects Office website.
(link sends e-mail)
Learning Opportunity: IRB Overview lecture in ICON
By rachel kinker, mpa .
Do you work with or teach individuals who are new to the University of Iowa and learning to conduct human subjects research? The recorded IRB Overview presentation posted in the IRB ICON Course for Researchers provides a general orientation to the UI IRB and the IRB approval requirements for human subjects research.
This is an excellent supplemental lecture for any research methods or responsible conduct of research course. It is also ideal for students doing research as a course requirement. Learners must access the IRB ICON course through the portal on the HSO website . After the first login, the course will appear in your ICON Dashboard.
This presentation covers:
Regulatory definition of human subjects research
Guidelines for human subjects research: why and when IRB approval is required
Basic ethical principles for the conduct of human subjects research
Student Principal Investigator (PI) training requirements (HawkIRB Part 1 and 2 trainings)
Criteria for IRB approval
Information about the UI IRB
What to expect from the IRB review process
Research off campus or outside the United States
Course-related student projects
Additional resources exist for courses where students complete a research project as a course requirement. The IRB policy on Course Related Student Projects outlines conditions under which IRB approval is not required for these projects. Instructors should use the Course Related Student Project Checklist to determine whether IRB approval may be required.
If your class needs further guidance on specific research-related topics, please reach out to [email protected] to discuss additional options.

NIH researchers discover a new face-detecting brain circuit – NIH
- This is What Drives the Migraine Headache': Scientists uncover 'missing link' in why some migraines happen – Live Science
- Implantable Microphone could lead to fully internal cochlear implants – Science Daily
- Scientists Discover New T cells and genes related to immune disorders – Science Daily
- Keeping us young? Grandchild caregiving and older adults' cognitive functioning - Newswise
IRB Efficiency Initiative Information Session
The Human Subjects Office invites the UI research community to attend monthly information sessions about the IRB Efficiency Initiative on the fourth Wednesday of the month from 12-1 pm, via Zoom. We will discuss the changes and demonstrate HawkIRB enhancements being implemented to streamline the IRB review process. The monthly sessions will cover upcoming enhancements and expected roll out dates. Pre-register to receive the Zoom link.
Wednesday, August 28, 2024
12:00 PM-1:00 PM
Pre-register to recieve the Zoom link
Office Hours
Human Subjects Office staff host IRB Office Hours via Zoom to provide assistance with electronic IRB applications (in HawkIRB) and to discuss study proposals prior to submission. All researchers are welcome to attend. No appointment is necessary.
Summer office hours run June 5th through August 28th.
Wednesdays (2:00 PM-4:00 PM) via Zoom
Visit the Human Subjects Office website for complete information about IRB Office Hours and the Zoom link.
Recorded Training
The IRB ICON Course for Researchers HawkIRB training sessions provide an orientation to the electronic IRB application and review system. These sessions are for anyone preparing to submit a HawkIRB application for the first time and for those who would like guidance about the proper completion of HawkIRB forms. Five recorded trainings are available 24/7.
The recorded trainings are available on ICON at IRB ICON Course for Researchers .
Note: HawkIRB training Parts 1 and 2 satisfy the Student PI Training Requirement.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Dissertation Prepared for the Degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY UNIVERSITY OF NORTH TEXAS December 2001 APPROVED: Barbara D. Merino, Major Professor and Program ... approach to accounting for human resources than participants who perceived reliability as being less important. A potential confounding explanation of the results is the varied
Human Resources Accounting (HRA) Practices on HR Managerial Decision-Making Process By Nivedita Sarker & Georgios Koilakos- Chouzouris Department of Business Administration Master´s Program in Management and Accounting Master's Thesis in Business Administration III, 30 Credits, Spring 2021 Supervisor: Zsuzsanna Vincze . ii .
The Shodhganga@INFLIBNET Centre provides a platform for research students to deposit their Ph.D. theses and make it available to the entire scholarly community in open access. Shodhganga@INFLIBNET. Osmania University. Department of Business Management.
Human Resource Accounting (HRA) is "the process of identifying, and measuring data about human resources and communicating this information to interested parties" ♦ (American Accounting Association, 1973, p. 169). Interested parties are divided into at least two groups: management and investors. The purpose of HRA is to improve the quality
This Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by the Graduate School at ScholarWorks at University of Montana. It has been accepted for inclusion in Graduate Student Theses, Dissertations, & Professional Papers by an ... the need for human resource accounting; (2) to explore and evaluate some possible methods of valuing and accounting ...
Video (online) Consult the top 50 dissertations / theses for your research on the topic 'Human resource accounting.'. Next to every source in the list of references, there is an 'Add to bibliography' button. Press on it, and we will generate automatically the bibliographic reference to the chosen work in the citation style you need: APA, MLA ...
