- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. We work 24/7. Just email us at:
- [email protected]


Research Paper vs Research Proposal v Thesis: 5 differences

Some students may be confused concerning the difference between a research proposal and a research paper. This is understandable if it is the first time a student is writing either of the two types of research.
This is because some students may have been used to writing essays that take a much simpler format and approach in writing the content.
Therefore, if you are one of those students who are not sure of the difference(s) between a research proposal and a research paper, do not worry.

Research Proposal vs Research Paper
Now, what is the difference between a research proposal and a research paper? This section will elaborate on the differences between the two while exploring their comparisons with other types of academic papers.
A research proposal is a preliminary paper that is submitted to the instructor so that the researcher can be granted permission to proceed with the actual research paper. It proposes what the research project will be all about. On the other hand, a research paper is an academic piece that presents what one found out after in-depth research on a specified topic.
Let us understand each of them in deeper detail. What this means is that a research proposal “proposes” what the researcher will be going to tackle within the main paper.
As such, they should clarify or provide details as to what the main research paper will be tackling the topic, the expected hypothesis and claims, the type of studies used, the methodologies, the population in which the research will be conducted, and the expected implications of the research.
A research proposal needs to demonstrate the importance of the actual research to the discipline and society in general. Without this, then the research proposal would not pass, and no actual research will be conducted to produce the research paper.
When it comes to the actual research paper, it can be regarded as the work that will be produced after the research proposal has been approved and a research go-ahead has been granted to the researcher(s).
Therefore, the research paper will be a complete paper that reports what has been researched, the findings of the studies conducted, and the discussions concerning the findings. It will not be like a research proposal that will be proposing things that will happen in the future.
It should be noted that this is a major or simplified difference between a research proposal and a research paper. The next sections of this article will discuss in detail the main differences between them, plus their differences with other types of papers.
Need Help with your Homework or Essays?
What is a research proposal.
A research proposal can be regarded as an academic preliminary request for research that is meant to be submitted to the instructor before the writer or student is given the go-ahead to proceed with writing the research paper.

What this means is that a research proposal will ‘propose’ what the research paper will be all about and the merits of the research to the discipline and society in general.
Therefore, a research proposal is written before a research paper is written.
If a research proposal fails to be approved, then the researcher or student will not be allowed to write a research paper.
What is a Research Paper?
A research paper can be regarded as a formal academic piece written by students or researchers after the instructor or academic committee has approved their research proposals to tackle a particular research topic in a specific discipline to find solutions through qualitative and/or quantitative studies.
Therefore, a research paper is a long piece of academic writing that utilizes the research proposal’s topic and claims to test a hypothesis. The research paper aims not to propose a study but to conduct an actual study that would benefit the discipline and society.
Differences between a Research Proposal and a Research Paper
As we have noted above, there is a big difference between a research proposal and a research paper. Below are some of the major differences between the two:
1. The Time of Being Written
One of the most notable differences between a research proposal and a research paper is that a research proposal is written before a research paper. This is because a research proposal is meant to ‘propose’ what the writer, student, or researcher is going to write in their main research paper. As such, a research proposal has to be approved before a research paper is written.
The second difference between a research proposal and a research paper is the purpose of the two pieces of writing. The main aim of a research proposal is to present to the instructor what will be tackled within the research paper.
On the other hand, the purpose of a research paper is to academically present research that has already been conducted by the writer or the researcher. A research paper is a final presentation concerning a particular topic.
3. Use of Grammatical Tenses
Another difference between a research proposal and a research paper is that while the proposal uses future tense (will be, shall be, and so on), a research paper uses a grammatical tense that describes things that have already been done.
This is because the research has already been conducted. When it comes to the analysis of the findings and discussions, the present tense can be used because things are unfolding.
4. Context and Audience
The context of a research proposal is to present “proposals” of ideas that will be used to build upon a research paper.
As such, the audience will be the instructor or a research committee that is meant to gauge the relevance of the proposal to the topic.
On the other hand, a research paper is not formulated to lead to research but to describe the research.
Therefore, a research paper will target the instructor and any reader who is interested in the topic, discipline, or study.
Finally, the difference between a research proposal and a research paper is the length. A research proposal is considerably shorter compared to a research paper because of the content. A research paper will contain a lot of detail concerning the topic, the type of research, the findings, discussions, and conclusions because research has already been conducted.
We can Write your Papers! No Plagiarism
Get that A on your next essay assignment without the hassles. Any topic or subject. 100% Plagiarism-Free Essays.
Difference Between a Thesis and a Research Proposal
The main difference between a thesis and a research proposal is their purpose. A thesis is a formal academic piece of writing done on a particular topic that has not yet been explored. This is why a thesis has a prospectus stage where the student has to consult with a committee. On the other hand, a research proposal proposes the topic and the research to be done.
Therefore, a research proposal will not require a prospectus stage or a committee, and it can be written by any student within an institution of higher learning.
However, an undergraduate student can also write a research proposal to their instructor to ‘propose’ a research paper.
Difference Between a Thesis and a Research Paper
The major difference between a thesis and a research paper is that a thesis is a longer and more detailed piece of writing that is written by post-graduate students, while a research paper will be comparatively shorter with fewer details because undergraduate students mostly write it.

As such, a thesis can take a very long time to write, for example, 20 years if it tackles socio-economic or environmental issues that may take a lot of time to unfold.
However, a research paper takes a shorter time to write. It may take even 3 months to complete a research paper because it does not explore very complex issues.
The length also matters. A thesis is longer than a research paper by far. Check out the optimal length for a thesis compared to a research paper length and notice the difference.
Check out the guide on the differences in thesis vs theory vs hypothesis to get a wider idea of the three. This will help you know how these three are applied in a dissertation of a research paper.

