

Art History
What this handout is about.
This handout discusses a few common assignments found in art history courses. To help you better understand those assignments, this handout highlights key strategies for approaching and analyzing visual materials.
Writing in art history
Evaluating and writing about visual material uses many of the same analytical skills that you have learned from other fields, such as history or literature. In art history, however, you will be asked to gather your evidence from close observations of objects or images. Beyond painting, photography, and sculpture, you may be asked to write about posters, illustrations, coins, and other materials.
Even though art historians study a wide range of materials, there are a few prevalent assignments that show up throughout the field. Some of these assignments (and the writing strategies used to tackle them) are also used in other disciplines. In fact, you may use some of the approaches below to write about visual sources in classics, anthropology, and religious studies, to name a few examples.
This handout describes three basic assignment types and explains how you might approach writing for your art history class.Your assignment prompt can often be an important step in understanding your course’s approach to visual materials and meeting its specific expectations. Start by reading the prompt carefully, and see our handout on understanding assignments for some tips and tricks.
Three types of assignments are discussed below:
- Visual analysis essays
- Comparison essays
- Research papers
1. Visual analysis essays
Visual analysis essays often consist of two components. First, they include a thorough description of the selected object or image based on your observations. This description will serve as your “evidence” moving forward. Second, they include an interpretation or argument that is built on and defended by this visual evidence.
Formal analysis is one of the primary ways to develop your observations. Performing a formal analysis requires describing the “formal” qualities of the object or image that you are describing (“formal” here means “related to the form of the image,” not “fancy” or “please, wear a tuxedo”). Formal elements include everything from the overall composition to the use of line, color, and shape. This process often involves careful observations and critical questions about what you see.
Pre-writing: observations and note-taking
To assist you in this process, the chart below categorizes some of the most common formal elements. It also provides a few questions to get you thinking.
Let’s try this out with an example. You’ve been asked to write a formal analysis of the painting, George Morland’s Pigs and Piglets in a Sty , ca. 1800 (created in Britain and now in the Virginia Museum of Fine Arts in Richmond).

What do you notice when you see this image? First, you might observe that this is a painting. Next, you might ask yourself some of the following questions: what kind of paint was used, and what was it painted on? How has the artist applied the paint? What does the scene depict, and what kinds of figures (an art-historical term that generally refers to humans) or animals are present? What makes these animals similar or different? How are they arranged? What colors are used in this painting? Are there any colors that pop out or contrast with the others? What might the artist have been trying to accomplish by adding certain details?
What other questions come to mind while examining this work? What kinds of topics come up in class when you discuss paintings like this one? Consider using your class experiences as a model for your own description! This process can be lengthy, so expect to spend some time observing the artwork and brainstorming.
Here is an example of some of the notes one might take while viewing Morland’s Pigs and Piglets in a Sty :
Composition
- The animals, four pigs total, form a gently sloping mound in the center of the painting.
- The upward mound of animals contrasts with the downward curve of the wooden fence.
- The gentle light, coming from the upper-left corner, emphasizes the animals in the center. The rest of the scene is more dimly lit.
- The composition is asymmetrical but balanced. The fence is balanced by the bush on the right side of the painting, and the sow with piglets is balanced by the pig whose head rests in the trough.
- Throughout the composition, the colors are generally muted and rather limited. Yellows, greens, and pinks dominate the foreground, with dull browns and blues in the background.
- Cool colors appear in the background, and warm colors appear in the foreground, which makes the foreground more prominent.
- Large areas of white with occasional touches of soft pink focus attention on the pigs.
- The paint is applied very loosely, meaning the brushstrokes don’t describe objects with exact details but instead suggest them with broad gestures.
- The ground has few details and appears almost abstract.
- The piglets emerge from a series of broad, almost indistinct, circular strokes.
- The painting contrasts angular lines and rectangles (some vertical, some diagonal) with the circular forms of the pig.
- The negative space created from the intersection of the fence and the bush forms a wide, inverted triangle that points downward. The point directs viewers’ attention back to the pigs.
Because these observations can be difficult to notice by simply looking at a painting, art history instructors sometimes encourage students to sketch the work that they’re describing. The image below shows how a sketch can reveal important details about the composition and shapes.

Writing: developing an interpretation
Once you have your descriptive information ready, you can begin to think critically about what the information in your notes might imply. What are the effects of the formal elements? How do these elements influence your interpretation of the object?
Your interpretation does not need to be earth-shatteringly innovative, but it should put forward an argument with which someone else could reasonably disagree. In other words, you should work on developing a strong analytical thesis about the meaning, significance, or effect of the visual material that you’ve described. For more help in crafting a strong argument, see our Thesis Statements handout .
For example, based on the notes above, you might draft the following thesis statement:
In Morland’s Pigs and Piglets in a Sty, the close proximity of the pigs to each other–evident in the way Morland has overlapped the pigs’ bodies and grouped them together into a gently sloping mound–and the soft atmosphere that surrounds them hints at the tranquility of their humble farm lives.
Or, you could make an argument about one specific formal element:
In Morland’s Pigs and Piglets in a Sty, the sharp contrast between rectilinear, often vertical, shapes and circular masses focuses viewers’ attention on the pigs, who seem undisturbed by their enclosure.
Support your claims
Your thesis statement should be defended by directly referencing the formal elements of the artwork. Try writing with enough specificity that someone who has not seen the work could imagine what it looks like. If you are struggling to find a certain term, try using this online art dictionary: Tate’s Glossary of Art Terms .
Your body paragraphs should explain how the elements work together to create an overall effect. Avoid listing the elements. Instead, explain how they support your analysis.
