Fall 2010 Presentations
- THE FOUNDATION
- OUR FOUNDER
- PGPF Facebook
- PGPF Twitter
- PGPF YouTube
- PGPF Linkedin

The Fiscal Challenge
Fiscal & economic impact, finding solutions, comprehensive plans, understanding the budget.
- Budget Process
National Security
Budget process reforms, what we're doing, research and analysis.
- Chart Archive
Education & Awareness
- Fiscal Confidence Index
- Current Debt and Deficit
- The Fiscal Summit
- Economic Forum
What You Can Do
I want to lead, i want to learn, register for the newsletter, resource library, budget, deficits, and debt, demographics, defense and national security, other programs, retirement security, taxes and revenues, infographics, you are here, the u.s. corporate tax system explained.
The U.S. corporate tax system is a subject of frequent debate, with significant implications for the nation’s economy and fiscal outlook. Over the past several years, lawmakers from both parties have pursued major changes to this area of the tax code, including the enactment of the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), which dramatically reduced the corporate tax rate.
Presently, revenues raised by the corporate income tax represent the third-largest category of federal tax revenue in the United States, trailing those generated from the individual income and payroll taxes. This explainer describes how the U.S. corporate income tax system works, the ways it has evolved in recent years, and the implications for the United States’ fiscal and economic condition.
How Does the U.S. Corporate Income Tax Work?
Like most other countries, the United States levies a tax on the net profits — that is, the total income minus the costs associated with generating that income — of corporations. The TCJA, enacted in December 2017, reduced the federal tax rate on corporations to 21 percent, a decrease of 14 percentage points from its previous level of 35 percent. The current rate of 21 percent is low by historical standards — in the 1950s and 1960s, the statutory rate averaged over 50 percent.
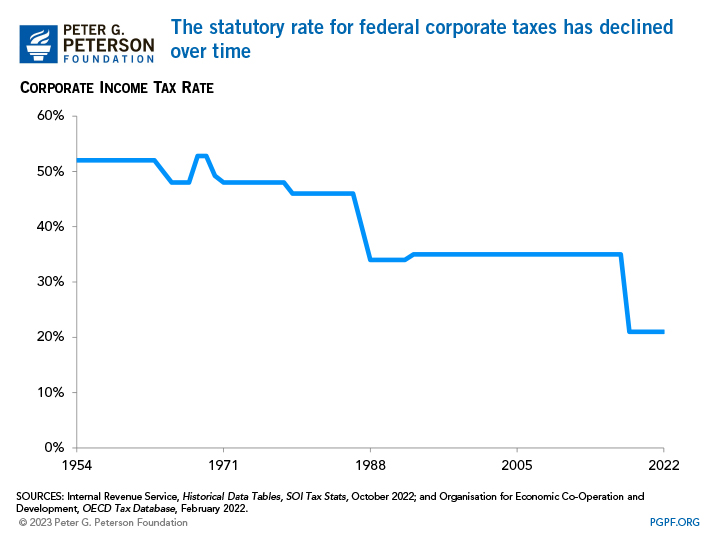
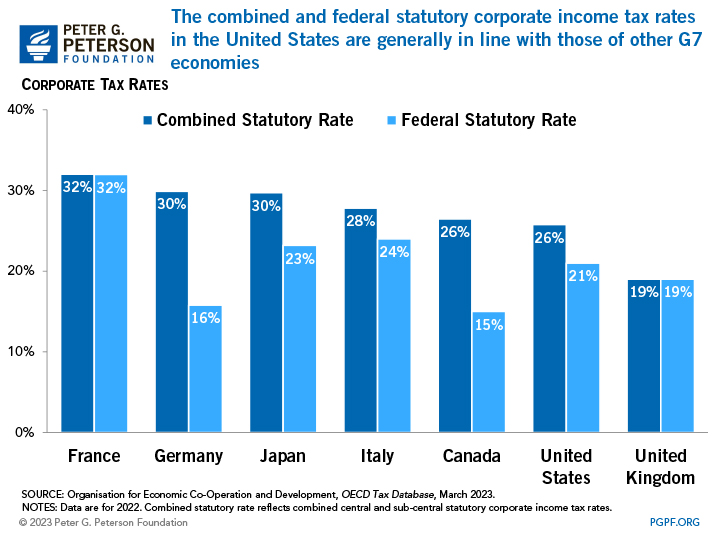