Josh Jasen or JJ as we fondly call him, is a senior academic editor at Grade Bees in charge of the writing department. When not managing complex essays and academic writing tasks, Josh is busy advising students on how to pass assignments. In his spare time, he loves playing football or walking with his dog around the park.
Related posts

Original, non-plagiarized Research
Get Original, Non-Plagiarized Research Papers Written from Scratch

Someone to format my paper in APA for me
How to Write and Cite Sources in APA and MLA for Term Papers

Background Information in an Essay
Background Information in an Essay: How to Write and Example
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Download Free PDF
The Difference between A Proposal and Thesis

2022, The Difference between A Proposal and Thesis
It is worth to note that every school/faculty or department of a given institution of higher learning has its unique format or guideline for proposal or thesis writing. An overwhelming majority of scholars and students of research find it difficult when it comes to giving a difference between A Proposal and Thesis.
Related papers
A thesis and a dissertation despite being used interchangeably, also have many differences in various aspects. Below we will give details on the 5 main differences of a thesis and dissertation.
Writing a research proposal is the most difficult part of thesis or dissertation writing. Hence, should you need help contact [email protected] or call +639156924624
Otolaryngology online, 2023
This book has been authored with PhD scholars in mind. The author believes that this would be a good starting point for these scholars. The following chapters have been included: Chapters: 1. Introduction to Thesis Writing 2. Choosing a Topic and Developing a Thesis Statement 3. Conducting Literature Review 4. Methodology and Data Collection 5. Writing the Introduction and Background of Your Thesis 6. Presenting Your Findings and Analysis 7. Writing the Discussion and Conclusion of Your Thesis 8. Formatting and Structuring Your Thesis 9. Referencing and Citations 10. Defending Your Thesis: Preparing for the Viva Voce 11. Revising and Editing Your Thesis 12. Time Management and Staying on Track 13. Overcoming Writer's Block and Staying Motivated 14. Using Technology and Tools to Enhance Your Thesis Writing Process 15. Publishing Your Thesis and Next Steps. 16. Data visualization 17. Statistical tools This book also contains tips about choosing an ideal thesis topic. It also warns the student about the various pitfalls involved in choosing a research topic. The topic on referencing citations would be very useful for even a novice researcher. This book also introduces the researcher to the myriad of software tools that are available to the scholar. Using these software tools would make the life of the researcher that much easier.
The paper gives advice on how to write a good PhD thesis in a Computing subject in the UK -assuming that one has done interesting, novel academic work and "just" needs to write up. The context of this document relates to my experience, opinion and practice in various roles as supervisor, examiner or examination panel chair in more than two dozens of PhD examinations. What I have expressed here is likely to be relevant to my own PhD students or those whose PhD thesis I examine within the British system. Many aspects of this paper are universally true for a number of subjects and countries while some are more specific to Computing and the UK. * This document is in development.
research proposal is a comprehensive plan for a research project. It is a written description of a research plan that has to be undertaken. It determines the specific areas of research, states the purpose, scope, methodology, overall organization and limitations of the study. It also estimates its requirements for equipment (if necessary), finance and possible personnel.
Indonesian Journal of EFL and Linguistics
The purposes of this research were to find out the students’ difficulties in developing a paragraph and to understand the students’ difficulties in implementing the writing elements in writing their undergraduate thesis proposals. This research used the descriptive qualitative method. The instrument used in this research were interviews, documentation, and Oshima & Hogue’s Paragraph Rubric. The research subject was 7 eighth-semester students of UINSI Samarinda. The data were collected from the background of the study of the student’s undergraduate thesis proposals and analyzed with the Miles and Huberman Model. The result showed that the difficulties in developing a paragraph experienced by the students were related to too specific and too general topic sentences, poor supporting sentences, the absence of concluding sentences, inconsistent topic discussion, and inharmonic sentences. At the same time, the students’ difficulties shown in implementing the writing elements were found in...
Academia Green Energy, 2024
Jornal do 59º Congresso Brasileiro de Direito do Trabalho, 2019
US Nuclear Weapons Policy: Confronting Today's …
A PEQUENA EMPRESA, 2022
International Advances in Art Therapy Research & Practice, 2021
Bulletin de l'Académie Internationale CONCORDE, 2023
SSRN Electronic Journal, 2000
European Ving Tsun Federation's Wing Chun Kung Fu , 2007
Review of International Studies, 2023
Elite Journal of Medical Sciences, 2024
European Urology Supplements, 2011
Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 2020
Epilepsy & Behavior, 2018
Journal of Marine Science and Application, 2017
Revista Española de Podología, 2022
ACI Structural Journal, 2019
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis, 1997
Electric Power Components and Systems, 2017
Related topics
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper
On the other hand, a research paper is analytical, argumentative and interpretative in nature. It involves the pursuit of knowledge and intelligent analysis of the information collected. It contains the idea of the author, often supported by expert opinions, research and information available in this regard.
Whether you are writing a thesis or research paper, they are equally challenging and take a lot of time to prepare. In this post, we will update you on all the points of difference between thesis and research paper.
Content: Thesis Vs Research Paper
- Key Elements
- Thesis Statement
How to start a research paper?
Comparison chart, what is thesis.
