

PhD vs Professional Doctorate: What’s the Difference?
The main difference between a PhD vs Professional Doctorate degree is their focus. A PhD is an academic research-focused degree awarded for original research and contribution to the knowledge base of a field.
At the same time, a professional doctorate is a practice-based degree designed to advance knowledge in a particular professional field and solve practical problems through research.
This article discusses the key differences between a PhD and a professional doctorate, including their goals, requirements, and outcomes.
Table of Contents
Goals of a phd and professional doctorate.
Higher education plays an essential role in one’s personal and professional development. The PhD and the professional doctorate are two of the most advanced degrees one can earn. While both degrees require rigorous academic work, there are significant differences between them.
In a PhD program, the primary goal is to conduct original research that contributes to the knowledge of a particular area.
Researchers in the PhD program will be able to perform independent research, contribute to the academic community, and push the boundaries of their fields. Students must produce a thesis that significantly contributes to their field to earn a PhD.
However, the main objective of a professional doctorate is to prepare professionals capable of applying research to solve real-world issues. Practitioners seeking advanced knowledge and skills can benefit from professional doctorates.
Students typically complete a research project addressing a practical problem in their field as part of a professional doctorate program emphasising professional practice.
Requirements of a PhD and Professional Doctorate
There are a variety of requirements for a PhD, depending on the institution and field of study, but most PhD programs require both coursework and research.
Students typically complete coursework and prepare for their comprehensive first stage viva voce during the first few years of their program. Following their viva exams, PhD students conduct research and write thesis for the remainder of the program.
Students pursuing a professional doctorate typically have to complete coursework and a research project.
In the coursework, students will gain advanced knowledge and skills in their field, while in the research project, students will address a practical problem. Industry partners or other professionals may collaborate on the research project.
Outcomes of a PhD and Professional Doctorate
The outcomes of a PhD and a professional doctorate differ significantly. PhDs are primarily academic degrees designed to prepare students for academic careers, research, or other scholarly pursuits. PhD graduates are often employed as professors, researchers, or consultants.
On the other hand, professional doctorates are designed to prepare students for advanced practice. Professional doctorates provide graduates with the knowledge and skills to solve real-world problems. Professional doctoral graduates typically work as practitioners, consultants, or executives.
Examples of PhD and Professional Doctorate Programs
Examples of PhD programs include Doctor of Philosophy in Human Resources Management, Doctor of Philosophy in Psychology, and Doctor of Philosophy in Law.
Examples of professional doctorate programs include Doctor of Education (EdD), Doctor of Business Administration (DBA), and Doctor of Public Health (DrPH).
The key differences between a PhD and a professional doctorate
Note that both degrees’ specific requirements, duration, and outcomes can vary depending on the institution and field of study. However, this table provides a general overview of the main differences between a PhD and a professional doctorate.
Which degree is more academically focused, a PhD or a professional doctorate?
A PhD is considered to be more academically focused than a professional doctorate. A PhD is designed to develop student’s research skills and contribute to advancing knowledge in a particular field, often leading to a career in academia or research.
In contrast, a professional doctorate is designed for students who want to apply research to solve practical problems in their professional field, such as education, business, or public health.
A professional doctorate program usually includes coursework and a research project focused on improving professional practice and solving real-world problems.
Are the research requirements for a PhD and a professional doctorate different?
PhDs and professional doctorates have different research requirements. As part of a PhD program, students typically conduct original research and write a doctoral thesis that contributes significantly to their study area. A PhD research generally aims to advance knowledge by advancing theory.
In contrast, a professional doctorate program typically requires students to apply existing research to solve practical problems in their professional field.
It is possible for professional doctorate programs to place a greater emphasis on coursework and practical training than PhD programs, as well as solving real-world problems and improving professional practice.
How do I choose a topic for my PhD or professional doctorate research project?
When choosing a topic for your PhD thesis or professional doctorate research project, it is important to consider your interests, goals, and field needs.
Identify the areas of your field that you find particularly interesting or challenging, and determine how your research can contribute to knowledge advancement or solve practical problems. In selecting a topic, seek guidance and support from faculty members and other professionals in your field.
Conducting a thorough review of existing literature in your area of interest will help you identify knowledge gaps your research can fill. Finally, make sure your chosen topic is feasible within the constraints of your program’s requirements and resources.
What are the most important skills and qualities for success in a PhD or professional doctorate program?
For success in a PhD or professional doctorate program, it is important to possess a strong work ethic, critical thinking skills, the ability to conduct independent research, time management skills, self-motivation, and effective communication abilities.
A PhD or professional doctoral student must be able to analyze complex information, synthesize information from various sources, and think creatively and critically.
You must manage your time effectively and work independently, as both programs require considerable self-direction and time management skills. In addition to writing and presenting research findings, effective communication skills are essential for success in these programs.
How important is the institution’s reputation when pursuing a PhD or professional doctorate?
A PhD or professional doctorate’s reputation can affect employment and funding opportunities after graduation, so it is crucial to consider it when pursuing one.
Students can benefit from the resources, faculty, and research opportunities of institutions with strong reputations in a particular field.
The degrees of graduates from prestigious institutions may also be valued more by employers, leading to greater opportunities.
However, it is important to note that a student’s research and accomplishments are ultimately the most important factors in determining their success, regardless of the institution they attended.
Conclusion: PhD vs Professional Doctorate
It is important to understand these differences when considering either degree because both require rigorous academic work, but their goals, requirements, and outcomes differ significantly.
While PhD and professional doctorate degrees require significant commitment, research, and advanced knowledge in a particular field, they differ in academic focus, research requirements, and career outcomes.
It is important to carefully consider your interests, goals, and field needs when deciding which degree to pursue. Ultimately, the choice between a PhD and a professional doctorate will depend on your career aspirations and the role you wish to play in advancing knowledge and solving problems in your field.
- Alison Lee, Marie Brennan & Bill Green, Higher Education Research & Development , “ Re‐imagining doctoral education: Professional Doctorates and beyond “.
- Dieter Fink, International Journal of Doctoral Studies , “ The Professional Doctorate: Its Relativity to the PhD and Relevance for the Knowledge Economy “.
- Ruth Neumann, Journal of Higher Education Policy and Management , “ Doctoral Differences: Professional doctorates and PhDs compared “.
Read more articles
Doctorate vs. PhD: Understanding the Key Differences [2025]