As an example, the following body paragraph illustrates this process using Morland’s painting:
Morland achieves tranquility not only by grouping animals closely but also by using light and shadow carefully. Light streams into the foreground through an overcast sky, in effect dappling the pigs and the greenery that encircles them while cloaking much of the surrounding scene. Diffuse and soft, the light creates gentle gradations of tone across pigs’ bodies rather than sharp contrasts of highlights and shadows. By modulating the light in such subtle ways, Morland evokes a quiet, even contemplative mood that matches the restful faces of the napping pigs.
This example paragraph follows the 5-step process outlined in our handout on paragraphs . The paragraph begins by stating the main idea, in this case that the artist creates a tranquil scene through the use of light and shadow. The following two sentences provide evidence for that idea. Because art historians value sophisticated descriptions, these sentences include evocative verbs (e.g., “streams,” “dappling,” “encircles”) and adjectives (e.g., “overcast,” “diffuse,” “sharp”) to create a mental picture of the artwork in readers’ minds. The last sentence ties these observations together to make a larger point about the relationship between formal elements and subject matter.
There are usually different arguments that you could make by looking at the same image. You might even find a way to combine these statements!
Remember, however you interpret the visual material (for example, that the shapes draw viewers’ attention to the pigs), the interpretation needs to be logically supported by an observation (the contrast between rectangular and circular shapes). Once you have an argument, consider the significance of these statements. Why does it matter if this painting hints at the tranquility of farm life? Why might the artist have tried to achieve this effect? Briefly discussing why these arguments matter in your thesis can help readers understand the overall significance of your claims. This step may even lead you to delve deeper into recurring themes or topics from class.
Tread lightly
Avoid generalizing about art as a whole, and be cautious about making claims that sound like universal truths. If you find yourself about to say something like “across cultures, blue symbolizes despair,” pause to consider the statement. Would all people, everywhere, from the beginning of human history to the present agree? How do you know? If you find yourself stating that “art has meaning,” consider how you could explain what you see as the specific meaning of the artwork.
Double-check your prompt. Do you need secondary sources to write your paper? Most visual analysis essays in art history will not require secondary sources to write the paper. Rely instead on your close observation of the image or object to inform your analysis and use your knowledge from class to support your argument. Are you being asked to use the same methods to analyze objects as you would for paintings? Be sure to follow the approaches discussed in class.
Some classes may use “description,” “formal analysis” and “visual analysis” as synonyms, but others will not. Typically, a visual analysis essay may ask you to consider how form relates to the social, economic, or political context in which these visual materials were made or exhibited, whereas a formal analysis essay may ask you to make an argument solely about form itself. If your prompt does ask you to consider contextual aspects, and you don’t feel like you can address them based on knowledge from the course, consider reading the section on research papers for further guidance.
2. Comparison essays
Comparison essays often require you to follow the same general process outlined in the preceding sections. The primary difference, of course, is that they ask you to deal with more than one visual source. These assignments usually focus on how the formal elements of two artworks compare and contrast with each other. Resist the urge to turn the essay into a list of similarities and differences.
Comparison essays differ in another important way. Because they typically ask you to connect the visual materials in some way or to explain the significance of the comparison itself, they may require that you comment on the context in which the art was created or displayed.
For example, you might have been asked to write a comparative analysis of the painting discussed in the previous section, George Morland’s Pigs and Piglets in a Sty (ca. 1800), and an unknown Vicús artist’s Bottle in the Form of a Pig (ca. 200 BCE–600 CE). Both works are illustrated below.

You can begin this kind of essay with the same process of observations and note-taking outlined above for formal analysis essays. Consider using the same questions and categories to get yourself started.
Here are some questions you might ask:
- What techniques were used to create these objects?
- How does the use of color in these two works compare? Is it similar or different?
- What can you say about the composition of the sculpture? How does the artist treat certain formal elements, for example geometry? How do these elements compare to and contrast with those found in the painting?
- How do these works represent their subjects? Are they naturalistic or abstract? How do these artists create these effects? Why do these similarities and differences matter?
As our handout on comparing and contrasting suggests, you can organize these thoughts into a Venn diagram or a chart to help keep the answers to these questions distinct.
For example, some notes on these two artworks have been organized into a chart:
As you determine points of comparison, think about the themes that you have discussed in class. You might consider whether the artworks display similar topics or themes. If both artworks include the same subject matter, for example, how does that similarity contribute to the significance of the comparison? How do these artworks relate to the periods or cultures in which they were produced, and what do those relationships suggest about the comparison? The answers to these questions can typically be informed by your knowledge from class lectures. How have your instructors framed the introduction of individual works in class? What aspects of society or culture have they emphasized to explain why specific formal elements were included or excluded? Once you answer your questions, you might notice that some observations are more important than others.
Writing: developing an interpretation that considers both sources
When drafting your thesis, go beyond simply stating your topic. A statement that says “these representations of pig-like animals have some similarities and differences” doesn’t tell your reader what you will argue in your essay.
To say more, based on the notes in the chart above, you might write the following thesis statement:
Although both artworks depict pig-like animals, they rely on different methods of representing the natural world.
Now you have a place to start. Next, you can say more about your analysis. Ask yourself: “so what?” Why does it matter that these two artworks depict pig-like animals? You might want to return to your class notes at this point. Why did your instructor have you analyze these two works in particular? How does the comparison relate to what you have already discussed in class? Remember, comparison essays will typically ask you to think beyond formal analysis.
While the comparison of a similar subject matter (pig-like animals) may influence your initial argument, you may find that other points of comparison (e.g., the context in which the objects were displayed) allow you to more fully address the matter of significance. Thinking about the comparison in this way, you can write a more complex thesis that answers the “so what?” question. If your class has discussed how artists use animals to comment on their social context, for example, you might explore the symbolic importance of these pig-like animals in nineteenth-century British culture and in first-millenium Vicús culture. What political, social, or religious meanings could these objects have generated? If you find yourself needing to do outside research, look over the final section on research papers below!
