🎧 Real entrepreneurs. Real stories.
Subscribe to The Hurdle podcast today!

How to Write a Financial Plan for a Business Plan

Noah Parsons
4 min. read
Updated July 11, 2024

Creating a financial plan for a business plan is often the most intimidating part for small business owners.
It’s also one of the most vital. Businesses with well-structured and accurate financial statements are more prepared to pitch to investors, receive funding, and achieve long-term success.
Thankfully, you don’t need an accounting degree to successfully create your budget and forecasts.
Here is everything you need to include in your business plan’s financial plan, along with optional performance metrics, funding specifics, mistakes to avoid , and free templates.
- Key components of a financial plan in business plans
A sound financial plan for a business plan is made up of six key components that help you easily track and forecast your business financials. They include your:
Sales forecast
What do you expect to sell in a given period? Segment and organize your sales projections with a personalized sales forecast based on your business type.
Subscription sales forecast
While not too different from traditional sales forecasts—there are a few specific terms and calculations you’ll need to know when forecasting sales for a subscription-based business.
Expense budget
Create, review, and revise your expense budget to keep your business on track and more easily predict future expenses.
How to forecast personnel costs
How much do your current, and future, employees’ pay, taxes, and benefits cost your business? Find out by forecasting your personnel costs.
Profit and loss forecast
Track how you make money and how much you spend by listing all of your revenue streams and expenses in your profit and loss statement.
Cash flow forecast
Manage and create projections for the inflow and outflow of cash by building a cash flow statement and forecast.
Balance sheet
Need a snapshot of your business’s financial position? Keep an eye on your assets, liabilities, and equity within the balance sheet.
What to include if you plan to pursue funding
Do you plan to pursue any form of funding or financing? If the answer is yes, you’ll need to include a few additional pieces of information as part of your business plan’s financial plan example.
Highlight any risks and assumptions
Every entrepreneur takes risks with the biggest being assumptions and guesses about the future. Just be sure to track and address these unknowns in your plan early on.
Plan your exit strategy
Investors will want to know your long-term plans as a business owner. While you don’t need to have all the details, it’s worth taking the time to think through how you eventually plan to leave your business.
- Financial ratios and metrics
With your financial statements and forecasts in place, you have all the numbers needed to calculate insightful financial ratios.
While including these metrics in your financial plan for a business plan is entirely optional, having them easily accessible can be valuable for tracking your performance and overall financial situation.
Key financial terms you should know
It’s not hard. Anybody who can run a business can understand these key financial terms. And every business owner and entrepreneur should know them.
Common business ratios
Unsure of which business ratios you should be using? Check out this list of key financial ratios that bankers, financial analysts, and investors will want to see.
Break-even analysis
Do you want to know when you’ll become profitable? Find out how much you need to sell to offset your production costs by conducting a break-even analysis.
How to calculate ROI
How much could a business decision be worth? Evaluate the efficiency or profitability by calculating the potential return on investment (ROI).
- How to improve your financial plan
Your financial statements are the core part of your business plan’s financial plan that you’ll revisit most often. Instead of worrying about getting it perfect the first time, check out the following resources to learn how to improve your projections over time.
Common mistakes with business forecasts
I was glad to be asked about common mistakes with startup financial projections. I read about 100 business plans per year, and I have this list of mistakes.
How to improve your financial projections
Learn how to improve your business financial projections by following these five basic guidelines.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- Financial plan templates and tools
Download and use these free financial templates and calculators to easily create your own financial plan.

Sales forecast template
Download a free detailed sales forecast spreadsheet, with built-in formulas, to easily estimate your first full year of monthly sales.
Download Template

Accurate and easy financial forecasting
Get a full financial picture of your business with LivePlan's simple financial management tools.
Get Started
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.
Table of Contents
- What to include for funding
Related Articles
6 Min. Read
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template

10 Min. Read
How to Write the Company Overview for a Business Plan

24 Min. Read
The 10 AI Prompts You Need to Write a Business Plan

How to Write a Competitive Analysis for Your Business Plan
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How to Write the Financial Section of a Business Plan
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Taking Stock of Expenses
The income statement, the cash flow projection, the balance sheet.
The financial section of your business plan determines whether or not your business idea is viable and will be the focus of any investors who may be attracted to your business idea. The financial section is composed of four financial statements: the income statement, the cash flow projection, the balance sheet, and the statement of shareholders' equity. It also should include a brief explanation and analysis of these four statements.
Think of your business expenses as two cost categories: your start-up expenses and your operating expenses. All the costs of getting your business up and running should be considered start-up expenses. These may include:
- Business registration fees
- Business licensing and permits
- Starting inventory
- Rent deposits
- Down payments on a property
- Down payments on equipment
- Utility setup fees
Your own list will expand as soon as you start to itemize them.
Operating expenses are the costs of keeping your business running . Think of these as your monthly expenses. Your list of operating expenses may include:
- Salaries (including your own)
- Rent or mortgage payments
- Telecommunication expenses
- Raw materials
- Distribution
- Loan payments
- Office supplies
- Maintenance
Once you have listed all of your operating expenses, the total will reflect the monthly cost of operating your business. Multiply this number by six, and you have a six-month estimate of your operating expenses. Adding this amount to your total startup expenses list, and you have a ballpark figure for your complete start-up costs.
Now you can begin to put together your financial statements for your business plan starting with the income statement.
The income statement shows your revenues, expenses, and profit for a particular period—a snapshot of your business that shows whether or not your business is profitable. Subtract expenses from your revenue to determine your profit or loss.
While established businesses normally produce an income statement each fiscal quarter or once each fiscal year, for the purposes of the business plan, an income statement should be generated monthly for the first year.
Not all of the categories in this income statement will apply to your business. Eliminate those that do not apply, and add categories where necessary to adapt this template to your business.
If you have a product-based business, the revenue section of the income statement will look different. Revenue will be called sales, and you should account for any inventory.
The cash flow projection shows how cash is expected to flow in and out of your business. It is an important tool for cash flow management because it indicates when your expenditures are too high or if you might need a short-term investment to deal with a cash flow surplus. As part of your business plan, the cash flow projection will show how much capital investment your business idea needs.
For investors, the cash flow projection shows whether your business is a good credit risk and if there is enough cash on hand to make your business a good candidate for a line of credit, a short-term loan , or a longer-term investment. You should include cash flow projections for each month over one year in the financial section of your business plan.
Do not confuse the cash flow projection with the cash flow statement. The cash flow statement shows the flow of cash in and out of your business. In other words, it describes the cash flow that has occurred in the past. The cash flow projection shows the cash that is anticipated to be generated or expended over a chosen period in the future.
There are three parts to the cash flow projection:
- Cash revenues: Enter your estimated sales figures for each month. Only enter the sales that are collectible in cash during each month you are detailing.
- Cash disbursements: Take the various expense categories from your ledger and list the cash expenditures you actually expect to pay for each month.
- Reconciliation of cash revenues to cash disbursements: This section shows an opening balance, which is the carryover from the previous month's operations. The current month's revenues are added to this balance, the current month's disbursements are subtracted, and the adjusted cash flow balance is carried over to the next month.
The balance sheet reports your business's net worth at a particular point in time. It summarizes all the financial data about your business in three categories:
- Assets: Tangible objects of financial value that are owned by the company.
- Liabilities: Debt owed to a creditor of the company.
- Equity: The net difference when the total liabilities are subtracted from the total assets .
The relationship between these elements of financial data is expressed with the equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity .
For your business plan , you should create a pro forma balance sheet that summarizes the information in the income statement and cash flow projections. A business typically prepares a balance sheet once a year.
Once your balance sheet is complete, write a brief analysis for each of the three financial statements. The analysis should be short with highlights rather than an in-depth analysis. The financial statements themselves should be placed in your business plan's appendices.
Related Articles
How to Develop a Small Business Financial Plan
By Andy Marker | April 29, 2022
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Financial planning is critical for any successful small business, but the process can be complicated. To help you get started, we’ve created a step-by-step guide and rounded up top tips from experts.
Included on this page, you’ll find what to include in a financial plan , steps to develop one , and a downloadable starter kit .
What Is a Small Business Financial Plan?
A small business financial plan is an outline of the financial status of your business, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow information. A financial plan can help guide a small business toward sustainable growth.

Financial plans can aid in business goal setting and metrics tracking, as well as provide proof of profitable ideas. Craig Hewitt, Founder of Castos , shares that “creating a financial plan will show you if your business ideas are sustainable. A financial plan will show you where your business stands and help you make better decisions about resource allocation. It will also help you plan growth, survive cash flow shortages, and pitch to investors.”
Why Is It Important for a Small Business to Have a Financial Plan?
All small businesses should create a financial plan. This allows you to assess your business’s financial needs, recognize areas of opportunity, and project your growth over time. A strong financial plan is also a bonus for potential investors.

Mark Daoust , the President and CEO of Quiet Light Brokerage, Inc., explains why a financial plan is important for small businesses: “It can sometimes be difficult for business owners to evaluate their own progress, especially when starting a new company. A financial plan can be helpful in showing increased revenues, cash flow growth, and overall profit in quantifiable data. It's very encouraging for small business owners who are often working long hours and dealing with so many stressful decisions to know that they are on the right track.”
To learn more about other important considerations for a small business, peruse our list of free startup plan, budget, and cost templates .
What Does a Small Business Financial Plan Include?
All small businesses should include an income statement, a balance sheet, and a cash flow statement in their financial plan. You may also include other documents, such as personnel plans, break-even points, and sales forecasts, depending on the business and industry.