If you’re interested in pursuing a doctoral degree, you may wonder about the differences between a doctorate vs. PhD.

A doctorate and a PhD are both terminal degrees that allow you to develop specialized knowledge and skills in your chosen field. But these degrees typically have different areas of focus, requirements, and career outcomes.
Understanding the difference between PhD and doctorate can help you pick the degree that most aligns with your career aspirations and interests.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
What’s the Difference Between Doctorate vs. PhD Degrees?
A doctorate and a Ph.D. are the highest college degrees students can earn. Graduates of both types of programs receive the title of “doctor” and may qualify for specialized careers in their fields.
But, while doctorate programs focus on professional competencies and knowledge, PhD programs prioritize academic research.
What Is a Doctorate Degree?
A doctorate degree is a professional degree that enables students to become experts in a specific field or industry. This degree focuses on applying academic research and theories in the workplace to improve performance and solve problems.
Courses vary by field and program but typically emphasize professional skills like collaboration, leadership, and project management. Additionally, many doctorate programs require students to complete a capstone project that addresses real issues affecting their industry.
Graduates often qualify for advanced administrative, leadership, and managerial positions in their fields.
What Is a PhD Degree?
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degree is an opportunity to strengthen your academic research skills and generate original knowledge. This degree trains students to become independent scholars who conduct cutting-edge research in their areas of expertise.
PhD curriculums cover advanced concepts and theories in a discipline. They also teach students qualitative and quantitative methodologies to design studies and conduct research. Additionally, most PhD programs require students to produce a dissertation that contributes fresh knowledge to the field.
Current professionals with PhDs often work as academic researchers and professors. They may also secure government and industry jobs.
Key Differences Between a PhD vs. Doctorate Degree
What’s a PhD degree ? What’s a doctorate degree? The main difference between a doctorate and a PhD is their area of focus. A doctorate prioritizes applied knowledge and professional skills, while a PhD emphasizes academic research. Let’s compare some more differences between a professional doctoral degree vs. PhD.
A doctorate enables students to become expert practitioners in their discipline. Students study existing concepts and theories and learn how to apply these ideas in the workplace.
By contrast, a PhD prepares students to conduct innovative research and educate others.
Goals and Outcomes
Doctorate programs help prepare students for senior administrative and leadership positions in their industries. They also help students enhance their professional competencies and tackle industry-specific challenges.
Students who pursue PhDs aim to advance their disciplines by generating new knowledge. They may also publish peer-reviewed research and teach undergraduate courses.
Student Population
Doctorate degrees are designed for current or aspiring working professionals who want to become industry leaders. These programs also enable students to increase their knowledge and credibility.
PhD programs attract students who want to expand their knowledge of research methodologies and theories. These learners also frequently pursue academic careers.
Admissions Requirements
Doctorate and PhD programs typically require students to have bachelor’s and master’s degrees.
Additionally, prospective doctorate students may be asked to provide evidence of work experience, while PhD students might demonstrate their research abilities with a writing sample.
Program Length
Requirements vary by program, but full-time students typically complete a doctorate in 3 to 5 years. Programs that require a capstone project may take longer. For those considering quick degrees, a number of universities now offer accelerated doctoral programs online .
PhD programs often take 4 to 7 years to finish. The speed at which students research and write their dissertations can significantly impact the timeline.
The curriculum for doctorate programs typically centers on practical skills and contemporary issues in the field. Topics may include communication, ethics, and leadership.
PhD programs offer classes on research methods, theories, and disciplinary trends. Students also learn how to write journal articles and present at conferences.
Assessment and Completion Requirements
Doctorate and PhD students both complete 2 or more years of coursework. They also demonstrate their knowledge during comprehensive exams.
Doctorate students may produce a capstone project that applies their knowledge to real problems. By contrast, PhD students write dissertations based on original research.
If You Have a PhD, Are You a Doctor?
Is a PhD a doctor ? While graduates who earn a PhD are referred to as doctors, a PhD is different from a Doctor of Medicine (MD).
Doctors with MDs are medical doctors who can legally prescribe medications, perform surgery, and treat patients. They typically apply existing medical knowledge instead of conducting research. Doctors with PhDs don’t have any of these abilities. Instead, they have specialized knowledge and perform academic research in a particular field.
PhD or Doctorate Degree – Which Is Right for You?
Understanding the difference between a doctorate and a PhD can help you select the right degree for you.
Professional doctorate degrees help students become leading practitioners and problem solvers. By contrast, PhD degrees enable students to hone their research skills and learn advanced concepts. Both degrees allow you to enrich your understanding of your chosen discipline or profession. They also help you boost your credentials and develop new skills.
After you decide between a doctorate degree vs. PhD, you can explore program options from accredited schools to find the best fit.
- QUICK LINKS
- How to enroll
- Career services
- Go to MyPhoenix
- Return to my application
- My saved programs
Comparing the differences between MD vs. PhD vs. professional doctorate