Supporting paragraphs
The rest of your comparison essay should address the points raised in your thesis in an organized manner. While you could try several approaches, the two most common organizational tactics are discussing the material “subject-by-subject” and “point-by-point.”
- Subject-by-subject: Organizing the body of the paper in this way involves writing everything that you want to say about Moreland’s painting first (in a series of paragraphs) before moving on to everything about the ceramic bottle (in a series of paragraphs). Using our example, after the introduction, you could include a paragraph that discusses the positioning of the animals in Moreland’s painting, another paragraph that describes the depiction of the pigs’ surroundings, and a third explaining the role of geometry in forming the animals. You would then follow this discussion with paragraphs focused on the same topics, in the same order, for the ancient South American vessel. You could then follow this discussion with a paragraph that synthesizes all of the information and explores the significance of the comparison.
- Point-by-point: This strategy, in contrast, involves discussing a single point of comparison or contrast for both objects at the same time. For example, in a single paragraph, you could examine the use of color in both of our examples. Your next paragraph could move on to the differences in the figures’ setting or background (or lack thereof).
As our use of “pig-like” in this section indicates, titles can be misleading. Many titles are assigned by curators and collectors, in some cases years after the object was produced. While the ceramic vessel is titled Bottle in the Form of a Pig , the date and location suggest it may depict a peccary, a pig-like species indigenous to Peru. As you gather information about your objects, think critically about things like titles and dates. Who assigned the title of the work? If it was someone other than the artist, why might they have given it that title? Don’t always take information like titles and dates at face value.
Be cautious about considering contextual elements not immediately apparent from viewing the objects themselves unless you are explicitly asked to do so (try referring back to the prompt or assignment description; it will often describe the expectation of outside research). You may be able to note that the artworks were created during different periods, in different places, with different functions. Even so, avoid making broad assumptions based on those observations. While commenting on these topics may only require some inference or notes from class, if your argument demands a large amount of outside research, you may be writing a different kind of paper. If so, check out the next section!
3. Research papers
Some assignments in art history ask you to do outside research (i.e., beyond both formal analysis and lecture materials). These writing assignments may ask you to contextualize the visual materials that you are discussing, or they may ask you to explore your material through certain theoretical approaches. More specifically, you may be asked to look at the object’s relationship to ideas about identity, politics, culture, and artistic production during the period in which the work was made or displayed. All of these factors require you to synthesize scholars’ arguments about the materials that you are analyzing. In many cases, you may find little to no research on your specific object. When facing this situation, consider how you can apply scholars’ insights about related materials and the period broadly to your object to form an argument. While we cannot cover all the possibilities here, we’ll highlight a few factors that your instructor may task you with investigating.
Iconography
Papers that ask you to consider iconography may require research on the symbolic role or significance of particular symbols (gestures, objects, etc.). For example, you may need to do some research to understand how pig-like animals are typically represented by the cultural group that made this bottle, the Vicús culture. For the same paper, you would likely research other symbols, notably the bird that forms part of the bottle’s handle, to understand how they relate to one another. This process may involve figuring out how these elements are presented in other artworks and what they mean more broadly.
Artistic style and stylistic period
You may also be asked to compare your object or painting to a particular stylistic category. To determine the typical traits of a style, you may need to hit the library. For example, which period style or stylistic trend does Moreland’s Pigs and Piglets in a Sty belong to? How well does the piece “fit” that particular style? Especially for works that depict the same or similar topics, how might their different styles affect your interpretation? Assignments that ask you to consider style as a factor may require that you do some research on larger historical or cultural trends that influenced the development of a particular style.
Provenance research asks you to find out about the “life” of the object itself. This research can include the circumstances surrounding the work’s production and its later ownership. For the two works discussed in this handout, you might research where these objects were originally displayed and how they ended up in the museum collections in which they now reside. What kind of argument could you develop with this information? For example, you might begin by considering that many bottles and jars resembling the Bottle in the Form of a Pig can be found in various collections of Pre-Columbian art around the world. Where do these objects originate? Do they come from the same community or region?
Patronage study
Prompts that ask you to discuss patronage might ask you to think about how, when, where, and why the patron (the person who commissions or buys the artwork or who supports the artist) acquired the object from the artist. The assignment may ask you to comment on the artist-patron relationship, how the work fit into a broader series of commissions, and why patrons chose particular artists or even particular subjects.
Additional resources
To look up recent articles, ask your librarian about the Art Index, RILA, BHA, and Avery Index. Check out www.lib.unc.edu/art/index.html for further information!
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Adams, Laurie Schneider. 2003. Looking at Art . Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Barnet, Sylvan. 2015. A Short Guide to Writing about Art , 11th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Tate Galleries. n.d. “Art Terms.” Accessed November 1, 2020. https://www.tate.org.uk/art/art-terms .
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Visual Analysis Essay: Example, Template & Writing Guide
A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence.
In this article, our custom writing experts will:
- explain what a visual analysis is;
- share useful tips on how to write a good visual analysis essay;
- provide an essay sample.
- 🎨 Visual Analysis Definition
- 🖼️ Analyzing a Painting
- 📷 Analyzing a Photograph
- 🗿 Analyzing a Sculpture
- 🏷️ Analyzing an Advertisement
- ✅ Visual Analysis Writing Guide
- 🤔 How to Reference a Painting
- 📑 Visual Analysis Example
- 💡 Visual Analysis Topics
🎨 What Is a Visual Analysis?
The primary objective of visual analysis is to understand an artwork better by examining the visual elements. There are two types of visual analysis: formal and contextual.