- Balance Sheet: A balance sheet determines the difference between your liabilities and assets to determine your equity. “A balance sheet is a snapshot of a business’s financial position at a particular moment in time,” says Yüzbaşıoğlu. “It adds up everything your business owns and subtracts all debts — the difference reflects the net worth of the business, also referred to as equity .” Yüzbaşıoğlu explains that this statement consists of three parts: assets, liabilities, and equity. “Assets include your money in the bank, accounts receivable, inventories, and more. Liabilities can include your accounts payables, credit card balances, and loan repayments, for example. Equity for most small businesses is just the owner’s equity, but it could also include investors’ shares, retained earnings, or stock proceeds,” he says.
- Cash Flow Statement: A cash flow statement shows where the money is coming from and where it is going. For existing businesses, this will include bank statements that list deposits and expenditures. A new business may not have much cash flow information, but it can include all startup costs and funding sources. “A cash flow statement shows how much cash is generated and used during a given period of time. It documents all the money flowing in and out of your business,” explains Yüzbaşıoğlu.
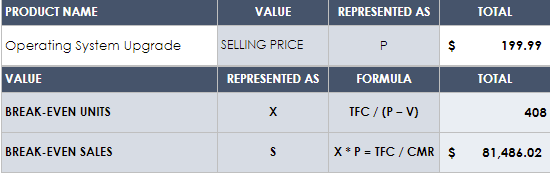
- Break-Even Analysis: A break-even analysis is a projection of how long it will take you to recoup your investments, such as expenses from startup costs or ongoing projects. In order to perform this analysis, Yüzbaşıoğlu explains, “You need to know the difference between fixed costs and variable costs. Fixed costs are the expenses that stay the same, regardless of how much you sell or don't sell. For example, expenses such as rent, wages, and accounting fees are typically fixed. Variable costs are the expenses that change in accordance with production or sales volume. “In other words, [a break-even analysis] determines the units of products or services you need to sell at least to cover your production costs. Generally, to calculate the break-even point in business, divide fixed costs by the gross profit margin. This produces a dollar figure that a company needs to break even,” Yüzbaşıoğlu shares.
- Personnel Plan: A personnel plan is an outline of various positions or departments that states what they do, why they are necessary, and how much they cost. This document is generally more useful for large businesses, or those that find themselves spending a large percentage of their budget on labor.
- Sales Forecast: A sales forecast can help determine how many sales and how much money you expect to make in a given time period. To learn more about various methods of predicting these figures, check out our guide to sales forecasting .
How to Write a Small Business Financial Plan
Writing a financial plan begins with collecting financial information from your small business. Create income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, and any other documents you need using that information. Then share those documents with relevant stakeholders.
“Creating a financial plan is key to any business and essential for success: It provides protection and an opportunity to grow,” says Yüzbaşıoğlu. “You can use [the financial plan] to make better-informed decisions about things like resource allocation on future projects and to help shape the success of your company.”
1. Create a Plan
Create a strategic business plan that includes your business strategy and goals, and define their financial impact. Your financial plan will inform decisions for every aspect of your business, so it is important to know what is important and what is at stake.
2. Gather Financial Information
Collect all of the available financial information about your business. Organize bank statements, loan information, sales numbers, inventory costs, payroll information, and any other income and expenses your business has incurred. If you have not already started to do so, regularly record all of this information and store it in an easily accessible place.
3. Create an Income Statement
Your income statement should display revenue, expenses, and profit for a given time period. Your revenue minus your expenses equals your profit or loss. Many businesses create a new statement yearly or quarterly, but small businesses with less cash flow may benefit from creating statements for shorter time frames.
4. Create a Balance Sheet
Your balance sheet is a snapshot of your business’s financial status at a particular moment in time. You should update it on the same schedule as your income statement. To determine your equity, calculate all of your assets minus your liabilities.
5. Create a Cash Flow Statement
As mentioned above, the cash flow statement shows all past and projected cash flow for your business. “Your cash flow statement needs to cover three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities,” suggests Hewitt. “Operating activities are the movement of cash from the sale or purchase of goods or services. Investing activities are the sale or purchase of long-term assets. Financing activities are transactions with creditors and investments.”
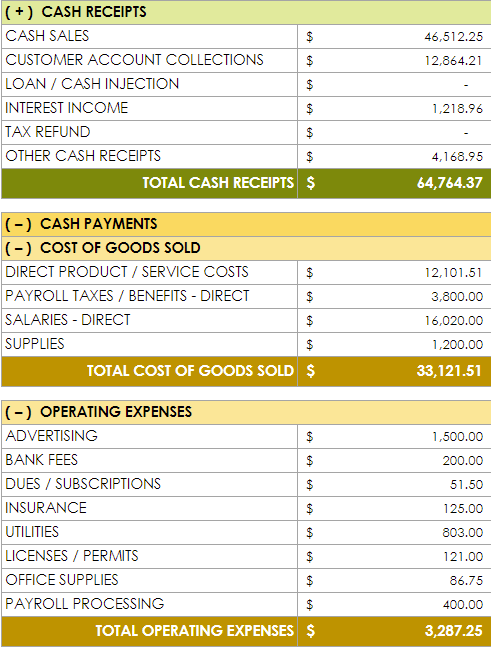
6. Create Other Documents as Needed
Depending on the age, size, and industry of your business, you may find it useful to include these other documents in your financial plan as well.
- Sales Forecast: Your sales forecast should reference sales numbers from your past to estimate sales numbers for your future. Sales forecasts may be more useful for established companies with historical numbers to compare to, but small businesses can use forecasts to set goals and break records month over month. “To make future financial projections, start with a sales forecast,” says Yüzbaşıoğlu. “Project your sales over the course of 12 months. After projecting sales, calculate your cost of sales (also called cost of goods or direct costs). This will let you calculate gross margin. Gross margin is sales less the cost of sales, and it's a useful number for comparing with different standard industry ratios.”
7. Save the Plan for Reference and Share as Needed
The most important part of a financial plan is sharing it with stakeholders. You can also use much of the same information in your financial plan to create a budget for your small business.