The current federal corporate tax rate is applied to all business income of C corporations, an Internal Revenue Service (IRS) designation that distinguishes a business as a taxable entity. Additionally, 44 states and the District of Columbia impose their own taxes on corporate income. Therefore, a C corporation operating in the United States could face a combined tax rate in excess of 21 percent. In 2022, corporations paid an average combined tax rate of 26 percent. For context, the average combined national and sub-national corporate income tax rate among G7 countries was 26 percent.
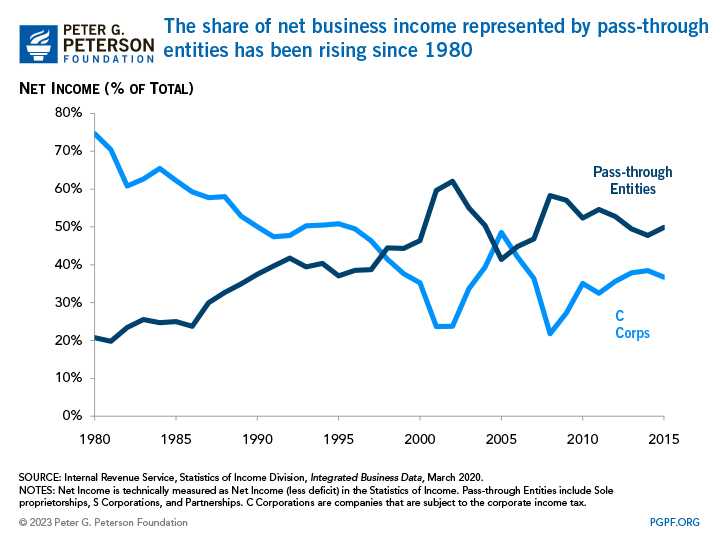
Importantly, not all businesses are taxed as corporations. Pass-through businesses, such as sole proprietorships, partnerships, S corporations, and limited liability companies allocate profits to their owners who then pay taxes on those profits through the individual income tax code. In recent years, pass-through entities have grown to represent an increasingly large percentage of all businesses, and therefore business income, in the United States. In 1980, for example, C corporations represented 17 percent of all businesses, but by 2015 (the year for which the most recent data are available) had come to represent just 5 percent. S corporations (companies with a small number of shareholders and who elect to pass corporate income, losses, deductions, and credits through to their shareholders for federal tax purposes) experienced the largest increase over this period, growing from just 4 percent of all businesses in 1980 to 13 percent in 2015.
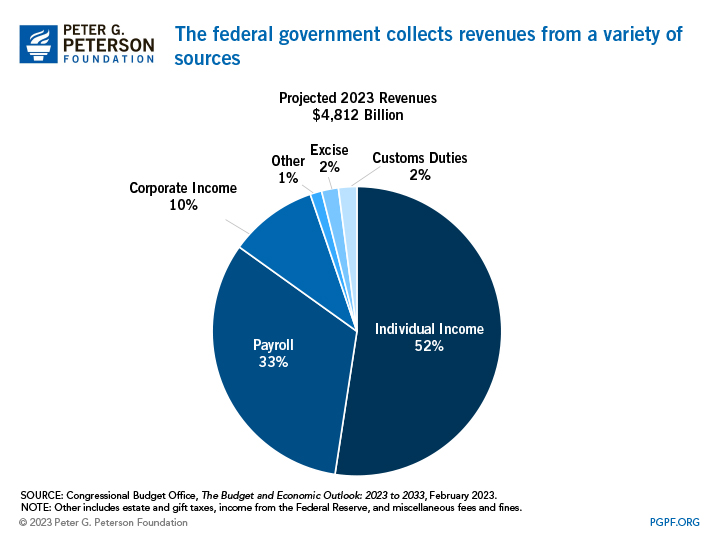
How Much Revenue from the Corporate Income Tax Does the Federal Government Collect?
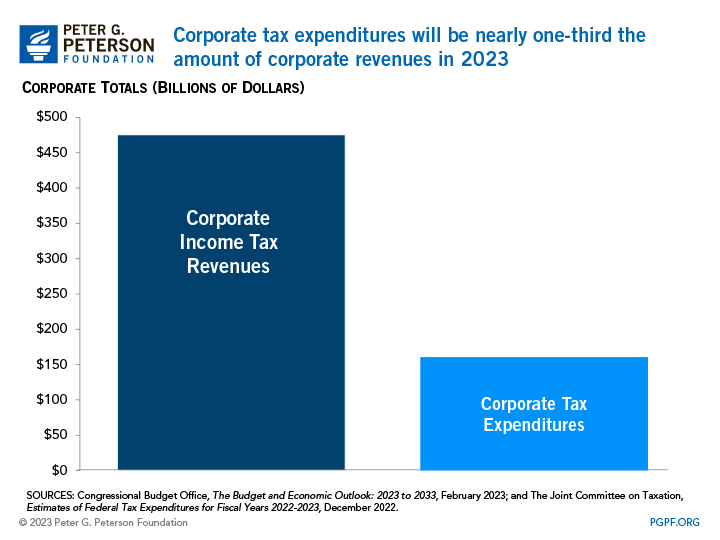
Corporate income taxes are the third-largest source of revenues for the federal government. However, as a share of total federal tax collections, the corporate income tax accounts for a relatively small amount. In 2023, the federal government is projected to collect $475 billion from the corporate income tax, just 10 percent of the total $4.8 trillion in federal tax revenues that year.
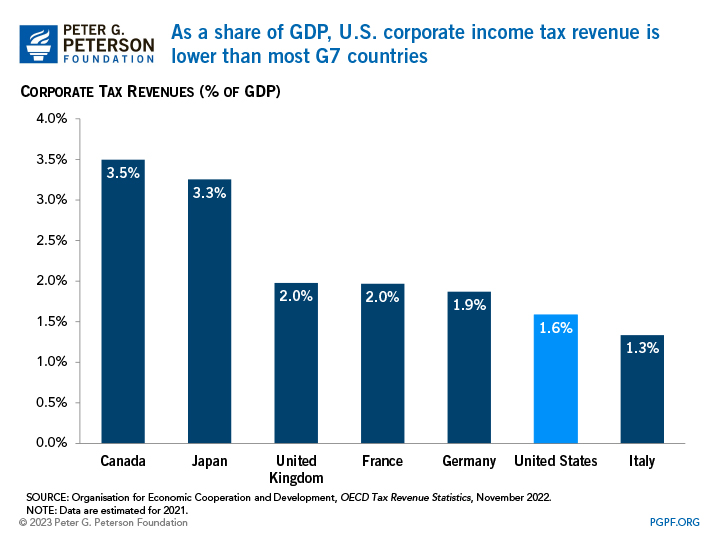
As the statutory rate has decreased and the prevalence of pass-through businesses has increased, revenues from corporate taxes have declined as a share of GDP. In the 1950s and 1960s, corporate tax revenues represented an average of 4.2 percent of GDP — in 2022, they represented just 1.7 percent.