Masters Thesis Human resource accounting: a framework for valuation and application. One aspect of the resources of an organization, thehuman element, has historically been difficult to value andreport. The intent of this study was to provide a frameworkfor valuing the investment in the human resources and forapplying this framework to the ...
Knowledge workers are an important resource for the typical modern business firm, yet financial reporting ignores such resources. Some researchers contend that the accounting profession has stressed reliability in order to make the accounting appear objective. Others concur, noting that accounting is an insecure profession and adopts strict rules when faced with uncertainty. Accountants have ...
Accountin g for Human Resources Revisited: Insights from the Intellectual Capital Field. 4. rces Revisited: Insights from the Intellectual Capital FieldRobin Roslender1 OverviewSince the mid-1980s, managerial accounting has been the site for a wide range of exciting developments that have resulted in its wholesale trans-formation.
Flamholtz (2002) states that human resource accounting involves ac- counting for human as part of the organization assets. In fact, human resources accounting is an attempt to identify and report the investment in manpower that expected to create benefits in excess of ordinary inter- ests for company in future.
The Shodhganga@INFLIBNET Centre provides a platform for research students to deposit their Ph.D. theses and make it available to the entire scholarly community in open access. Shodhganga@INFLIBNET. Dayalbagh Educational Institute. Department of Accountancy and Law.
A sixth [ 951 ] Eric G. Flamholtz, Maria L. Bullen and Wei Hua Human resource accounting: a historical perspective and future implications Management Decision 40/10 [2002] 947±954 application is that an international certified public accounting firm has initiated a project to develop an operational system of accounting for the cost and value ...
10. Abstract: Human Resource Accounting (HRA) is a new branch. of accounting. It follows the traditional concept that all. expenditure on human capital formation is taken as a charge. against the ...
The current study attempts to map the intellectual structure of Human Resource Accounting to understand the research gaps and future trajectories. The study employs systematic literature review technique to extract relevant literature, bibliometric analysis to map the intellectual structure of research in human resource accounting, to identify underlying research themes and content analysis to ...
This value complements the position of human resource accounting to cover the aporetic problems between humans, accounting, and God.Theoretical and practical implications: First, human resource ...
Human Resource accounting reflected the potential of the human resources of an organization in monetary terms, in its financial statements. First six questions are asked relating to current practices in HRA. Other than question 3 and 4, have 60-75% responses are in favour. Mean is between 14-19.
Aditi Dixit (2 005): In this Ph.D. thesis in order to know the Human Resource Accounting of BHEL questionnaire was circulated and chi-square test was applied. It was found that as such there was no proper accounting of Human Resource but it is useful to know ... Human Resource Accounting by giving reasons for developing Human Resource accounting
Prince et al (2013) examined the human resource accounting and its impact on organizational performance. The study made use of cross-sectional data drawn from the Nigerian Stock ... in his Ph.D dissertation investigated human resource accounting and the quality of financial reporting of quoted service companies in Nigeria. The data collected ...
Key Words: human asset, financial statement, amortization, efficiency, profitability, learning curve INTRODUCTION American Accounting Association's (1973) has defined Human Resource Accounting(HRA) as "the process of identifying and measuring data about human resources and communicating this information to interested parties".
The study assesses the impact of Human Resource Accounting (HRA) on the performance of Nigerian firms (2012 - 2016) with the use of secondary data, sourced from ten (10) purposively selected ...
Human Resources Accounting (HRA) is an accounting tool developed to account for people as organisational resources by providing information on the estimated value and the cost of investment on the human resources in an organisation to the stakeholders. It was developed to overcome the weakness of the traditional accounting system,
human resource development professionals' competencies and career success in the service industry: a qualitative study, cheryl deponte. pdf. evaluating healthcare student learning performance during the initial year of the covid-19 pandemic: a case study, maria d. garcia-villarreal. pdf
In the quest to gain a competitive edge, you must seek resources beyond the classroom. Integrating information or data from these resources can fortify your understanding of human resources and help you stay abreast of industry trends. Here's what the experts recommend: Dr. Spell: "Read daily the Wall Street Journal and the New York Times ...
Become a Motley Fool member today to get instant access to our top analyst recommendations, in-depth research, investing resources, and more. Learn More Cathie Wood Thinks This Artificial ...
NOTE: Honors, master's, and doctoral thesis and dissertation projects always require IRB approval if they involve research with human subjects. If any aspect of the class project is intended to be used for a thesis or dissertation, students must obtain IRB approval prior to any study activities (recruitment, data collection, etc.).