The thesis is a document containing the research and findings that students submit to get the professional qualification or degree . It has to be argumentative, which proposes a debatable point with which people could either agree or disagree. In short, it is a research report in writing that contains a problem which is yet to be dealt with.
In a thesis, the researcher puts forth his/her conclusion. The researcher also gives evidence in support of the conclusion.
Submission of the thesis is a mandatory requirement of a postgraduate course and PhD degree. In this, the primary focus is on the novelty of research along with the research methodology.
It is all about possibilities, by introducing several anti-thesis. Also, it ends up all the possibilities by nullifying all these anti-thesis.
Key Elements of Thesis
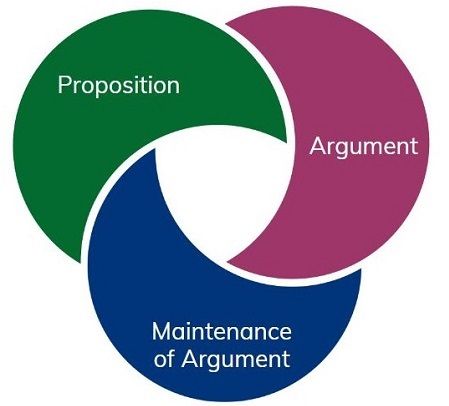
- Proposition : The thesis propagates an idea, hypothesis or recommendation.
- Argument : Gives reasons for accepting the proposition instead of just asserting a point of view.
- Maintenance of argument : The argument should be made cogent enough by providing suitable logic and adequate evidence.
Features of An Ideal Thesis
- An Ideal thesis is expected to add fresh knowledge to the existing theory.
- It communicates the central idea of the research in a clear and concise manner.
- An effective thesis is more than a simple statement, fact or question.
- It answers why and how questions concerned with the topic.
- To avoid confusion, it is worded carefully.
- It outlines the direction and scope of your essay.
- It gives reasons to the reader to continue reading.
Also Read : Difference Between Thesis and Dissertation
What is Thesis Statement?
A thesis statement is a sentence of one line, usually written at the end of your first paragraph. It presents the argument to the reader.
It is a blueprint of your thesis that directs the writer while writing the thesis and guides the reader through it.
What is Research Paper?
Research Paper is a form of academic writing. It is prepared on the basis of the original research conducted by the author on a specific topic, along with its analysis and interpretation of the findings.
An author generally starts writing a research paper on the basis of what he knows about the topic and seeks to find out what experts know. Further, it involves thorough and systematic research on a particular subject to extract the maximum information.
In short, a research paper is a written and published report containing the results of scientific research or a review of published scientific papers. Here, the scientific research is the primary research article, while the review of a published scientific paper is the review article.
In case of the primary research article, the author of the research paper provides important information about the research. This enables the scientific community members to:
- Evaluate it
- Reproduce the experiments
- Assess the reasoning and conclusions drawn
On the other hand, a review article is written to analyze, summarize and synthesize the research carried out previously.
When a research work is published in a scientific journal, it conveys the knowledge to a larger group of people and also makes people aware of the scientific work. Research work published as a research paper passes on knowledge and information to many people. The research paper provides relevant information about the disease and the treatment options at hand .
To start writing a research paper, one should always go for a topic that is interesting and a bit challenging too. Here, the key to choosing the topic is to pick the one that you can manage. So, you could avoid such topics which are very technical or specialized and also those topics for which data is not easily available. Also, do not go for any controversial topic.
The researcher’s approach and attitude towards the topic will decide the amount of effort and enthusiasm.
Steps for writing Research Paper
The total number of pages included in a Research Paper relies upon the research topic. It may include 8 to 10 pages, which are:
- Introduction
- Review of Literature
- Methodology
- Research Analysis
- Recommendations
Also Read : Difference Between Research Proposal and Research Report
Key Differences Between Thesis and Research Paper
- A thesis implies an original, plagiarism-free, written academic document that acts as a final project for a university degree of a higher level. But, Research Paper is a novel, plagiarism-free long essay. It portrays the interpretation, evaluation or argument submitted by a researcher.
- The thesis acts as a final project. Whereas a research paper is a kind of research manual of journals.
- The length of the thesis is around 20,000 to 80,000 words. On the contrary, the length of the research paper is relative to the study.
- The thesis focuses on the central question or statement of an intellectual argument that entails further research. On the contrary, the research paper is concerned with proving the central argument.
- The purpose of submitting the thesis is to get the degree or professional qualification. It also presents the knowledge of the candidate in the respective field. Conversely, the aim of publishing research papers is to prove credibility and contribute knowledge in the respective field.
- While the student submits the thesis to the educational committee or panel of professors who review it. In contrast, scientists and other researchers read and review the research paper.
- Preparation and completion of thesis is always under the guidance of a supervisor. For submission of the thesis, the university assigns a supervisor to each student, under whose guidance the thesis must be completed. As against, no supervisor is appointed as a guide in case of a research paper.
- The thesis contains a broader description of the subject matter. In contrast, the research paper contains a narrow description of the subject matter.
Once the research paper is published, it increases the fellowship and job opportunities for new researchers. On the other hand, thesis writing will enable the students to get the desired degree at the end of the course they have opted.
You Might Also Like:

Dr. Owenga says
February 23, 2023 at 2:38 pm
So good and informative. These are quite beneficial insights. Thanks
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
[email protected]
- English English Spanish German French Turkish