- A formal analysis focuses on artwork elements such as texture, color, size, and line. It aims to organize visual information and translate it into words. A formal analysis doesn’t interpret the piece.
- Unlike formal analysis, contextual analysis’ primary goal is to connect artwork to its purpose or meaning within a culture. A contextual analysis includes formal analysis. Additionally, it discusses an artwork’s social purpose and significance.
Usually, students deal with formal visual analysis. Before starting to work on your essay, make sure to ask your professor whether to include contextual analysis or not.
The Purpose of Analyzing Images
Why is visual analysis important? What does it help to learn? There are several things that visual analysis helps with:
- It allows students to enhance their appreciation of art.
- It enables students to develop the ability to synthesize information.
- It encourages students to seek out answers instead of simply receiving them.
- It prompts higher-order critical thinking and helps to create a well-reasoned analysis.
- By conducting visual analysis, students learn how to support and explain their ideas by studying visual information.
What Is Formal Analysis: Art History
When we look at an artwork, we want to know why it was created, who made it, and what its function was. That’s why art historians and researchers pay special attention to the role of artworks within historical contexts.
Visual analysis is a helpful tool in exploring art. It focuses on the following aspects:
- Interpretation of subject matter ( iconography). An iconographic analysis is an explanation of the work’s meaning. Art historians try to understand what is shown and why it is depicted in a certain way.
- The analysis of function. Many works of art were designed to serve a purpose that goes beyond aesthetics. Understanding that purpose by studying their historical use helps learn more about artworks. It also establishes a connection between function and appearance.
Formal Analysis: Art Glossary
Now, let’s look at some visual elements and principles and learn how to define them.
Visual Elements :
- Lines can be obvious, or they can be formed by the placement of objects. They can vary in length, width, and direction.
- Shapes are two-dimensional. They can be geometric or organic. Familiar shapes help us focus on particular parts of an artwork.
- Forms are three-dimensional. Such figures as cylinders, pyramids, and spheres are forms.
- Color is light that reflects off of objects. Its main characteristics are hue, value, and intensity. Colors can also be warm or cool.
- A texture is a feel, appearance, or quality of a surface of an object. It can be used in two-dimensional and three-dimensional artworks.
- Space is a feeling of depth. It also refers to the artist’s use of the area within the painting. Space can be positive or negative.
Visual Principles :
- Balance is the distribution of visual elements and weights of objects, colors, textures, and space. Balance can be symmetrical and asymmetrical.
- Emphasis defines the center of interest in a painting and catches the viewer’s attention. It’s usually different from the rest of the work.
- Subordination supports the center of interest. It is a part of an artwork that is played down to let the emphasis stand out.
- Rhythm is the relationship between elements. It creates a visual tempo and establishes a sense of harmony by repeating certain features.
- Movement is the path the viewer’s eyes follow, coming to the focal points of a work. The movement is usually directed by the lines, shapes, and colors of an art piece.
🖼️ Visual Analysis Essay: Analyzing a Painting
To write an excellent formal visual analysis, you need to consider as many visual principles and elements as you can apply. In the formal analysis part:
- Target your description;
- Address only those elements relevant to your essay;
- Pay attention to visual elements and principles;
- Introduce the subject of the painting and describe it;
- Explain why you have decided to discuss specific elements;
- Discuss the relationship between visual elements of the artwork;
- Use the vocabulary terms.
If you are asked to do a contextual analysis , you may want to:
- Focus on the historical importance of an artwork;
- Explore the style or movement associated with an artwork;
- Learn about the historical context and the public’s reaction to the artwork;
- Learn about the author and how they’ve created the piece of art.

Art Analysis Template & Example
Here is a template you can use for your essay.
Part 1: Description
Give a brief description of the painting. What do you see? What areas of the artwork grab your attention?
Part 2: Analysis
In the analysis part, pay attention to visual elements and principles. Describe them and say how they all come together.
Part 3: Interpretation
Look at the artwork from a cultural perspective. What does the author express? What does it mean to the viewer?
Part 4: Evaluation
Finally, state your personal opinion. What do you feel when you look at the art piece?
Now, let’s take a look at an essay example.
Description: Starry Night (1889) is Vincent van Gogh’s oil painting of a night landscape brimmed with whirling clouds, luminous stars, and a bright crescent moon. The artist uses a mix of warm, cold, and neutral colors. Yellows on top of blues create a clear contrast, making the stars and crescent moon stand out.
Analysis: In Starry Night , van Gogh uses his unique thick brush strokes. The technique adds depth and rich texture to the painting. The use of whites and yellows draws more attention to the sky. Vertical lines in the form of a cypress tree and a church tower break up the composition.
Interpretation: Through his painting, van Gogh contrasts life and death, brightly shining stars, and a gloomy yet peaceful village.
Evaluation: Starry Night is a painting that reflects Vincent van Goh’s inner world. It embodies his unique style and personality. The piece has a major influence on modern art.
📷 Visual Analysis Essay on a Photograph
Analyzing photos has a lot in common with paintings. There are three methods on which photo visual analysis relies: description, reflection, and formal analysis. Historical analysis can be included as well, though it is optional.
- Description. It implies looking closely at the photo and considering all the details. The description needs to be objective and consists of basic statements that don’t express an opinion.
- Reflection. For the next step, focus on the emotions that the photograph evokes. Here, every viewer will have a different opinion and feelings about the artwork. Knowing some historical context may be helpful to construct a thoughtful response.
- Formal analysis. Think of the visual elements and principles. How are they represented in the photograph?
- Historical analysis. For a contextual analysis, you need to pay attention to the external elements of the photograph. Make sure that you understand the environmental context in which the photo was taken. Under what historical circumstances was the picture made?