The share of corporate income tax revenues as a percentage of the economy in the United States is one of the lowest among G7 countries who, on average, collect 2.3 percent of GDP from that source.
One reason that corporate income tax revenues represent such a small percentage relative to the size of the U.S. economy is the offsetting effect of tax expenditures . Tax expenditures include exclusions, exemptions, deductions, and credits that reduce total tax liability. In 2022, the reduced tax rate on the income of controlled foreign corporations, the credit for depreciation of business equipment, and the credit for increasing research and development activities collectively reduced total federal corporate income tax revenues by over $100 billion. In 2023, the United States will forgo $161 billion in revenues due to corporate tax expenditures.
The federal government collects low levels of revenues from the corporate income tax system and forgoes billions of dollars in collections to tax expenditures. As annual deficits continue to widen and the national debt reaches historically unprecedented levels , many economists and experts suggest various tax reforms , including some to the corporate tax code that can help make our nation’s fiscal outlook more sustainable.
Solutions Initiative 2024
National debt clock.
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
PPT Bundles
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

Corporate Tax Planning Powerpoint PPT Template Bundles
Introducing our comprehensive Corporate Tax Planning PowerPoint PPT presentation, designed to empower businesses with strategic financial insights. Navigate the complex landscape of corporate tax with ease using this visually engaging resource. Explore effective Tax Strategies to maximize savings and minimize liabilities, unlocking the potential for sustainable growth. Dive into the realm of Tax Optimization, discovering key methods to enhance fiscal efficiency. Uncover valuable insights into Tax Deductions and Incentives, ensuring your organization capitalizes on available opportunities. This PPT is a dynamic tool for executives, finance professionals, and decision makers, providing a strategic roadmap to navigate corporate tax complexities. Elevate your financial planning and secure long term success with our Corporate Tax Planning PPT.

- Add a user to your subscription for free
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
If you require a professional template with great design, then this Corporate Tax Planning Powerpoint PPT Template Bundles is an ideal fit for you. Deploy it to enthrall your audience and increase your presentation threshold with the right graphics, images, and structure. Portray your ideas and vision using twelve slides included in this complete deck. This template is suitable for expert discussion meetings presenting your views on the topic. With a variety of slides having the same thematic representation, this template can be regarded as a complete package. It employs some of the best design practices, so everything is well-structured. Not only this, it responds to all your needs and requirements by quickly adapting itself to the changes you make. This PPT slideshow is available for immediate download in PNG, JPG, and PDF formats, further enhancing its usability. Grab it by clicking the download button.

People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
- Complete Decks , All Decks , Finance and Accounting , General , Mini Decks , General , Finance And Accounting
- Corporate Tax ,
- Tax Strategies ,
- Tax Optimization ,
- Tax Deductions ,
- Tax Incentives
Corporate Tax Planning Powerpoint PPT Template Bundles with all 20 slides:
Use our Corporate Tax Planning Powerpoint PPT Template Bundles to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.

Ratings and Reviews
by Dallas Medina
January 9, 2024
by Jack Johnson
January 7, 2024


- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Taxation Corporate Tax
Published by Norah Knight Modified over 6 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Taxation Corporate Tax"— Presentation transcript:

T2.1 Chapter Outline Chapter 2 Financial Statements, Taxes, and Cash Flow Chapter Organization 2.1The Balance Sheet 2.2The Income Statement 2.3Cash Flow.

Slide 7-1 Assignments For next class: Problems: C4-33, C4-34, C4-35, C4-37, C4-38, C4-40, C4-41, C4-42.

Financial Statements, Cash Flow, and Taxes

2-1 CHAPTER 2 Financial Statements, Cash Flow, and Taxes Balance sheet Income statement Statement of cash flows Accounting income vs. cash flow MVA and.

Ch. 2 - Understanding Financial Statements, Taxes, and Cash Flows , Prentice Hall, Inc.

Analysis of Income Taxes and Employee Stock Options Chapter 14 Robinson, Munter and Grant.

Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Foundations of Financial Management—The Ties That Bind.

Chapter 11 Summary. Major Categories Operating Income Before Other Gains/Losses and Tax Expense Income from Continuing Operations +/- Gains or Losses.

GBUS502 Vicentiu Covrig 1 Financial statements and cash flow (chapter 3)

Financial statements Financial statements are general summaries of economic activity because user groups have diverse interests. 1.

Accounting for Financial Management

Chapter Objectives Be able to: n Explain the nature of the different types of property income. n Differentiate between the different methods of computing.

Ch. 1 - Introduction to Financial Management 2000, Prentice Hall, Inc.

Real Estate Investment Chapter 6 Property Taxes and Income Taxes © 2011 Cengage Learning.

Overview of Finance. Financial Management n The maintenance and creation of economic value or wealth.

© 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 2-1 Chapter Two Financial Statements, Cash Flows, Taxes, and the Language of Finance Principles of Corporate Finance.

Financial Statements, Cash Flow, and Taxes Key Financial Statements Balance Sheet Income Statement Statement of Stockholders’ Equity Statement.