Thesis vs. Research Paper: Know the Differences
It is not uncommon for individuals, academic and nonacademic to use “thesis” and “research paper” interchangeably. However, while the thesis vs. research paper puzzle might seem amusing to some, for graduate, postgraduate and doctoral students, knowing the differences between the two is crucial. Not only does a clear demarcation of the two terms help you acquire a precise approach toward writing each of them, but it also helps you keep in mind the subtle nuances that go into creating the two documents. This brief guide discusses the main difference between a thesis and a research paper.
This article discusses the main difference between a thesis and a research paper. To give you an opportunity to practice proofreading, we have left a few spelling, punctuation, or grammatical errors in the text. See if you can spot them! If you spot the errors correctly, you will be entitled to a 10% discount.
It is not uncommon for individuals, academic and nonacademic to use “thesis” and “research paper” interchangeably. After all, both terms share the same domain, academic writing . Moreover, characteristics like the writing style, tone, and structure of a thesis and research paper are also homogenous to a certain degree. Hence, it is not surprising that many people mistake one for the other.
However, while the thesis vs. research paper puzzle might seem amusing to some, for graduate, postgraduate and doctoral students, knowing the differences between the two is crucial. Not only does a clear demarcation of the two terms help you acquire a precise approach toward writing each of them, but it also helps you keep in mind the subtle nuances that go into creating the two documents.
Defining the two terms: thesis vs. research paper
The first step to discerning between a thesis and research paper is to know what they signify.
Thesis: A thesis or a dissertation is an academic document that a candidate writes to acquire a university degree or similar qualification. Students typically submit a thesis at the end of their final academic term. It generally consists of putting forward an argument and backing it up with individual research and existing data.
How to Write a Perfect Ph.D. Thesis
How to Choose a Thesis or Dissertation Topic: 6 Tips
5 Common Mistakes When Writing a Thesis or Dissertation
How to Structure a Dissertation: A Brief Guide
A Step-by-Step Guide on Writing and Structuring Your Dissertation
Research Paper: A research paper is also an academic document, albeit shorter compared to a thesis. It consists of conducting independent and extensive research on a topic and compiling the data in a structured and comprehensible form. A research paper demonstrates a student's academic prowess in their field of study along with strong analytical skills.
7 Tips to Write an Effective Research Paper
7 Steps to Publishing in a Scientific Journal
Publishing Articles in Peer-Reviewed Journals: A Comprehensive Guide
10 Free Online Journal and Research Databases for Researchers
How to Formulate Research Questions
Now that we have a fundamental understanding of a thesis and a research paper, it is time to dig deeper. To the untrained eye, a research paper and a thesis might seem similar. However, there are some differences, concrete and subtle, that set the two apart.
1. Writing objectives
The objective behind writing a thesis is to obtain a master's degree or doctorate and the ilk. Hence, it needs to exemplify the scope of your knowledge in your study field. That is why choosing an intriguing thesis topic and putting forward your arguments convincingly in favor of it is crucial.
A research paper is written as a part of a course's curriculum or written for publication in a peer-review journal. Its purpose is to contribute something new to the knowledge base of its topic.
2. Structure
Although both documents share quite a few similarities in their structures, the framework of a thesis is more rigid. Also, almost every university has its proprietary guidelines set out for thesis writing.
Comparatively, a research paper only needs to keep the IMRAD format consistent throughout its length. When planning to publish your research paper in a peer-review journal, you also must follow your target journal guidelines.
3. Time Taken
A thesis is an extensive document encompassing the entire duration of a master's or doctoral course and as such, it takes months and even years to write.
A research paper, being less lengthy, typically takes a few weeks or a few months to complete.
4. Supervision
Writing a thesis entails working with a faculty supervisor to ensure that you are on the right track. However, a research paper is more of a solo project and rarely needs a dedicated supervisor to oversee.
5. Finalization
The final stage of thesis completion is a viva voce examination and a thesis defense. It includes proffering your thesis to the examination board or a thesis committee for a questionnaire and related discussions. Whether or not you will receive a degree depends on the result of this examination and the defense.
A research paper is said to be complete when you finalize a draft, check it for plagiarism, and proofread for any language and contextual errors . Now all that's left is to submit it to the assigned authority.
What is Plagiarism | How to Avoid It
How to Choose the Right Plagiarism Checker for Your Academic Works
5 Practical Ways to Avoid Plagiarism
10 Common Grammar Mistakes in Academic Writing
Guide to Avoid Common Mistakes in Sentence Structuring
In the context of academic writing, a thesis and a research paper might appear the same. But, there are some fundamental differences that set apart the two writing formats. However, since both the documents come under the scope of academic writing, they also share some similarities. Both require formal language, formal tone, factually correct information & proper citations. Also, editing and proofreading are a must for both. Editing and Proofreading ensure that your document is properly formatted and devoid of all grammatical & contextual errors. So, the next time when you come across a thesis vs. research paper argument, keep these differences in mind.
Editing or Proofreading? Which Service Should I Choose?
Thesis Proofreading and Editing Services
8 Benefits of Using Professional Proofreading and Editing Services
Achieve What You Want with Academic Editing and Proofreading
How Much Do Proofreading and Editing Cost?
If you need us to make your thesis or dissertation, contact us unhesitatingly!
Best Edit & Proof expert editors and proofreaders focus on offering papers with proper tone, content, and style of academic writing, and also provide an upscale editing and proofreading service for you. If you consider our pieces of advice, you will witness a notable increase in the chance for your research manuscript to be accepted by the publishers. We work together as an academic writing style guide by bestowing subject-area editing and proofreading around several categorized writing styles. With the group of our expert editors, you will always find us all set to help you identify the tone and style that your manuscript needs to get a nod from the publishers.
English formatting service
You can also avail of our assistance if you are looking for editors who can format your manuscript, or just check on the particular styles for the formatting task as per the guidelines provided to you, e.g., APA, MLA, or Chicago/Turabian styles. Best Edit & Proof editors and proofreaders provide all sorts of academic writing help, including editing and proofreading services, using our user-friendly website, and a streamlined ordering process.
Get a free quote for editing and proofreading now!
Visit our order page if you want our subject-area editors or language experts to work on your manuscript to improve its tone and style and give it a perfect academic tone and style through proper editing and proofreading. The process of submitting a paper is very easy and quick. Click here to find out how it works.
Our pricing is based on the type of service you avail of here, be it editing or proofreading. We charge on the basis of the word count of your manuscript that you submit for editing and proofreading and the turnaround time it takes to get it done. If you want to get an instant price quote for your project, copy and paste your document or enter your word count into our pricing calculator.