Photo Analysis Essay Tips
These helpful tips that will help you with analyzing a photograph.
- Choose an image that has many lines, shapes, people, or interestingly positioned objects.
- When discussing visual elements and principles, use terms such as “frame magnetism,” “line direction,” visual weight,” and “human figures.”
- Avoid telling the story of the photograph or explaining its hidden meaning.
- Don’t create lists of descriptions. Instead, use well-organized paragraphs.
- Avoid spelling mistakes.
🗿 Visual Analysis Essay: Analyzing a Sculpture
Visual analysis of a sculpture is slightly different from the one of a painting or a photograph. However, it still uses similar concepts, relies on visual elements and principles. When you write about sculpture, consider:
- Medium, size, and technique. What is the sculpture made of? Is it done in a negative or positive technique?
- Color and lightning. If the sculpture is painted, describe its color. Did the sculptor consider the lighting of the sculpture’s initial location?
- Human body and scale. If a human body is a part of an artwork, consider how it is depicted. Also, note the scale of the sculpture relative to the viewer.
- Function. What was the sculpture’s purpose? For instance, you can mention if it represented a religious belief or honored someone.
- Composition. Look at how the sculpture is organized and whether it has a focal point.
Visual Analysis Essay on a Sculpture: Writing Tips
A sculpture analysis consists of the following parts:
- Description . Include specific details, such as what the sculpture may represent. For instance, the human figure may be an athlete, an ancient God, a poet, etc. Consider their pose, body build, and attire.
- Formal analysis . Here, visual elements and principles become the focus. Discuss the color, shape, technique, and medium.
- Contextual analysis . If you decide to include a contextual analysis, you can talk about the sculpture’s function and how it conveys ideas and sentiments of that period. Mention its historical and cultural importance.
When it comes to sculpture analysis, you may also want to collect technical data such as:
- The size of the sculpture
- Medium (the material)
- The current condition (is it damaged, preserved as a fragment, or as a whole piece)
- Display (Was a sculpture a part of an architectural setting, or was it an independent piece of work?)
For instance, if you were to do a visual analysis of Laocoön and His Sons , you could first look up such details:
- Location: Discovered in a Roman vineyard in 1506
- Current location: Vatican
- Date: Hellenistic Period (323 BCE – 31 CE)
- Size: Height 208 cm; Width 163 cm; Depth 112 cm
- Material: Marble
- Current condition: Missing several parts.
🏷️ Visual Analysis Essay on an Advertisement
Visuals are used in advertisements to attract attention or convince the public that they need what is being advertised. The purpose of a visual argument is to create interest. Advertisements use images to convey information and communicate with the audience.
When writing a visual analysis of an advertisement, pay attention to the following:
- text elements,
- illustrations,
- composition.
All of this influences how the viewer perceives the information and reacts to it.
When you write about an advertisement, you conduct a rhetorical analysis of its visual elements. Visual rhetoric is mainly directed at analyzing images and extracting information from them. It helps to understand the use of typography, imagery, and the arrangement of elements on the page.
Think of the famous visual rhetoric examples such as the We can do it! poster or a Chanel №5 commercial. Both examples demonstrate how persuasive imagery has been used throughout history.
How to Write a Visual Analysis Paper on an Advertisement
The presentation of visual elements in advertising is essential. It helps to convince the audience. When you analyze visual arguments, always keep the rhetorical situation in mind. Here are some crucial elements to focus on:
- Audience. Who is the advertisement targeted at?
- Purpose. What does the image try to convey to the audience?
- Design. How is the information presented? What colors are used? Are there any highlights or repetitions?
- Strategies. Does the image use any humor, celebrities, or cultural references to make the point?
- Medium. Is there any text within the picture? If so, how does it work together with the image to create an intended effect?
- Context. Who are the characters of an advertisement? Where are they?
- Subtext. What are the implications behind the words used in the picture?
✅ How to Write a Visual Analysis Paper: Step by Step
Whether you analyze a painting, an advertisement, or a sculpture, the overall structure of your analysis paper will be the same. So, let’s look at how to organize and write your visual analysis essay.
Visual Analysis Essay: Pre-Writing Stage
Writing a formal analysis is a skill that requires practice. Being careful and attentive during the pre-writing stage is essential if you want to create a good and well-structured visual analysis.
Visual analysis essay mainly consists of two components:
- Description of the selected image or object,
- Interpretation built on the visual evidence.
During the pre-writing stage:
- Collect general information about an artwork. Describe it briefly. Pay special attention to visual elements and principles:
- Develop an interpretation. Think critically. What does the information in your notes imply? How can it be interpreted?
- Support your ideas. To do it, refer to the visual elements directly. Avoid generalizing art and double-check your prompts.