Written by Michael Feder

Reviewed by Marc Booker , PhD, Vice Provost, Strategy
What is a doctorate? Breaking down the three types
Some people might confuse an MD (Doctor of Medicine) with a PhD (Doctor of Philosophy), and vice versa. While both an MD and a PhD are prestigious degrees near the top of the academic ladder , they each have a different meaning and come with very different requirements.
Different still from both of those degrees are professional doctorates, which allow industry professionals to translate their education and experience into credibility and leadership through research. Professional doctorates have similar requirements to PhDs, such as a dissertation and residency, but focus on the application of research and professional growth over original research.
Upon graduation, those who have earned any of these three degrees can call themselves a “doctor,” but the path to a degree, the purpose behind it and its applications vary based on the choice. MD graduates want to work in medicine and healthcare. PhDs want to bring new knowledge and research to the world. A practice-based doctoral graduate wants to grow in their professional expertise. (If the last one sounds like you, University of Phoenix can help!)
Keep reading to learn more about these doctoral programs and which is right for you.
What does MD stand for?
MD is an abbreviation for Doctor of Medicine and identifies a medical practitioner who has completed undergraduate studies and four years of medical school. An MD program teaches medical students about the human body and diseases through a combination of classroom instruction and hands-on clinical labs.
Several types of physicians might have this degree, depending on their area of study. For example, medical practitioners with an MD degree might become a medical doctor and potentially specialize in dermatology, cardiovascular disease, family medicine, oncology, pediatrics, neurology or preventive medicine. As you can see, this degree can lead to a variety of career paths, depending on which specialty interests you and what your medical education is.
How to earn an MD
Becoming a Doctor of Medicine requires a significant investment of time and money, but the reward can be well worth it. Before medical school, you’ll need to take the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT®) and earn a passing score. You’ll also need to build a portfolio of coursework and experience to help you gain admittance to medical school.
Medical school typically takes students four years to complete. You’ll learn the latest techniques and approaches for patient assessment, diagnosis and treatment. Medical schools commonly provide a combination of classroom, research and clinical experience. You’ll work alongside peers and healthcare professionals as you develop skills in general medicine.
You’ll choose a field to specialize in during your final year of medical school. Students have more than 120 options to choose from when specializing, including primary care, pediatrics, geriatrics, emergency medicine and family medicine.
After graduating, you’ll complete residency training to further develop skills in your specialty. Residency typically lasts three to seven years, depending on the field you’ve selected. During the residency portion of your education, you’ll treat patients under the supervision of more experienced physicians.
Even after you begin to practice as an MD, the educational portion of your career never stops. As practices change, patient needs evolve and research continues, MDs benefit from ongoing education to stay current.
What does PhD stand for?
A PhD, or Doctor of Philosophy, is a doctoral degree that recognizes graduates who have completed a full postsecondary program. Students can earn a PhD in more fields than philosophy. After completing the necessary coursework, original research and hands-on experience, you can earn a PhD in fields like science, the humanities and engineering.
Earning a PhD can help unlock a wide range of potential career opportunities. Computer engineers, research scientists, statisticians, healthcare administrators, professors, chemists and other careers commonly require a PhD degree, in addition to appropriate undergraduate study.
How to earn a PhD
Becoming a PhD is also a serious commitment that requires an investment of time, money and energy.
Here is what’s typically required to become a PhD:
- Complete a bachelor’s degree in your field
- Complete a master’s degree in an appropriate field
- Pass any program entrance exams
- Fulfill coursework, research and hands-on lab requirements in your program
- Finalize and defend your dissertation as a doctoral candidate (unless your program specifies otherwise)
It’s important to note that many PhD programs have different requirements, prerequisites and parameters for students. Check with your preferred institution for a more detailed explanation of these requirements.
What is a professional doctorate?
While some professional or practice-based doctorate programs are medical, others are designed for professionals in other fields . These programs are meant for scholar-practitioners in disciplines like education, business or psychology. One of the key differences between this degree and a PhD is the focus on applying research to a professional setting rather than conducting theoretical and research-focused studies. Often, programs are differentiated as academic versus professional.
Examples of doctoral degrees are Doctor of Education, Doctor of Nursing Practice and Doctor of Business Administration. Each of these programs focuses on a specific discipline and applying research in those areas to a professional setting.
How to earn a doctorate
While practitioner doctoral programs teach different skills, they all share common requirements. You’ll need to complete a bachelor’s degree in your field and sometimes a master’s degree, depending on program requirements.
After completing the necessary coursework and research, students also typically need to finish a supervised thesis and defend their dissertation or capstone project-specific coursework, research and hands-on labs alongside other students in the same field. However, this will depend on the specific program and its requirements.
What does the title “Dr.” really mean?
The term “doctor” or “Dr.” is commonly used today to describe a wide variety of occupations. Students who complete a doctoral degree can earn the title of “Dr.” even though they earned their credentials in a non-medical field like education or business management.
While a variety of professionals can earn a doctorate, the term is often still reserved for medical practitioners . In conventional use, doctors typically refer to medical physicians. However, it is appropriate to use “Dr.” if you graduated from any of the three programs discussed above.
Practitioner doctoral degree programs at University of Phoenix
While University of Phoenix (UOPX) does not have MD or PhD programs, it does offer several professional doctoral degrees that can be earned completely online. Students might choose the UOPX programs because classes are flexible and offered online, and because of the University’s unique “ Scholar-Practitioner-Leader model .”
If you are curious about a doctoral degree, the following programs are available at UOPX:
- Doctor of Business Administration : This doctorate can help you gain strategic vision and skills to position yourself as a business leader. It explores how to solve organizational problems, how to design and conduct research studies, how to introduce innovative business ideas to the industry and more.
- Doctor of Management : This doctorate equips you with critical thinking skills to find creative solutions to complex problems.
- Doctor of Education : This doctoral program prepares you to use analytical, critical and innovative thinking to improve performance and solve complex problems in education.
- Doctor of Health Administration : If you’re a health professional who is seeking greater responsibility in shaping the future of the health sector, this doctorate can help you meet the challenges inherent to today’s healthcare landscape, including economic fluctuations, burgeoning patient needs and industry-changing legislation.
- Doctor of Nursing Practice : This doctorate is designed for working nurses who require a doctorate for advanced practice or nurses who desire their terminal degree. It does not prepare students for professional certification or state licensure as a nurse or as an advanced practice nurse.
These doctoral studies are only some of the many options for professionals who want to gain the highest academic credentials in their fields. Doctoral programs offer significant benefits to program graduates, including newly developed skills, insight into field trends, hands-on research opportunities and leadership capabilities.
Completing a doctoral program is also a strong indication to employers that you’re serious about your career and your field. With so many options for advanced study, these programs are available for most major fields. Even if you have already completed a bachelor’s or master’s degree in your discipline, a doctorate lends further credibility to your reputation and can help prepare you for a leadership position.