24/7 customer support | Live support
Contact us to get support with academic editing and proofreading. We have a 24/7 active live chat mode to offer you direct support along with qualified editors to refine and furbish your manuscript.

Stay tuned for updated information about editing and proofreading services!
Follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and Medium .
For more posts, click here.
- Editing & Proofreading
- Citation Styles
- Grammar Rules
- Academic Writing
- Proofreading
- Microsoft Tools
- Academic Publishing
- Dissertation & Thesis
- Researching
- Job & Research Application
Similar Posts
How to Determine Variability in a Dataset
How to Determine Central Tendency
How to Specify Study Variables in Research Papers?
Population vs Sample | Sampling Methods for a Dissertation
7 Issues to Avoid That may Dent the Quality of Thesis Writing
How to Ensure the Quality of Academic Writing in a Thesis and Dissertation?
How to Define Population and Sample in a Dissertation?
Recent Posts
ANOVA vs MANOVA: Which Method to Use in Dissertations?
They Also Read

Preparing a research paper is the most painstaking and challenging task for many individuals. However, with rigorous practice, it would be much hassle-free for you to sum up entirely. Are you thinking of the best ways to write an impactful research paper? We are here to help you! We present an easy-to-follow rubric that will help you draft an impeccable research paper.

Writing assignments is not like any other homework you’ve ever done or will do in your academic life. Writing assignments demands unrestrained dedication and plenty of willpower. You cannot just open a book and copy-paste its contents with some rephrasing. To write a better assignment, you need to work hard, you need to research, plan, draft, and edit carefully. Writing an assignment paper is one thing and writing an impactful assignment paper that instills a positive impression of you in your professor’s books and elicits good grades out of him/her is another one. The following tips will help you write a perfect assignment paper.

If you are just starting with academic writing, you may feel overwhelmed by the pressure that academic writing usually imposes. However, as demanding as it may seem, you can easily master academic writing if you know the right rules to follow. This article particularly reaches out to beginners in academic writing to help you master this form of writing. Here, we will go through the basic language rules that apply to all kinds of academic writing (generally) and will help you master it in no time.

For academic achievement, staying ahead of the pack is always a crucial issue. Taking advantage of professional academic editing and proofreading can help you reach your potential and increase chances of your work being published in professional journals. It requires a broad-ranging comprehension to fix a document exceptionally. Therefore, academic editing and proofreading are a critical part of the writing process.
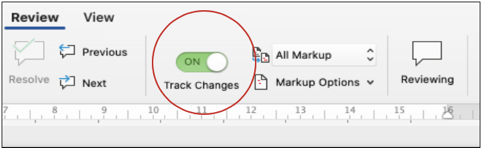
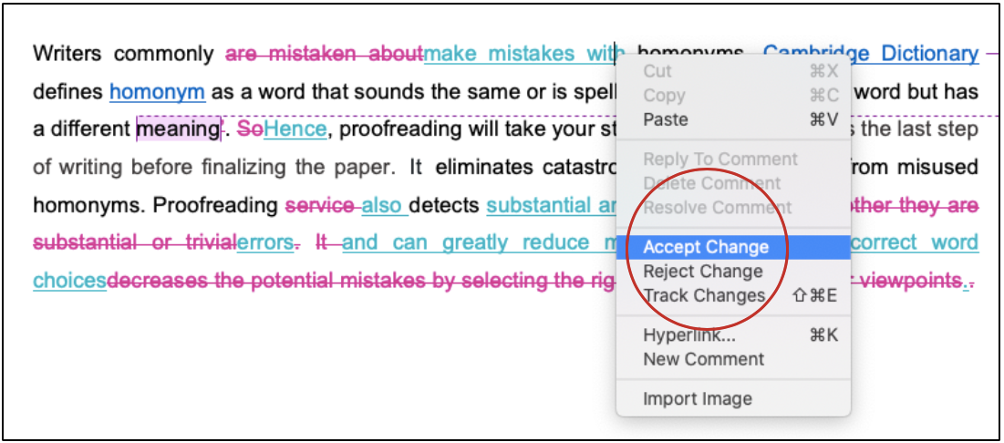
Track changes function in Microsoft Word 2021 for macOS is a very handy tool to track your revisions, corrections, changes, edits, and even suggestions and comments while you’re reviewing a document. When an editor or proofreader wants to return a revised document to a client with his/her all revisions visibly marked, and so clients can accept or reject, or the suggested changes appear in the margins of the returned document, he/she needs Track Changes function of Microsoft Word.