Visual Analysis Essay Outline
You can use this art analysis template to structure your essay:
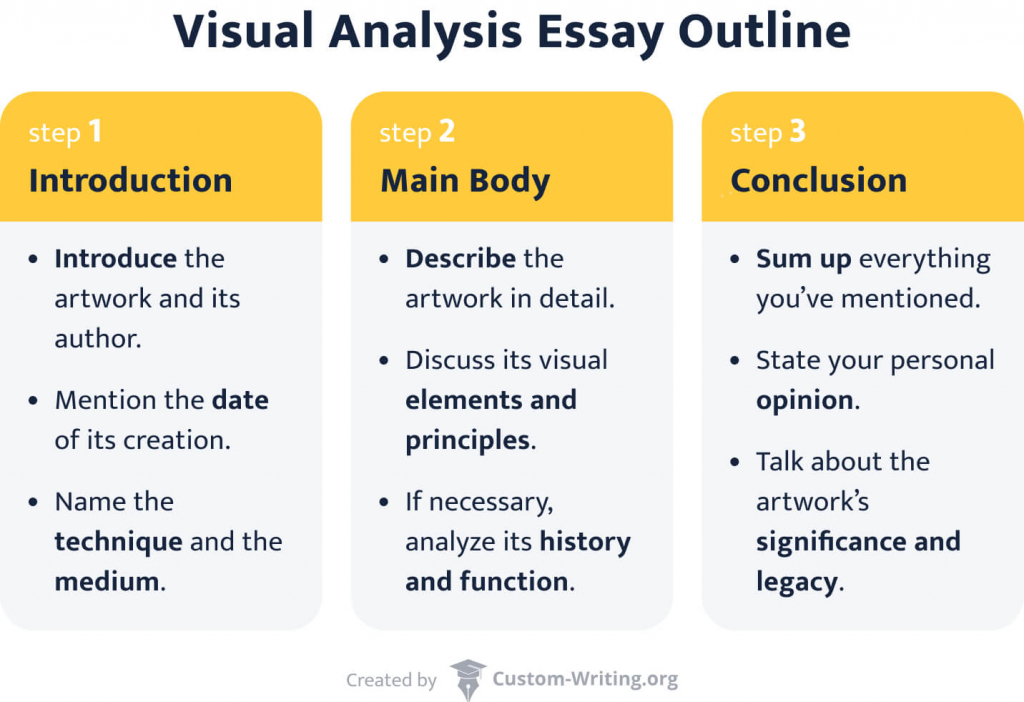
How to Start a Visual Analysis Essay
Every analysis starts with an introduction. In the first paragraph, make sure that:
- the reader knows that this essay is a visual analysis;
- you have provided all the necessary background information about an artwork.
It’s also important to know how to introduce an artwork. If you’re dealing with a panting or a photograph, it’s better to integrate them into the first page of your analysis. This way, the reader can see the piece and use it as a reference while reading your paper.
Art Thesis Statement Examples & Tips
To create a strong visual analysis thesis statement, you should relate it to an artwork’s meaning, significance, or effect. Your interpretation should put out an argument that someone could potentially disagree with.
For instance, you can consider how formal elements or principles impact the meaning of an artwork. Here are some options you can consider:
- Focus on interpreting how formal elements and principles give meaning to the artwork.
In Starry Night , the village is painted with dark colors, but the brightly lit windows create a sense of comfort.
- Comment on the overall organization of an art piece.
Van Gogh’s swirling sky directs the viewer’s eye around the painting.
- Another option is to relate the painting to the other artworks you have studied or seen before.
If we compare Munch’s The Scream to van Gogh’s Starry Night , we can see that a similar swirling technique was used to paint the sky.
If your focus is the contextual analysis, you can find the connection between the artwork and the artist’s personal life or a historical event.
How to Write Visual Analysis Body Paragraphs
Body paragraphs of formal analysis consist of two parts—the description and the analysis itself. Let’s take Klimt’s The Kiss as an example:
Description: The painting shows an embracing couple concealed behind a large golden cloak. Two distinct parts constitute the image. First, the part of the cloak covering the man has a repeating geometric black and white motif. Meanwhile, the second part of the cloak, covering the woman, has flowers and circles on it.
Analysis: The author uses predominantly warm shades such as gold and bronze brown. Spatial flatness using two-dimensional patterns was deliberately employed except at the couple’s exposed skin. Klimt was heavily influenced by the art of Japan, ancient Egypt, and Byzantine Ravenna, which preferred two-dimensional perspective styles to emphasize human subject matter.
Interpretation: Gustav Klimt’s The Kiss is the reflection of tenderness and passion. Klimt was working on The Kiss during his Golden Phase. Within the paintings of that period, Klimt treats the human figures as two-dimensional. They are also all surrounded by flat, brightly composed, and highly ornamental decorations.
Evaluation: The Kiss is a very significant piece for several reasons. It represents the apex of Klimt’s Golden Period and shows his distinctive style. The piece is also a fantastic example of the Art Nouveau movement.
Visual Analysis Essay Conclusion
When you work on the conclusion, try to conclude your paper without restating the thesis. At the end of your essay, you can present an interesting fact. You can also try to:
- Compare an artwork to similar ones;
- Contrast your own ideas on the piece with the reaction people had when it was first revealed.
- Talk about an artwork’s significance to the culture and art in general.
🤔 How to Reference a Painting in an Essay
When you work on visual analysis, it is important to know how to write the title of an artwork properly. Citing a painting, a photograph, or any other visual source, will require a little more information than citing a book or an article. Here is what you will need:
- Size dimensions
- Current location
- Name of the piece
- Artist’s name
- Date when artwork was created
If you want to cite a painting or an artwork you saw online, you will also need:
- The name of the website
- Website URL
- Page’s publication date
- Date of your access
How to Properly Credit an Artwork in APA
To reference a work you see in person, use these elements:
- Artist’s last name, artist’s first initial. (Year).
- Title of painting [Description of material].
- Museum, city, state abbreviation/country.
Picasso, P. (1905). Au Lapin Agile [Oil canvas]. Metropolitan Museum Of Art, New York City, NY.
To reference a work you see online, use the same elements and add the following:
- Name of source website (publication date or n.d. if no date is given).
- Retrieved from: URL of the website.
Picasso, P. (1905). Au Lapin Agile [Oil canvas]. Metropolitan Museum Of Art, New York City, NY. The Met (n.d.). Retrieved from: https://www.metmuseum.org
How to Properly Credit an Artwork in MLA
Here’s how to reference a work you see in person:
- Artist’s last name, artist’s first name.
- Title of artwork or description.
- Year of creation, museum, city.
Monet, Claude. Cliff Walk at Pourville . 1882, Art Institute of Chicago, Chicago
To reference a work you see online, add one more element:
- Title of the website , URL.