ABOUT THE AUTHOR
A graduate of Johns Hopkins University and its Writing Seminars program and winner of the Stephen A. Dixon Literary Prize, Michael Feder brings an eye for detail and a passion for research to every article he writes. His academic and professional background includes experience in marketing, content development, script writing and SEO. Today, he works as a multimedia specialist at University of Phoenix where he covers a variety of topics ranging from healthcare to IT.


ABOUT THE REVIEWER
Dr. Marc Booker, University of Phoenix Vice Provost for Strategy, has more than two decades of experience working with online and distance education students at the post-secondary level. He currently oversees critical path academic initiatives to improve the student experience. Dr. Booker is a regular speaker, author and contributor to national higher education associations.
This article has been vetted by University of Phoenix's editorial advisory committee. Read more about our editorial process.
Read more articles like this:

What Does a Postsecondary Education Entail?
Online degrees.
June 29, 2023 • 9 minutes

Can I Go to a University Without Taking the SAT or ACT?
July 21, 2023 • 7 minutes

Careers With a Doctor of Education Degree
April 28, 2021 • 4 minute read
- Online Degrees
- Tuition & Financial Aid
- Transferring Credit
- The Franklin Experience
Request Information
We're sorry.
There was an unexpected error with the form (your web browser was unable to retrieve some required data from our servers). This kind of error may occur if you have temporarily lost your internet connection. If you're able to verify that your internet connection is stable and the error persists, the Franklin University Help Desk is available to assist you at [email protected] , 614.947.6682 (local), or 1.866.435.7006 (toll free).
Just a moment while we process your submission.
Popular Posts

Professional Doctorate or Ph.D.: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better?
Understanding the differences between a professional doctorate and a Ph.D. is a lot more important than it used to be. That’s because the relatively new professional doctorate is growing in availability, which means it is likely growing in popularity, too.
As professional doctorates come into their own against the ever-popular Ph.D., it becomes a little more challenging to decide which one is better. While both are advanced degrees that can be great for your career, the key to answering the question of which is better starts with understanding what makes them different.
Is a Professional Doctorate the Same as a Ph.D.?
Think of the professional doctorate (also known as an applied doctorate) and the Ph.D. as fraternal twins. They are similar, but not identical.
When it comes to similarities, both degrees are applicable to a variety of career paths, including faculty and adjunct educators and corporate professionals. Of course, some positions, such as teaching at a Tier 1 research institute, require a Ph.D. Other careers, such as analyst and consultant, do well by the applied doctorate degree.
A professional doctorate enables both subject mastery and field application whereas a Ph.D. typically is academically focused.
In short, the difference is application (professional doctorate) vs. academic (Ph.D.). Here’s a more detailed comparison of the two degrees:

Earning a doctorate is challenging and rewarding, but do you know what to really expect? Download this free guide for tips and insights to help you prepare for success.
Applied doctoral programs: 4 facts you should know.
Ultimately, only you can decide if an applied doctorate or a Ph.D. is better for you, so here are some things to know to help you decide which is right for you.
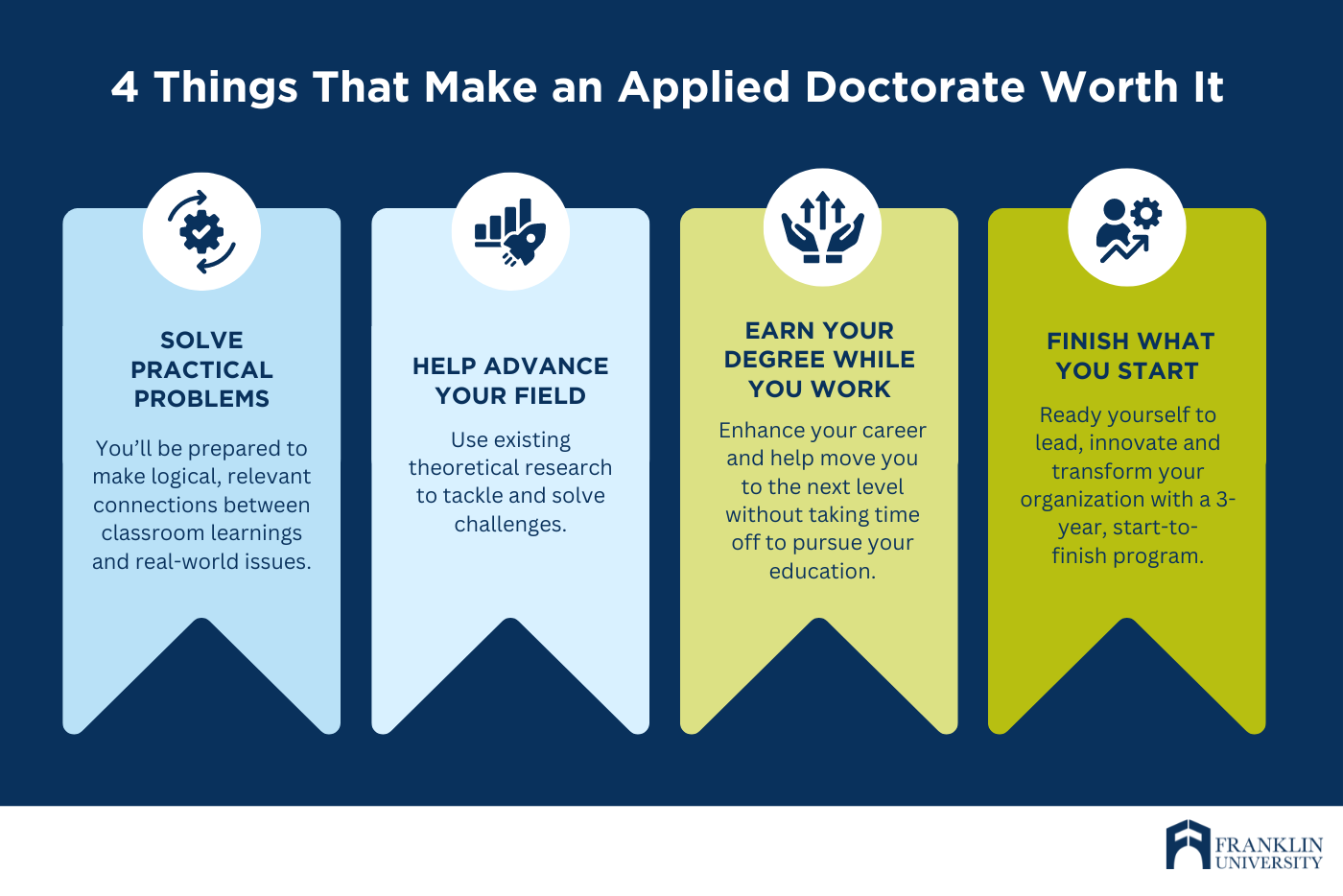
1. An applied doctorate can help you solve practical problems in your field. If new research isn’t your thing but evaluating the research of others to solve a problem, uncover an idea or innovate a solution, then an applied doctorate could be ideal.
An applied doctoral program will instruct you in the core technical aspects of quality research. It also will help you further develop and refine your communication skills and technological capabilities. With this type of terminal degree, you’ll be prepared to make logical, relevant connections between classroom learnings and real-world issues.
By combining both research and application, an applied doctorate’s research side can arm you with deeper insight, while the application side can help you make impactful organization-wide decisions to tackle issues, overcome challenges and leverage opportunities.
2. An applied doctorate can help you advance your field through applied research and development. Both the Ph.D. and the applied doctorate can help you advance your field. Both involve research.
The difference, then, is in who does the research, how the research is presented, and in what way the research is applied.
Primarily, Ph.D.s broaden their field by conducting new research and developing theories. Those who hold a professional doctorate, however, use existing theoretical research to tackle and solve challenges.
3. An applied doctorate offers non-traditional learners more flexibility. While there are exceptions, many Ph.D. programs require a full-time commitment.
If you’re looking for a professional doctorate to enhance your career and help move you to the next level without taking time off to pursue your education on a full-time basis, then an applied doctoral could offer the flexibility you need to earn it.
Here are a few things to look for as you explore both Ph.D. and applied doctorate programs:
- Online courses vs. on-campus classes
- Residency requirements
- Research focus
- Dissertation structure
- Doctoral student support and learning communities
Remember to choose the program that suits your learning style, as well as your personal and professional situation.
4. An applied doctorate can help you finish what you start. Let’s face it. It can be tough to finish a doctorate. The life changes accompanying Ph.D. studies can be disruptive and oftentimes overwhelming. Choosing the right research focus can be difficult and laborious. Financial stress, isolation, advisor process and more can be reason enough to abandon the program before completion. And the dissertation process? It can be downright intimidating. In short, earning a Ph.D. can be a long, arduous process.
An applied doctorate on the other hand, especially one that’s designed to be a 3-year, start-to-finish program, can prepare you to lead, innovate, and transform your organization. With a program that offers 360-degree support throughout the program, you’ll have the academic support and resources you need to be accountable to the program and yourself.
Professional Doctorate or Ph.D.: Which Is Right for Me?
Hopefully, you’re now better able to see the differences between a professional doctorate and a Ph.D.
The more you know about the differences–and your interests, goals, and ambitions–the more likely you are to make the best decision for your future. Just remember to prepare yourself mentally, emotionally, socially, financially and academically, and the right doctoral degree program will put you on a clear, straightforward path to earning your degree.