Additionally, be sure to conduct regular reviews, as things will inevitably change. “My best tip for small businesses when creating a financial plan is to schedule reviews. Once you have your plan in place, it is essential that you review it often and compare how well the strategy fits with the actual monthly expenses. This will help you adjust your plan accordingly and prepare for the year ahead,” suggests Janet Patterson, Loan and Finance Expert at Highway Title Loans.
Small Business Financial Plan Example
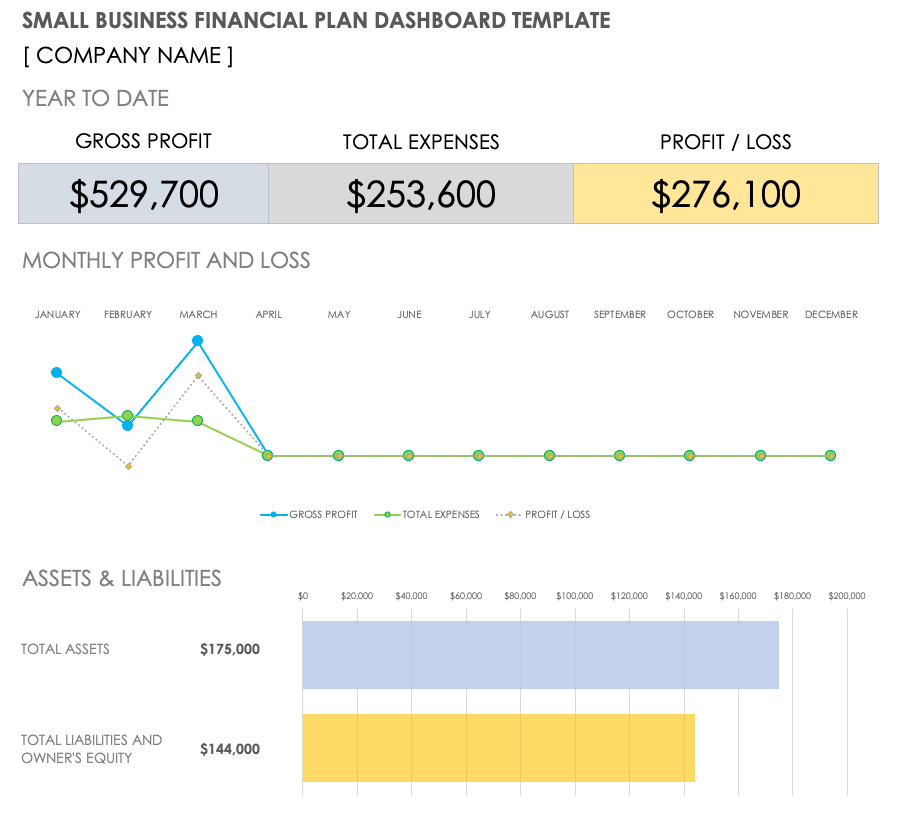
Download Small Business Financial Plan Example Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Here is an example of what a completed small business financial plan dashboard might look like. Once you have completed your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statements, use a template to create visual graphs to display the information to make it easier to read and share. In this example, this small business plots its income and cash flow statements quarterly, but you may find it valuable to update yours more often.
Small Business Financial Plan Starter Kit
Download Small Business Financial Plan Starter Kit
We’ve created this small business financial plan starter kit to help you get organized and complete your financial plan. In this kit, you will find a fully customizable income statement template, a balance sheet template, a cash flow statement template, and a dashboard template to display results. We have also included templates for break-even analysis, a personnel plan, and sales forecasts to meet your ongoing financial planning needs.
Small Business Income Statement Template
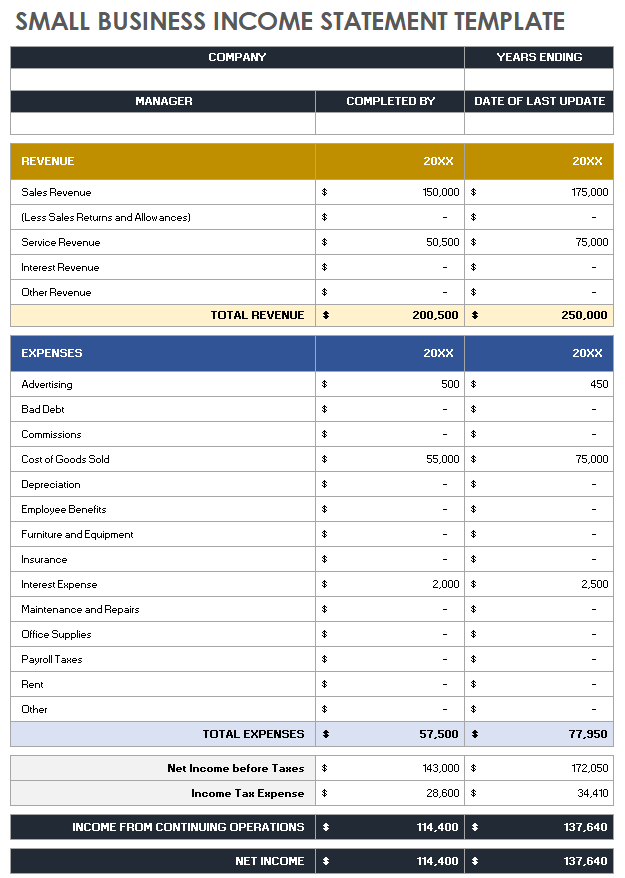
Download Small Business Income Statement Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this small business income statement template to input your income information and track your growth over time. This template is filled to track by the year, but you can also track by months or quarters. The template is fully customizable to suit your business needs.
Small Business Balance Sheet Template
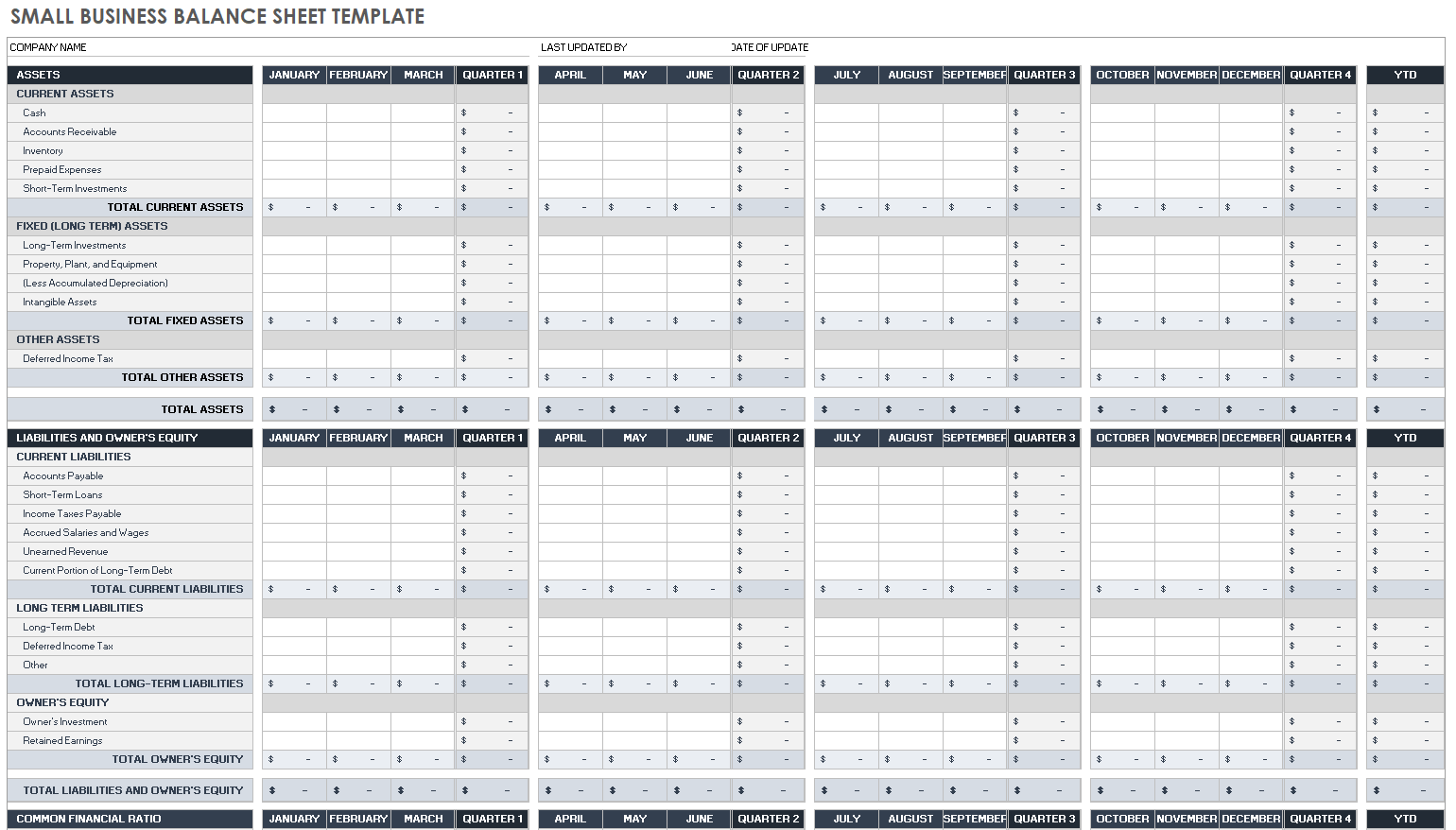
Download Small Business Balance Sheet Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
This customizable balance sheet template was created with small businesses in mind. Use it to create a snapshot of your company’s assets, liabilities, and equity quarter over quarter.
Small Business Cash Flow Statement Template
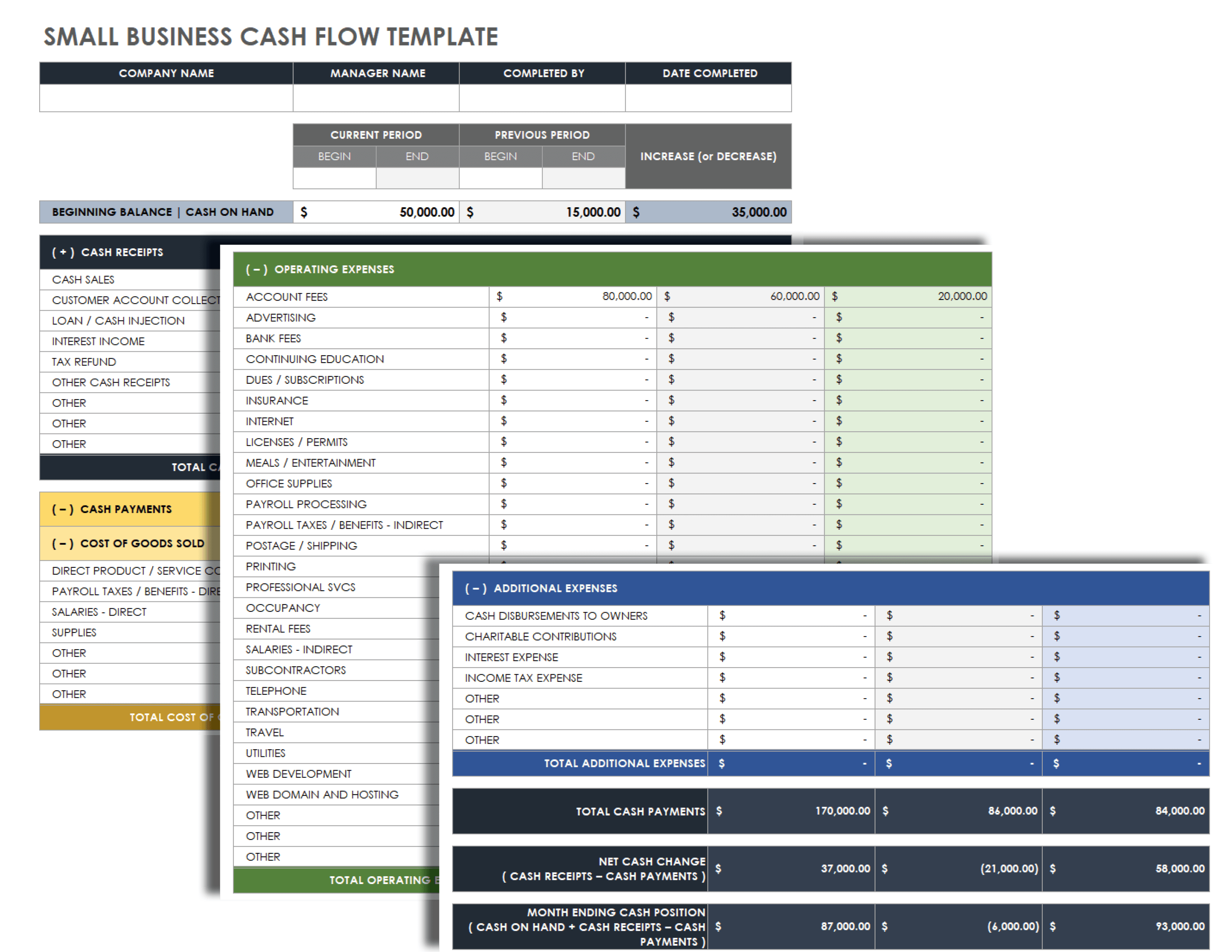
Download Small Business Cash Flow Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this customizable cash flow statement template to stay organized when documenting your cash flow. Note the time frame and input all of your financial data in the appropriate cell. With this information, the template will automatically generate your total cash payments, net cash change, and ending cash position.
Break-Even Analysis Template
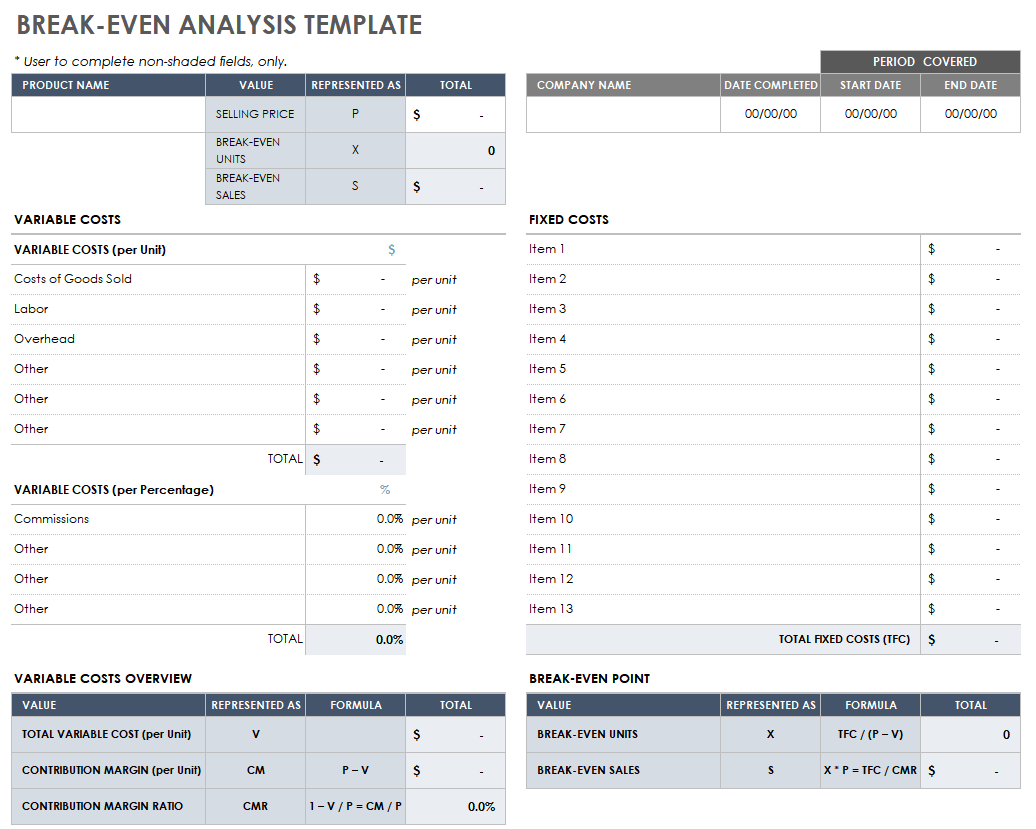
Download Break-Even Analysis Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
This powerful template can help you determine the point at which you will break even on product investment. Input the sale price of the product, as well as its various associated costs, and this template will display the number of units needed to break even on your initial costs.
Personnel Plan Template
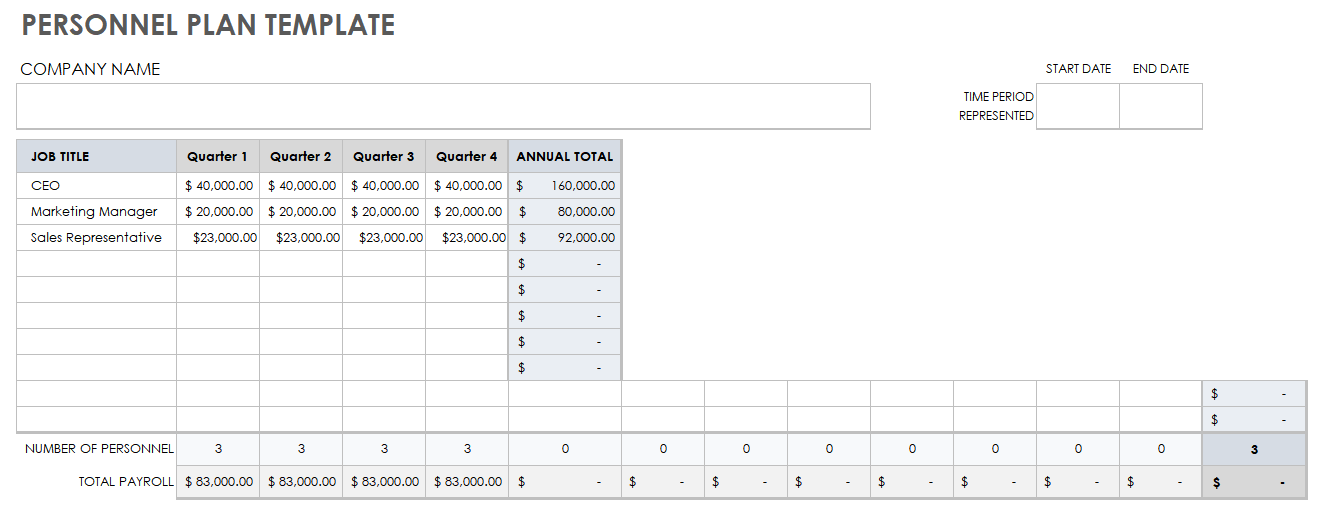
Download Personnel Plan Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this simple personnel plan template to help organize and define the monetary cost of the various roles or departments within your company. This template will generate a labor cost total that you can use to compare roles and determine whether you need to make cuts or identify areas for growth.
Sales Forecast Template
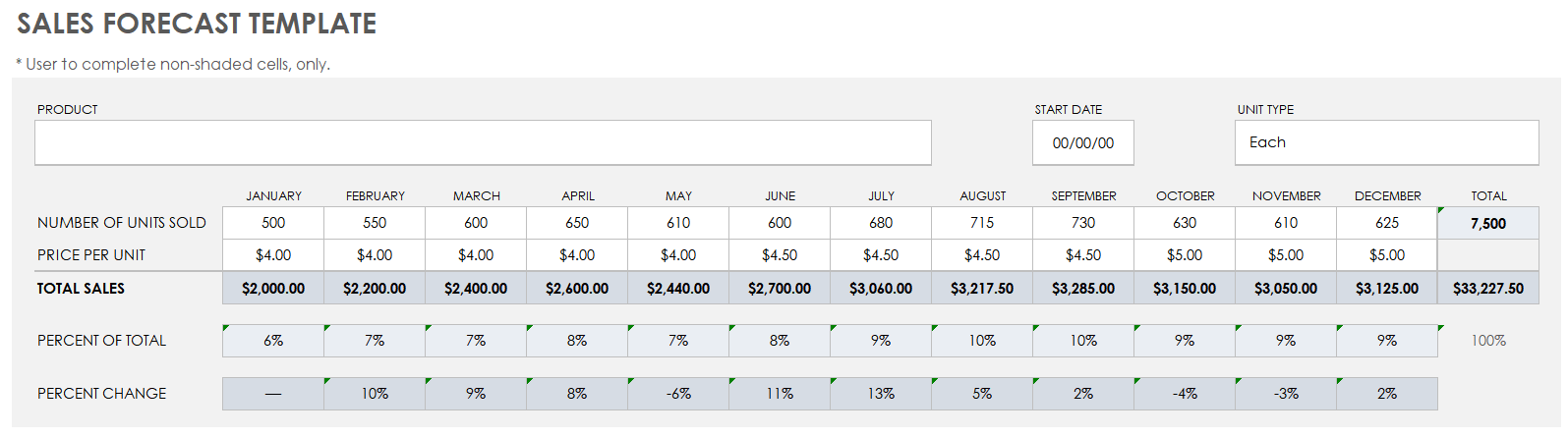
Download Sales Forecast Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this customizable template to forecast your sales month over month and determine the percentage changes. You can use this template to set goals and track sales history as well.
Small Business Financial Plan Dashboard Template
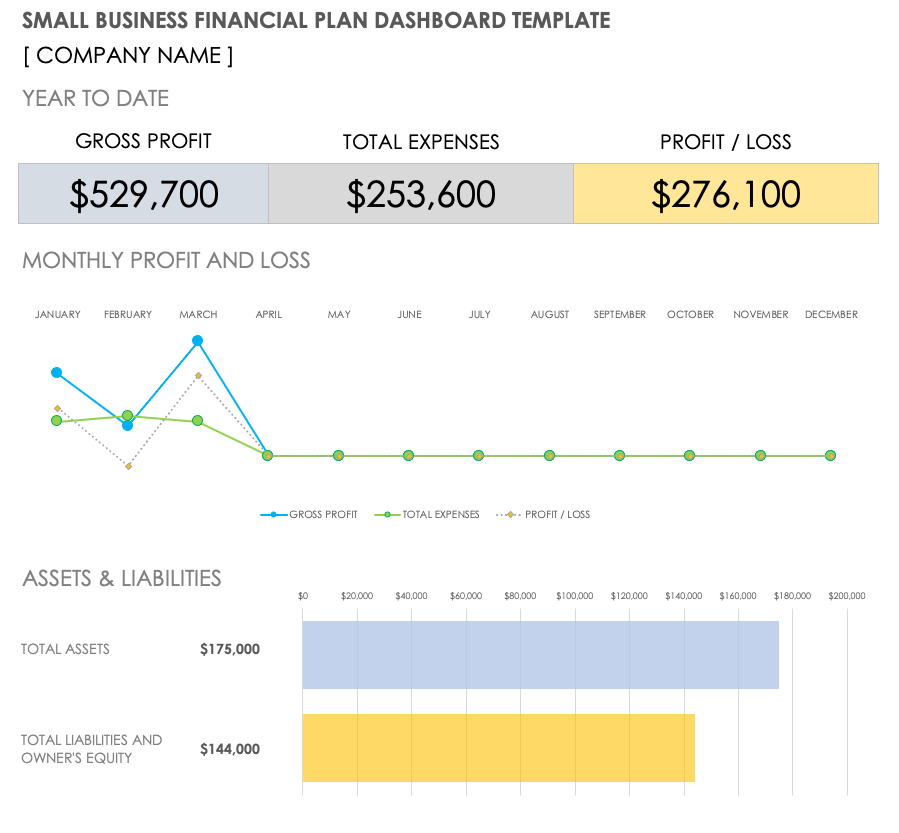
Download Small Business Financial Plan Dashboard Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
This dashboard template provides a visual example of a small business financial plan. It presents the information from your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in a graphical form that is easy to read and share.
Tips for Completing a Financial Plan for a Small Business
You can simplify the development of your small business financial plan in many ways, from outlining your goals to considering where you may need help. We’ve outlined a few tips from our experts below:

- Outline Your Business Goals: Before you create a financial plan, outline your business goals. This will help you determine where money is being well spent to achieve those goals and where it may not be. “Before applying for financing or investment, list the expected business goals for the next three to five years. You can ask a certified public accountant for help in this regard,” says Thé. The U.S. Small Business Administration or a local small business development center can also help you to understand the local market and important factors for business success. For more help, check out our quick how-to guide on writing a business plan .
- Make Sure You Have the Right Permits and Insurance: One of the best ways to keep your financial plan on track is to anticipate large expenditures. Double- and triple-check that you have the permits and insurances you need so that you do not incur any fines or surprise expenses down the line. “If you own your own business, you're no longer able to count on your employer for your insurance needs. It's important to have a plan for how you're going to pay for this additional expense and make sure that you know what specific insurance you need to cover your business,” suggests Daost.
- Separate Personal Goals from Business Goals: Be as unbiased as possible when creating and laying out your business’s financial goals. Your financial and prestige goals as a business owner may be loftier than what your business can currently achieve in the present. Inflating sales forecasts or income numbers will only come back to bite you in the end.
- Consider Hiring Help: You don’t know what you don’t know, but fortunately, many financial experts are ready to help you. “Hiring financial advisors can help you make sound financial decisions for your business and create a financial roadmap to follow. Many businesses fail in the first few years due to poor planning, which leads to costly mistakes. Having a financial advisor can help keep your business alive, make a profit, and thrive,” says Hewitt.
- Include Less Obvious Expenses: No income or expense is too small to consider — it all matters when you are creating your financial plan. “I wish I had known that you’re supposed to incorporate anticipated internal hidden expenses in the plan as well,” Patterson shares. “I formulated my first financial plan myself and didn’t have enough knowledge back then. Hence, I missed out on essential expenses, like office maintenance, that are less common.”
Do Small Business Owners Need a Financial Planner?
Not all small business owners need a designated financial planner, but you should understand the documents and information that make up a financial plan. If you do not hire an advisor, you must be informed about your own finances.
Small business owners tend to wear many hats, but Powell says, “it depends on the organization of the owner and their experience with the financial side of operating businesses.” Hiring a financial advisor can take some tasks off your plate and save you time to focus on the many other details that need your attention. Financial planners are experts in their field and may have more intimate knowledge of market trends and changing tax information that can end up saving you money in the long run.
Yüzbaşıoğlu adds, “Small business owners can greatly benefit from working with a financial advisor. A successful small business often requires more than just the skills of an entrepreneur; a financial advisor can help the company effectively manage risks and maximize opportunities.”
For more examples of the tasks a financial planner might be able to help with, check through our list of free financial planning templates .
Drive Small Business Success with Financial Planning in Smartsheet
Discover a better way to connect your people, processes, and tools with one simple, easy-to-use platform that empowers your team to get more done, faster.
With Smartsheet, you can align your team on strategic initiatives, improve collaboration efforts, and automate repetitive processes, giving you the ability to make better business decisions and boost effectiveness as you scale.
When you wear a lot of hats, you need a tool that empowers you to get more done in less time. Smartsheet helps you achieve that. Try free for 30 days, today .
Connect your people, processes, and tools with one simple, easy-to-use platform.