Research Statement vs Research Proposal
If you’re in academia or planning to pursue higher education, you’ve probably come across the terms “research statement” and “research proposal.” At first glance, they might seem similar, but they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics.
In this post, we’ll break down the differences between these two important documents and help you understand when and how to use each one.
What You'll Learn
What is a Research Statement?
A research statement is a brief document that outlines your research interests, experience, and future plans. It’s like a snapshot of your academic journey and where you want to go next.

Key Features of a Research Statement
- Length : Usually short, typically 1-3 pages.
- Purpose : To give an overview of your research background and goals.
- Audience : Often read by hiring committees or graduate school admissions teams.
- Content : Includes past research, current interests, and future directions.
- Tone : Professional and confident, showcasing your expertise.
When Do You Need a Research Statement?
You might need to write a research statement when:
- Applying for academic jobs (like professor positions)
- Submitting applications to graduate school programs
- Seeking research funding or grants
- Updating your professional portfolio
Example of a Research Statement (Excerpt)
Here’s a brief example of what part of a research statement might look like:
“As a marine biologist, my research focuses on the impact of climate change on coral reef ecosystems. Over the past five years, I have conducted extensive field studies in the Great Barrier Reef, analyzing the resilience of various coral species to rising ocean temperatures. My current work involves developing new methods for coral restoration using 3D printing technology. In the future, I plan to expand this research to other reef systems around the world, with the goal of creating a global network of coral restoration sites.”
What is a Research Proposal?
A research proposal is a detailed plan for a specific research project. It’s like a roadmap that outlines the what, why, and how of your intended research.
Key Features of a Research Proposal
- Length : Usually longer, typically 10-25 pages (can be shorter or longer depending on requirements).
- Purpose : To convince others that your research idea is worthwhile and feasible.
- Audience : Often read by funding agencies, dissertation committees, or research supervisors.
- Content : Includes research question, literature review, methodology, timeline, and budget.
- Tone : Formal and detailed, demonstrating thorough planning.
When Do You Need a Research Proposal?
You might need to write a research proposal when:
- Applying for research funding or grants
- Starting a Ph.D. program or planning your dissertation
- Pitching a new research project to your department or institution
- Collaborating with other researchers or institutions on a joint project
Example of a Research Proposal (Excerpt)
Here’s a brief example of what part of a research proposal might look like:
“Project Title: The Impact of Microplastics on Marine Mammal Health in the North Atlantic
- Introduction: Microplastic pollution has become a significant concern in marine ecosystems worldwide. This study aims to investigate the presence and effects of microplastics in the digestive systems of various marine mammal species in the North Atlantic Ocean.
- Research Questions: a) What is the prevalence of microplastic ingestion among different marine mammal species in the North Atlantic? b) How does microplastic ingestion correlate with the health status of these marine mammals? c) What are the potential long-term implications of microplastic pollution on marine mammal populations in the region?
- Methodology: We will collect and analyze stomach contents and tissue samples from stranded marine mammals along the coastlines of the North Atlantic. Additionally, we will conduct field observations and health assessments of living populations…”
Key Differences Between Research Statements and Research Proposals
Now that we’ve looked at each document separately, let’s compare them side by side to highlight the main differences:
- Research Statement: Broad overview of your entire research career and interests
- Research Proposal: Focused on a specific project or study
- Research Statement: General and concise
- Research Proposal: Highly detailed and comprehensive
- Research Statement: Covers past, present, and future research interests
- Research Proposal: Focuses on a future project with a specific timeline
- Research Statement: To showcase your research expertise and potential
- Research Proposal: To gain approval or funding for a specific research project
- Research Statement: Often less structured, more like a narrative
- Research Proposal: Highly structured with specific sections (e.g., literature review, methodology)
- Research Statement: Aims to impress and inform the reader about your capabilities
- Research Proposal: Aims to persuade the reader to support or fund your project
- Research Statement: May include some references, but not extensively
- Research Proposal: Requires extensive literature review and citations
How to Write an Effective Research Statement
Now that we understand what a research statement is, let’s look at how to write one that stands out.
1. Start with a Strong Opening
Begin your research statement with a powerful opening that grabs the reader’s attention. This could be a brief story about what inspired your research interests or a compelling statistic that highlights the importance of your work.
Example: “When I first witnessed the devastating effects of coral bleaching during a diving expedition in 2015, I knew my life’s work would be dedicated to understanding and preserving these vital marine ecosystems.”
2. Highlight Your Research Journey
Describe your research background and how your interests have evolved over time. This shows your growth as a researcher and your ability to adapt to new challenges.
Example: “My early work focused on cataloging coral species diversity in the Caribbean. As I observed the rapid decline of certain species, my research shifted towards understanding the factors contributing to coral resilience in the face of climate change.”
3. Showcase Your Achievements
Mention your key accomplishments, such as publications, grants, or impactful findings. Be specific and quantify your achievements where possible.
Example: “My research on heat-resistant coral strains led to the publication of three peer-reviewed articles in leading marine biology journals and secured a $500,000 grant from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.”
4. Explain Your Current Research Focus
Clearly articulate your current research interests and ongoing projects. This demonstrates that you’re actively engaged in your field and have a clear direction.
Example: “Currently, I’m leading a team of researchers in developing innovative coral transplantation techniques using 3D-printed reef structures. Our preliminary results show a 40% increase in coral survival rates compared to traditional methods.”
5. Outline Your Future Research Plans
Describe your future research goals and how they build upon your previous work. This shows that you have a long-term vision and are committed to making a lasting impact in your field.
Example: “In the coming years, I plan to expand our coral restoration techniques to other reef systems around the world. I’m particularly interested in establishing a global network of coral nurseries to preserve genetic diversity and enhance reef resilience.”
6. Connect Your Research to Broader Impacts
Explain how your research contributes to your field and society at large. This helps the reader understand the significance of your work beyond academia.
Example: “By developing more effective coral restoration techniques, my research not only contributes to marine conservation but also helps protect coastal communities that rely on healthy reef systems for food security and economic stability.”
7. Maintain a Clear and Concise Style
Keep your writing clear, concise, and free of jargon. Remember that your audience may include people from different academic backgrounds.
8. Proofread and Revise
Always proofread your research statement carefully and ask colleagues for feedback. A polished, error-free document shows professionalism and attention to detail.
How to Write an Effective Research Proposal
Writing a research proposal requires careful planning and attention to detail. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you create a compelling proposal:
1. Choose a Compelling Title
Your title should be clear, concise, and accurately reflect the content of your proposal. It should grab the reader’s attention and give them a good idea of what your research is about.
Example: “Harnessing Artificial Intelligence to Predict and Prevent Coral Reef Bleaching Events”
2. Write an Engaging Introduction
Start with a brief background of the research problem and explain why it’s important. State your research question or hypothesis clearly.
Example: “Coral reefs, often called the ‘rainforests of the sea,’ are facing unprecedented threats due to climate change. This research aims to develop an AI-powered early warning system for coral bleaching events, potentially revolutionizing our ability to protect these crucial ecosystems.”