Related Articles

Franklin University 201 S Grant Ave. Columbus , OH 43215
Local: (614) 797-4700 Toll Free: (877) 341-6300 [email protected]
Copyright 2024 Franklin University
LET US HELP
Welcome to Capella
Select your program and we'll help guide you through important information as you prepare for the application process.
FIND YOUR PROGRAM
Connect with us
A team of dedicated enrollment counselors is standing by, ready to answer your questions and help you get started.

- Capella University Blog
- PhD/Doctorate
The difference between a PhD and professional doctorate
March 27, 2018
Whatâs the difference between a PhD and a professional doctorate?
Some people say that a PhD prepares you to teach, while a professional doctorate is more geared toward a professional career. But the answer to the question is more complex.
Leaders in corporate organizations often benefit greatly from having a PhD, and individuals with a professional doctorate may hold adjunct or even regular faculty posts at universities. Everyone who obtains a doctoral degree from Capella University is a scholar-practitionerâmeaning they are equipped with a deep understanding of foundational theory and how it directly applies to the current and future needs of their profession, as well as the skills and knowledge to research, teach, consult, and lead.
Deciding whether to pursue a PhD or professional doctorate can be a complex process. The differences between the two doctoral program types vary in every fieldâand they are also evolving. In terms of programs at Capella, all doctoral programs require coursework and an independent research project. Some require comprehensive exams, and many include residencies.
The primary difference between PhD and professional doctorate programs is the type of research conducted in the independent research phase.
PhD students are expected to create, expand, and contribute to knowledge, research, and theory in their field of study. This kind of discovery is often called original research.
Professional doctorate students are expected to expand and apply existing knowledge and research to existing problems in their professional field. This is often referred to as applied research.
The following graphic shows the differences between a PhD program and a professional doctorate program:
- Degree Focus
- Independent Research Project
- Career Intention*
Contribute new knowledge aimed at solving real-world problems.
Professional Doctorate
Apply existing knowledge aimed at solving real-world problems.
Five-chapter dissertation.
Five-chapter applied dissertation or paper, product, or portfolio
More interest in consulting and/or conducting research.
More interest in practicing directly in the profession.
*In many instances, both a PhD and professional doctorate prepare students for teaching at the college or university level.
Ultimately, deciding whether to pursue a PhD or professional doctorate in your field of study should start with assessing your career goals and how you plan to apply your degree, and determining the kind of research that interests you most.
Capella University offers PhD and/or professional doctorate degree programs in business, information technology, education, nursing, health care, psychology, counseling, social work, and public service. Learn more about Capellaâs doctoral degree programs.
You may also like

Can I transfer credits into a doctoral program?
January 8, 2020

What are the steps in writing a dissertation?
December 11, 2019

The difference between a dissertation and doctoral capstone
November 25, 2019
Start learning today
Get started on your journey now by connecting with an enrollment counselor. See how Capella may be a good fit for you, and start the application process.
Please Exit Private Browsing Mode
Your internet browser is in private browsing mode. Please turn off private browsing mode if you wish to use this site.
Are you sure you want to cancel?