- Creating a Small Business Financial Plan

Written by True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
Reviewed by subject matter experts.
Updated on September 02, 2023
Are You Retirement Ready?
Table of contents, financial plan overview.
A financial plan is a comprehensive document that charts a business's monetary objectives and the strategies to achieve them. It encapsulates everything from budgeting and forecasting to investments and resource allocation.
For small businesses, a solid financial plan provides direction, helping them navigate economic challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and ensure sustainable growth.
The strength of a financial plan lies in its ability to offer a clear roadmap for businesses.
Especially for small businesses that may not have a vast reserve of resources, prioritizing financial goals and understanding where every dollar goes can be the difference between growth and stagnation.
It lends clarity, ensures informed decision-making, and sets the stage for profitability and success.
Understanding the Basics of Financial Planning for Small Businesses
Role of financial planning in business success.
Financial planning is the backbone of any successful business endeavor. It serves as a compass, guiding businesses toward profitability, stability, and growth.
With proper financial planning, businesses can anticipate potential cash shortfalls, make informed investment decisions, and ensure they have the capital needed to seize new opportunities.
For small businesses, in particular, tight financial planning can mean the difference between thriving and shuttering. Given the limited resources, it's vital to maximize every dollar and anticipate financial challenges.
Through diligent planning, small businesses can position themselves competitively, adapt to market changes, and drive consistent growth.
Core Components of a Financial Plan for Small Businesses
Every financial plan comprises several core components that, together, provide a holistic view of a business's financial health and direction. These include setting clear objectives, estimating costs , preparing financial statements , and considering sources of financing.
Each component plays a pivotal role in ensuring a thorough and actionable financial strategy .
For small businesses, these components often need a more granular approach. Given the scale of operations, even minor financial missteps can have significant repercussions.
As such, it's essential to tailor each component, ensuring they address specific challenges and opportunities that small businesses face, from initial startup costs to revenue forecasting and budgetary constraints.
Setting Clear Small Business Financial Objectives
Identifying business's short-term and long-term financial goals.
Every business venture starts with a vision. Translating this vision into actionable financial goals is the essence of effective planning.
Short-term goals could range from securing initial funding and achieving a set monthly revenue to covering startup costs. These targets, usually spanning a year or less, set the immediate direction for the business.
On the other hand, long-term financial goals delve into the broader horizon. They might encompass aspirations like expanding to new locations, diversifying product lines, or achieving a specific market share within a decade.
By segmenting goals into short-term and long-term, businesses can craft a step-by-step strategy, making the larger vision more attainable and manageable.
Understanding the Difference Between Profitability and Cash Flow
Profitability and cash flow, while closely linked, are distinct concepts in the financial realm. Profitability pertains to the ability of a business to generate a surplus after deducting all expenses.
It's a metric of success and indicates the viability of a business model . Simply put, it answers whether a business is making more than it spends.
In contrast, cash flow represents the inflow and outflow of cash within a business. A company might be profitable on paper yet struggle with cash flow if, for instance, clients delay payments or unexpected expenses arise.
For small businesses, maintaining positive cash flow is paramount. It ensures that they can cover operational costs, pay employees, and reinvest in growth, even if they're awaiting payments or navigating financial hiccups.
Estimating Small Business Startup Costs (for New Businesses)
Fixed vs variable costs.
When embarking on a new business venture, understanding costs is paramount. Fixed costs remain consistent regardless of production levels. They include expenses like rent, salaries, and insurance . These are predictable outlays that don't fluctuate with business performance.
Variable costs , conversely, change in direct proportion to production or business activity. Think of costs associated with materials for manufacturing or commission for sales .
For a startup, delineating between fixed and variable costs aids in crafting a more dynamic budget, allowing for adaptability as the business scales and evolves.
One-Time Expenditures vs Ongoing Expenses
Startups often grapple with numerous upfront costs. From purchasing equipment and setting up a workspace to initial marketing campaigns, these one-time expenditures lay the foundation for business operations.
They differ from ongoing expenses like utility bills, raw materials, or employee wages that recur monthly or annually.
For a small business owner, distinguishing between these costs is critical. One-time expenditures often demand a larger chunk of initial capital, while ongoing expenses shape the monthly and annual budget.
By categorizing them separately, businesses can strategize funding needs more effectively, ensuring they're equipped to meet both immediate and recurrent financial obligations.
Funding Sources for Small Businesses
Personal savings.
This is often the most straightforward way to fund a startup. Entrepreneurs tap into their personal savings accounts to jumpstart their business.
While this method has the benefit of not incurring debt or diluting company ownership, it intertwines the individual's personal financial security with the business's fate.
The entrepreneur must be prepared for potential losses, and there's the evident psychological strain of putting one's hard-earned money on the line.
Loans can be sourced from various institutions, from traditional banks to credit unions . They offer a substantial sum of money that can be paid back over time, usually with interest .
The main advantage of taking a loan is that the entrepreneur retains full ownership and control of the business.
However, there's the obligation of monthly repayments, which can strain a business's cash flow, especially in its early days. Additionally, securing a loan often requires collateral and a sound credit history.
Investors, including angel investors and venture capitalists , offer capital in exchange for equity or a stake in the company.
Angel investors are typically high-net-worth individuals who provide funding in the initial stages, while venture capitalists come in when there's proven business potential, often injecting larger sums. The advantage is substantial funding without the immediate pressure of repayments.
However, in exchange for their investment, they often seek a say in business decisions, which might mean compromising on some aspects of the original business vision.
Grants are essentially 'free money' often provided by government programs, non-profit organizations, or corporations to promote innovation and support businesses in specific sectors.
The primary advantage of grants is that they don't need to be repaid, nor do they dilute company ownership. However, they can be highly competitive and might come with stipulations on how the funds should be used.
Moreover, the application process can be lengthy and requires showcasing the business's potential or alignment with the specific goals or missions of the granting institution.