© 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied, or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
- Tax Research The gold standard of insightful and timely tax intelligence
- Fixed Assets Automatically and accurately calculate depreciation
- Tax Provision The most powerful ASC 740 engine on the market
- Workpapers Automated data prep and spreadsheets tailored for tax
- Income Tax Planner Powerful income tax planning and projection tool
- Corporate Tax Analyzer Automate complex corporate income tax scenarios
- Innovating With AI See our newest AI solutions, inspired by you
- Large Corporations Work smarter with tax solutions that help you strategize
- Mid-Market Corporations Add more value without adding to your workload
- Advisory Firms Access all the tools you need to support your clients
- Government Get all you need to maximize efficiency and reduce risk
- International The tools you need to accurately and confidently handle cross-border transactions
- Getting Started Modernize your tax workflow with integrated tools
- About Our Authors See the winners of our coveted tax awards
- Press Releases Read our latest news and product updates
- Our Approach to AI Discover our formula for powerful AI tools you can trust
- Request Pricing
Corporate Tax Planning Strategies
Plan a tax strategy that reduces risk with a complete picture of what’s on the horizon.
Corporate tax professionals often face significant changes in corporate taxation across federal, state, and international jurisdictions – and this year is no exception. Bloomberg Tax helps you plan ahead with expert analysis.
Request Demo
Corporate tax planning topics
Federal Tax Planning Strategies State Tax Planning for Corporations International Tax Planning for U.S. Corporations OECD Inclusive Framework
Prepare for tax filing season with confidence
Bloomberg Tax provides comprehensive global research, news, and technology services to give corporate tax professionals the timely, accurate, and in-depth information they need to plan and comply with confidence.
Save time with practice tools
Increase efficiency with exclusive timesaving practice tools, including chart builders, interactive forms, client letters, transactional diagrams, elections and compliance statements, and tax prep guides. Real-world examples are fully integrated with expert analysis to get you to the right answers quickly.
Reduce risk with primary sources
Go straight to every primary source you need to stay compliant. With Internal Revenue Code dating back to 1913, regulations and procedures, state laws, and international tax treaties, our collection of primary sources is fully integrated across our tools so you can work with certainty.
Plan with confidence using Tax Management Portfolios
Understand the principles and nuances of more than 500 complex tax issues. Written by a network of more than 1,000 leading outside practitioners with deep expertise, this essential resource provides a depth of real-world experience not found in any other tax research solution available today.
Stay informed with expert news and analysis
Access concise coverage of tax news and breaking developments with special reports, roadmaps, our Daily Tax Report, and other expertly prepared content. Our network of seasoned tax and accounting reporters and specialists shares the latest news, trends, and issues to keep you up to date with the news that impacts your company and clients as it happens.
Having the right tax strategy can help corporate tax professionals stay ahead of tax law changes that may affect their business entity’s tax liability. Changes to tax provisions and new legislation present new tax challenges but can also offer opportunities to help reduce a business’s tax burden.
This planning guide highlights several potential tax-saving opportunities and key considerations to help you leverage all available credits and deductions, ensure a smooth filing process, and avoid errors that could trigger an audit.
How does deferring income help?
Although C corporations enjoy a flat 21% statutory tax rate and pass-through entities are taxed at lower rates following the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), income deferral remains an important consideration in business tax planning. If a taxpayer expects taxable income to be higher in one year than the next, or if the taxpayer anticipates being taxed at a lower rate the next year, the taxpayer may benefit by deferring income into that next tax year. Of course, if a business owner is subject to the individual alternative minimum tax (AMT), an S corporation is subject to the passive investment income tax, or a C corporation may be subject to the corporate alternative minimum tax (AMT), this type of standard tax planning may not be warranted. Some ways to defer income are discussed below.
Use of cash method of accounting
By adopting the cash method of accounting instead of the accrual method, a taxpayer generally can put itself in a better position for accelerating deductions and deferring income. An automatic change to the cash method can be made by the due date of the return including extensions.
A business entity generally must obtain IRS consent to change either an overall method of accounting or the accounting treatment of any material item. To do so, the business generally must file Form 3115 , Application for Change in Accounting Method .
Certain C corporations and partnerships with a C corporation partner with average annual gross receipts of $27 million or less for the prior three tax years can make an automatic change to the cash method.
Provided inventories are not a material income-producing factor, sole proprietors, limited liability companies (LLCs), partnerships, and S corporations can change to the cash method of accounting without regard to their average annual gross receipts.