- ACADEMIC ADVICE
What’s the Difference Between a Ph.D. and a Doctorate?
- July 8, 2024
Table of Contents
Research (academic), applied (professional), what is a ph.d., is a ph.d. higher than a professional doctorate, doctoral study vs. dissertation, who is it for, what do you learn in each, can a ph.d. be called a doctor, the bottom line, what’s the difference between a ph.d. and a doctorate, are ph.d. and doctorate terms interchangeable, what are examples of other doctorate degrees besides a ph.d., do ph.d. and doctorate programs have different structures or requirements, which is more academic-focused: ph.d. or other doctorate degrees, can ph.d. holders and other doctorate degree holders use the title “dr.”.
The terms Ph.D. and Doctorate are often used interchangeably when considering advanced degrees in academia. Both degrees involve rigorous academic study and research, but their focus, duration, and requirements differ. Hence, these significant differences between the two are worth understanding before deciding which path to pursue.
In this article, we will explore the difference between a Ph.D. and a doctorate, including their definitions, the types of programs they are offered in, and the career opportunities they lead to.
What Is a Doctorate?
A doctorate degree is the highest level of academic degree that can be awarded by a university. It typically requires a minimum of three to five years of advanced study and research beyond a bachelor’s or master’s degree .
Doctoral programs are designed to prepare individuals for advanced careers in academia, research, or other professional fields. There are two main types of doctorates: Research (Academic) and Applied (Professional). Let’s talk about each in more detail.
A research doctorate, also known as an academic doctorate, is a type of doctoral degree focused on original research and advancing knowledge in a specific academic field. These programs require students to take advanced coursework in their field and complete original research contributing to the body of knowledge in their study area.
The research component is typically the program’s centerpiece, and students are expected to produce a dissertation or thesis that represents a significant contribution to their field of study. A research doctorate is highly valued in academia, and graduates often pursue careers as professors, researchers, or scholars in their field.
While a significant time commitment and dedication are required, they provide individuals with the skills and knowledge necessary to make contributions to their field and advance their careers in academia. Examples of research doctorates include the Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.), Doctor of Science (D.Sc.), and Doctor of Education (Ed.D.) , among others.
An applied doctorate, or professional doctorate, is a type of doctoral degree that focuses on applying knowledge and skills in a specific profession or industry. These programs emphasize the practical application of research and theories to solve real-world problems in their field.
The curriculum includes coursework designed to enhance students’ professional skills, including leadership , management, or organizational behavior. An applied doctorate program’s capstone project or dissertation addresses a real-world problem or issue within the student’s profession or industry. The research is conducted in collaboration with professionals in the field.
While applied doctorate programs require a significant time commitment and dedication to a specific profession, they provide individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to become experts in their field and make a great impact. Graduates of such programs are well-prepared to take on leadership roles in their profession. The degree can lead to higher salaries and career advancement.
Examples of applied doctorates include the Doctor of Education (Ed.D.), Doctor of Business Administration (DBA), and Doctor of Psychology (Psy.D.), among others.
Students who have completed advanced studies in a particular academic field and contributed original research to that field are awarded a Ph.D., also known as a Doctor of Philosophy. Ph.D. programs are geared toward developing independent scholars who can conduct original research and advance knowledge in their chosen fields.
The coursework of a Ph.D. program involves advanced studies in the student’s area of interest, coupled with a significant research component. Students must produce a dissertation or thesis that adds to the existing body of knowledge in their field of study.
Ph.D. programs generally require multiple years to complete and lead to opportunities for graduates to work as professors, scholars, or researchers within their field of specialization.
While Ph.D. degrees are commonly associated with academic careers, they can also offer advantages for graduates seeking positions in government or industry, as they demonstrate expertise in a specific area and an aptitude for original research.
Comparing a Ph.D. to a professional doctorate is difficult, as both degrees have distinct characteristics and are designed for different purposes.
A Ph.D. is primarily a research-focused degree focused on producing independent scholars who can conduct original research and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in a particular field.
On the other hand, a professional doctorate focuses on the application of knowledge and skills in a specific profession or industry. These programs typically emphasize the practical application of research and theories to solve real-world problems in their field.
Graduates of professional doctorate programs are well-prepared to take on leadership roles in their profession, and the degree can lead to career advancement and higher salaries.
So, in terms of purpose and focus, Ph.D. and professional doctorate degrees are different. It’s not a matter of one being higher than the other, but rather, it depends on an individual’s career goals and aspirations. Both degrees are considered terminal degrees, meaning they represent the highest level of academic achievement in their respective fields.
The Difference Between a Ph.D. and a Doctorate
Understanding the differences between a Ph.D. and a professional doctorate can help you make an informed decision about which program is right for you and your career goals. And while both types of degrees require extensive study and research, there are significant differences between the two.
One of the key differences between a Ph.D. and a professional doctorate is the focus of the doctoral study. Ph.D. programs typically focus on producing independent scholars who can conduct original research and advance knowledge in their chosen field.
In contrast, professional doctorate programs emphasize the practical application of research and theories to solve real-world problems in their field.
While both degrees require extensive research, Ph.D. programs often require a significant original contribution to the field in the form of a dissertation, while professional doctorate programs typically require a capstone project or applied research project that demonstrates the student’s ability to apply their knowledge to a real-world problem.
Ph.D. programs are geared toward individuals interested in pursuing an academic career, such as becoming a professor or researcher. These programs prepare students for a life of scholarship and original research.
On the contrary, professional doctorate programs are geared toward professionals already working in a specific profession or industry and wanting to advance their careers through further education. These programs provide students with the knowledge and skills needed to take on leadership roles in their profession or industry.
The content of the curriculum in Ph.D. and professional doctorate programs differs significantly. Ph.D. programs aim to give students extensive knowledge of their field of study and equip them with the skills to conduct original research.
✅ Request information on BAU's programs TODAY!
First Name*
*By submitting this form, you consent to the personal data provided above to be processed, used, and/or retained by Bay Atlantic University and its members, officers, employees, and representatives for communication, promotional, and marketing purposes.
On the other hand, professional doctorate programs have a practical focus, with students taking courses that prepare them for leadership positions in their respective professions or industry, including management, ethics , and professional communication.
The title “Doctor” is used to refer to someone who has earned a doctoral degree, whether it is a Ph.D. or a professional doctorate. In academic and professional settings, it is common for individuals with a Ph.D. to be referred to as “Dr.” along with their name, just as someone with a professional doctorate would be.
However, it’s important to note that the title “Doctor” does not necessarily indicate that the person is a medical doctor or a physician. Additionally, it is worth noting that different countries and cultures have different conventions for how the title “Doctor” is used, so it’s always a good idea to check local customs and norms to ensure proper usage.
The decision to pursue a Ph.D. or a professional doctorate ultimately depends on your individual career goals and aspirations. Both degrees are highly respected and can lead to exciting and fulfilling careers.
Remember, the pursuit of advanced education is a challenging but rewarding journey that leads toward new opportunities, personal growth, and the chance to make a positive impact in your field.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A Ph.D. is one type of doctorate degree but not all doctorate degrees are Ph.Ds. Ph.D. stands for Doctor of Philosophy and is typically research-focused , while a doctorate encompasses a broader range of degrees.
Not exactly. People often use “ Ph.D. ” colloquially to refer to any doctoral degree, but strictly speaking, a Ph.D. is a specific type of doctorate degree focused on original research.
Other doctorate degrees include Doctor of Education (Ed.D.), Doctor of Business Administration (DBA), Doctor of Psychology (Psy.D.), Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP), and many more depending on the field of study.
Ph.D. programs emphasize research and typically require a dissertation based on original research. Other doctorate programs may have different requirements, such as applied projects, clinical practice, or professional portfolios , depending on the field .
Ph.D. programs are often considered more academically rigorous and research-oriented compared to professional or practice-based doctorate programs, which may focus more on applied knowledge and skills.
Yes, both Ph.D. holders and other doctorate degree holders are entitled to use the title “ Dr. ” as a prefix to their name. This title denotes their attainment of a doctoral degree in their respective field of study.
Bay Atlantic University
Leave a reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
You May Also Like
- 8 minute read
Most Sought-After Programming Languages in 2023
- February 21, 2022
- 5 minute read
Finest Accounting Skills You Need for Career Success
- March 13, 2022
- 6 minute read
How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- November 27, 2022
- 7 minute read
8 Easy Ways to Build Relationships with Your Students
- May 10, 2022
How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D.?
- February 22, 2023
8 Types of Learning Styles | The Definitive Guide
- March 7, 2024
- 82 shares 38 0 44
- INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS
British English vs. American English: Discover Key Differences
- November 13, 2024
What Is the F1 Visa? Guide for International Students
Why studying abroad is a game changer for your future, fun esl reading activities to boost your students’ skills.
- November 5, 2024
Request information on BAU's programs TODAY!