3. Conduct a Thorough Literature Review
Demonstrate your knowledge of the existing research in your field. Identify gaps in the current understanding that your research will address.
Example: “While numerous studies have documented the causes and effects of coral bleaching (Smith et al., 2018; Jones & Lee, 2020), there’s a lack of predictive models that can accurately forecast bleaching events on a local scale. This research builds upon the work of Zhang (2021) on using machine learning for environmental prediction…”
4. Clearly State Your Research Objectives
List your specific research goals or questions. These should be clear, measurable, and achievable within the scope of your project.
Example: “The objectives of this study are to:
- Develop an AI model that can predict coral bleaching events with 85% accuracy at least two weeks in advance.
- Identify the most critical environmental factors contributing to bleaching events in different reef ecosystems.
- Create a user-friendly interface for reef managers to access and interpret bleaching predictions.”
5. Describe Your Methodology in Detail
Explain how you plan to conduct your research. Include information about data collection methods, analysis techniques, and any special equipment or resources you’ll need.
Example: “We will collect real-time data from a network of underwater sensors installed at 20 reef sites across the Great Barrier Reef. This data will include water temperature, pH levels, salinity, and light intensity. We’ll combine this with satellite imagery and historical bleaching data to train our AI model using deep learning algorithms…”
6. Outline Your Timeline
Provide a realistic schedule for your research activities. Break down your project into phases and estimate how long each will take.
Example: “Phase 1 (Months 1-3): Literature review and data collection setup Phase 2 (Months 4-9): Data collection and AI model development Phase 3 (Months 10-18): Model testing and refinement Phase 4 (Months 19-24): Field trials and system optimization”
7. Discuss Potential Challenges and Solutions
Show that you’ve thought about possible obstacles and have plans to overcome them. This demonstrates your problem-solving skills and realistic approach.
Example: “One potential challenge is the reliability of underwater sensors in harsh marine environments. To mitigate this, we’ll use redundant sensors and develop a maintenance schedule to ensure consistent data collection. We’ll also implement data interpolation techniques to handle any gaps in the dataset.”
8. Include a Budget
If you’re seeking funding, provide a detailed budget that outlines all the costs associated with your research. Be realistic and justify major expenses.
Example: “Equipment costs:
- Underwater sensors (20 sets): $40,000
- High-performance computing cluster: $25,000
- Field research boat rental: $10,000 per year
Personnel costs:
- Principal Investigator (25% time): $30,000 per year
- Two graduate research assistants: $25,000 each per year …”
9. Emphasize the Significance and Potential Impact
Explain why your research matters and how it could benefit your field or society at large. This helps justify the resources and support you’re requesting.
Example: “By developing an accurate early warning system for coral bleaching, this research has the potential to save countless reef ecosystems worldwide. It could provide reef managers with crucial time to implement protective measures, potentially preserving biodiversity and the livelihoods of millions who depend on healthy coral reefs.”
10. Include References
Provide a comprehensive list of all the sources you cited in your proposal. Follow the citation style required by your institution or funding agency.
11. Proofread and Seek Feedback
Carefully review your proposal for clarity, coherence, and typos. Ask colleagues or mentors to read it and provide feedback. A polished, well-written proposal greatly increases your chances of success.
Tips for Success in Both Research Statements and Proposals
Whether you’re writing a research statement or a proposal, these general tips can help you create a more effective document:
- Know Your Audience : Tailor your language and level of detail to who will be reading your document. A proposal for a highly specialized grant might use more technical language than a general research statement for a broad academic hiring committee.
- Be Clear and Concise : Avoid jargon and overly complex sentences. Your ideas should be easy to understand, even for someone who isn’t an expert in your specific field.
- Show Enthusiasm : Let your passion for your research shine through. Enthusiasm can be contagious and may help engage your readers.
- Highlight Your Unique Perspective : What makes your research or approach special? Don’t be afraid to emphasize what sets you apart from others in your field.
- Use Strong, Active Language : Instead of saying “Research was conducted,” say “I conducted research.” Active voice makes your writing more engaging and clearly shows your role in the work.
- Proofread Carefully : Typos and grammatical errors can distract from your message and make your document seem less professional. Take the time to proofread carefully or ask someone else to review your work.
- Follow Instructions : If you’re given specific guidelines for format, length, or content, make sure to follow them exactly. Failing to do so can sometimes result in automatic rejection, regardless of the quality of your content.
- Tell a Story : While maintaining a professional tone, try to create a narrative that ties your past work, current interests, and future plans together coherently. This can make your document more memorable and engaging.
- Be Realistic : Especially in research proposals, make sure your goals and timelines are achievable. Overpromising can hurt your credibility.
- Update Regularly : Especially for research statements, make sure to update your document regularly to reflect your most recent work and interests.
Related Articles
140 + Expository Essay Topics Ideas: Definition|Types|Outline|Guide|Topics Examples
130 + Best Research Topic about Nursing – Types & How to Choose a Nursing Research Topic
“Research Statement” vs. “Research Plan” for assistant professor applications
Research statement
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
To wrap up our discussion, let’s address some common questions about research statements and proposals:
1. How long should a research statement be?
A research statement is typically 1-3 pages long, but always check specific guidelines as requirements can vary.
2. Do I need to include references in a research statement?
While not always required, including a few key references can strengthen your research statement. However, it shouldn’t read like a literature review.
3. How detailed should the methodology be in a research proposal?
Your methodology should be detailed enough that another researcher in your field could understand and potentially replicate your approach. However, you don’t need to include every minor detail.
4. Can I use the same research statement for different job applications?
While you can use the same basic structure, it’s best to tailor your research statement to each specific position or institution you’re applying to.
5. How often should I update my research statement?
It’s a good idea to review and update your research statement at least once a year, or whenever you have significant new research developments.
6. What if I don’t have many research accomplishments yet?
Focus on your research interests, any relevant coursework or projects, and your future research goals. Everyone starts somewhere!
7. Is it okay to discuss failed experiments in a research proposal?
If relevant, discussing how you’ve learned from past challenges can demonstrate your problem-solving skills and resilience. However, focus more on your successes and future plans.
8. How technical should my language be in these documents?
This depends on your audience. For a specialized committee in your field, you can use more technical language. For a general audience, err on the side of clarity and simplicity.
9. Should I include personal information in my research statement?
While you can briefly mention what inspired your research interests, a research statement should focus primarily on your academic and professional experiences and goals.
10. How important is the budget section in a research proposal?
Very important! A well-thought-out, realistic budget demonstrates that you’ve carefully planned your research and understand what resources you’ll need.
11. Can I submit the same research proposal to multiple funding agencies?
While the core of your proposal might remain the same, it’s important to tailor each submission to the specific requirements and priorities of each funding agency.
12. What if my research plans change after submitting a proposal?
Some degree of flexibility is usually expected in research. If you receive funding and need to make significant changes to your plan, communicate with your funding agency about the necessary adjustments.
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Post navigation
Previous post.
📕 Studying HQ
Typically replies within minutes
Hey! 👋 Need help with an assignment?
🟢 Online | Privacy policy
WhatsApp us