Installment sales
Generally, a sale occurs on the transfer of property. If gain will be realized on the sale, income recognition will normally be deferred under the installment method until payments are received, so long as one payment is received in the year after the sale. Therefore, if a business is expecting to sell property prior to the end of a tax year, and it makes economic sense, the taxpayer should consider selling the property and reporting the gain under the installment method to defer payments (and tax) until the next tax year or later.
Delay billing
If a taxpayer uses the cash method of accounting, the taxpayer may consider delaying year-end billing to clients so that payments are not received until the next tax year.
Defer interest and dividends
Interest income earned on Treasury securities and bank certificates of deposit with maturities of one year or less is not includible in income until received. To defer interest income, the taxpayer could consider buying short-term bonds or certificates that will not mature until the next tax year.
A taxpayer will be taxed only on dividends for which there is constructive receipt before year-end. Owners of closely held corporations may consider delaying dividends unless other provisions prevent such delay.
Should an owner of a closely held family business consider gifting interests?
Owners of closely held businesses may want to consider gifting an interest in the business (corporate stock or interests in family limited partnerships or LLCs). A taxpayer may take advantage of valuation discounts (marketability and minority discounts) and the gift tax exclusion of $17,000 per donee ($34,000 when gift-splitting) when gifting family business interests before year-end.
Should a corporate taxpayer accelerate income into the current year?
A business taxpayer may benefit from accelerating income into the current year. For example, the taxpayer may anticipate being taxed at a higher rate the next tax year, being subject to the corporate alternative minimum tax (AMT) in 2023, or perhaps the taxpayer needs additional income this year to take advantage of an offsetting deduction or credit that will not be available in a future tax year. Note, however, that accelerating income into the current tax year could be disadvantageous if the taxpayer expects to be in the same or lower tax bracket the next year.
Early collection
A business that reports business income and expenses on a cash basis could issue bills and pursue collection before the end of the current year. Also, the taxpayer could check to see if clients or customers are willing to pay for next year’s goods or services in advance. Any income received using these steps will shift income from the next tax year to the current one.
Qualified dividends
Qualified dividends are subject to rates similar to capital gains rates. Qualified dividend income is generally subject to a 15% or 20% rate, dependent upon statutory thresholds. The thresholds are not tied to specific income tax brackets, but roughly speaking, the 20% rate applies to those in the 37% rate bracket and most of those in the 35% bracket, while the 15% rate applies to those at or above the 22% bracket. Note that qualified dividends may be subject to an additional 3.8% net investment income tax. Qualified dividends are typically dividends from domestic and certain foreign corporations. The corporate board may consider the tax impact of declaring a dividend on its shareholders. If a controlling shareholder is not in the highest capital gains bracket for the current tax year, but expects to be in a higher bracket the next year, the controlling shareholder should consider authorizing any dividend payment prior to the end of the current tax year to utilize the more favorable 15% tax rate.
Are there business deductions that can be accelerated into the current year?
If a business uses the accrual method, business accounts receivable should be analyzed and those receivables that are totally or partially worthless should be written off. By identifying specific bad debts, the taxpayer should be entitled to a deduction. The taxpayer may be able to complete this process after year’s end if the write-off is reflected in year-end financial statements. For nonbusiness bad debts (such as uncollectible loans), the debts must be wholly worthless to be deductible, and will probably only be deductible as a capital loss.
Current-year bonuses
In general, a taxpayer’s liability for employee bonuses accrues and is deductible for the current year even though the bonus is paid in the following year, if all the events are satisfied that fix the liability and the taxpayer does not have a unilateral right to cancel the bonus at any time prior to payment.
Generally, the taxpayer may accelerate the bonus deduction into the current year while the employees will report the income in the following year if they are cash method taxpayers. Furthermore, any compensation arrangement that defers payment will be currently deductible only if paid within 2.5 months after the employer’s year-end.
Suspended passive losses
Generally, a taxpayer may have passive losses that have been suspended and not yet allowed as a deduction. Determine what might be done to identify and absorb or release the suspended losses as part of the taxpayer’s overall tax planning.
Prepayment of taxes
For taxpayers that pay payroll taxes on a quarterly basis, consider accelerating 4th quarter payroll taxes at Dec. 31 year-end and don’t wait until January.
Consider accelerating state income estimated taxes and property taxes if possible if the taxpayer would benefit from a current year state income tax deduction. AMT should be considered for pass-through entities taxed at individual rates if accelerating state income and property taxes.