IMAGES
COMMENTS
But there are differences between the types of doctoral degrees. Learn more about a PhD vs. a professional doctorate below. Is a Professional Doctorate the Same as a PhD? Professional doctorate and PhD degrees are considered terminal degrees, meaning when you earn either degree, you will have achieved the highest formal degree in the field.
Apr 26, 2023 · The main difference between a PhD vs Professional Doctorate degree is their focus. A PhD is an academic research-focused degree awarded for original research and contribution to the knowledge base of a field.
Dec 2, 2024 · What’s a doctorate degree? The main difference between a doctorate and a PhD is their area of focus. A doctorate prioritizes applied knowledge and professional skills, while a PhD emphasizes academic research. Let’s compare some more differences between a professional doctoral degree vs. PhD. Purpose. A doctorate enables students to become ...
Jun 22, 2023 · A PhD, or Doctor of Philosophy, is a doctoral degree that recognizes graduates who have completed a full postsecondary program. Students can earn a PhD in more fields than philosophy. After completing the necessary coursework, original research and hands-on experience, you can earn a PhD in fields like science, the humanities and engineering.
Other careers, such as analyst and consultant, do well by the applied doctorate degree. A professional doctorate enables both subject mastery and field application whereas a Ph.D. typically is academically focused. In short, the difference is application (professional doctorate) vs. academic (Ph.D.).
The primary difference between a professional doctorate and a PhD is the focus. PhDs are focused on academic research and adding new knowledge to the field, while professional doctorates are focused on practical application. Is a PhD Higher Than a Doctorate? In most cases, a PhD has equal standing to a professional doctorate.
Jan 16, 2024 · A professional doctorate is a type of degree program that combines advanced study with practical application in a specific field or industry, such as business administration. It differs from a traditional doctor of philosophy program by emphasizing real-world application of knowledge to meet career goals. 3. PhD vs professional doctoral degree?
Mar 27, 2018 · The primary difference between PhD and professional doctorate programs is the type of research conducted in the independent research phase. PhD students are expected to create, expand, and contribute to knowledge, research, and theory in their field of study. This kind of discovery is often called original research.
Aug 2, 2021 · When earning a doctorate degree, there are two main options: a professional doctorate and a Doctor of Philosophy degree (PhD). While these are both advanced degree programs that are found at many different universities, there are many differences to be aware of before choosing which degree you want to pursue.
Jul 8, 2024 · The Difference Between a Ph.D. and a Doctorate. Understanding the differences between a Ph.D. and a professional doctorate can help you make an informed decision about which program is right for you and your career goals. And while both types of degrees require extensive study and research, there are significant differences between the two.