Preparing Key Financial Statements for Small Businesses
Income statement (profit & loss).
An Income Statement , often termed as the Profit & Loss statement , showcases a business's financial performance over a specific time frame. It details revenues , expenses, and ultimately, profits or losses.
By analyzing this statement, business owners can pinpoint revenue drivers, identify exorbitant costs, and understand the net result of their operations.
For small businesses, this document is instrumental in making informed decisions. For instance, if a certain product line is consistently unprofitable, it might be prudent to discontinue it. Conversely, if another segment is thriving, it might warrant further investment.
The Income Statement, thus, serves as a financial mirror, reflecting the outcomes of business strategies and decisions.
Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet offers a snapshot of a company's assets , liabilities , and equity at a specific point in time.
Assets include everything the business owns, from physical items like equipment to intangible assets like patents .
Liabilities, on the other hand, encompass what the company owes, be it bank loans or unpaid bills.
Equity represents the owner's stake in the business, calculated as assets minus liabilities.
This statement is crucial for small businesses as it offers insights into their financial health. A robust asset base, minimal liabilities, and growing equity signify a thriving enterprise.
In contrast, mounting liabilities or dwindling assets could be red flags, signaling the need for intervention and strategy recalibration.
Cash Flow Statement
While the Income Statement reveals profitability, the Cash Flow Statement tracks the actual movement of money.
It categorizes cash flows into operating (day-to-day business), investing (buying/selling assets), and financing (loans or equity transactions) activities. This statement unveils the liquidity of a business, indicating whether it has sufficient cash to meet immediate obligations.
For small businesses, maintaining positive cash flow is often more vital than showcasing profitability.
After all, a business might be profitable on paper yet struggle if clients delay payments or unforeseen expenses emerge.
By regularly reviewing the Cash Flow Statement, small business owners can anticipate cash crunches and strategize accordingly, ensuring seamless operations irrespective of revenue cycles.

Small Business Budgeting and Expense Management
Importance of budgeting for a small business.
Budgeting is the financial blueprint for any business, detailing anticipated revenues and expenses for a forthcoming period. It's a proactive approach, enabling businesses to allocate resources efficiently, plan for investments, and prepare for potential financial challenges.
For small businesses, a meticulous budget is often the linchpin of stability, ensuring they operate within their means and avoid financial pitfalls.
Having a well-defined budget also fosters discipline. It curtails frivolous spending, emphasizes cost-efficiency, and sets clear financial boundaries.
For small businesses, where every dollar counts, a stringent budget is the gateway to financial prudence, ensuring that funds are utilized judiciously, fostering growth, and minimizing wastage.
Strategies for Reducing Costs and Optimizing Expenses
Bulk purchasing.
When businesses buy supplies in large quantities, they often benefit from discounts due to economies of scale . This can significantly reduce per-unit costs.
However, while bulk purchasing leads to immediate savings, businesses must ensure they have adequate storage and that the products won't expire or become obsolete before they're used.
Renegotiating Vendor Contracts
Regularly reviewing and renegotiating contracts with suppliers or service providers can lead to better terms and lower costs. This might involve exploring volume discounts, longer payment terms, or even bartering services.
Building strong relationships with vendors often paves the way for such negotiations.
Adopting Energy-Saving Measures
Simple changes, like switching to LED lighting or investing in energy-efficient appliances, can lead to long-term savings in utility bills. Moreover, energy conservation not only reduces costs but also minimizes the environmental footprint, which can enhance the business's reputation.

Embracing Technology
Modern software and technology can streamline business processes. Automation tools can handle repetitive tasks, reducing labor costs.
Meanwhile, data analytics tools can provide insights into customer preferences and behavior, ensuring that marketing budgets are used effectively and target the right audience.
Streamlining Operations
Regularly reviewing and refining business processes can eliminate redundancies and improve efficiency. This might mean merging roles, cutting down on unnecessary meetings, or simplifying supply chains. A leaner operation often translates to reduced expenses.
Outsourcing Non-core Tasks
Instead of maintaining an in-house team for every function, businesses can outsource tasks that aren't central to their operations.
For instance, functions like accounting , IT support, or digital marketing can be outsourced to specialized agencies, often leading to cost savings and access to expert skills.
Cultivating a Culture of Frugality
Encouraging employees to adopt a cost-conscious mindset can lead to collective savings. This can be fostered through incentives, regular training, or even simple practices like recycling and reusing office supplies.
When everyone in the organization is attuned to the importance of cost savings, the cumulative effect can be substantial.

Forecasting Small Business Revenue and Cash Flow
Techniques for predicting future sales in a small business, past sales data analysis.
Historical sales data is a foundational element in any forecasting effort. By reviewing previous sales figures, businesses can identify patterns, understand seasonal fluctuations, and recognize the effects of past initiatives.
This information offers a baseline upon which to build future projections, accounting for known recurring variables in the business cycle .
Market Research
Understanding the larger market dynamics is crucial for accurate forecasting. This involves tracking industry trends, monitoring shifts in consumer behavior, and being aware of potential market disruptions.
For instance, a sudden technological advancement can change consumer preferences or regulatory changes might impact an industry.
Local Trend Analysis
For small businesses, localized insights can be especially impactful. Observing local competitors, understanding regional consumer preferences, or noting shifts in the local economy can offer precise data points.
These granular details, when integrated into a larger forecasting model, can enhance prediction accuracy.
Customer Feedback
Direct feedback from customers is an invaluable source of insights. Surveys, focus groups, or even informal chats can reveal customer sentiments, preferences, and potential future purchasing behavior.
For instance, if a majority of loyal customers express interest in a new product or service, it can be indicative of future sales potential.
Moving Averages
This technique involves analyzing a series of data points (like monthly sales) by creating averages from different subsets of the full data set.
For yearly forecasting, a 12-month moving average can be used to smooth out short-term fluctuations and highlight longer-term trends or cycles.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical tool used to identify relationships between variables. In sales forecasting, it can help understand how different factors (like marketing spend, seasonal variations, or competitor actions) relate to sales figures.
Once these relationships are understood, businesses can predict future sales based on planned actions or expected external events.