Monet, Claude. Cliff Walk at Pourville . 1882, Art Institute of Chicago, Chicago. Artic.edu , https://www.artic.edu
How to Properly Credit an Artwork in Chicago Format
For works you see in person, use these elements:
- Title of painting.
- Year painting was created.
- Description of materials.
- Dimensions if relevant.
- Museum, city.
Bacon, Francis. Study After Velázquez’s Portrait of Pope Innocent X . 1953. Oil on canvas. 153cm x 118cm. Des Moines Art Center, Iowa.
If you see the work online, add two more elements:
- Accessed month, day, year.
Bacon, Francis. Study After Velázquez’s Portrait of Pope Innocent X . 1953. Oil on canvas. 153cm x 118cm. Des Moines Art Center, Iowa. Accessed July 24, 2020. https://www.francis-bacon.com
📝 Visual Analysis Essay Example
Below, you will find visual analysis examples to help you with your assignment. First of all, check out an image analysis essay example of the painting called Battle of Grunwald by the Polish painter Jan Matejko.
Art Analysis Essay Example
Battle of Grunwald is an oil painting by Jan Matejko. It shows the victory of the allied Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and Grand Duchy of Lithuania over the Teutonic Order in 1410. The painting’s color scheme and brushstroke techniques help express the atmosphere of a fiery battle and set a heroic mood.
The painting’s primary strength is its robust color scheme. Warm tones like reds, oranges, and yellows dominate the foreground, suggesting an intense battle and the blood spilled. Cooler blues and greens appear in the background, likely symbolizing the peaceful landscape before the clash.
The author uses loose brushstrokes and blending techniques to depict a hazy atmosphere of the battle. Besides, Matejko utilizes impasto, a technique involving thick layers of paint, which adds texture to the painting.
Jan Matejko’s Battle of Grunwald symbolizes Polish victory and nationalism. Through his painting, the artist contrasts life and death and accentuates the sacrifice of Polish soldiers for the nation. However, critics argue that Matejko minimizes the role of Lithuanian allies, who, in fact, made a major contribution to victory.
The Battle of Grunwald effectively shows the chaos and heroism of the battle. Thanks to its blurring lines and color scheme, it has a strong impact on viewers. While some criticize its historical accuracy, the painting still represents a powerful symbol of Polish resilience.
More Visual Analysis Examples
Finally, here’s a sample visual analysis of Rodin’s sculpture The Thinker in APA format. Feel free to download it below.
Many people believe that works of art are bound to be immortal. Indeed, some remarkable masterpieces have outlived their artists by many years, gaining more and more popularity with time. Among them is The Thinker , a brilliant sculpture made by Auguste Rodin, depicting a young, athletic man, immersed deep into his thoughts.
You can also look at the following essay samples to get even more ideas.
- The Protestors Cartoon by Clay Bennett: Visual Analysis
- Visual Analysis – Editorial Cartoon
- Visual Analysis: “Dust Storm” Photo by Steve McCurry
- Visual, Aural, Read & Write, Kinesthetic Analysis
💡 Visual Analysis Essay Topics
There are a lot of artworks and advertisements that can be analyzed and viewed from different perspectives. Here are some essay topics on visual analysis that you may find helpful:
- Analyze Gustav Klimt’s The Kiss (1907-1908).
- The theme of humanity and The Son of Man (1964) by René Magritte.
- The use of visual elements in Almond Blossom by Vincent van Gogh (1888-1890).
- Identity and Seated Harlequin (1901) by Picasso .
- Explore the themes of Paul Klee ’s The Tree of Houses , 1918.
- Objectives, activities, and instructions of Pietro Perugino’s fresco The Delivery of the Keys to Saint Peter .
- Reflection on social issues of the time in Two Fridas by Frida Kahlo and Untitled by Ramses Younan.
- Analyze the importance of Mural (1943) by Jackson Pollock.
- The political message in John Gast’s painting American Progress (1872).
- Describe the visual techniques used in Toy Pieta by Scott Avett .
- The interpretation of the painting Indian Fire God by Frederic Remington.
- Explore the historical significance and aesthetic meaning of Ognissanti Madonna by Giotto di Bondone .
- Analyze different interpretations of The Three Dancers by Pablo Picasso .
Photography:
- The idea behind Lindsay Key (1985) by Robert Mapplethorpe.
- Explore the mythical appeal of Robert Capa’s photograph The Falling Soldier (Spain, 1936) from Death in Making photobook.
- Describe Two Boys with Fish (2018) from Faith series by Mario Macilau.
- Kevin Carter’s Starving Child and Vulture (1993) as the representation of photojournalism.
- The story behind Philippe Halsman’s Dali Atomicus , 1948.
- Describe The Starving Boy in Uganda photograph by Mike Wells
- Analyse the view of a historic disaster in San Francisco photograph by George R. Lawrence.
- The statement behind Eddie Adams’s photo Shooting a Viet Cong Prisoner .
- How is Steve McCurry’s perception of the world reflected in his photo Afghanistan Girl .
- Analyze the reflection of Ansel Adams’s environmental philosophy in his photo Moon and Half Dome (1960).
- Describe Girl on the Garda Lake (2016) by Giuseppe Milo.
- Combination of internal geometry and true-to-life moments in Behind the Gare Saint Lazare by Henri Cartier-Bresson .
- Modern art and Couple on Seat by Lynn Chadwick (1984.)
- Analyze the biblical context of Pieta (1498-1499) by Michelangelo.
- The use of shapes in Louise Bourgeois’ Spider (1996.)
- Analysis of the symbolism behind The Thinker (1880) by Rodin.
- The historical meaning of Fountain (1917) by Duchamp .