What tax credits are available to corporate taxpayers?
Generally, tax credits reduce a taxpayer’s liability on a dollar-for-dollar basis. There are many tax credits available to corporate taxpayers. Specifically, consider the taxpayer’s eligibility for the following credits.
Research and development (R&D) tax credit
Some business projects, such as those involving development of new or more reliable products, processes, or techniques, may be eligible for the R&D tax credit. Eligible small businesses ($50 million or less in gross receipts) may claim the R&D tax credit against alternative minimum tax liability of individuals, and the credit can be used by certain qualified small businesses against the employer’s payroll tax (i.e., FICA) liability.
Employer wage credit for employees in the uniformed services
Some employers continue to pay all or a portion of the wages of employees who are called to active service. The amount of the credit is equal to 20% of the first $20,000 of differential wage payments to each employee for the taxable year. Employers of any size with a written plan for providing such differential wage payments are eligible for the credit.
Work opportunity credit
The work opportunity credit is an incentive provided to employers that hire individuals in groups whose members historically have had difficulty obtaining employment. The credit gives a business an expanded opportunity to employ new workers and to be eligible for a tax credit based on the wages paid. The credit is available for first-year wages paid or incurred in the tax year for employees hired and who began work before Dec. 31 of that tax year. Employers that hire members of targeted groups, including qualified long-term unemployed individuals (i.e., those who have been unemployed for 27 weeks or more), will be entitled to a credit equal to 40% of the first $6,000 of wages. Employers that hire qualified veterans will be entitled to a credit equal to 40% of a higher wage limit, with the wage limit dependent on the reason for qualification.
Small employer pension plan startup cost credit
Certain small business employers that didn’t have a pension plan for the preceding three years may claim a nonrefundable income tax credit for expenses of establishing and administering a new retirement plan for employees. The credit applies to 50% of qualified administrative and retirement-education expenses for each of the first three plan years. The credit is limited to the greater of (a) $500; or (b) the lesser of (i) $250 for each eligible employee, or (ii) $5,000. Thus, the maximum available credit is limited to $5,000 per year.
Small employer retirement savings auto-enrollment credit
Starting in 2020, certain small business employers that include an eligible automatic contribution arrangement in a qualified employer plan may claim a nonrefundable income tax credit of $500 for each of the first three plan years.
Employer-provided child care credit
Employers may claim a credit of up to $150,000 for supporting employee child care or child care resource and referral services. The credit is allowed for a percentage of “qualified child care expenditures,” including for property to be used as part of a qualified child care facility, for operating costs of a qualified child care facility, and for resource and referral expenditures.
Low-income housing credit
The low-income housing credit is a tax credit which may be claimed over a 10-year period by owners of residential rental property used for low-income housing. The amount of credit available depends on whether expenditures were federally subsidized. Among other requirements, low-income housing units may not be used on a “transient” basis. The IRS and Treasury have provided limited exceptions to the transiency rule, including one for disaster relief.
After a major disaster, a state housing credit agency may permit owners within its jurisdiction to provide temporary emergency housing (not to exceed 12 months) to displaced individuals who were living within the agency’s jurisdiction at the time of the disaster. Before housing any displaced individuals, the owner must obtain written approval from the agency to participate in “temporary emergency housing” relief. An individual is a displaced individual if the individual was displaced from their principal place of residence as a result of a major disaster and the principal place of residence is in a city, county, or other local jurisdiction designated for “individual assistance” by FEMA. The temporary housing of displaced individuals in low-income units without meeting the documentation requirements will not cause the building to suffer a reduction in qualified basis that would cause the recapture of low-income housing credits.
Employer credit for Family and Medical Leave Act wages
An eligible employer may take a paid family and medical leave credit of between 12.5% and 25% of the wages paid to the employee, depending on what portion of the employee’s normal wages is paid during the leave (minimum 50% of wages).
New Markets Tax Credit
Taxpayers may claim a New Markets Tax Credit equal to 39% of any capital invested in a qualified community development entity. The credit is claimed in seven annual installments beginning in the year of the original investment.
Energy investment credit
The energy investment credit is available for investments in certain alternative and renewable energy property and renewable electricity production facilities. The credit is either 10% or 30% of the basis of energy property placed in service during the tax year.
Rehabilitation tax credit
Qualified expenses incurred in the rehabilitation of certified historic structures are eligible for a credit of 20% of such expenses. The credit is claimed in five equal annual installments beginning with the year in which the rehabilitated property is placed in service.
What income exclusions are available?
Stock acquisitions that qualify as “small business stock” under §1202 are subject to special exclusion rules upon their sale as long as a five-year holding period is satisfied. S corporation stock does not qualify for the exclusion. A 100% gain exclusion applies for qualified small business stock acquired after Sept. 27, 2010, and held for more than five years. A 75% exclusion applies for qualified small business stock acquired after Feb. 17, 2009, and before Sept. 28, 2010 (and held for at least five years). A 50% exclusion applies for qualified small business stock acquired before Feb. 18, 2009 (and held for at least five years).
What business deductions are available?
Qualified business income.
Individual taxpayers with qualified business income (QBI) from a pass-through entity (partnership or S corporation) or a sole proprietorship may be entitled to a deduction equal to the lesser of the deductible amount of the QBI or 20% of taxable income. The deduction applies to reduce taxable income and is available whether or not the taxpayer itemizes. The deduction does not impact the calculation of self-employment tax.
The trade or business of being an employee is not a qualified trade or business and, therefore, no deduction is allowed for income from the trade or business of being an employee.
The deductible amount of QBI is generally 20%. However, if the taxpayer’s taxable income (not factoring in the deduction) exceeds $340,100 (for married taxpayers filing jointly) or $170,050 (for all other taxpayers), the deduction is subject to a limitation based on W-2 wages paid by the business.
Limitation on business interest expense
The deduction for net interest expenses incurred by a corporation is limited to the sum of business interest income, 30% of the business’s adjusted taxable income (ATI), and floor plan financing interest, though taxpayers with average annual gross receipts of $27 million or less are exempt from the limit. Further, the limitation does not apply to the trade or business of being an employee, electing real property trades or businesses, electing farming businesses, or certain regulated utilities.
Excess business loss