Understanding the Cash Cycle of Business
The cash cycle encompasses the time it takes for a business to convert resource investments, often in the form of inventory, back into cash.
This involves the processes of purchasing inventory, selling it, and subsequently collecting payment. A shorter cycle implies quicker cash turnarounds, which are vital for liquidity.
For small businesses, a firm grasp of the cash cycle can aid in managing cash flow more effectively.
By identifying bottlenecks or delays, businesses can strategize to expedite processes. This might involve renegotiating payment terms with suppliers, offering discounts for prompt customer payments, or optimizing inventory levels to prevent overstocking.
Ultimately, understanding and optimizing the cash cycle ensures that a business remains liquid and agile.
Preparing for Seasonality and Unexpected Changes
Seasonality affects many businesses, from the ice cream vendor witnessing summer surges to the retailer bracing for holiday shopping frenzies.
By analyzing historical data and market trends, businesses can prepare for these cyclical shifts, ensuring they stock up, staff appropriately, and market effectively.
Small businesses, often operating on tighter margins , need to be especially vigilant. Beyond seasonality, they must also brace for unexpected changes – a local construction project obstructing store access, a sudden competitor emergence, or unforeseen regulatory changes.
Building a financial buffer, diversifying product or service lines, and maintaining flexible operational strategies can equip small businesses to weather these unforeseen challenges with resilience.
Securing Small Business Financing and Capital
Role of debt and equity financing.
When businesses seek external funding, they often grapple with the debt vs. equity conundrum. Debt financing involves borrowing money, typically via loans. While it doesn't dilute ownership, it necessitates regular interest payments, potentially impacting cash flow.
Equity financing, on the other hand, entails selling a stake in the business to investors. It might not demand regular repayments, but it dilutes ownership and might influence business decisions.
Small businesses must weigh these options carefully. While loans offer a structured repayment plan and retained control, they might strain finances if the business hits a rough patch.
Equity financing, although relinquishing some control, might bring aboard strategic partners, offering expertise and networks in addition to funds.
The optimal choice hinges on the business's financial health, growth aspirations, and the founder's comfort with sharing control.
Choosing Between Different Types of Loans
A staple in the lending arena, term loans offer businesses a fixed amount of capital that is paid back over a specified period with interest. They're often used for significant one-time expenses, such as purchasing machinery, real estate , or even business expansion.
With predictable monthly payments, businesses can plan their budgets accordingly. However, they might require collateral and a robust credit history for approval.
Lines of Credit
Unlike term loans that provide funds in a lump sum, a line of credit grants businesses access to a pool of funds up to a certain limit.
Businesses can draw from this line as needed, only paying interest on the amount they use. This makes it a versatile tool, especially for managing cash flow fluctuations or unexpected expenses. It serves as a financial safety net, ready for use whenever required.
As the name suggests, microloans are smaller loans designed to cater to businesses that might not need substantial amounts of capital. They're particularly beneficial for startups, businesses with limited credit histories, or those in need of a quick, small financial boost.
Since they are of a smaller denomination, the approval process might be more lenient than traditional loans.
Peer-To-Peer Lending
A contemporary twist to the traditional lending model, peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms connect borrowers directly with individual lenders or investor groups.
This direct model often translates to quicker approvals and competitive interest rates as the overheads of traditional banking structures are removed. With technology at its core, P2P lending can offer a more user-friendly, streamlined process.
However, creditworthiness still plays a pivotal role in determining interest rates and loan amounts.
Crowdfunding and Alternative Financing Options
In an increasingly digital age, crowdfunding platforms like Kickstarter or Indiegogo have emerged as viable financing avenues.
These platforms enable businesses to raise small amounts from a large number of people, often in exchange for product discounts, early access, or other perks. This not only secures funds but also validates the business idea and fosters a community of supporters.
Other alternatives include invoice financing, where businesses get an advance on pending invoices, or merchant cash advances tailored for businesses with significant credit card sales.
Each financing mode offers unique advantages and constraints. Small businesses must meticulously evaluate their financial landscape, growth trajectories, and risk appetite to harness the most suitable option.
Small Business Tax Planning and Management
Basic tax obligations for small businesses.
Navigating the maze of taxation can be daunting, especially for small businesses. Yet, understanding and fulfilling tax obligations is crucial.
Depending on the business structure—whether sole proprietorship , partnership , LLC , or corporation—different tax rules apply. For instance, while corporations are taxed on their earnings, sole proprietors report business income and expenses on their personal tax returns.
In addition to income taxes, small businesses may also be responsible for employment taxes if they have employees. This covers Social Security , Medicare , federal unemployment, and sometimes state-specific taxes.
There might also be sales taxes, property taxes, or special state-specific levies to consider.
Consistently maintaining accurate financial records, being aware of filing deadlines, and setting aside funds for tax obligations are essential practices to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
Advantages of Tax Planning and Potential Deductions
Tax planning is the strategic approach to minimizing tax liability through the best use of available allowances, deductions, exclusions, and breaks.
For small businesses, effective tax planning can lead to significant savings.
This might involve strategies like deferring income to a later tax year, choosing the optimal time to purchase equipment, or taking advantage of specific credits available to businesses in certain sectors or regions.
Several potential deductions can reduce taxable income for small businesses. These include expenses like rent, utilities, business travel, employee wages, and even certain meals.
By keeping abreast of tax law changes and actively seeking out eligible deductions, small businesses can optimize their financial landscape, ensuring they're not paying more in taxes than necessary.
Importance of Hiring a Tax Professional or Accountant
While it's feasible for small business owners to manage their taxes, the intricate nuances of tax laws make it beneficial to consult professionals.
An experienced accountant or tax consultant can not only ensure compliance but can proactively recommend strategies to reduce tax liability.
They can guide businesses on issues like whether to classify someone as an employee or a contractor, how to structure the business for optimal taxation, or when to make certain capital investments.
Beyond just annual tax filing, these professionals offer year-round counsel, helping businesses maintain clean financial records, stay updated on tax law changes, and plan for future financial moves.
The investment in professional advice often pays dividends , saving businesses from costly mistakes, penalties, or missed financial opportunities.
Regularly Reviewing and Adjusting the Small Business Financial Plan
Setting checkpoints and milestones.
Like any strategic blueprint, a financial plan isn't static. It serves as a guiding framework but should be flexible enough to adapt to evolving business realities.
Setting regular checkpoints— quarterly , half-yearly, or annually—can help businesses assess whether they're on track to meet their financial objectives.
Milestones, such as reaching a specific sales target, launching a new product, or expanding into a new market, offer tangible markers of progress. Celebrating these victories can bolster morale, while any shortfalls can serve as lessons, prompting strategy tweaks. F
or small businesses, where agility is an asset, regularly revisiting the financial plan ensures that the business remains aligned with its overarching financial goals while being responsive to the dynamic marketplace.
Using Financial Ratios to Monitor Business Health
Financial ratios offer a distilled snapshot of a business's health. Ratios like the current ratio ( current assets divided by current liabilities ) can shed light on liquidity, indicating whether a business can meet short-term obligations.
The debt-to-equity ratio , contrasting borrowed funds with owner's equity, offers insights into the business's leverage and potential financial risk.
Profit margin , depicting profitability relative to sales, can highlight operational efficiency. By consistently monitoring these and other pertinent ratios, small businesses can glean actionable insights, understanding their financial strengths and areas needing attention.
In a realm where early intervention can stave off major financial setbacks, these ratios serve as vital diagnostic tools, guiding informed decision-making.
Pivoting Strategies Based on Financial Performance
In the ever-evolving world of business, flexibility is paramount. If financial reviews indicate that certain strategies aren't yielding anticipated results, it might be time to pivot.
This could involve tweaking product offerings, revising pricing strategies, targeting a different customer segment, or even overhauling the business model.
For small businesses, the ability to pivot can be a lifeline. It allows them to respond swiftly to market changes, customer feedback, or internal challenges.
A robust financial plan, while offering direction, should also be pliable, accommodating shifts in strategy based on real-world performance. After all, in the business arena, adaptability often spells the difference between stagnation and growth.

Bottom Line
Financial foresight is integral for the stability and growth of small businesses. Effective revenue and cash flow forecasting, anchored by historical sales data and enhanced by market research, local trends, and customer feedback, ensures businesses are prepared for future demands.
With the unpredictability of the business environment, understanding the cash cycle and preparing for unforeseen challenges is essential.
As businesses contemplate external financing, the decision between debt and equity and the myriad of loan types, should be made judiciously, keeping in mind the business's health, growth aspirations, and risk appetite.
Furthermore, diligent tax planning, with professional guidance, can lead to significant financial benefits. Regular reviews using financial ratios allow businesses to gauge their performance, adapt strategies, and pivot when necessary.
Ultimately, the agility to adapt, guided by a well-structured financial plan, is pivotal for businesses to thrive in a dynamic marketplace.
Creating a Small Business Financial Plan FAQs
What is the importance of a financial plan for small businesses.
A financial plan offers a structured roadmap, guiding businesses in making informed decisions, ensuring growth, and navigating financial challenges.
How do forecasting revenue and understanding cash cycles aid in financial planning?
Forecasting provides insights into expected income, aiding in budget allocation, while understanding cash cycles ensures effective liquidity management.
What are the core components of a financial plan for small businesses?
Core components include setting objectives, estimating startup costs, preparing financial statements, budgeting, forecasting, securing financing, and tax management.
Why is tax planning vital for small businesses?
Tax planning ensures compliance, optimizes tax liabilities through available deductions, and helps businesses save money and avoid penalties.
How often should a small business review its financial plan?
Regular reviews, ideally quarterly or half-yearly, ensure alignment with business goals and allow for strategy adjustments based on real-world performance.
About the Author
True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide , a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University , where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon , Nasdaq and Forbes .
Related Topics
- Average Cost of a Certified Financial Planner
- Benefits of Having a Financial Planner
- Cash Flow Management
- Charitable Financial Planning
- Debt Reduction Strategies
- Disadvantages of Not Having a Financial Plan
- Divorce Financial Planning
- Education Planning
- Fee-Only Financial Planning
- Financial Contingency Planning
- Financial Planner Fee Structure
- Financial Planner for Retirement
- Financial Planning Pyramid
- Financial Planning and Analysis
- Financial Planning and Investment
- Financial Planning for Allied Health Professionals
- Financial Planning for Married Couples
- Financial Planning for Military Families
- Financial Planning for Retirement
- Financial Planning for Startups
- Financial Planning in Your 20s
- Financial Planning vs Budgeting
- Financial Planning vs Financial Management
- Financial Tips for Young Adults
- How to Build a 5-Year Financial Plan
- Limitations of Financial Planning
- Military Spouse Financial Planning
- The Function of a Financial Planner
- When Do You Need a Financial Planner?
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
Meet top certified financial advisors near you.
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.
Fact Checked
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications.
They regularly contribute to top tier financial publications, such as The Wall Street Journal, U.S. News & World Report, Reuters, Morning Star, Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg, Marketwatch, Investopedia, TheStreet.com, Motley Fool, CNBC, and many others.
This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year.
We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources.
Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs.
How It Works
Step 1 of 3, ask any financial question.
Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Your information is kept secure and not shared unless you specify.