- Analyze the Miniature Statue of Liberty by Willard Wigan
- The combination of Egyptian culture and classical Greek ideology in statue of Osiris-Antinous.
- Reflection of the civilization values in emperor Qin’s Terracotta Army .
- The aesthetic and philosophical significance of Michelangelo’s David .
- Explore the controversial meaning of Damien Hirst’s sculpture For the Love of God (2007).
- Analyze the elements of art and design used in The Thinker by August Rodin.
- Symbolic elements in the Ancient Greek statues of Zeus .
- Depiction of the fundamental aspects of Buddhism in The Parinirvana of Siddhartha/Shakyamuni.
Advertisement:
- How Volkswagen : Think Small (1960) ad changed advertising.
- Analyze the use of figures in California Milk Processor Board: Got Milk? (1993) ad campaign .
- Analyze the use of colors in Coca-Cola — The Pause that Refreshes (1931.)
- Explore the historical context of We Can Do It! (1942) campaign.
- The importance of a slogan in 1947: A Diamond Is Forever by De Beers.
- Examine the specifics of visual advert: dogs and their humans.
- Describe the use of visual techniques in Kentucky Fried Chicken company’s advertisement.
- Analyze the multiple messages behind the print ad of JBL .
- Discuss the methods used in Toyota Highlander advertisement .
- Elucidation of people’s dependency on social networks in the advertising campaign Followers by Miller Lite.
- The use of the visual arguments in Schlitz Brewing Company advertisement .
- The role of colors and fonts in Viva la Juicy perfume advertisement .
Thanks for reading through our article! We hope you found it helpful. Don’t hesitate to share it with your friends.
Further reading:
- How to Write a Lab Report: Format, Tips, & Example
- Literature Review Outline: Examples, Approaches, & Templates
- How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step [2024 Upd.]
- How to Write a Term Paper: The Ultimate Guide and Tips
🔍 References
- Art History: University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Visual Analysis: Duke University
- Writing a Formal Analysis in Art History: Hamilton College
- Contextual Analysis: Pine-Richland School District
- How to Analyze an Artwork: Student Art Guide
- Introduction to Art Historical Analysis: Khan Academy
- Guidelines for Analysis of Art: University of Arkansas at Little Rock
- Elements of Art: Getty.edu
- Formal or Critical Analysis: LibreTexts
- Analyzing a Photograph: University of Oregon
- Picture Composition Analysis and Photo Essay: University of Northern Iowa
- Visual Analysis Guidelines: Skidmore College
- How to Analyze Sculpture: NLA Design and Visual Arts: WordPress
- Visual Rhetoric: Purdue University
- Formal Visual Analysis: The Elements & Principles of Composition
- Share to Facebook
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...
![writing an essay about a painting Critical Writing: Examples & Brilliant Tips [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/fingers-note-report-journalist-filling-284x153.jpg)
Any critique is nothing more than critical analysis, and the word “analysis” does not have a negative meaning. Critical writing relies on objective evaluations of or a response to an author’s creation. As such, they can be either positive or negative, as the work deserves. To write a critique, you...

If you are assigned to write a rhetorical analysis essay, you have one significant advantage. You can choose a text from an almost infinite number of resources. The most important thing is that you analyze the statement addressed to an audience. The task of a rhetorical analysis essay is to...

Any literary analysis is a challenging task since literature includes many elements that can be interpreted differently. However, a stylistic analysis of all the figurative language the poets use may seem even harder. You may never realize what the author actually meant and how to comment on it! While analyzing...

As a student, you may be asked to write a book review. Unlike an argumentative essay, a book review is an opportunity to convey the central theme of a story while offering a new perspective on the author’s ideas. Knowing how to create a well-organized and coherent review, however, is...

The difference between an argumentative and persuasive essay isn’t always clear. If you’re struggling with either style for your next assignment, don’t worry. The following will clarify everything you need to know so you can write with confidence. First, we define the primary objectives of argumentative vs. persuasive writing. We...

You don’t need to be a nerd to understand the general idea behind cause and effect essays. Let’s see! If you skip a meal, you get hungry. And if you write an essay about it, your goal is achieved! However, following multiple rules of academic writing can be a tough...
![writing an essay about a painting How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 101 Guide [+ Examples]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/young-writer-taking-notes-284x153.jpg)
An argumentative essay is a genre of academic writing that investigates different sides of a particular issue. Its central purpose is to inform the readers rather than expressively persuade them. Thus, it is crucial to differentiate between argumentative and persuasive essays. While composing an argumentative essay, the students have to...
![writing an essay about a painting How to Title an Essay: Guide with Creative Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/close-up-woman-making-greeting-card-new-year-christmas-2021-friends-family-scrap-booking-diy-writing-letter-with-best-wishes-design-her-homemade-card-holidays-celebration-284x153.jpg)
It’s not a secret that the reader notices an essay title first. No catchy hook or colorful examples attract more attention from a quick glance. Composing a creative title for your essay is essential if you strive to succeed, as it: Thus, how you name your paper is of the...

The conclusion is the last paragraph in your paper that draws the ideas and reasoning together. However, its purpose does not end there. A definite essay conclusion accomplishes several goals: Therefore, a conclusion usually consists of: Our experts prepared this guide, where you will find great tips on how to...
![writing an essay about a painting How to Write a Good Introduction: Examples & Tips [2024 Upd.]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/closeup-shot-woman-working-studying-from-home-with-red-coffee-cup-nearby-284x153.jpg)
A five-paragraph essay is one of the most common academic assignments a student may face. It has a well-defined structure: an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Writing an introduction can be the most challenging part of the entire piece. It aims to introduce the main ideas and present...
do you review and edit visual arts extended essay

IMAGES
VIDEO