Taxpayers other than C corporations are not allowed to deduct excess business loss. An excess business loss for the tax year is the amount by which aggregate deductions of the taxpayer attributable to trades or businesses of the taxpayer, less the sum of aggregate gross income, exceeds $540,000 (for married taxpayers filing jointly) or $270,000 (for all other taxpayers). Any excess business loss is carried forward and treated as part of the taxpayer’s net operating loss carryforward in succeeding taxable years. Pass-through entities are limited in deducting active business losses against nonbusiness income.
Equipment purchases
Corporations purchasing equipment may make a “§179 election,” which allows them to expense (i.e., currently deduct) otherwise depreciable business property, including computer software and qualified real property. Air conditioning and heating units placed in service since 2016 are eligible and continue to be eligible for this deduction. Certain improvements to nonresidential real property (roofs, heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning property, fire protection and alarm systems, and security systems), that may not be eligible for bonus depreciation, are eligible under §179 . Taxpayers may elect to expense up to $1,080,000 of equipment costs (with a phase-out for purchases exceeding $2,700,000). The deduction is subject to a business income limit.
In addition, careful timing of equipment purchases can result in favorable depreciation deductions. In general, under the “half-year convention,” taxpayers may deduct six months’ worth of depreciation for equipment that is placed in service on or before the last day of the tax year. If more than 40% of the cost of all personal property placed in service occurs during the last quarter of the year, however, a “mid-quarter convention” applies, which lowers the depreciation deduction.
Bonus depreciation
For property acquired after Sept. 27, 2017, and placed in service during the current tax year, a taxpayer may deduct 100% of the cost of qualified property. Bonus depreciation applies to new as well as used property, so taxpayers planning to acquire a business should consider whether structuring the acquisition as an asset acquisition rather than a stock acquisition would be advantageous.
Vehicles weighing more than 6,000 pounds
A popular strategy is to purchase a vehicle for business purposes that exceeds the depreciation limits set by statute (i.e., a vehicle rated more than 6,000 pounds). Doing so wouldn’t subject the purchase to the dollar limit for depreciation of passenger vehicles of $11,200 in 2022 (if bonus depreciation is taken, the amounts increase to $19,200). For SUVs (rated between 6,000 and 14,000 pounds gross vehicle weight) the expensing amount is limited to $27,000.
NOL carryforward and carryback
If a corporation expects to suffer a net operating loss (NOL) for the tax year, it may generally carry the loss forward indefinitely. A farming loss may be carried back two years or forward indefinitely. Non-life insurance companies with a net operating loss may carry the loss back two years but may only carry the loss forward 20 years. Corporations may elect to waive the carryback period and instead choose to only carry forward losses. If the taxpayer has any net operating loss carryforwards from prior tax years, deductions for losses arising before 2018 are deductible up to 100% of taxable income, while deductions for losses arising after 2017 are limited to 80% of taxable income.
A corporation that expects a tax loss for the current year and that has paid estimated taxes should consider seeking a quick refund of overpayments. A corporation may file Form 4466 , Corporation Application for Quick Refund of Overpayment of Estimated Tax , to recover any overpayment of estimated tax for the tax year over the final income tax liability expected for the tax year. Be aware that if a corporation has a loss one year and income the next, it will have to make estimated tax payments for that next year.
Inventories of subnormal goods
A business should check for subnormal goods in inventory. Subnormal goods are goods that are unsalable at normal prices or unusable in the normal way due to damage, imperfections, shop wear, changes of style, odd or broken lots, or other similar causes, including second-hand goods taken in exchange. If a business has subnormal inventory as of the end of the tax year, the taxpayer can take a deduction for any write-downs associated with that inventory provided they offer it for sale within 30 days of the inventory date. The inventory does not have to be sold within the 30-day timeframe.
Business travel, meals, and entertainment expenses
Although significantly limited, business deductions for meal and entertainment expenses are still available in certain circumstances.
Charitable contributions
A charitable contribution deduction is available to businesses. A corporation is generally allowed to deduct charitable contributions up to 10% of its taxable income for cash contributions. Under the CARES Act, the corporate limitation was temporarily increased to 25% of taxable income for cash contributions made in calendar year 2021. Contributions from pass-through entities are allocated to individual equity interest holders and are subject to the individual’s limitations. An individual is generally allowed to deduct charitable contributions up to 60% of adjusted gross income. Certain contributions of property are subject to additional limits as well as additional recordkeeping and substantiation requirements.
Should a corporation make an S corporation election?
For an otherwise eligible C corporation, consider whether an S corporation election would make sense. A detailed tax analysis needs to be prepared, which should include a comparative discounted after-tax, cash-flow analysis of C status versus S status. The analysis would focus on the marginal and effective tax rates on corporate income under various scenarios as a C corporation and S corporation.
Passive income and S corporations
S corporations that were formerly C corporations, and that have subchapter C earnings and profits at year-end, need to monitor the amount of their passive income, or subject themselves to the passive income tax for termination of their S corporation status. S corporations can avoid both consequences by electing to distribute the subchapter C earnings and profits first, or by making a consent dividend election. Either the distribution or consent dividend can purge the S corporation of all its earnings and profits at year-end. For the closely held C corporation, an S corporation election needs to be considered from time to time.
In considering a conversion to S status, the C corporation must first confirm its eligibility. A key component of this analysis will include assumptions on potential sources of passive investment income the converting C corporation may have as an S corporation, e.g., gross receipts from royalties, rents, dividends, interest, or annuities. If the converting C corporation will have accumulated earnings and profits at the end of any of its Subchapter S tax years, and it has the requisite gross receipts from passive investment income, a passive investment income tax may apply.
S corporations with recognized built-in gains subject to the built-in gains tax can offset these gains with recognized built-in losses before the corporation’s tax year ends and eliminate the tax.
What health care and other benefit planning is available?
Pay or play excise tax.
A corporate taxpayer that has 50 or more full-time equivalent employees could be subject to an excise tax, which could be as much as $2,750 per full-time employee, for failure to offer a health care plan that is minimum essential coverage to at least 95% of the full-time employees if at least one employee obtains subsidized coverage through a public health insurance exchange. The first 30 workers are excluded from this calculation. If the taxpayer does offer coverage but it is not adequate or is unaffordable, the excise tax could be $4,120 for each full-time employee who obtains subsidized coverage through an exchange.
Smaller employers should review whether they have undergone, or will soon undergo, any changes to their business structure that would require them to be aggregated with other entities and subject them to potential liability. Larger employers should consider their health care plan options in light of this potential excise tax liability.