Step 2 of 3
Our team will connect you with a vetted, trusted professional.
Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise.

Step 3 of 3
Get your questions answered and book a free call if necessary.
A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.

Where Should We Send Your Answer?

Just a Few More Details
We need just a bit more info from you to direct your question to the right person.
Tell Us More About Yourself
Is there any other context you can provide.
Pro tip: Professionals are more likely to answer questions when background and context is given. The more details you provide, the faster and more thorough reply you'll receive.
What is your age?
Are you married, do you own your home.
- Owned outright
- Owned with a mortgage
Do you have any children under 18?
- Yes, 3 or more
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
- $50k - $250k
- $250k - $1m
Pro tip: A portfolio often becomes more complicated when it has more investable assets. Please answer this question to help us connect you with the right professional.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
- I would prefer remote (video call, etc.)
- I would prefer in-person
- I don't mind, either are fine
What's your zip code?
- I'm not in the U.S.
Submit to get your question answered.
A financial professional will be in touch to help you shortly.

Part 1: Tell Us More About Yourself
Do you own a business, which activity is most important to you during retirement.
- Giving back / charity
- Spending time with family and friends
- Pursuing hobbies
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
Part 3: confidence going into retirement, how comfortable are you with investing.
- Very comfortable
- Somewhat comfortable
- Not comfortable at all
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
- Very confident
- Somewhat confident
- Not confident / I don't have a plan
What is your risk tolerance?
How much are you saving for retirement each month.
- None currently
- Minimal: $50 - $200
- Steady Saver: $200 - $500
- Serious Planner: $500 - $1,000
- Aggressive Saver: $1,000+
How much will you need each month during retirement?
- Bare Necessities: $1,500 - $2,500
- Moderate Comfort: $2,500 - $3,500
- Comfortable Lifestyle: $3,500 - $5,500
- Affluent Living: $5,500 - $8,000
- Luxury Lifestyle: $8,000+
Part 4: Getting Your Retirement Ready
What is your current financial priority.
- Getting out of debt
- Growing my wealth
- Protecting my wealth
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have.
- Tax planning expertise
- Investment management expertise
- Estate planning expertise
- None of the above
Where should we send your answer?
Submit to get your retirement-readiness report., get in touch with, great the financial professional will get back to you soon., where should we send the downloadable file, great hit “submit” and an advisor will send you the guide shortly., create a free account and ask any financial question, learn at your own pace with our free courses.
Take self-paced courses to master the fundamentals of finance and connect with like-minded individuals.
Get Started
To ensure one vote per person, please include the following info, great thank you for voting., get in touch with a financial advisor, submit your info below and someone will get back to you shortly..
Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » startup, business plan financials: 3 statements to include.
The finance section of your business plan is essential to securing investors and determining whether your idea is even viable. Here's what to include.

If your business plan is the blueprint of how to run your company, the financials section is the key to making it happen. The finance section of your business plan is essential to determining whether your idea is even viable in the long term. It’s also necessary to convince investors of this viability and subsequently secure the type and amount of funding you need. Here’s what to include in your business plan financials.
[Read: How to Write a One-Page Business Plan ]
What are business plan financials?
Business plan financials is the section of your business plan that outlines your past, current and projected financial state. This section includes all the numbers and hard data you’ll need to plan for your business’s future, and to make your case to potential investors. You will need to include supporting financial documents and any funding requests in this part of your business plan.
Business plan financials are vital because they allow you to budget for existing or future expenses, as well as forecast your business’s future finances. A strongly written finance section also helps you obtain necessary funding from investors, allowing you to grow your business.
Sections to include in your business plan financials
Here are the three statements to include in the finance section of your business plan:
Profit and loss statement
A profit and loss statement , also known as an income statement, identifies your business’s revenue (profit) and expenses (loss). This document describes your company’s overall financial health in a given time period. While profit and loss statements are typically prepared quarterly, you will need to do so at least annually before filing your business tax return with the IRS.
Common items to include on a profit and loss statement :
- Revenue: total sales and refunds, including any money gained from selling property or equipment.
- Expenditures: total expenses.
- Cost of goods sold (COGS): the cost of making products, including materials and time.
- Gross margin: revenue minus COGS.
- Operational expenditures (OPEX): the cost of running your business, including paying employees, rent, equipment and travel expenses.
- Depreciation: any loss of value over time, such as with equipment.
- Earnings before tax (EBT): revenue minus COGS, OPEX, interest, loan payments and depreciation.
- Profit: revenue minus all of your expenses.
Businesses that have not yet started should provide projected income statements in their financials section. Currently operational businesses should include past and present income statements, in addition to any future projections.
[Read: Top Small Business Planning Strategies ]
A strongly written finance section also helps you obtain necessary funding from investors, allowing you to grow your business.
Balance sheet
A balance sheet provides a snapshot of your company’s finances, allowing you to keep track of earnings and expenses. It includes what your business owns (assets) versus what it owes (liabilities), as well as how much your business is currently worth (equity).
On the assets side of your balance sheet, you will have three subsections: current assets, fixed assets and other assets. Current assets include cash or its equivalent value, while fixed assets refer to long-term investments like equipment or buildings. Any assets that do not fall within these categories, such as patents and copyrights, can be classified as other assets.
On the liabilities side of your balance sheet, include a total of what your business owes. These can be broken down into two parts: current liabilities (amounts to be paid within a year) and long-term liabilities (amounts due for longer than a year, including mortgages and employee benefits).
Once you’ve calculated your assets and liabilities, you can determine your business’s net worth, also known as equity. This can be calculated by subtracting what you owe from what you own, or assets minus liabilities.
Cash flow statement
A cash flow statement shows the exact amount of money coming into your business (inflow) and going out of it (outflow). Each cost incurred or amount earned should be documented on its own line, and categorized into one of the following three categories: operating activities, investment activities and financing activities. These three categories can all have inflow and outflow activities.
Operating activities involve any ongoing expenses necessary for day-to-day operations; these are likely to make up the majority of your cash flow statement. Investment activities, on the other hand, cover any long-term payments that are needed to start and run your business. Finally, financing activities include the money you’ve used to fund your business venture, including transactions with creditors or funders.
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
Follow us on Instagram for more expert tips & business owners’ stories.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
More tips for your startup
How to use ai tools to write a business plan, writing a business plan here's how to do it, section by section, how to start a small business at home: 7 tips for success.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The financial section of a business plan is one of the most essential components of the plan, as you will need it if you have any hope of winning over investors or obtaining a bank loan. Even if ...
Always include a description of your future strategic financial plans, like paying off debt or selling your business. Financial projections. ... Example lean business plan. Before you write your business plan, read this example business plan written by a fictional business owner, Andrew, who owns a toy company. ...
Creating a financial plan for a business plan is often the most intimidating part for small business owners. It's also one of the most vital. Businesses with well-structured and accurate financial statements are more prepared to pitch to investors, receive funding, and achieve long-term success.
The financial section of your business plan determines whether or not your business idea is viable and will be the focus of any investors who may be attracted to your business idea. The financial section is composed of four financial statements: the income statement, the cash flow projection, the balance sheet, and the statement of shareholders ...
The financials section of your business plan tells you and your potential investors, loan providers or partners whether your business idea makes economic sense. Without an impressive financials ...
Building business plan financials involves forecasting the three financial statements : income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. Financial projections should be based on market research and industry trends, as well as your unique business model and goals.
Financial plans can aid in business goal setting and metrics tracking, as well as provide proof of profitable ideas. Craig Hewitt, Founder of Castos, shares that "creating a financial plan will show you if your business ideas are sustainable.A financial plan will show you where your business stands and help you make better decisions about resource allocation.
Financial Plan Overview. A financial plan is a comprehensive document that charts a business's monetary objectives and the strategies to achieve them. It encapsulates everything from budgeting and forecasting to investments and resource allocation.. For small businesses, a solid financial plan provides direction, helping them navigate economic challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and ...
A financial plan is an integral part of an overall business plan, ensuring financial objectives align with overall business goals. It typically contains a description of the business, financial statements, personnel plan, risk analysis and relevant key performance indicators (KPIs) and ratios.
Business plan financials is the section of your business plan that outlines your past, current and projected financial state. This section includes all the numbers and hard data you'll need to plan for your business's future, and to make your case to potential investors. You will need to include supporting financial documents and any ...