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The main difference between a thesis and a research proposal is their purpose. A thesis is a formal academic piece of writing done on a particular topic that has not yet been explored. This is why a thesis has a prospectus stage where the student has to consult with a committee. On the other hand, a research proposal proposes the topic and the ...
A research proposal outlines your intended path, while a thesis presents the culmination of your investigation. Grasping the nuances between these two critical documents is crucial for navigating your academic trajectory successfully. In this article, we'll explore: Definitions and purposes of research proposals and theses
An overwhelming majority of scholars and students of research find it difficult when it comes to giving a difference between A Proposal and Thesis. It is with this reason that Prof. Ramah seeks to enlighten the general public on this matter. Table 1.1 shows a summarized Difference between a Proposal and Thesis.
Papers vs. proposals Key points: Papers and proposals make the same two key arguments Key arguments are o Research is exciting—important and innovative o Science is sound/ feasible; results are/ will be reliable Difference between future and past research require different ways of making these arguments
The main difference between research proposal and research report is that research proposal defines the planning stage of the research work, which is prepared in written format, to know its worth. On the other hand, the research report signifies the concluding stage of the research work.
How to Write a Research Proposal and a Thesis - 2 nd ed. M.E. Hamid (2013) ( 12 ) RE F E R E N C E S ( B IB L I O G R A P H Y )
Key Differences Between Thesis and Research Paper. A thesis implies an original, plagiarism-free, written academic document that acts as a final project for a university degree of a higher level. But, Research Paper is a novel, plagiarism-free long essay. It portrays the interpretation, evaluation or argument submitted by a researcher.
Defining the two terms: thesis vs. research paper. The first step to discerning between a thesis and research paper is to know what they signify. Thesis: A thesis or a dissertation is an academic document that a candidate writes to acquire a university degree or similar qualification. Students typically submit a thesis at the end of their final ...
In some countries, whenever someone applies for a Ph.D. admission, the universities ask for a research proposal. A research proposal includes a literature review and bibliography. If the research is paper-based research, i.e. no popular survey or experiment is involved, I see no further need for research work.
Key Differences Between Research Statements and Research Proposals. Now that we've looked at each document separately, let's compare them side by side to highlight the main differences: Scope. Research Statement: Broad overview of your entire research career and interests; Research Proposal: Focused on a specific project or study; Level of ...