Health reimbursement arrangements
Certain small employers that want to assist their employees in obtaining health insurance may choose to set up a qualified small employer health reimbursement arrangement (QSEHRA). The QSEHRA, unlike other health reimbursement arrangements, is a tax-favored arrangement that is not considered a group health plan and does not expose the employer to excise taxes for not satisfying Affordable Care Act insurance market requirements. It’s available to employers that have fewer than 50 full-time equivalent employees, do not offer any health plan, and meet other requirements.
Credit for employee health insurance expenses of small employers
Some small employers that provide health coverage to their employees through a Small Business Health Options Program (SHOP) Exchange may be eligible to claim a credit if they pay for at least half of the premiums for health insurance coverage for their employees. Generally, employers with 10 or fewer full-time equivalent employees (FTEs) and an average annual per-employee wage of $28,700 or less are eligible for the full credit. In 2022, the credit amount begins to phase out for employers with either 11 FTEs or an average annual per-employee wage of more than $28,700. The credit is phased out completely for employers with 25 or more FTEs or an average annual per-employee wage of $57,400 or more. The credit is available on a sliding scale for up to 50% of the employer’s contribution toward employee health insurance premiums. The credit is available only for two consecutive taxable years after 2013, so it is not available to a taxpayer if, for example, the taxpayer or a predecessor claimed it for 2019–2020, or 2020–2021.
Preparing and filing corporate tax returns
A corporation must file a tax return every taxable year, regardless of the relevant amount of gross income. C corporations file Form 1120 , which is due by the 15th day of the fourth month following the close of the corporation’s taxable year. A calendar year corporation, for example, files its return by April 15. Exception: for June 30 fiscal year C corporation filers, the filing deadline is Sept. 15.
There is generally an automatic six-month extension for calendar year C corporations, and an automatic seven-month extension for fiscal-year C corporations with a taxable year ending on June 30.
Corporate taxpayers should be made aware of any penalties that may apply. The tax code imposes a host of penalties for late-filed returns, failing to file returns, failing to furnish information returns, and failing to pay tax. Many penalties are subject to inflation adjustments.
Estimated tax payments
A corporation (other than a large corporation) generally may be able to avoid any underpayment penalties by paying estimated taxes based on 100% of the tax shown on the prior year return. A large corporation is a corporation that had taxable income of $1 million or more for any of the three tax years immediately preceding the current year.
Documentation
Before the end of the year the corporation should hold any required board meetings, properly document any minutes, and collect any documentation that may be needed to substantiate tax returns upon audit.
Tax planning resources and expert insights from Bloomberg Tax
Year-round, proactive tax planning is an important way for corporate tax professionals to add strategic value to their organization and optimize their tax position. But preparing a corporate tax return involves navigating a multitude of potential pitfalls and errors that could trigger an audit, like updated or expired tax provisions, changes to tax credits, and new reporting obligations. Download the 2022 Corporate Tax Survey to better understand the greatest risks, challenges, and expected changes that corporate tax teams are facing across the U.S.
Stay on top of the dynamic field of corporate tax planning with expert analysis, comprehensive coverage, news, and practice tools from Bloomberg Tax . See how technology company Match Group uses Bloomberg Tax Research to save time and money understanding complex tax issues. Request a demo to learn more.
Recommended for you
Discover the new generation bloomberg tax suite.
Our suite of integrated solutions automates tedious work, minimizes risk, and frees up time to do more strategic work.
Historical U.S. Federal Corporate Income Tax Rates & Brackets, 1909-2020
Historical federal corporate income tax a corporate income tax (cit) is levied by federal and state governments on business profits. many companies are not subject to the cit because they are taxed as pass-through businesses , with income reportable under the individual income tax . rates and brackets, 1909 to 2020, u.s. corporation income collections, 1934 to 2020, stay informed on the tax policies impacting you..
Subscribe to get insights from our trusted experts delivered straight to your inbox.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Notes: /1 Source taxation is assumed to continue in the extractive industries. /2 Minimum tax on both outgoing and inbound investment. /3 Benefit mainly from inbound minimum. /4 Gain most sure if apportionment largely by employment. /5 Assumes apportionment partly by sales, all countries using the same formula; normal return assumed to be taxed.
Corporate Taxation Class Materials - Spring 2019. Syllabus (Spring 2019) Memorandum Summarizing Corporate Taxation Course (2019) Corporate Tax Casebook Update (2018) Tax Rate Comparison Chart (Fall 2015) 2015 Joint Committee Report on Business Taxation; Tax Treatment of Corporate Debt and Equity (JCX-45-16) Spring 2019 Powerpoint Presentations
The U.S. Corporate Tax System Explained. Apr 5, 2023. The U.S. corporate tax system is a subject of frequent debate, with significant implications for the nation’s economy and fiscal outlook. Over the past several years, lawmakers from both parties have pursued major changes to this area of the tax code, including the enactment of the 2017 ...
Corporate tax was backbone of progressivity in the US in mid-20th century (tax at source of 50% of real corporate pro ts) 2018 Trump tax reform cut Fed corporate tax from 35% to 21% and lowered revenue by almost half ) Explains why the top 400 face a lower rate than other income groups in 2018 6
That is, the income of certain business types passes through to their owners where it is taxed at individual income tax rates. Examples of these alternative “pass-through” forms of organization include sole proprietorships, partnerships, subchapter S corporations, and limited liability companies (LLCs).1. This report provides a general ...
If you require a professional template with great design, then this Corporate Tax Planning Powerpoint PPT Template Bundles is an ideal fit for you. Deploy it to enthrall your audience and increase your presentation threshold with the right graphics, images, and structure. Portray your ideas and vision using twelve slides included in this ...
following World War II. The corporate tax reached its post-World War II era peak in 1952 at 5.9% of gross domestic product (GDP). In 2021 (the most recent year that is not an estimate), the corporate tax generated revenue equal to approximately 1.7% of GDP. The corporate tax has also decreased in significance relative to other revenue sources.
For CCPC : 13.5% on active business income ≤ $500,000 25% on active business income > $500,000 44.7% on investment income 38% on realized capital gains. Download ppt "Taxation Corporate Tax". Corporate Tax Step 1: Calculation of Taxable Income Net Sales Chapter 5 - Taxes Corporate Tax Step 1: Calculation of Taxable Income Net Sales - Cost of ...
Preparing and filing corporate tax returns. A corporation must file a tax return every taxable year, regardless of the relevant amount of gross income. C corporations file Form 1120, which is due by the 15th day of the fourth month following the close of the corporation’s taxable year. A calendar year corporation, for example, files its ...
The Revenue Reconciliation Act of 1993 increased the maximum corporate tax rate to 35% for corporations with. taxable income over $10 million. Corporations with taxable income over $15. million are subject to an additional tax of. 3% of the excess over $15 million, or. $100,000, whichever is smaller. $50,000-$75,000.